Using Accounting Setup Manager
This chapter covers the following topics:
- Creating Accounting Setups
- Legal Entities Overview
- Creating Accounting Setup Structures
- Completing Accounting Options
- Reporting Currencies
- Ledger Balancing Segment Value Assignments
- Subledger Accounting Options
- Operating Units
- Intercompany Accounts
- Intracompany Balancing Rules
- Sequencing
- Secondary Ledgers
- Completing Accounting Setup
Creating Accounting Setups
This section includes the following parts:
Accounting Setup Process
The accounting setup process consists of three main steps and are described in the following table:
-
Create an accounting setup structure.
-
Update accounting options.
-
Complete the accounting setup.
The following table provides the steps to create an accounting setup. Repeat these steps for each accounting setup defined. The steps in bold italics are required.
| Create Accounting Structure | Complete Accounting Options | Complete Accounting Options (continued) |
|---|---|---|
| Assign legal entities | Complete ledger options. | Define and assign operating units to the primary ledger. |
| Specify the ledger attributes for the primary ledger. | Complete reporting currencies. | Define intercompany accounts. |
| Specify the ledger attributes for one or more secondary ledgers. | Assign balancing segment values to legal entities | Define intracompany balancing rules. |
| Assign reporting currencies. | Assign balancing segment values to ledgers. | Define sequencing options. |
| Define subledger accounting options. | Complete secondary ledger setup steps. | |
| Complete accounting setup. |
Accounting Setup Prerequisites
Complete General Ledger Setup Steps
To create accounting setups, complete the General Ledger prerequisites, such as defining a chart of accounts and accounting calendar.
Additional Information: Setting Up General Ledger, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
Define Additional Subledger Accounting Methods
To use additional subledger accounting methods other than Standard Accrual or Standard Cash, define them using Subledger Accounting . When defining ledgers in Accounting Setup Manager, assign a subledger accounting method if planning to use Subledger Accounting to integrate data from transaction sources.
Perform this step for each subledger accounting method.
Additional Information: Subledger Accounting Options
Accounting Setup Manager Pages
The Accounting Setup Manager provides the following pages:
Legal Entities Pages
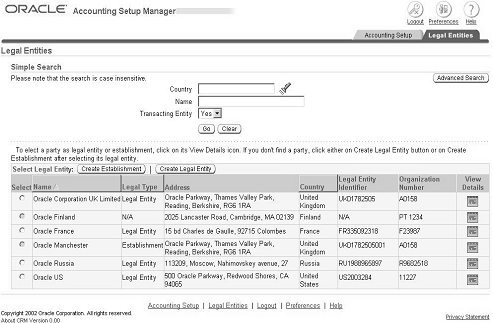
The Legal Entities page allows you to do the following:
-
Create new legal entities and assign specific balancing segment values to legal entities to help identify legal entities during transaction processing and reporting. You can take full advantage of all of the legal entity-related features, such as Intercompany Accounting.
-
Query existing legal entities, view their attributes, and make updates to the legal entities .
-
Update balancing segment values assigned to legal entities.
-
Enter an end-date to deactivate a legal entity.
Additional Information: Legal Entities Overview
Accounting Setups Pages
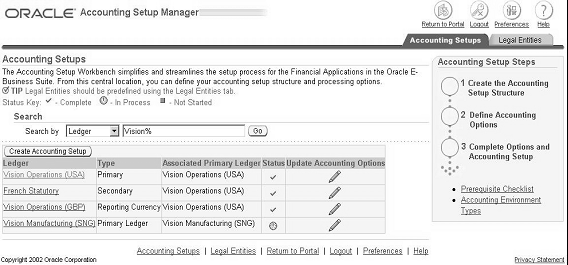
You can perform the following in the Accounting Setups page:
-
Create new accounting setups.
-
Query existing accounting setups (named after the primary ledger) by legal entity or ledger.
-
Update the accounting options for an accounting setup to modify the related setup components.
-
Query existing legal entities and view their attributes.
-
Identify the associated primary ledger for any legal entity, ledger, operating unit, and reporting currency.
-
View the status of accounting setups.
Accounting Options Pages
After creating an accounting setup structure, update the accounting options immediately after creating the structure or later.
