1 Overview to Product Data Management - Discrete
This chapter contains these topics:
The Product Data Management (PDM) system enables you to organize and maintain information about each item you manufacture. Use the Product Data Management system to define the relationships between inventory items (and other purchased or non-stock items) and how they can be combined to manufacture a saleable product.
This system provides basic data for other manufacturing systems. You should verify that your product data is accurate to ensure the efficiency of associated systems such as Shop Floor Control and Master Production Scheduling.
1.1 System Integration
PDM integrates with the following systems:
| System | Description |
|---|---|
| Inventory Management | Supplies the basic information about each item (or ingredient), such as part number, description, unit of measure, stocking type, location, and material cost. |
| Shop Floor Control | Uses bills of material and routings to process work orders and schedule work activity within the plant. |
| Manufacturing and Distribution Planning |
|
| Product Costing and Manufacturing Accounting |
|
| Sales Order and Purchase Order Management | Uses bills of material for kit processing. |
| Resource Requirements Planning | Retrieves a master scheduled item's multi-level bill of material and selects the routings for the components. |
Figure 1-1 Product Data Management System
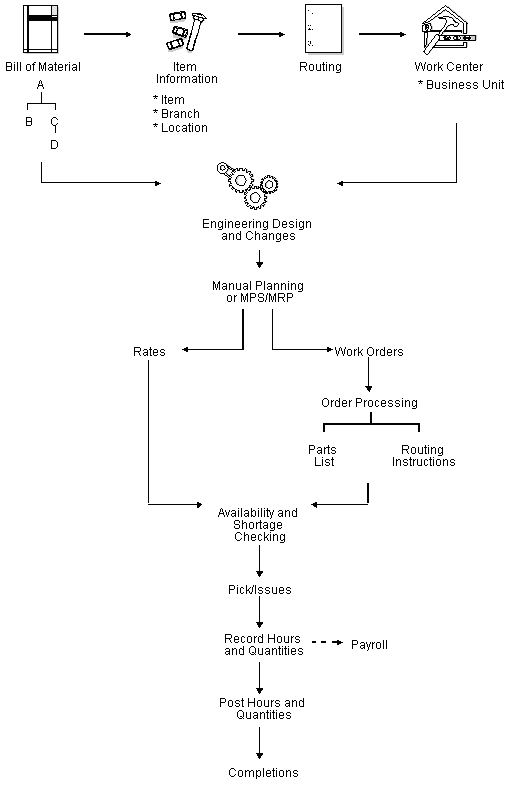
Description of "Figure 1-1 Product Data Management System"
1.2 Features
The Product Data Management system includes the following:
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bills of material |
|
| Work centers |
|
| Routings |
|
| Engineering Change Management |
|
1.3 System Concepts
The Product Data Management system encompasses:
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Bills of material | The components and relationships required to produce a parent item. |
| Routings | The operations required to produce the parent item. |
| Work centers | The facilities on the shop floor where the routing operations occur. |
| Engineering change orders (ECOs) | The document that you use to define and implement changes to your products, production lines, and assembly processes. |
1.3.1 Enterprise Requirements Planning and Execution Review
Product Data Management is one of many systems within the Enterprise Requirements Planning and Execution (ERPx) system.
Use the ERPx system to coordinate your inventory and labor resources to deliver products according to a managed schedule. It is a closed-loop manufacturing system that formalizes company and operations planning, and the implementation of those plans.
The ERPx system includes the following JD Edwards World systems:
Figure 1-2 Enterprise Requirements Planning and Execution (ERPxE)
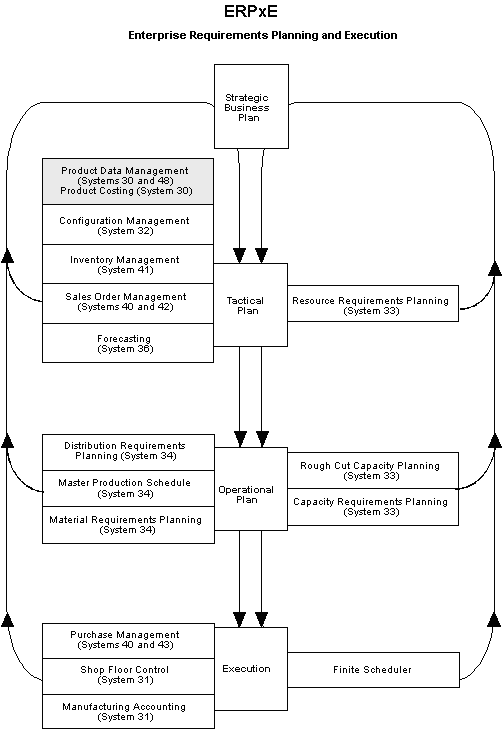
Description of "Figure 1-2 Enterprise Requirements Planning and Execution (ERPxE)"
1.4 Menu Overview
JD Edwards World systems are menu-driven. System functions are organized according to their function and frequency of use. Access the Product Data Management system menus from the Manufacturing Systems menu.
Figure 1-3 Menu Overview for Manufacturing Systems
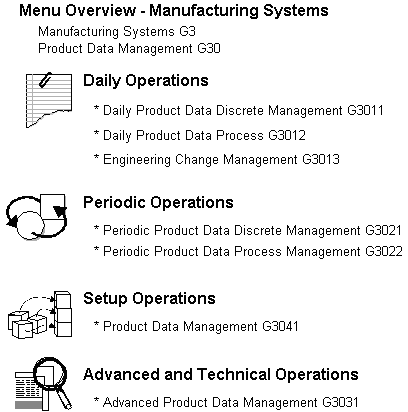
Description of "Figure 1-3 Menu Overview for Manufacturing Systems"
1.4.1 Fast Path Commands
The following table illustrates the fast path commands you can use to move among the Product Data Management menus:
| Fast Path | Menu | Title |
|---|---|---|
| APD | G3031 | Advanced PDM |
| DEC | G3013 | Engineering Change Management |
| ECO | G3013 | Engineering Change Management |
| DPDD | G3011 | Daily PDM Discrete |
| DPDP | G3012 | Daily PDM Process |
| PPDD | G3021 | Periodic PDM Discrete |
| PPDP | G3022 | Periodic PDM Process |
| SPD | G3041 | Setup PDM |