8 Tax Rates and Areas
This chapter contains these topics:
8.1 About Tax Rates and Areas
This chapter describes how to maintain the current and anticipated tax rates and their effective dates. Use the Tax Rates & Areas program (P4008) to set up a tax area. A tax area is a physical geographical area. Each geographical area can be assessed taxes by different tax authorities for different purposes and for different tax rates.
The program also provides features for specialized situations.
-
For Canada, you can set up PST (either as a tax on a tax or as a pre-GST tax) and set up GST input credits.
-
For Tennessee, you can identify a maximum unit cost.
8.1.1 Definition of a Tax Area
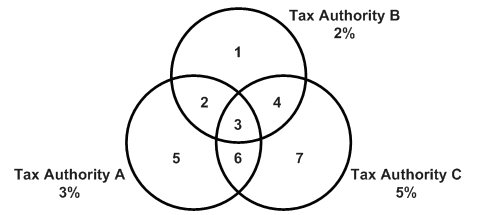
The following diagram illustrates how some tax areas could be organized.
The three circles represent three tax authorities. The seven numbered areas represent tax areas.
Notice that tax authority jurisdiction can overlap and that a tax area can be assessed taxes by one or more tax authorities. The tax rate for a tax authority does not vary from one tax area to another. Tax authority A assesses a 3% tax in tax areas 2, 3, 5, and 6.
For each tax area, however, the total tax burden can vary. It is the cumulative effect of multiple tax authorities for a single tax area that causes the tax burden to vary from one tax area to another. For example, the businesses located in tax area 5 must remit tax to only one tax authority (Tax Authority A for 3%). Businesses in tax area 2 remit taxes to two tax authorities (Tax Authorities A for 3% and B for 2%) and businesses in tax area 3 remit taxes to all three tax authorities.
In the United States, the states, cities, and special districts are tax authorities and can assess sales taxes. For example, the tax state of Colorado, the city of Denver, and the Regional Transportation District (RTD) each have a specific jurisdiction and those jurisdictions can overlap. The tax burden can vary depending on where the seller resides. For example, a seller in one part of Colorado could collect a Colorado state sales tax (3.5%), a Denver city sales tax (3.5%), and an RTD tax (.3%) to total 7.3% for the tax rate/area. A seller in another part of Colorado could collect a Colorado state sales tax (3.5%) and a Grand Junction city sales tax (2.5%) to total 6% for the tax rate/area.
In Canada, the federal government and provinces are tax authorities. Their jurisdictions overlap. The Canadian Federal government assesses a Value Added Tax (VAT), called a goods and services tax (GST). Each Province assesses a Provincial Sales Tax (PST) which varies from province to province.
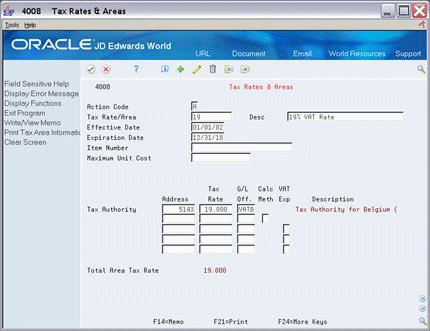
In Belgium, there is only one tax authority for VAT (called TVA taxes).
In Italy, there is also only one tax authority for VAT (called IVA taxes).
8.1.2 Guidelines
Follow these guidelines for setting up tax rates and areas:
-
Tax Authorities. You must set up tax authorities in the Address Book system (as described in the chapter Tax Authorities) before you can set up tax rate/areas.
-
Compound Taxes. You can define a compound tax for a tax rate/area.
-
In Canada, you can identify compound taxes with tax explanation code C (GST + seller-assessed PST) and B (GST + self-assessed PST). When you use tax explanation codes B and C, you must also set the Calc Meth (Calculation Method) field to Y.
To view an example, see Tax Area (Calculated as a Tax on a Tax) in the section Section 8.5, "Canadian Considerations" in this chapter.
