2 Setup Requirements
This chapter contains these topics:
2.1 About Setup Requirements
To process business transactions in Belgium, you must set up your system to meet specific requirements.
JD Edwards World software setup requirements for Belgium consist of the following tasks:
-
Setting up user display preferences.
-
Setting up user-defined codes for Belgium.
-
Setting up for Belgium VAT reporting.
2.2 Setting Up User Display Preferences
From Advanced and Technical Operations (G9), choose Security Officer
From Security Officer (G94), choose Library List Control
From Library List Control (G944), choose User Display Preferences
Alternately, you can use Hidden Selection 85 from any command line to access the User Display Preferences screen.
Much of the JD Edwards World software country-specific functionality utilizes country-server technology. Country-server technology was developed to isolate country-specific functionality from the base software. For example, if during normal transaction processing, you need to capture additional information about a supplier or validate a tax identification number to meet country-specific requirements, that additional function is performed by a country server rather than by the base software.
To take full advantage of localized solutions for your business, you must set up your user display preferences to use the appropriate country server. To do this, specify a country code in your user display preference. The country code that you designate for a user indicates which country server to use.
You can also set up user display preferences to utilize other features in the software. For example, specify a date format to control how the system displays dates (such as DDMMYY, the typical European format) or a language to override the base language.
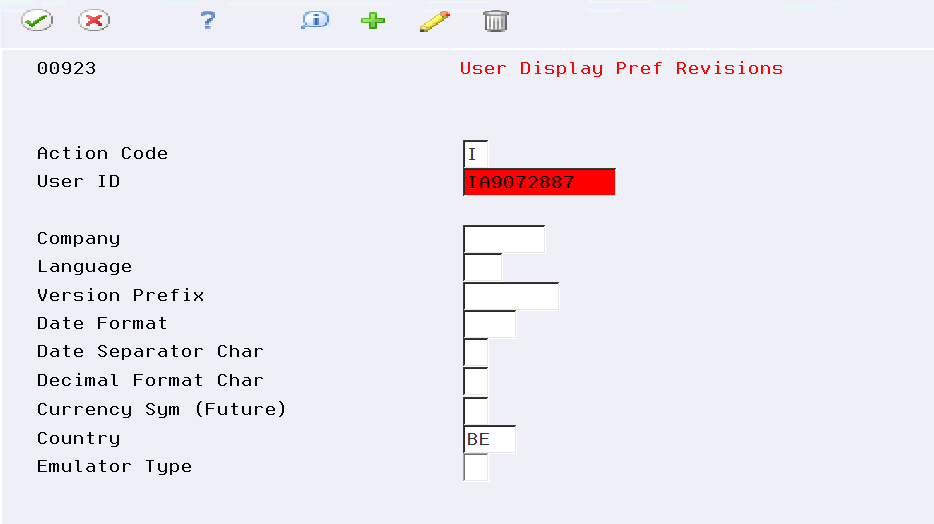
To set up user display preferences
On User Display Preferences
-
To locate the preferences for a specific user, complete the following field:
-
User ID
-
-
Use the Inquire action.
The system displays the preferences for the user
-
Complete the following field:
-
Country
-
-
To further define the user preferences, complete the following optional fields:
Company
Language
Version Prefix
Date Format
Date Separator Character
Decimal Format Character
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| User ID | The IBM-defined user profile. |
| Country | A user-defined code (system 00, type CN) that identifies a country. The country code has no effect on currency conversion.
The Address Book system uses the country code for data selection and address formatting. Screen-specific information If you use any of the JD Edwards World software localized systems (systems 74, 75, or 76), the country code that you specify activates the country-server for that country. |
| Company | A code that identifies a specific organization, fund, entity, and so on. This code must already exist in the Company Constants file (F0010). It must identify a reporting entity that has a complete balance sheet. At this level, you can have intercompany transactions.
Note: You can use company 00000 for default values, such as dates and automatic accounting instructions (AAIs). You cannot use it for transaction entries. Screen-specific information Complete the Company field to default the selected companies within transaction processing. |
| Language | A user-defined code (system 01/type LP) that specifies a language to use in forms and printed reports.
In the JD Edwards World software, if you leave the Language field blank, the system uses the language that you specify in your user preferences. If you do not specify a language in your user preferences, the system uses the default language for the system. Before any translations can become effective, a language code must exist at either the system level or in your user preferences. Screen-specific information A user-defined code for a language. The system uses the language code you type on this screen as your default language. To view a translated screen or report, a record for that translated screen or report must exist in the Vocabulary Overrides file. When you access a screen, the translated screen appears. When you run a report, the system prints the report in your base language. |
| Version Prefix | Identifies a default prefix to assign when creating DREAM Writer versions. Versions can then be suffixed with additional characters.
Screen-specific information Identifies a default prefix to assign when creating DREAM Writer versions. Versions can then be suffixed with an alpha-numeric character up to 6 positions in length. |
| Date Format | This is the format of a date as stored in the database. If you leave this value blank, the value will display according to the settings of the operating system on the workstation. With NT, the settings for the operating system of the workstation are controlled by the Regional Settings in the Control Panel. |
| Date Separator Char | The character entered in this field is used to separate the month, day, and year of a given date.
NOTE: If an asterisk is entered (*), a blank is used for the date separator. If left blank, the system value is used for the date separator. |
| Decimal Format Char | The character entered in this field is used to signify the fractions from whole numbers - the positions to the left of the decimal.
If left blank, the system value is used as the default. |
See Also:
- Appendix A, "Translation Issues" for information about using JD Edwards World software in a multi-language environment
2.3 Setting Up User-Defined Codes for Belgium
Many fields throughout the JD Edwards World software accept only user-defined codes (UDCs). You can customize your system by setting up and using user-defined codes that meet the specific needs of your business environment.
User-defined codes are either soft-coded or hard-coded. You can customize any user-defined code that is soft-coded to accommodate your specific business needs. You can also set up additional soft-coded user-defined codes. You cannot customize a user-defined code that is hard-coded.
User-defined codes are stored in tables that relate to specific systems and code types. For example, 12/FM represents system 12 (Fixed Assets) and user-defined code list FM (Finance Methods). User-defined code tables determine what codes are valid for the individual fields in your system. If you enter a code that is not valid for a field, the system displays an error message. For example, when you enter an invoice, you can enter a user-defined code to specify the payment instrument. The system does not accept a payment instrument that is not in the user-defined list of valid payment instruments.
You can access all user-defined code files through a single user-defined code screen. After you select a user-defined code screen from a menu, change the System Code field and the User-Defined Codes field to access another user-defined code file.
Note:
User-defined codes are central to JD Edwards systems. You should be thoroughly familiar with user-defined codes before you change them.Set up the following user-defined codes to process VAT reports in Belgium:
| Code | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Identification Type (system 74B, type IT) | Set up user-defined codes to define the document used to identify the representative of the reporting company. Examples of values are:
|
| File Type (system 74B, type FT) | Set up each of the file type load. Examples of values are:
|
| Code Tax Amount (system 74B, type CT) | This user-defined code specifies the code tax amount related to the tax area and document. Examples of values are:
|