 Step Types
Step Types
This chapter discusses:
Step types and their associated actions.
Common actions.
Reserved words.
Functions.
 Step Types
Step Types
This section lists each of the PTF step types and defines the actions associated with the step type. The object types are listed in alphabetical order.
 Browser
Browser
These are the actions associated with the Browser step type.

 Close
CloseDescription
Closes the current browser (that is, the one with the execution focus).

 FrameSet
FrameSetDescription
Sets the focus in a browser frame.
Embedded frames include a number, such as ptModFrame_1. You can substitue ## for the number, for example ptModFrame_## and PTF will search through all frames starting with ptModFrame_ and use the one with the highest number.

 Start
StartDescription
Starts the browser instance where the test will be executed. Uses the URL from the selected execution option.

 Start_Login
Start_LoginDescription
Starts the browser instance where the test will be executed and logs into the PeopleSoft application. Uses the URL, user ID, and password from the selected execution option and the language selected in the test Language field.

 WaitForNew
WaitForNewDescription
Waits for a new browser to appear, then continues execution with the new browser.
Specify a timeout value in seconds in the Value column. The default is 10.
 Button
Button
These are the actions associated with the Button step type.

 Click
ClickDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Click.

 Exists
ExistsDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Exists.

 Get_Property
Get_PropertyDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Get_Property.
 Chart
Chart
These are the actions associated with the Chart step type.

 ChartClick
ChartClickDescription
Performs a click in a chart section.
Parameters
|
chart=value; |
The index for the chart image on the page. |
|
idx=value; url=value; alt=value; |
The section recognition string. It can be the section index, the section URL, or the alternative text. |

 GetText
GetTextDescription
Returns the text value for the specified chart section.
Parameters
|
chart=value; |
The index for the chart image on the page. |
|
idx=value; url=value; alt=value; |
The section recognition string. It can be the section index, the section URL, or the alternative text. |
|
ret=&variable; |
The return value. |
Example
This is an example of the GetText action for a Chart stept type:
 CheckBox
CheckBox
These are the actions associated with the CheckBox step type.

 Exists
ExistsDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Exists.

 GetLabel
GetLabelDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See GetLabel.

 Get_Property
Get_PropertyDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Get_Property.

 Set_Value
Set_ValueDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Set_Value.

 Verify
VerifyDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Verify.
 ComboBox
ComboBox
These are the actions associated with the ComboBox step type.

 Exists
ExistsDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Exists.

 Get_Property
Get_PropertyDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Get_Property.

 GetLabel
GetLabelDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See GetLabel.

 Set_Value
Set_ValueDescription
Sets the field value in the ComboBox to the value specified in Value.
You can also use this action with the #LIST# reserved word to verify whether items exist in the list.
When used with #LIST#, Set_Value returns an error if the expected value (the bracketed value) is not the same as the actual value.
Example
This example sets the field value to French and verifies that the values English, French, and Finnish exist in the list.
See Also

 Verify
VerifyDescription
Compares the value in the browser to the expected value and adds a Pass or Fail log entry for the validation. Use a vertical pipe (|) to separate values to be verified. Use square brackets ([]) to specify which value is expected to be selected.
Example
This example verifies that the field value is set to Two and verifies that the values One and Three exist:
 Conditional
Conditional
These are the actions associated with the Conditional step type.

 If_Then
If_ThenDescription
Evaluates the logical expression in the Recognition field. If the expression evaluates to True, the system executes the steps between the If_Then step and the End_If step or the Else step, if it exists. If the expression evaluates to False, the system jumps to the Else step, if it exists, or to the End_If step if there is no Else, and continues execution.
If_Then supports these logical operators:
<>, >=, <=, >, <, =

 Else
ElseDescription
(Optional) If the logical expression evaluates to False, the system executes the steps between the Else step and the End_If step.

 End_If
End_IfDescription
The close statement of the If_Then construct.
Example
This example shows the use of the Conditional construct:
 DataMover
DataMover
This is the action associated with the DataMover step type.

 Exec
ExecDescription
Executes a DataMover script. The output folder will be the one selected for the PeopleSoft Data Mover output folder..If the output path is not set in the execution options, it uses the system temp folder.
Example
This example shows the use of the Exec action:
 Div
Div
This is the action associated with the Div step type.

 Click
ClickDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Click.
 Execution
Execution Use the Execution actions in shell tests to modify the behavior of tests during execution. You typically set these options as you are developing tests to facilitate the development process.
The Execution step type is available only in shell tests.

 Skip_PageSave
Skip_PageSaveDescription
Specify True or False in the Recognition column. Specify True to skip Page.Save steps. You would, for instance, select this option to avoid creating duplicate values if you plan to run a test repeatedly.
This action overrides the Skip PageSave setting in Execution Options.

 Skip_RunRequest
Skip_RunRequestDescription
Specify True or False in the Recognition column. Specify True to skip Process.Run steps.
This action overrides the Skip RunRequest setting in Execution Options.
|
True |
Skip Process.Run steps. |
|
False |
Execute Process.Run steps. |

 Skip_Login
Skip_LoginDescription
SpecifyTrue or False in the Recognition column. Specify True to skip Browser.Start_Login steps.
|
True |
Skip Browser.Start_Login steps. |
|
False |
Execute Browser.Start_Login steps. |

 StopOnError
StopOnErrorDescription
Specify True or False in the Recognition column. Specify True to stop execution when a Fail is logged.
This action overrides the Stop on Error setting in Test Editor.
|
True |
Stop execution when a test encounters a Fail. |
|
False |
Continue execution when a test encounters a Fail. |
See Also
Configuring Execution Options.
 File
File
This is the action associated with the File step type. The File step type corresponds to the object in PIA that allows users to upload files to the PeopleSoft application.

 Upload
UploadDescription
Uploads a file.
In the Recognition column specify the string to get the object from the page. In the Value column specify a full file pathname.
Example
This example shows the use of the Upload action:
![]()
Example of the File Upload action
 HTMLTable
HTMLTable
These are the actions associated with the HTMLTable step type.