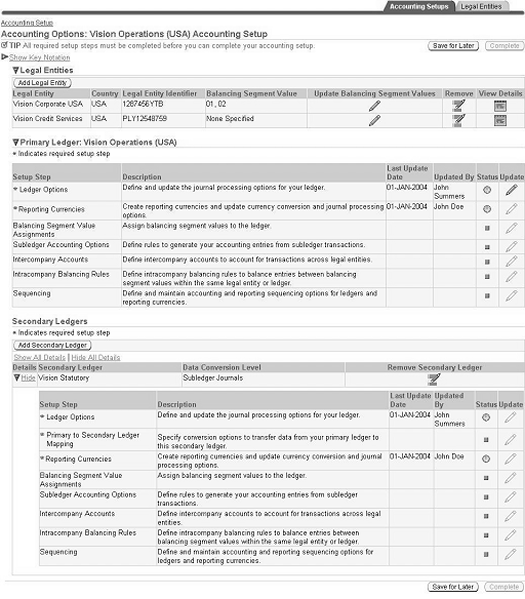
Accounting Setup Manager Checklist
The following table describes the steps to create accounting setups using Accounting Setup Manager. Each required setup step must be completed before you can complete your accounting setup.
| Step Number | Required | Step |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Optional | Define Legal Entities If you plan to record accounting transactions for one or more legal entities, you can use the Legal Entities tab in Accounting Setup Manager or Oracle Legal Entity Configurator to define your legal entities. Note: If you plan to use jurisdictions that do not come seeded, you can define your own jurisdictions using Legal Entity Configurator before you define legal entities. A jurisdiction is the intersection of the physical territory and type of legislation within which judicial authority may be exercised. The jurisdiction is used to assign a territory to a legal entity.
|
| Step 2 | Required | Create Accounting Setup Structure
Repeat this step for each accounting setup. Additional Information: Creating Accounting Setup Structures |
| Step 3 | Required | Complete ledger options. Define and update journal and transaction processing options for the ledger. If a secondary ledger is assigned, complete the ledger options for the primary ledger before completing the ledger options for the secondary ledger. Repeat this step for all ledgers in an accounting setup. Additional Information: Ledger Options |
| Step 4 | Conditionally Required | Complete reporting currencies. If reporting currencies are assigned to the accounting setup when creating the accounting setup structure, it is required to complete the currency conversion options for each reporting currency. Assign reporting currencies to the primary or secondary ledger at any time. Repeat this step for each reporting currency assigned. Additional Information: Reporting Currencies |
| Step 5 | Optional | Assign balancing segment values to legal entities. If you did not assign balancing segment values to legal entities when you created them, you can assign them now. It is strongly recommended that you assign specific balancing segment values to each legal entity to help identify legal entities during transaction processing and reporting. Note: See Balancing Segment Value Assignments |
| Step 6 | Optional | Assign balancing segment values to ledger. If you assigned balancing segment values to legal entities and want to reserve one or more balancing segment values for adjustments or nonlegal entity related transactions, assign specific balancing segment values to the ledger. For the accounting setup with no legal entity assigned, assign balancing segment values to the ledger to indicate which values are to be used for journal processing in the ledger. If balancing segment values are not assigned to the ledger, then all values will be available. Repeat this step for each ledger. Additional Information: Ledger Balancing Segment Value Assignments |
| Step 7 | Conditionally Required | Define Subledger Accounting options. If a Subledger Accounting Method is assigned to the ledger, complete the Subledger Accounting options to provide instructions on how to create the accounting from Oracle financial subledgers or external systems to one or more ledgers in General Ledger. Repeat this step for each ledger that has a subledger accounting method assigned. Additional Information: Subledger Accounting Options |
| Step 8 | Optional | Define operating units. If using an accounting setup that has legal entities assigned, define operating units for your primary ledger.
Additional Information: Operating Units |
| Step 9 | Optional | Define intercompany accounts. If the accounting setup has legal entities with specific balancing segment values assigned, define intercompany accounts. Intercompany accounts account for intercompany transactions between legal entities. Additional Information: Intercompany Accounts |
| Step 10 | Conditionally Required | Define intracompany balancing rules. If the Intracompany Balancing option for the ledger is enabled, define Intracompany Balancing rules to provide instructions on how to balance journal entries between balancing segment values for the same legal entity or ledger. Repeat this step for each ledger that has this option enabled. Additional Information: Intracompany Balancing Rules |
| Step 11 | Optional | Define Sequencing. Define accounting and reporting sequencing options for ledgers and reporting currencies. Repeat this step for each ledger.
Additional Information: Defining Sequences, Oracle Financials Implementation Guide |
| Step 12 | Conditionally Required | Complete primary to secondary ledger mapping. If using secondary ledgers, specify how to convert subledger journals, General Ledger journals, or balances from the primary ledger to the secondary ledger. For example, if the secondary ledger uses a different chart of accounts and currency from the primary ledger, assign a chart of accounts mapping and currency conversion rules. Perform this step once for each secondary ledger that is assigned to an accounting setup. Additional Information: Primary to Secondary Ledger Mapping |
| Step 13 | Required | Complete the Accounting Setup After all required setup steps for both the primary and secondary ledgers of an accounting setup are completed, complete the accounting setup by clicking Complete on the Accounting Options page. This button is enabled after all required setup steps have a Complete status. Review the successful completion of the General Ledger Accounting Setup Program in the Concurrent Manager before proceeding. Perform this step once for each accounting setup. Additional Information: Completing Accounting Setup |
| Step 14 | Optional | Perform additional General Ledger setup steps. Take advantage of additional General Ledger features, such as ledger sets and data access sets, to improve processing efficiency and add additional security to secure access to ledgers.