-
Another way to specify a compound tax is with tax explanation code V+. When you use this code, leave the Calc Meth (Calculation Method) field blank. It is not applicable.
For more information about tax explanation codes, see thChapter 9, "Tax Explanation Codes". For information about how the system posts compound taxes, see the chapters Chapter 22, "Entry for A/P, A/R, and Sales Orders" and Chapter 21, "Posting for A/P, A/R, Purchase Orders, and Sales Orders".
-
-
European Unions. You must set up a tax rate/area for items taxable for European Union countries and items taxable from non-member countries. The EU Sales Listing uses this information for selection criteria.
-
Tennessee Maximum Unit Cost. If you have the JD Edwards World Distribution software and operate in Tennessee, this field can be very useful.
If you buy or sell in multiple units of measure, you need to define tax rate/areas for each unit of measure for an item number. The tax calculation will compare the item unit cost to the maximum unit cost. If the item unit cost is larger than the maximum, the system calculates the taxable amount using the maximum cost. The difference between the original taxable amount and the recalculated taxable amount is stored in the non-taxable field of the transaction and in the Tax Work file (F0018).
You can suppress this field with processing options.
-
VAT Input Credits. You can indicate the percent of VAT that is not eligible for input credits. For the tax authorities you indicate, the system does not add the percentages to the overall rate (the Total Area Tax Rate field). The system uses the percentage to calculate the VAT portion in the G/L distribution.
To view an example of a VAT input credit, see Tax Area with GST Input Credits inSection 8.5, "Canadian Considerations" in this chapter.
-
Tax-Free Products. If your company deals with zero-rated (tax-free) products, you must establish a tax rate/area that has a tax authority with a 0% (zero percent) tax rate.
-
Maximum Characters. For Canadian self-assessed PST and for United States use tax, do not set up a tax rate/area that has more than eight characters. The tax offset for self-assessed taxes can be made to the account with the tax rate/area as the subsidiary number (which is limited to eight characters).
8.2 Adding Tax Rates & Areas (P4008)
From the Master Directory menu (G), type 29
From the General Systems menu (G00), select Tax Processing & Reporting
From the Tax Processing & Reporting menu (G0021), select Tax Rates & Areas.
You can use this program to inquire on, add, change, and delete tax rate/areas.
On Tax Tate & Areas
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Tax Rate/Area
-
Description
-
Effective Date
-
Expiration Date
You may set up a default Expiration Date to be used in the processing options for P4008.
-
Tax Authority Address
-
Tax Rate
-
-
Complete the following fields, as needed.
-
Item Number
-
Maximum Unit Cost
-
G/L Offset
-
Calculation Method
-
VAT Expense
-
When you add a tax rate/area with multiple tax rates, the program displays the total tax rate to be applied to goods and services.
8.3 Changing Expiration Dates
From the Master Directory menu (G), type 29
From the General Systems menu (G00), select Tax Processing & Reporting
From the Tax Processing & Reporting menu (G0021), select Tax Rates & Areas.
You may change the expiration date on an existing tax/rate and area. For example, if you entered a tax rate/area with an expiration date of 12/31/18 and the tax rate will be in effect beyond that date, you may extend the expiration date to a date in the future.
To change the expiration date, inquire on the tax rate/area, update the Expiration Date field and use the Change action.
8.3.1 Changes to Tax Rate Area with No Overlap
There are times when you will need to change your system's tax rate/area because the taxing authority has changed an existing tax rate and the expiration date of the existing tax rate does not overlap the effective date of the new tax rate.
When you change the Tax Rate/Area, use the Add action to create a new record to the tax file, F4008, rather than change the existing record.