 CellClick
CellClickDescription
Clicks on a specific HTMLTable cell based on the index parameter.
|
index=I/R/C: |
The table, row, column index string. For example: index=&CellIndex index=1/2/3 ; In the second example, CellClick clicks on the third column of the second row of the first table. |

 CellClickOnChkB
CellClickOnChkBDescription
Clicks the check box specified in the table cell location based on the index parameter.
|
index=I/R/C: |
The table, row, column index string. For example: index=&CellIndex index=1/2/3; In the second example, this function clicks on a checkbox within the third column of the second row of the first table. |
|
chkidx=value; |
The CheckBox object index inside the cell. |
|
check=value; |
check=Y – Select the checkbox. check=N – Clear the checkbox. This parameter is optional. The default value is Y. |

 CellClickOnImage
CellClickOnImageDescription
Clicks the image specified in the table cell location based on the index parameter.
Parameters
|
index=I/R/C: |
The table, row, column index string. For example: index=&CellIndex index=1/2/3; In the second example, this function clicks on an image within the third column of the second row of the first table. |
|
name=value; |
The HTMLImage's NameProp value. |

 CellClickOnLink
CellClickOnLinkDescription
Clicks the link specified in the table cell location based on the index parameter.
Parameters
|
index=I/R/C: |
The table, row, column index string. For example: index=&CellIndex index=1/2/3; In the second example, this function clicks on a link within the third column of the second row of the first table. |
|
link=value; |
The link text value. |

 CellExists
CellExistsDescription
Determines whether a cell exists.
Parameters
|
index=I/R/C: |
The table, row, column index string. For example: index=&CellIndex index=1/2/3; In the second example, this function verifies whether a cell exists within the third column of the second row of the first table. |
|
ret=&variable |
The return value. True – the cell exists. False – the cell does not exist. |

 CellGetIndex
CellGetIndexDescription
Searches the page for the text value specified in the text parameter and returns the index string for the first cell that contains the text. The index string is in the form of I/R/C, where I is the table index, R is the row number, and C is the column number. Other actions, such as CellClick, CellGetValue, and so on, use an index string to reference a specific cell.
Parameters
|
text=value; |
The text to look for on the page. |
|
equal=value; |
equal=true performs an exact match on the text to search for. This is the default for this optional parameter. equal=false uses a LIKE statement when performing the search. |
|
ret=&variable |
The return value is an index string in the form of I/R/C, where I is the table index, R is the row number, and C is the column number. For example: ret=&CellIndex |

 CellGetValue
CellGetValueDescription
Returns the contents of an HTMLTableCell.
Parameters
|
index=I/R/C: |
The table, row, column index string. For example: index=&CellIndex index=1/2/3; In the second example, this function returns the contents of the third column of the second row of the first table. |
|
ret=&variable |
The return value. |

 ColCount
ColCountDescription
Returns the number of columns for the HTMLTable row.
Parameters
|
table=value; |
The table index. |
|
row=value; |
The row index. |
|
index=I/R/C: |
An index string in the form of I/R/C, where I is the table index, R is the row number, and C is the column number. As an alternative to specifying the table and row parameters, you can specify an index string, such as the return value from a CellGetIndex action. For example: index=&CellIndex; |
|
ret=&variable |
The return value. |

 RowCount
RowCountDescription
Returns the number of rows for the HTMLTable.
Parameters
|
table=value; |
The table index. |
|
index=I/R/C: |
An index string in the form of I/R/C, where I is the table index, R is the row number, and C is the column number. As an alternative to specifying the table parameter, you can specify an index string, such as the return value from a CellGetIndex action. For example: index=&CellIndex; |
|
ret=&variable |
The return value. |
Example
This is an example of several of the HTMLTable actions:
 Image
Image
These are the actions associated with the Image step type.

 Click
ClickDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Click.

 Exists
ExistsDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Exists.

 Get_Property
Get_PropertyDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Get_Property.

 RightClick
RightClickDescription
Performs a right-click on the image. This action is supported only for a related-content image glyph.
 Link
Link
These are the actions associated with the Link step type.

 Click
ClickDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Click.

 Exists
ExistsDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Exists.

 Get_Property
Get_PropertyDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Get_Property.
 Log
Log
Use the Message, Pass, Warning, and Fail log actions to write entries to the execution log.
Text specified in the Recognition field is written to the log and is displayed as a line in the tree view and in the Message field in the Details pane. Text in the Value field is written to the log and is displayed in the Details field in the Details pane when the corresponding line is selected in the tree view.
Use the Snapshot action to capture a screen image.
These are the actions to add entries to the execution log.

 Fail
FailDescription
Logs an entry with a status of Fail.

 Message
MessageDescription
Logs a message with a status of Info.

 Pass
PassDescription
Logs an entry with a status of Pass.

 SnapShot
SnapShotDescription
Logs an entry with an image of the current screen.

 Warning
WarningDescription
Logs an entry with a status of Warning.
Example
This example shows how the Log actions log text:
This log example shows how text from the Log actions appears in the Log Viewer:
 LongText
LongText
These are the actions associated with the LongText step type.

 Exists
ExistsDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Exists.

 Get_Property
Get_PropertyDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Get_Property.

 GetLabel
GetLabelDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See GetLabel.

 Set_Value
Set_ValueDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Set_Value.

 SetValue_InModal
SetValue_InModalDescription
Use the SetValue_InModal action to set the value of a long text field on a modal page.

 Verify
VerifyDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Verify.
 Loop
Loop
These are the actions associated with the Loop step type.

 Do
DoDescription
Executes the steps between the Loop.Do step and the Loop.End_Loop until a Loop.Exit step is encountered.
Example
This example shows the Loop.Do construct:

 End_Loop
End_LoopDescription
Terminates a Loop.Do or Loop.While construct.

