57 Set Up Revaluation Indices
This chapter contains the topic:
A revaluation index is a numerical value that you use to recalculate, or restate, the costs of your assets, most often in economies affected by hyperinflation or in situations where there are wide fluctuations in supply and demand for the assets. You can set up revaluation indices to restate cost in terms of either constant currency accounting or current cost. Typically, index values are obtained from either governments or outside agencies.
57.1 Setting Up Revaluation Indices
From Fixed Assets (G12), enter 27
From Advanced Operations (G1231), choose Revalue Assets
From Asset Revaluation (G1234), choose Revaluation Index
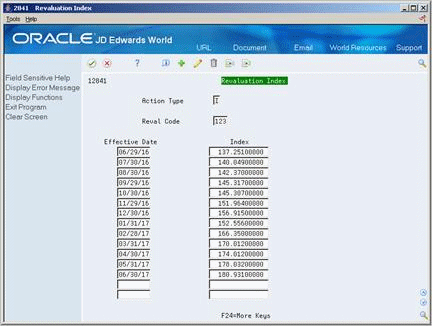
You can set up revaluation indices to conform to whatever periodic recalculation is necessary. In truly hyperinflationary economies, some as high as triple digit, this might be a daily procedure. The setup also accommodates weekly, monthly, quarterly, annual, or other periodic intervals as needed. You create tables of indices, each identified by a revaluation code. You can create as many revaluation codes as you need in user defined code table 12/RI.
On Revaluation Index
Complete the following fields:
-
Reval Code
-
Effective Date
-
Index
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Revaluation Code | A code which makes the Revaluation Index table (F12841) unique. |
| Date - Beginning Effective | The date on which an address, item, transaction, or table becomes active or the date from which you want transactions to display. The system uses this field depending on the program. For example, the date you enter in this field might indicate when a change of address becomes effective, or it could be a lease effective date, a price or cost effective date, a currency effective date, a tax rate effective date, and so on. |
| Rate Factor | A number that identifies the index or rate for calculations. The system multiplies the "from" amounts by this factor to calculate the amounts to be distributed. You can specify either positive or negative numbers and eight or fewer decimals. If you specify more than eight decimal positions, the system rounds to eight positions. If you leave this field blank, the default is 1.
If you specify a large whole number and a large number of decimal positions, the system might not be able to display the entire number. Even though all decimal positions cannot be displayed, they are stored (up to eight) correctly in the table. Note: For annual budgets, you can specify zero to remove all balances and start over. Form-specific information For Fixed Asset Revaluation, this is either an index or factor, depending on how the revaluation calculation is done. As an index, this value is the numerator of a fraction that is multiplied by the original cost of an asset to determine the revalued amount. The denominator of the fraction is the index from either the acquisition date or the depreciation start date, as designated in the processing options of the revaluation journal program. As a factor, this value is simply multiplied by the original cost to determine the revalued amount. These calculations also apply to depreciation amounts. |