Caution:
When changing the tax rate for an existing record, DO NOT use the 'C' (Change) action code. Using the Change action causes integrity issues for transactions associated with the old tax rate, as there will no longer be a record in the F4008 with the corresponding tax rate.The actual rate is not stored in the transaction detail files. The system looks to the F4008 file to find the rate corresponding to effective date range. For example:
To change the tax rate area with no overlap
For example, the Tax Rate/Area DEN has an effective date of 09/01/10 and an expiration date of 08/31/15. When you add the new Tax Rate/Area DEN for the next date range, enter an effective date greater than 08/31/15, such as 09/01/15.
On Tax Tate & Areas
-
Inquire on the existing tax rate/area.
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Effective Date
-
Expiration Date
-
Tax Rate
-
-
Use the Add action and press Enter.
8.3.2 Changes to Tax Rate Area with an Overlap
There are times when you need to change the tax rate/area because the taxing authority has changed the existing tax rate and the existing tax rate overlaps the effective date of the new rate.
Note:
You cannot have overlapping dates between the effective date of the new tax rate and the expiration date of the existing tax rate.Changing the tax rate when effective dates overlap is a two step process. First change the expiration date on the existing tax rate/area. Then, follow the steps to add a new rate.
Example: Tax rate changes and the new effective date is before current expiration date:
Effective date of existing rate: 1/1/2010
Expiration date of existing rate: 12/31/2020
Effective date of new rate: 1/1/2015
Expiration date of new rate: 12/31/2025
-
Inquire on existing Tax Rate/Area and change the expiration date from 12/31/20 to 12/31/14.
-
Add in the new rate, with effective date of 1/1/15, expiration date of 12/31/2025.
8.4 Creating Memos for Tax/Rate Areas
You can create free-format text (memos) about the tax rate/area, using the Memo Function
On Tax Tate & Areas
-
Press (F14).
-
Type memo information.
-
Press Enter to save your memo.
To view a memo about the tax rate/area
When you have a memo about the tax rate/area, the system displays a highlighted message to the right of the Action Code field on the Tax Rates & Areas screen. The system also highlights the Tax Rate/Area field.
To print tax/rate areas information
To print the tax rate/area information, press F21.
Note:
This prints ALL tax rate/areas.8.5 Canadian Considerations
How you set the Calc Meth (Calculation Method) field controls whether the system calculates PST as a tax on a tax or calculates PST pre-GST. The information on the following screens is an example, and may not be completely accurate.
To setup your tax calculation to calculate Tax on Tax
To setup your tax calculation to calculate Tax on Tax
The Calculation Method (Calc Meth) field controls how the system calculates taxes. A 'Y' in the Calc Meth field indicates that tax rate is calculated as a tax on a tax. An 'N' in the Calc Meth field indicates that tax rate calculate PST against the value of the product.
On Tax Rates & Areas
Figure 8-3 Tax Rates and Areas screen (Calc Meth field)
Description of "Figure 8-3 Tax Rates and Areas screen (Calc Meth field)"
-
On the fist Tax Authority line, complete the following fields for the GST tax authority:
-
Address
-
Tax Rates
-
G/L Off
-
-
On the second Tax Authority line, complete the following fields for the PST tax authority:
-
Address
-
Tax Rates
-
G/L Off.
Note:
List any additional PST tax authorities on the remaining lines.
-
-
Do one of the following:
-
Enter Y in the Calc Meth (Calculation Method) field to calculate tax on tax.
-
-
Enter N in the Calc Meth field to calculate tax based on the value of the product.
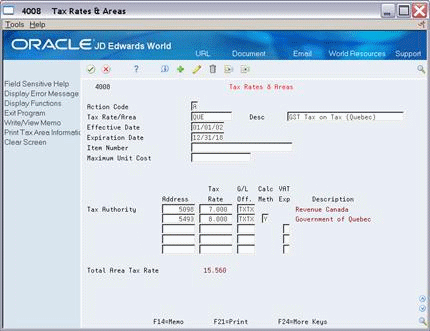
In this example, the Total Area Tax Rate field is 15.560.