 Exit
ExitDescription
Exits a Loop.For or Loop.While construct. Execution continues with the step following the End_Loop step. Typically, a Loop.Exit step is placed within a conditional construct.

 While
WhileDescription
Executes the steps between the Loop.While step and the Loop.End_Loop while the expression in the Recognition field evaluates to True.
When the expression evaluates to false, flow skips to the step following the End_Loop step.
Example
The following example shows the Loop.While construct:

 For
ForSyntax
&variable=begin_value to end_value;
Description
Executes the steps between the Loop.For step and the Loop.Next step until the expression in the Recognition field evaluates to False, then flow skips to the step following the Loop.Next step.
Parameters
|
&variable |
The variable to be used in the comparison. This variable is incremented in the Loop.Next step. |
|
begin_value |
The starting value. |
|
end_value |
The ending value. |

 Next
NextDescription
Terminates a Loop.For construct. Loop.Next increments the variable in the Loop.For step.
See Add.
Example
The following example shows the Loop.For construct:
 MultiSelect
MultiSelect
These are the actions associated with the MultiSelect step type.

 Exists
ExistsDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Exists.

 Get_Property
Get_PropertyDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Get_Property.

 GetLabel
GetLabelDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See GetLabel.

 Set_Value
Set_ValueDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Set_Value.

 Verify
VerifyDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Verify.
 Page
Page
These are the actions associated with the Page step type.

 Expand
ExpandDescription
Attempts to expand all the collapsed sections on the current page.

 Go_To
Go_ToDescription
Accesses a page by selecting a page tab. Enter the page name in the Recognition field.
Example
This example shows the use of the Go_To action:

 Prompt
PromptDescription
Opens a component based on the MENU.COMPONENT.MARKET recognition string.
If the component has a search page, use the Page.PromptOk action to close the search page.
In the Value field, you must provide an action. The valid values are:
add
add update
add correct
update
update all
correction

 PromptOK
PromptOKDescription
Closes the search page. If the specified action is update, this action selects the first returned value.
Example
This example shows the use of the Prompt and Prompt OK actions:

 Save
SaveDescription
Attempts to save the current page. This action checks for the SkipSavePage flag in the execution options.

 SecPage_Close
SecPage_CloseDescription
Closes the secondary page.

 SecPage_Open
SecPage_OpenDescription
Opens a secondary page.
Parameters
|
page= value |
Specify the name of the secondary page. |
Example
The following example shows the SecPage_Open action:
 Process
Process
The Process actions run processes through Process Scheduler.

 Run
RunDescription
Runs a Process Scheduler process.
Parameters
|
prcname=value; |
The process name. |
|
prctype=value: |
The process type. |
|
wait=value; |
True - the test waits for the process to finish. False - the test does not wait for the process to finish. The default is False. |
|
outtype=value; |
The process output type. |
|
outformat=value; |
The process output format. |
|
outfile=value; |
The process output file. |
|
expected=value; |
Defines the expected status for the process when it completes. Expected status is based on status values returned in the Run Status column in Process Monitor. For example:
If the final status equals the expected status, then a Pass is logged; if not, a Fail is logged. |
|
ret=&variable |
The return value. True - the process completed successfully. False - the process did not complete successfully. |
Example
This example shows the use of the Run action to run a process:

 Run_Def
Run_DefDescription
Changes the default behavior of the run process. Insert these steps prior to the Process Run step that they modify. This action only supports one parameter per step. For multiple parameters, you will need multiple steps.
Parameters
|
RunButton=value; |
The run button name. |
|
ProcessMonitorLink=value; |
The Process Monitor link name. |
|
ProcessInstanceField=value; |
The field where the process instance ID will appear. |
|
QueuedTimeout=value; |
Overwrites the local option value (in minutes). |
|
PostingTimeout=value; |
Overwrites the local option value (in minutes). |
|
ProcessingTimeout=value; |
Overwrites the local option value (in minutes). |
|
ExceptionTimeout=value; |
General timeout, in minutes, for all the states that are not in the local option. |
|
QueuedResult=value; |
Overwrites the local option value. Valid values are FAIL and WARN. |
|
PostingResult=value; |
Overwrites the local option value. Valid values are FAIL and WARN. |
See Also
 Pwd
Pwd
These are the actions associated with the Pwd step type.

 Exists
ExistsDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Exists.

 GetLabel
GetLabelDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See GetLabel.

 Set_Value
Set_ValueDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Set_Value.
 Query
Query
This is the action associated with the Query step type.

 Exec
ExecDescription
Runs a public query in PeopleSoft Query and downloads the results. To run a private query, use the Exec_Private action.

 Exec_Private
Exec_PrivateDescription
Runs a private query in PeopleSoft Query and downloads the results.
|
outFile=value; |
The query output file. |
|
outFolder=value ; |
The folder where the result will be saved. If this parameter is missing, the system will use the value in the local option. |
|
outFormat=value; |
The file format that will be used to download the result file. If this parameter is missing, the system will use the value in the local option. |
|
param=value; |
The list of comma delimited values for all the query parameters. |
|
0rows=value; |
If the query returns zero rows, add a log entry of type value. Valid values are Pass, Fail, or Warning. |
|
Nrows=value; |
If the query returns one or more rows, add a log entry of type value. Valid values are Pass, Fail, or Warning. |
Use the following formats to specify query parameters:
|
Page Control |
Format |
|
Text |
param=value |
|
Radio button |
param={RB}value |
|
Combo box |
param={CB}value |
|
Check box |
param={CH}value |
|
Text box |
param={EB}value |
 Radio
Radio
These are the actions associated with the Radiostep type.

 Exists
ExistsDescription
The value property is required to validate whether a radio button exists on the page. It can be defined in the Recognition field using value=value or in the Value field.
See Exists.
Example
In the following example, in the first step the value property is set in the Value field. In the second step, the value is set in the Recognition field using the Value= parameter.
![]()
Example of setting the value for a Radio step type

 Get_Property
Get_PropertyDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Get_Property.

