26 Work with Parent/Child Relationships
Address book records are organized into multiple levels of parent/child relationships, arranged in tree-like structures. Use parent/child relationships for e-mail distribution lists and A/R and A/P reporting structures.
This chapter contains these topics:
26.1 Objectives
-
To create and revise organizational structures
-
To sequence organizational structures
26.2 About Parent/Child Relationships
After you enter addresses in the Address Book system, you can define parent/child relationships among them. You can set up these relationships for:
-
Accounts receivable structures
-
Accounts payable structures
-
Reporting structures within your organization
You can define two types of structures:
-
A structure in which an address can appear multiple times
-
A structure in which an address can appear only once
The following graphic illustrates the structural relationship between a company and its subsidiaries:
Figure 26-1 Structural Relationship Between a Company and Its Subsidiaries
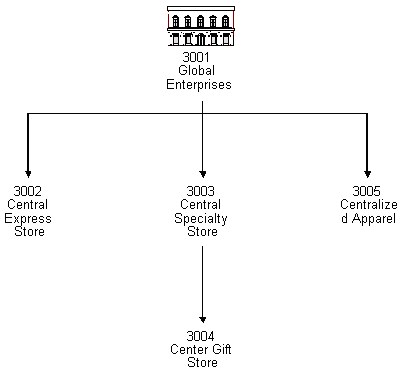
Description of "Figure 26-1 Structural Relationship Between a Company and Its Subsidiaries"
26.3 Creating Parent/Child Relationships
From Address Book (G01), enter 27
From A/B Advanced and Technical Operations (G0131), choose Organizational Structure
From Address Book Organizational Structure (G01311), choose Structure Revisions
You can create parent/child relationships for use in e-mail, A/R, and A/P. For example, in A/R you create parent/child relationships for receipt processing, as well as credit and collection processing for sending invoices and statements.
To create parent/child relationships
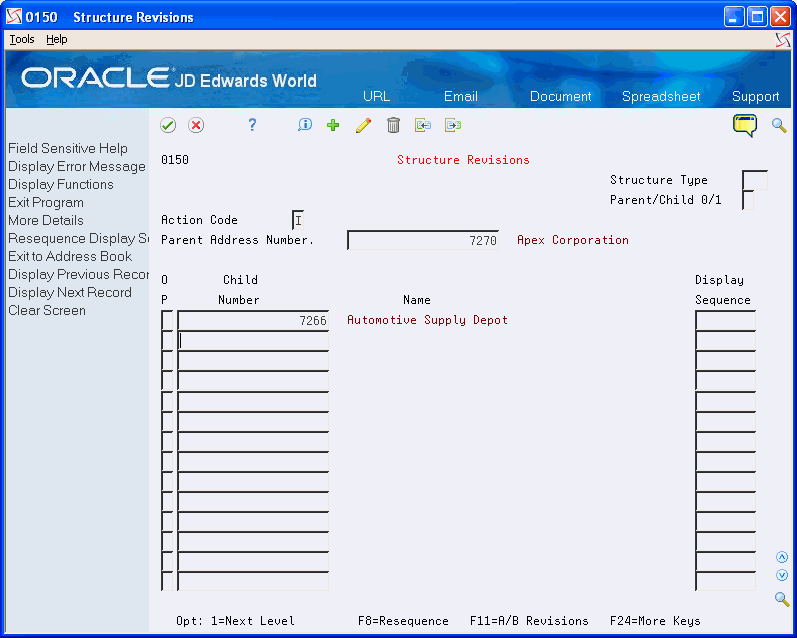
On Structure Revisions
-
Complete the following fields for inquiry:
-
Parent Address Number
-
Structure Type (optional)
-
Parent/Child 0/1 (optional)
-
-
Access the detail area (F4).
Figure 26-3 Structure Revisions (Detail) screen
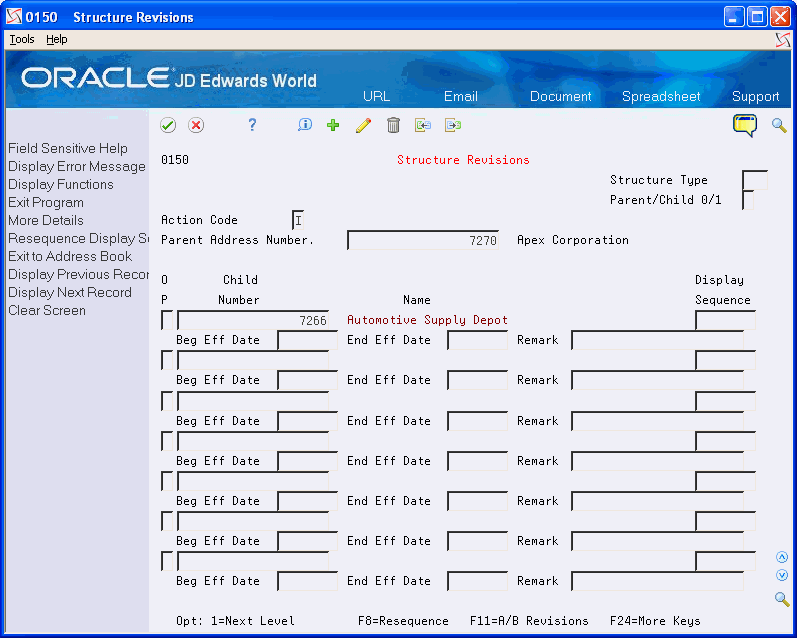
Description of "Figure 26-3 Structure Revisions (Detail) screen"
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Child Number
-
Display Sequence
-
Beginning Effective Date (optional)
-
Ending Effective Date (optional)
-
Remark (optional)
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Child Number | The address book number that you want to assign as a child of the parent address number. |
| Structure Type | A user-defined code (01/TS) that identifies a type of organizational structure with its own hierarchy in the Address Book system. For example, Accounts Receivable or e-mail.