Note:
You can calculate a tax on a tax with tax explanation code C (GST + seller-assessed PST) and B (GST + self-assessed PST). For a tax on a tax, you must also set the Calc Meth (Calculation Method) field to Y. Another way to specify a tax on a tax is with tax explanation code V+. When you use V+, leave the Calc Meth field blank. It is not applicable.To Work with GST Input Credits
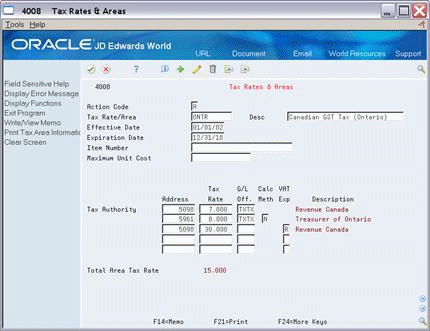
You can indicate the percent of GST that is not eligible for input credits.
On Tax Rates & Areas
Figure 8-4 Tax Rates and Areas screen (Tax Authority fields)
Description of "Figure 8-4 Tax Rates and Areas screen (Tax Authority fields)"
-
On the first Tax Authority line, complete the following fields for the GST tax authority:
-
Address
-
Tax Rates
-
G/L Off.
-
-
On the second Tax Authority line, complete the following fields for the PST tax authority:
-
Address
-
Tax Rates
-
G/L Off.
-
-
On Tax Authority lines 3 through 5, complete the following fields
-
Address
-
G/L Off.
-
-
Enter R in the following field for lines 3 through 5, as needed.
-
VAT Exp
-
-
Enter the percentage NOT eligible for input credits in the following field:
-
Tax Rate
Note:
The system does not add these percentages to the overall rate (the Total Area Tax Rate field). The system uses the percentage to calculate the GST portion in the G/L distribution. -
-
Press Enter.
8.6 United States (Sales and Use Tax) Considerations
If your company deals only with sales and use taxes, you need to evaluate which JD Edwards World systems your company owns.
-
If you own only the A/R or A/P systems, you do not need to enter information in the G/L Offset field (these systems ignore values in this field).
-
If you own the Sales Order or Purchase Management systems (or own these systems along with the A/R or A/P systems), generally, you must enter information in the G/L Offset field.
8.6.1 A/P and A/R Processing
Figure 8-5 Tax Rates and Areas screen (G/L Off field empty
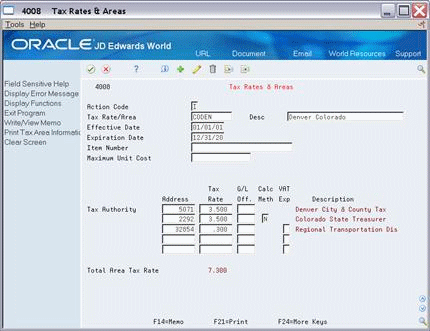
Description of "Figure 8-5 Tax Rates and Areas screen (G/L Off field empty"
The tax rate/area above has three tax authorities for a total sales tax of 7.3%. Notice that the G/L Off (General Ledger Offset) field is blank. The A/R system does not create an entry to the sales tax payable account.
8.6.2 Purchase and Sales Order Management
Figure 8-6 Tax Rates and Areas screen (G/L Off field with input)
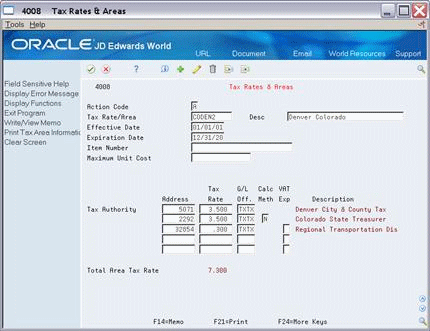
Description of "Figure 8-6 Tax Rates and Areas screen (G/L Off field with input)"
The G/L Off (General Ledger Offset) field specifies an offset account for the sales taxes that are payable.