 GetLabel
GetLabelDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See GetLabel.

 Set_Value
Set_ValueDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Set_Value.

 Verify
VerifyDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Verify.
 RichText
RichText
These are the actions associated with the RichText step type.

 GetLabel
GetLabelDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See GetLabel.

 Set_Value
Set_ValueDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Set_Value.
 Scroll
Scroll
These are the actions associated with the Scroll step type.
The Scroll ID field is required for all Scroll action types.
See Also
Incorporating Scroll Handling.

 Action
ActionDescription
Takes an action based on the row specified by Key_Set.
Parameters
|
ret=&variable; |
The return value. It returns the position index for the field acted upon, based on the row identified using Key_Set. |
Specify the action in the Value column.
This table lists the valid values for the Action action.
|
Value |
Description |
|
ins |
Insert a row. If the current row is the first row, then use the existing row. |
|
ins+ |
Always insert a row. |
|
delins |
Delete all rows, and then insert into the first row. |
|
del |
Delete the row specified by the Key_Set action. |
|
delall |
Delete all rows. No further processing. |
|
delsel |
Look for the row and delete it. Do not add a fail if the row does not exist. |
|
upd |
Find a specified row to work with. If the row is not found, insert a new row or use the first row for the first time. |
|
upd+ |
Find a specified row to work with. If is not found, always insert a new row. |
|
sel |
Find a row specified by the Key_Set action. |
|
find |
Use the scroll Find link. Format: find=text_to_find |
|
not |
Check that the row is not in the scroll. Add a Fail to the log if the row is found. |

 Definition
DefinitionDescription
Use the Definition action to override the default name object of scroll buttons and the scroll parent. This is necessary, for example, when a page uses custom objects (such as links or pushbuttons) to handle conventional scroll actions such as adding or deleting rows from the scroll.
Parameters
|
def=value; |
One of the definition values. Example:
The following table gives valid values for the def parameter. |
|
type=value; |
Thestep type for the new action. Example 1:
Example 2:
|
|
value=value; |
The scroll parent variable or the new object recognition string. Example 1:
Example 2:
|
This table lists the valid values for the def parameter:
|
Value |
Description |
|
add |
Override the Add new row button. |
|
del |
Override the Delete row button. |
|
next |
Override the Next button. |
|
prev |
Override the Previous button. |
|
first |
Override the First button. |
|
last |
Override the Last button. |
|
parent |
Reassign the parent for a specific scroll area. |

 ModalGrid_Close
ModalGrid_CloseDescription
Closes a modal grid.

 ModalGrid_Open
ModalGrid_OpenDescription
Opens a modal grid.

 Key_Set
Key_SetDescription
Defines each key field of a scroll. Use multiple Key_Set steps for scrolls with multiple key fields.
Specify the step type and field name as parameters. Specify the key value in the Value column.
Parameters
|
type=value; |
The step type for the key field. Example:
|
|
name=value; |
The name of the key field. |

 Reset
ResetDescription
Resets all the scroll variables and closes the scroll section in the log.

 RowCount
RowCountDescription
Returns the number of rows for the defined scroll.
Example
These examples show the use of scroll actions:
This example uses the Definition action with the def=Add parameter to assign the Add action to the image $ICField3$newm$0$$mg$0:
![]()
Example of a Definition action with def=Add parameter
In this example the Definition action with a def=parent parameter reassigns the parent:
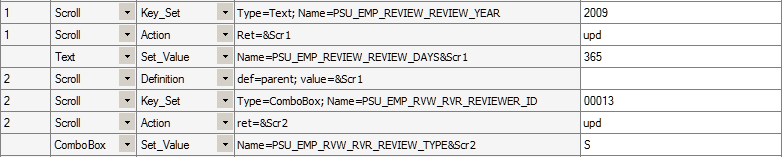
Example of the Definition action with the def=parent paramenter
 Span
Span
These are the actions associated with the Span step type.

 Click
ClickDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Click.

 Exists
ExistsDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Exists.

 Get_Property
Get_PropertyDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Get_Property.

 GetLabel
GetLabelDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See GetLabel.

 MouseOver
MouseOverDescription
Fires the mouseover event to show a popup page. Enter the page name in the Recognition field.
See Also

 MouseOverClose
MouseOverCloseDescription
Fires the mouseout event to close a popup page. Enter the page name in the Recognition field.
See Also
Example
The following examples show how MouseOver and MouseOverClose can be used with popup pages.
To record a verification of a field value in a mouseover popup window:
From the recorder tool bar, click and drag the Verify icon and hover over the field with a popup window.
Wait until the popup window appears.
Move the cursor to the field you want to check, then release the mouse button.
PTF Recorder generates the following steps:
To record an action for an object inside a mouseover popup window:
Click and drag the Verify icon and hover over the field with a popup window.
Wait until the popup window appears, then release the mouse button.
Perform the action you want to record, such as clicking a URL link.
PTF Recorder generates the following steps:

 Verify
VerifyDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Verify.
Example
This step validates a Span object that contains informational text:
![]()
Example of the Span.Verify action
 Test
Test
This is the action associated with the Test step type.

 Exec
ExecDescription
Calls another test or library test.
Specify the child test name in the Recognition field and one or more test case names in the Value field, separated by commas.
You can also click in the Recognition field then click the elipsis icon and select a test case to automically populate the Recognition and Value fields with the test name and the test case name.
Test.Exec supports the use of parameters that enable you to pass dynamic values from a calling test to a library test.
Right-click the test name in the Recognition field and select Open Test to open the child test.
Use the #IGNORE reserved word in the Value field to skip the call to the child test for a given test case.
See Using Parameters with Library Tests.
Example
This test calls the test COPY_USER_PROFILE with the DEFAULT, CASE_01, and CASE_02 test caseS, then skips the call to PROCESS:
 Text
Text
These are the actions associated with the Text step type.

 Exists
ExistsDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Exists.

