37 Set Up PM Schedule Information
This chapter contains these topics:
37.1 Setting Up PM Schedule Information
Preventive maintenance (PM) schedules are the foundation of your preventive maintenance program. PM schedules determine the types of service and the frequency of each service type for each piece of equipment that you maintain.
Before you can use the preventive maintenance features of Equipment/Plant Maintenance, you must provide the system with standard procedures and maintenance rules.
You can assign standard procedures to various maintenance tasks when you set up a PM schedule for a piece of equipment. The system uses standard procedures in the same way as user defined codes, with the exception that you can attach virtually unlimited text to a standard procedure.
Maintenance rules determine when the system schedules preventive maintenance tasks. In addition, maintenance rules can:
-
Determine the status of scheduled tasks.
-
Assign default values for the assigned work order.
-
Assign default values for the business unit to be charged for the maintenance task.
-
Determine when maintenance is due based on threshold percentages.
37.2 Setting Up Standard Procedures
From Equipment/Plant Management (G13), enter 29
From Equipment/Plant Management Setup (G1341), choose Preventive Maintenance
From Maintenance Setup (G1345), choose Standard Procedures
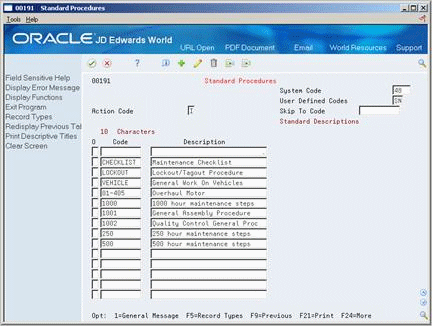
You can define standard procedures (standard instructions) that apply to your PM schedules and work orders. You can then add unlimited text to describe the procedures. For example, assume that you have set up a service type for a 500-hour equipment inspection. You can define a standard procedure for a 500-hour equipment inspection and add text that describes the steps required for the inspection.
You can also copy text from other standard procedures. For example, you can copy text from a 250-hour inspection that also applies to the procedures for a 500-hour inspection.
After you set up standard procedures, you can attach them to the following programs:
-
Work Order Entry
-
Item PM Schedule
-
Equipment Work Order Routings
Setting up standard procedures consists of the following tasks:
-
To define standard procedures
-
To add text to a procedure
-
To copy text from other procedures
Complete the following fields to define each procedure:
-
Code
-
Description
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Code | This column contains a list of valid codes for a specific user defined code list. The number of characters that a code can contain appears in the column title. |
On Standard Procedures
-
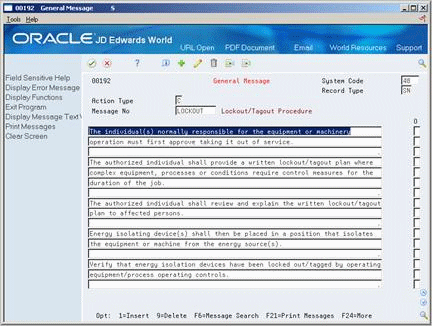
Choose General Message for each procedure for which you want to add text.
-
On General Message, enter text for each standard procedure.
To copy text from other procedures
On Standard Procedures
-
Choose the General Message option for each procedure for which you want to add text.
-
On General Message, choose Message Search.
Figure 37-3 General Message Search screen
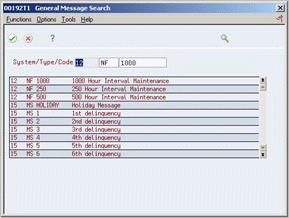
Description of "Figure 37-3 General Message Search screen"
-
On General Message Search, complete the following fields to narrow your search to a particular message:
-
System
-
Type (Optional)
-
Code (Optional)
-
-
Choose Enter.
-
To import the text into the procedure, choose Select.
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| System Code | A user defined code (98/SY) that identifies a JD Edwards World system. |
| Record Type | Identifies the table that contains user defined codes. The table is also referred to as a code type. |
37.3 Setting Up Maintenance Rules
From Equipment/Plant Management (G13), enter 29
From Equipment/Plant Management Setup (G1341), choose Preventive Maintenance
From Maintenance Setup (G1345), choose Maintenance Rules Table
To use the preventive maintenance features in Equipment/Plant Maintenance, you must set up maintenance rules. Maintenance rules determine the maintenance status that the system assigns to a PM for a service type when the service type is due to be performed.
For example, assume you have defined a service type for equipment lubrication, with a 100-hour maintenance interval. Also assume that you have defined maintenance rules for that service type that direct the system to assign a maintenance status of 50 (Maintenance Due) whenever 100 hours have elapsed. After 100 hours have elapsed and you update the PM schedule status, the system automatically assigns a maintenance status of 50 to the PM for equipment lubrication.