Form-specific information The system uses the blank structure type for Parent/Child relationships that you set up in Customer Master Information (P01053) or Supplier Master Information (P01054). For Authorized Alternate Payee processing in the Accounts Payable system, the structure type is A85. |
| Parent/Child 0/1 | Determines whether child addresses or parent addresses will be displayed. Valid values are:
0 – Child addresses (default) 1 – Parent addresses 2 – The entire structure (parents and all children) |
| Beg Eff Date | The date on which the address book record will appear in the structure. The Beginning Effective Date field will prevent the address number from occurring in the structure until the beginning effective date is the same as the current date. If left blank, the address number will always occur in a structure unless there is an ending effective date. |
| End Eff Date | The date on which the address book record will cease to exist in the structure. |
| Remark | A generic field that you use for a remark, description, name, or address. |
| Sequence | A number that reorders a group of records on the form.
Form-specific information Type 1 next to the address book number you want displayed first. Type 2 next to the address book number you want displayed second, and so on. |
26.3.1 What You Should Know About
26.4 Viewing Parent/Child Relationships
From Address Book (G01), enter 27
From A/B Advanced and Technical Operations (G0131), choose Organizational Structure
From Address Book Organizational Structure (G01311), choose Structure Inquiry
After you create parent/child relationships, you can view all or part of the structure rather than each individual parent and children within the structure in any of the following ways:
-
With the levels indented or aligned
-
Through certain levels
-
Through certain dates
You can also:
-
Revise parent/child relationships on Structure Revisions
-
Revise address book information on Address Book Revisions
-
View information for a particular address on the Central Information File (CIF) Index
26.4.1 Before You Begin
-
To preload certain header information, set the appropriate processing option
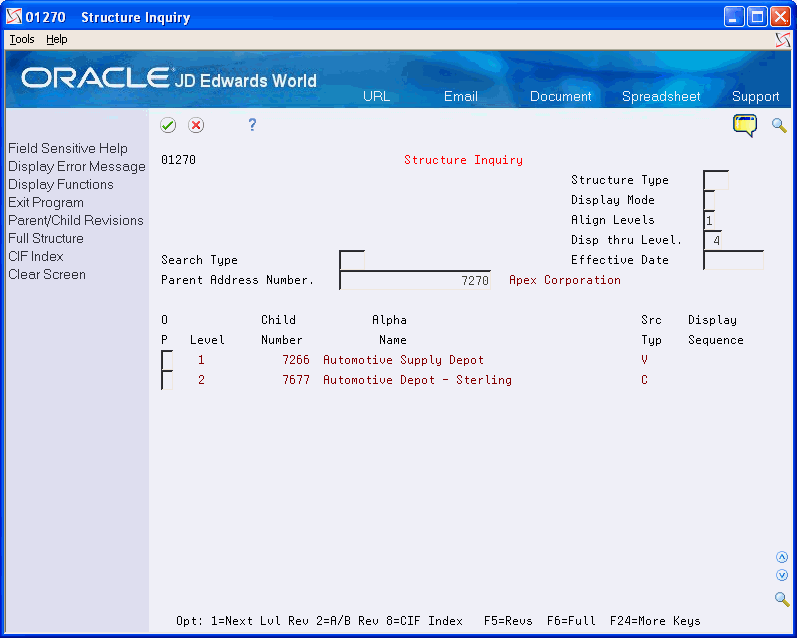
To view parent/child relationships
Complete the following field:
-
Parent address number
Depending on how you set the processing option, the system preloads the following information:
-
Display mode
-
Align levels
-
Display thru level
-
Effective date
-
Structure type
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Align Levels | A code that determines whether levels are indented or aligned on the form. Valid values are:
0 – indented 1 – aligned |
| Disp thru Level | A number indicating the level of a child in the relationship to its parent in a hierarchy. |
26.5 Printing Parent/Child Relationships
From Address Book (G01), enter 27
From A/B Advanced and Technical Operations (G0131), choose Organizational Structure
From Address Book Organizational Structure (G01311), choose Structure Print
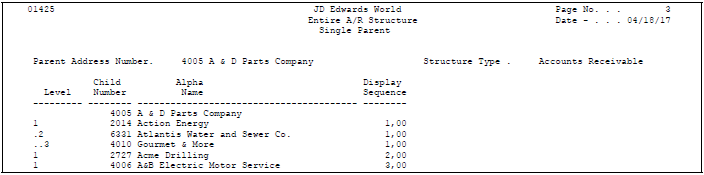
After viewing an organizational structure, you might want to print it. You can print:
-
A single parent/multiple child organizational structure
-
The entire structure type with all of its associated parents and children
Printing this report is especially helpful when researching accounts receivable relationships.
26.5.1 Processing Options
See Section 53.1, "Address Book Organization Structure Revisions (P0150)."