 Get_Property
Get_PropertyDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Get_Property.

 GetLabel
GetLabelDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See GetLabel.

 Set_Value
Set_ValueDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Set_Value.

 Verify
VerifyDescription
The description for this action is in the Common Actions section.
See Verify.
 Variable
Variable
This is the action associated with the Variable step type.

 Set_Value
Set_ValueDescription
Assigns a value to the given variable.
Example
This example shows how to set a variable and how to use variables in other steps:

Example of the Set_Value action
See Also
 Wait
Wait
These are the actions associated with the Wait step type.

 For_Seconds
For_SecondsDescription
Specify in the Recognition field the number of seconds PTF will wait before proceeding to the next step.

 For_Value
For_ValueDescription
Wait until the field contains the value specified in the Value field.
Parameters
|
type= value |
Specify the step type, such as Text, Combobox, Link, and so on. |
|
timeout=value |
[Optional] Specify the time out value, in seconds. The default is 300 seconds. |
|
refresh=value |
[Optional] Specify the refresh button name. If the refresh= parameter is specified, PTF waits five seconds between each validation process and the refresh click. |
Example
This example shows the use of Wait:
 Common Actions
Common Actions
The actions in this section can be used with multiple step types. The step types that support the action are listed with each action.

 Click
ClickDescription
Performs a mouse click on the specified object.
This is the list of objects that support this action:
Example
This example shows the use of the Click action with a Button object and a Link object:

 Exists
ExistsDescription
Checks whether the object exists on the page.
This is the list of objects that support this action:
Button
See Button.
CheckBox
See CheckBox.
ComboBox
See ComboBox.
Image
See Image.
Link
See Link.
LongText
See LongText.
MultiSelect
See MultiSelect.
Pwd
See Pwd.
Radio
Refer to the Radio step type entry for details.
See Radio.
Span
See Span.
Text
See Text.
Parameters
|
ret=&variable; |
ret=true – the object exists ret=false – the object does not exist |
|
expected=value |
Specify expected=true or expected=false. Logs a Pass or Fail based on whether the ret parameter matches the expected parameter. |
Example
This example shows the use of the Exists action:

 Get_Property
Get_PropertyDescription
Gets the property value of an HTML object based on the prop=value parameter and assigns it to the variable in ret=&variable.
Use the HTML Browser feature of the Message tool to identify the properties and values of an object.
Some objects have properties that are different from what you might expect.
For example:
The value property for a check box returns Y for selected, N for deselected.
Combo boxes return the translate value of the selection for the value property.
The full text of the selected item is available as the text property.
Radio buttons return the translate value of the selection for the value property.
The label of the selected item is a separate label object.
This is the list of objects that support this action:
Button
See Button.
CheckBox
See CheckBox.
ComboBox
See ComboBox.
Image
See Image.
Link
See Link.
LongText
See LongText.
MultiSelect
See MultiSelect.
Radio
Refer to the Radio step type entry for details.
See Radio.
Span
See Span.
Text
See Text.
Parameters
|
prop=value; |
The property name. |
|
ret=&variable; |
The return value. |
Example
This example shows the use of the Get_Property action:

 GetLabel
GetLabelDescription
Gets the label for the specified HTML object.
This is the list of objects that support this action:
CheckBox
See CheckBox.
ComboBox
See ComboBox.
LongText
See LongText.
MultiSelect
See MultiSelect.
Pwd
See Pwd.
Radio
Refer to the Radio step type entry for details.
See Radio.
RichText
Refer to the RichText step type entry for details.
See RichText.
Span
See Span.
Text
See Text.

 Set_Value
Set_ValueDescription
Sets the field value in the browser object.
This is the list of objects that support this action:
CheckBox
See CheckBox.
ComboBox
See ComboBox.
LongText
Use the SetValue_InModal action to set the value of a long text field on a modal page.
See SetValue_InModal.
See LongText.
MultiSelect
See MultiSelect.
Pwd
See Pwd.
Radio
Refer to the Radio step type entry for details.
See Radio.
Text
See Text.
Example
This is an example of the use of the Set_Value action:

 Verify
VerifyDescription
Compares the value in the browser to the expected value, and adds a pass or fail log entry for the validation.
This is the list of objects that support this action:
CheckBox
See CheckBox.
ComboBox
See ComboBox.
LongText
See LongText.
MultiSelect
See MultiSelect.
Radio
Refer to the Radio step type entry for details.
See Radio.
Span
See Span.
Text
See Text.
Example
This is an example of the Verify action:
 Reserved Words
Reserved Words
This section defines PTF reserved words. The reserved words are listed alphabetically.

 #CHECK#
#CHECK#
Description
The #CHECK# reserved word modifies the behavior of a Set_Value action to be more like a Verify action. This can be useful when you want to set data in a particular field for one test case and verify the data in the same field for a different test case.
Note. If the values are not equal, PTF will always try to update the value (unless the object is display-only). If the values are equal, PTF will not update the value.
Example
For example, a text box could be set and verified with the following two steps:
![]()
Example of setting a value and verifying a value in two steps
Suppose, however, that the test calls for using two test cases. The first test case sets the calculation name equal to KUSPTEST. The second test case verifies the value of KUSPTEST.
The test case that sets the value to KUSPTEST would be constructed as shown in the first step of the previous example. The test case that verifies the value as KUSPTEST would be constructed as shown in the following example:
![]()
Example of setting a value and verifying a value using #CHECK#

 #DIS#
#DIS#
Description
This reserved word verifies a value and also checks whether the object is display-only. It logs a Fail if the object is not display-only or if the expected value does not match the application value.
If you use #DIS# without a value, then the value is ignored and #DIS# only checks for whether the field is disabled.
This reserved word is useful when, for example, PeopleCode is expected to make an object visible but not editable.
Example
The following example checks whether the Benefit Commencement Date field date is display-only and the value is equal to 07/12/2000:
![]()
Example of using #DIS#