In addition to assigning a maintenance status to PMs, you use maintenance rules to:
-
Define the threshold percentage when maintenance is due.
-
Determine the assigned work order status, type, and priority, if you use model work orders.
-
Specify whether the system assigns the Charge to Business Unit on the assigned work order based on the Charge to Business Unit on the model work order or the responsible business unit from the equipment master.
-
Specify the status of associated service types that might already be scheduled and combine work orders for associated service types on to the work order for the primary service type.
-
Specify the approval type for assigned work orders.
-
Specify whether the description that appears on assigned work orders is based on the service type description or the description on the model work order.
37.3.1 How Does the System Apply Maintenance Rules?
When the system searches for rules to apply to a maintenance task, it uses the following sequence:
-
Search for and apply a rule for which both an equipment number and a service type have been assigned.
-
Search for and apply a rule for which an equipment number has been assigned, but no service type.
-
Search for and apply a rule for which a service type has been assigned, but no equipment number.
-
Apply a global default rule for which no equipment number or service type has been assigned.
Figure 37-4 Maintenance Rules Table screen
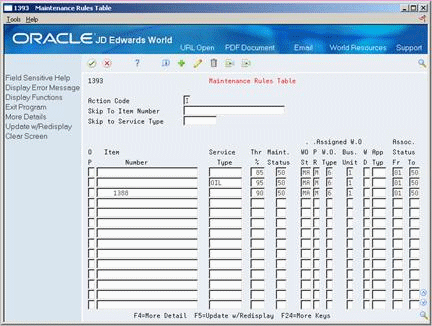
Description of "Figure 37-4 Maintenance Rules Table screen"
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Item Number
-
Service Type
-
Thr (Threshold) %
-
Maint. Status
-
-
Complete the following Assigned W.O. fields:
-
WO St (Status)
-
PR (WO Priority)
-
W.O. Type
-
Bus. Unit
-
WD (WO Description Flag)
-
App (Approval) Typ
-
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Assoc. (Associated) Status From
-
Assoc. Status To
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Threshold Percent | A percentage measure that indicates how close a piece of equipment is to needing maintenance. This percentage is based on the greater of the actual date, miles, hours, or fuel consumption. A percentage of 090 indicates that the piece of equipment is 10% away from needing maintenance. A percentage greater than 100 indicates that maintenance is past due.
Note: Miles, hours, and fuel are only examples of statistical units. You can define other statistical units appropriate to your organization within the Equipment/Plant Management automatic accounting instructions. |
| Maint Status | A user defined code (12/MS) that indicates the maintenance status of a piece of equipment, such as 50 for maintenance due or 60 for waiting for parts.
Note: Status code 98 is reserved for canceled maintenance. Status code 99 is reserved for completed maintenance. Status code 01, the default, is reserved for initial maintenance setup. |
| WO St | A user defined code (system 00, type SS) that describes the status of a work order. |
| Priority | A user defined code (system 00, type PR) that indicates the relative priority of a work order or engineering change order in relation to other orders.
A processing option for some forms lets you enter a default value for this field. The value then displays automatically in the appropriate fields on any work order you create on those forms and on the Project Setup screen. You can either accept or override the default value. |
| W.O. Type | A user defined code (00/TY) that indicates the type classification of a work order or engineering change order.
You can use work order type as a selection criteria for work order approvals. |
| Bus Unit | A code that determines which Business Unit will be used as the Charge to Business Unit on Assigned Work Orders that are created when items are scheduled for maintenance.
Values are: 1 – Use the Charge to Business Unit from the Model Work Order on the Assigned Work Orders. 2 – Use the Responsible Business Unit from the Item Master (F1201) as the Charge to Business Unit on the Assigned Work Orders. |
| W D | A code that determines which Description will be used as the Description on Assigned Work Orders that are created when items are scheduled for maintenance. Values are:
1 – Use the Description from the Model Work Order on the Assigned Work Orders. 2 – Use the Description from the Service Type on the Assigned Work Orders. |
| App Typ | A user defined code (system 48, type AP) indicating the type of work order approval path that a work order follows. You can use processing options to specify a default approval type based on the type of work order.
Form-specific information This is the approval path that the work order follows when you create a PM work order. |
| Assoc Status | The first code in a range of codes that identifies which associated service types already scheduled for maintenance should be grouped together. These service types are grouped with the primary service type and assigned to the same work order. For example, if a monthly vehicle inspection and an annual vehicle inspection occur in the same month, the system would group the monthly inspection (associated service type) with the annual inspection (primary service type) and assign it to the same work order. |
37.3.2 What You Should Know About
See Also:
-
Section 15.6, "Creating a Model Work Order" for more information about assigned work orders
-
Section 15.3, "Linking Service Types"or more information about associated service types and threshold percentage