 #DTTM
#DTTM
Description
Similar to #TODAY, the #DTTM reserved word inserts the current date and time into a field in the application.
See Also

 #EXIST#
#EXIST#
Description
Verifies the existence of a field.
If the field exists in the application, a Pass is logged. If the field is not found, a Fail is logged.
If a value is passed after the closing # and the field exists, PTF tries to set the field to that value.
Example
In this example, the first step checks for whether the Benefit Plan field exists in the application and logs a Fail if it is not found. The second step not only checks for the existence of the field, it attempts to enter the value KUHP into it:
![]()
Example of using #EXIST#
See Also

 #FAIL#
#FAIL#
Description
This reserved word works the same as #CHECK# but does not update the value after performing the comparison. If a mismatch is found, a Fail is logged; otherwise, a Pass is logged.
You would use #FAIL# rather than #CHECK# when you do not want to update the field if a mismatch exists.
Example
In this example, the PTF test logs a Fail if the Summary Calculation Name field is not equal to KUSPTEST:
![]()
Example of #FAIL#
See Also

 #IGNORE
#IGNORE
Description
Place the #IGNORE reserved word in the Value field of a Test.Exec step to skip the call to the child test. Suppose you have a parent test with two test cases. In the first test case, the parent test calls a child test. In the second test case, the parent does not call the child. Use the #IGNORE reserved word in the Value field with the second test case to skip calling the child for that test case.
In this example, the first step for the test case calls the test CHILD_ONE with test case CASE_01. The second step skips the call to CHILD_TWO for this test case.

 #LIKEF#
#LIKEF#
Description
The #LIKEF# and #LIKEW# reserved words are similar to the #FAIL# and #WARN# reserved words except that they look for similar values, not an exact match. If a similar match is not found, #LIKEF# logs a Fail and #LIKEW# logs a Warning.
Similar to the behavior of #FAIL# and #WARN# (and unlike the behavior of #CHECK#), if the comparison fails, PTF does not update the value. The steps only affect the error state of the execution log.
This table details ways #LIKEW# or #LIKEF# can match strings:
|
Type of Match |
Pattern |
Match (Log a Pass) |
No Match (Log a Fail or Warn) |
|
Multiple characters |
a*a |
aa, aBa, aBBBa |
ABC |
|
Multiple characters |
*ab* |
abc, AABB, Xab |
aZb , bac |
|
Multiple characters |
ab* |
abcdefg, abc |
cab, aab |
|
Special character |
a[*]a |
a*a |
Aaa |
|
Single character |
a?a |
aaa, a3a, aBa |
ABBBa |
|
Single digit |
a#a |
a0a, a1a, a2a |
aaa, a10a |
|
Range of characters |
[a-z] |
f, p, j |
2, & |
|
Outside a range |
[!a-z] |
9, &, % |
b, a |
|
Not a digit |
[!0-9] |
A, a, &, |
0, 1, 9 |
|
Combined |
a[!b-m]# |
~ An9, az0, a99 |
abc, aj0 |
Example
Suppose a test requires verification of only the first several characters of a text entry. In the following example, the first step logs a Fail if the first two characters of the Benefit Plan field are not equal to US. The second step logs a Fail unless the first two characters of the Benefit Plan field are equal to US and the last character is equal to 1:
#LIKEF# and #LIKEW# only compare the date text of a date/time value. For example, some fields contain the current date and time. Use the #LIKEF##TODAY* construction to compare just the date portion of a Datetime field and ignore the time portion.
For example:
![]()
Example of using #LIKEF##TODAY*

 #LIKEW#
#LIKEW#
Description
The #LIKEW# reserved word is used the same as #LIKEF# except it logs a Warning rather than a Fail. For complete details for using #LIKEW# see #LIKEF#.
See Also

 #LIST#
#LIST#
Description
This reserved word checks the values of a ComboBox. It works with either the full text entries in the combo box or the metadata translation (XLAT) values of the entries.
Use #LIST# with a Set_Value action to check one or more values and then set an item in a drop-down list box, list the items separated by a vertical pipe (|) and place brackets ([]) around the item that you want to select. If the value in the field is not the same as the value in brackets, PTF logs an error and sets the value in the field to the value in brackets.
Example
This example shows the use of the #LIST# reserved word:
In this example, the first step verifies the existence of items in the list. The second step verifies that the items exist and verifies that Individual is selected.
![]()
Example of using #LIST#
This example is similar to the previous example, but it refers to the entries by the metadata translation (XLAT) values rather than the text that actually appears in the combo box:
![]()
Example of using #LIST# with translate values

 #NOTEXIST#
#NOTEXIST#
Description
The opposite of the #EXIST# reserved word, #NOTEXIST# verifies that a field does not exist.
If the field does not exist, a Pass is logged. If the field does exist, a Fail is logged.
See Also

 #NOTHING
#NOTHING
Description
PTF ignores any step with a Set_Value or Verify action where the Value field is empty, or blank. The #NOTHING reserved word enables you to use SET_VALUE to set a field to blank or select a blank value from a drop-down list box. You can use #NOTHING with a Verify action to verify that a field is blank.
The #NOTHING reserved word does not have a closing pound sign (#). It cannot be used in combination with other reserved words.
Note. Leaving the Value field of a test step blank does not have the same effect as using the #NOTHING reserved word. PTF ignores any Set_Value or Verify action where the Value field is blank.
Example
In the following example, in the first step #NOTHING selects a blank value in the Calculation Reason field and then, in the next step, it verifies that the field is blank:
![]()
Example of using #NOTHING

 #PREFIX#
#PREFIX#
Description
The #PREFIX# reserved word substitutes the text in the Prefix field in the Test Editor for the #PREFIX# string in the Value field.
This substitution is useful when developing a test that adds new data. It enables you to modify each new added record slightly so that the test is able to successfully add unique data each time the test is executed.
Example
Suppose you entered add in the Prefix field, as in this example:
Example of Prefix field
The following test step would enter the value addUSER into the User ID field:
Note. The #PREFIX# reserved word can only be used at the beginning of the text in the Value field.

 #TODAY
#TODAY
Description
Substitutes the current date.
Note. The #TODAY reserved word does not have a closing pound sign (#). It cannot be followed by another reserved word.
Example
Suppose you have the following test instruction:
12. Enter the current date into the Event Date field.
The following step sets the value of the Event Date field to the date at the moment of test execution:
![]()
Example of using #TODAY
You can use the + or – operators in conjunction with the #TODAY reserved word to reference a date in the future or past. In this example, the test verifies that the calculation event date is 10 days in the future:
![]()
Example of using #TODAY+10

 #WARN#
#WARN#
Description
This reserved word works the same as #CHECK# but does not update the value after performing the comparison. If a mismatch is found, a Warning is logged; otherwise, a Pass is logged.
You would use #WARN# rather than #CHECK# when you do not want to update the field if a mismatch exists.
See Also
 System Variables
System Variables
System variables are populated by PTF at runtime. The following table lists PTF system variables.
|
Variable |
Description |
|
%env.toolsrel% |
The PeopleTools version. |
|
%env.database% |
Database name. |
|
%env.appserver% |
Application server name. |
|
%eo.name% |
Current execution option name. |
|
%eo.platform% |
Execution option platform. |
|
%eo.dbname% |
Execution option database name. |
|
%eo.dbserver% |
Execution option database server name. |
|
%eo.dbuser% |
Execution option database user name. |
|
%eo.pserver% |
Execution option process server. |
|
%eo.dbname% |
Execution option database name. |
|
%eo.pshome% |
Execution option PS_HOME path. |
|
%eo.verbose% |
Execution option verbose flag. |
|
%test% |
Current test name. |
|
%case% |
Current test case name. |
|
%component% |
Current component name. |
|
%page% |
Current page name. |
|
%log.id% |
Current log number. |
|
%pid% |
The last process instance number. |
 Functions
Functions
This section lists the PTF functions.

 Add
Add
Syntax
Add(number1|number2[|number3]...)
Description
Use the Add function to add a series of numbers. Decimals and negative numbers are supported.
Parameters
|
number1 |
Number to be added. |
|
number2 |
Number to be added. |
|
number3… |
(Optional) A series of additional numbers to be added. |
Returns
Sum of the numbers in the parameters.
Example
The following table presents examples of using Add.
|
Expression |
Result |
|
Add(10| -12| -3| 4| 6) |
5 |
|
Add(10.43| 10.55| -6.789| -178) |
-163.809 |

 Concat
Concat
Syntax
Concat(string1|string2[|string3…])
Description
Concatenates the strings in the parameters.
Parameters
|
string1 |
Beginning string for concatenation |
|
string2 |
A string to be concatenated to string1. |
|
string3… |
Additional strings to be concatenated. |
Returns
Returns a string resulting from concatenating the strings in the parameters.
Example
The following table presents examples of using the concat function:
|
Expression |
Result |
|
concat(hello |and |welcome |to |PTF) |
hello and welcome to PTF |

 Date
Date
Syntax
Date()
Description
Returns the current date, using the date format specified in the current execution option.
Returns
The current date.
Example
The following table presents example of using the Date function:
|
Expression |
Result |
|
Date() |
07/04/2011 |

 Divide
Divide
Syntax
Divide(number1|number2[|dec=dec_places])
Description
Use the Divide function to perform division. Decimals and negative numbers are supported. Optionally specify the number of decimal places.
Parameters
|
number1 |
The dividend. |
|
number2 |
The quotient. |
|
dec=dec_places |
(Optional) The number of decimal places. The maximum is 10. The default is zero. Note that "dec=" must be included in the parameter. |
Returns
The result of dividing number1 by number2 rounded to dec_places decimals.
Example
The following table presents examples of using the Divide function:
|
Expression |
Result |
|
Divide(75| 13.5) |
6 |
|
Divide(-75| 13.5| dec=5) |
-5.55556 |

 GetField
GetField
Syntax
GetField(string, segment, delimiter)
Description
GetField returns the substring from a specified segment of a character-delimited text string.
Parameters
|
string |
A character-delimited text string. |
|
segment |
An integer specifying which segment of the string will be returned, counting left to right. Specify a negative integer to count right to left. |
|
delimiter |
The character that delimits each segment in the string. |
Returns
Returns the substring between the delimiters in the specified segment of the string.
Example
The following table presents examples of using GetField.
|
Expression |
Result |
|
GetField(a/b/c| 1| /) |
a |
|
GetField(a/b/c| 2| /) |
b |
|
GetField(a/b/c| 5| /) |
blank |
|
GetField(a/b/c| -1|/) |
c |

 InStr
InStr
Syntax
InStr(string|within_string)
Description
Locates a substring within a string of text and returns the starting position of the substring as an integer..
Parameters
|
substring |
The text you are searching for. The string parameter is not case sensitive. |
|
within_string |
The text string you are searching within. |
Returns
Returns an integer indicating the starting position of substring in within_string.
InStr returns 0 if substring does not appear in within_string. It returns 1 if within_string is empty.
Example
The following table presents examples of using the InStr function.
|
Expression |
Result |
|
instr(ABCDEFG|c) |
3 |
|
instr(ABCDEFG|C) |
3 |
|
instr(ABCDEFG|CDE) |
3 |
|
instr(ABCDEFG|zz) |
0 |
|
instr(ABCDEFG|) |
1 |
|
instr(ABCDEFG|A) |
1 |

 LCase
LCase
Syntax
LCase(string)
Description
Converts a string to lowercase.
Parameters
|
string |
The string to be converted. |
Returns
Returns a string resulting from converting string to lowercase.
Example
The following table presents example of using the LCase function.
|
Expression |
Result |
|
lcase(Hello World 1234) |
hello world 1234 |

 Left
Left
Syntax
Left(string|length)
Description
Extracts a substring of a specified number of characters from the left side of a string.
Parameters
|
string |
A string from which to extract a substring. |
|
length |
A number specifying the number of characters in the substring. |
Returns
Returns a substring length characters long from the left side of a string.
Example
The following table presents example of using Left function.
|
Expression |
Result |
|
left(Hello World|5) |
Hello |

 Len
Len
Syntax
Len(string)
Description
Returns the length of string as an integer.
Parameters
|
string |
A text string. |
Returns
Returns an integer indicating the length of string.
Example
The following table presents example of using Len function.
|
Expression |
Result |
|
len(Hello World) |
12 |

 Multiply
Multiply
Syntax
Multiply(number1|number2[|dec=dec_places])
Description
Use the Multiply function to perform multiplication. Decimals and negative numbers are supported. Optionally specify the number of decimal places.
Parameters
|
number1 |
First factor. |
|
number2 |
Second factor. |
|
dec_places |
(Optional) The number of decimal places. The maximum is 10. The default is zero. Note that "dec=" must be included in the parameter. |
Returns
The result of multiplying number1 by number2 rounded to dec_places decimals.
Example
The following table presents examples of using Multiply function.
|
Expression |
Result |
|
Multiply(10.3| 13.45) |
139 |
|
Multiply(10.3| -13.45|dec=3) |
-138.535 |

 Now
Now
Syntax
Now()
Description
Returns the current datetime, using the date format specified in the current execution option.
Returns
The current datetime.
Example
The following table presents example of using Now function.
|
Expression |
Result |
|
Now() |
07/04/2011 12:20 PM |

 Replace
Replace
Syntax
Replace(source|find|replace)
Description
Use the Replace function to replace every occurrence of a substring found in a string with a new substring.
Parameters
|
source |
A string in which you want to replace substrings. |
|
find |
A string equal to the substring of source you want to replace. |
|
replace |
A string with which to replace occurrences of find in source. |
Returns
Returns a string resulting from replacing every occurrence of find found in source with replace.
Example
The following table presents example of using Replace function.
|
Expression |
Result |
|
replace(original text|i|77) |
Or77g77nal text |

 Right
Right
Syntax
Right(string|length)
Description
Use the Right function to extract a substring of a specified number of characters from the right side of a string.
Parameters
|
string |
A string from which to extract a substring. |
|
length |
A number specifying the number of characters in the substring. |
Returns
Returns a substring length characters long from the right side of a string.
Example
The following table presents example of using Replace function.
|
Expression |
Result |
|
right(Hello World|5) |
World |

 Round
Round
Syntax
Round(number|[|dec=dec_places])
Description
Use the Round function to round a number. Decimals and negative numbers are supported. Optionally specify the number of decimal places.
Parameters
|
number1 |
First factor. |
|
number2 |
Second factor. |
|
dec_places |
(Optional) The number of decimal places. The maximum is 10. The default is zero. Note that "dec=" must be included in the parameter. |
Returns
The result of rounding number1 to dec_places decimal places.
Example
The following table presents example of using Round function.
|
Expression |
Result |
|
Round(-130.456) |
-130 |
|
Round(-130.456|dec=2) |
-130.46 |
|
Round(-130.455|dec=2) |
-130.45 |

 Sum
Sum
Syntax
Sum,Index, value, delimiter)
Description
Sum works with the HTMLTable indexes.
Parameters
|
Index |
The HTMLTable index string, such as 2/5/4. An index string is the return value of CellGetIndex. See CellGetIndex. |
|
Value |
The value that you want to add or subtract. The default action is addition. |
|
Section |
The section of the index that will be modified. |
|
Delimiter |
The character that delimits each section in the text value. |
Example
The following table presents examples of using Sum.
|
Expression |
Result |
|
Sum(2/5/4, 2, 1, /) |
4/5/4 2 is added to the first section of the string. |
|
Sum(2/5/4, -1, 3, /) |
2/5/3 |
|
Sum(&index, -4, 3, /) |
4 is subtracted from the third section of the string in the variable &index. |

 Subtract
Subtract
Syntax
Subtract(number1|number2[|number3]...])
Description
Use the Subtract function to subtract a series of numbers. Numbers can be decimal and negative.
Parameters
|
number1 |
Initial number. |
|
number2 |
Number to be subracted. |
|
number3… |
(Optional) A series of additional numbers to be subtracted. |
Returns
The result of subtracting number2, number3, etc., from number1.
Example
The following table presents examples of using Subtract function.
|
Expression |
Result |
|
Subtract(10|2|3) |
5 |
|
Subtract(10|-2|-3) |
15 |

 SubStr
SubStr
Syntax
SubStr(source_str|start_pos[|length])
Description
Extracts a substring of a specified number of characters beginning at a specified location in a source string.
If length is not specified, SubStr returns the substring starting at the position specified in start_pos and continuing to the end of the string.
Parameters
|
source_str |
A string from which to extract a substring. |
|
start_pos |
A number representing the character position in source_str where the substring starts, starting at 1. |
|
length |
A number specifying the number of characters in the substring. |
Returns
Returns a string equal to a substring length characters long beginning at character start_pos of source_str.
Example
The following table presents examples of using SubStr function.
|
Expression |
Result |
|
substr(12345678|2|3) |
234 |
|
substr(12345678|2) |
2345 |

 Trim
Trim
Syntax
Trim(string)
Description
Returns a string with all leading and trailing spaces removed.
Parameters
|
string |
A text string. |
Returns
Returns a string with all leading and trailing spaces removed.
Example
The following table presents example of using trim function.
|
Expression |
Result |
|
trim( Hello World ) |
Hello World |

 UCase
UCase
Syntax
UCase(string)
Description
Converts a string to uppercase.
Parameters
|
string |
The string to be converted. |
Returns
Returns a string resulting from converting string to uppercase.
Example
The following table presents example of using UCase function.
|
Expression |
Result |
|
ucase(Hello World 1234) |
HELLO WORLD 1234 |