|
| Step 15 | Required | Assign profile options to responsibilities. To control access to ledgers used by General Ledger users, assign a data access set to the profile option GL: Data Access Set for each General Ledger responsibility. If using subledgers, you should also set the SLA: Enable Data Access Security in Subledgers profile option to control the generation of accounting entries for subledger transactions. This profile option determines whether the General Ledger Data Access Set security mechanism is applied for a subledger application responsibility when viewing, reporting, or creating subledger journal entries associated with a given ledger. The General Ledger Data Access Set security mechanism is always applied for responsibilities associated with the General Ledger application. The profile option enables you to combine data access security with subledger transaction security and therefore control access to subledger journal entries depending on the ledger to which they belong. For example, you can implement a Multiple Organizations Security Profile that allows you to create Oracle Receivables invoices for two different operating units, each associated with different ledgers, but restrict drill-down from the subledger transaction to the associated subledger journal entry based upon the destination ledger contained in the Access Set. If you skip this step, you cannot control access to ledgers and process data optimally in Oracle subledgers and General Ledger.
|
Legal Entities Overview
Define one or more legal entities using Accounting Setup Manager's Legal Entities tab if planning to assign legal entities to accounting setups.
You can also define legal entities using Legal Entity Configurator. The Legal Entity pages of Accounting Setup Manager are the same as the Legal Entity pages in Legal Entity Configurator. The only difference is that you can assign balancing segment values to legal entities using Accounting Setup Manager.
Additional Information: See Overview, Oracle Financials Implementation Guide.
Balancing Segment Value Assignments
Assigning balancing segment values to legal entities is optional; however, it is strongly recommended that you assign specific balancing segment values to each legal entity to help identify legal entities during transaction processing and reporting. This is particularly important for accounting setups that use the accounting setup where multiple legal entities share the same primary ledger.
By assigning balancing segment values to legal entities, you can also take advantage of all of the legal entity accounting features available, such as intercompany accounting.
If you do not assign any balancing segment values to your legal entities, then all balancing segment values will be available for transaction processing.
Note: If using multiple value sets for the balancing segment across charts of accounts, be sure to assign the correct value set to the legal entity. Once assigned, you cannot remove the value set from legal entities. However, there is no harm in assigning the wrong value set or assigning balancing segment values for the wrong value set; the system will ignore it during transaction processing.
Tip: If you are unsure about the value set to assign to each legal entity, allow Accounting Setup Manager to do it. When assigning a legal entity to an accounting setup, Accounting Setup Manager automatically assigns the correct value set associated with the legal entity's primary ledger and secondary ledger, if used.
Using Balancing Segment Values for Transaction Processing
Any balancing segment values assigned to a legal entity are automatically assigned to the legal entity's ledger when completing the accounting setup.
When entering transactions using Oracle subledgers, use only the valid balancing segment values that are assigned to the legal entity.
When entering journals in General Ledger, use only the valid balancing segment values assigned to the ledger's legal entities and the ledger itself.
If no balancing segment values are assigned to the legal entities or ledgers, then all balancing segment values will be available to enter transactions and journal entries.
Special Note for Disabling Legal Entities: If disabling a legal entity by entering an end date, also enter end dates for all assigned balancing segment values to prevent the use of the balancing segment value.
Completing Accounting Setups
If you have an accounting setup with multiple legal entities assigned and specific balancing segment values assigned to legal entities, you cannot complete the accounting setup if the following violations exist:
-
overlapping balancing segment values assigned to the legal entities for the same accounting setup
-
balancing segment values assigned to some, not all, of the legal entities assigned to the same accounting setup
Note: Accounting Setup Manager does not check for overlapping balancing segment values assigned to legal entities in different accounting setups. Therefore, ensure that the correct balancing segment values are assigned to legal entities in all accounting setups.
Note: Before the accounting setup is complete, delete and add balancing segment values to legal entities at any time. After completing the accounting setup, you cannot delete balancing segment values from legal entities; you can end date the balancing segment value to prevent the use of it.
Designating the Balancing Segment for a Chart of Accounts
It is recommended that you designate the balancing segment of the chart of accounts as the legal entity or company segment. If there are multiple legal entities that use different charts of accounts, limit the number of value sets you define for the balancing segment to ease maintenance efforts. This allows you to share value sets across multiple charts of accounts and assign unique balancing segment values for each legal entity that is consistent across charts of accounts.
Defining Legal Entities Using Accounting Setup Manager
Use the Create Legal Entity page to create legal entities.
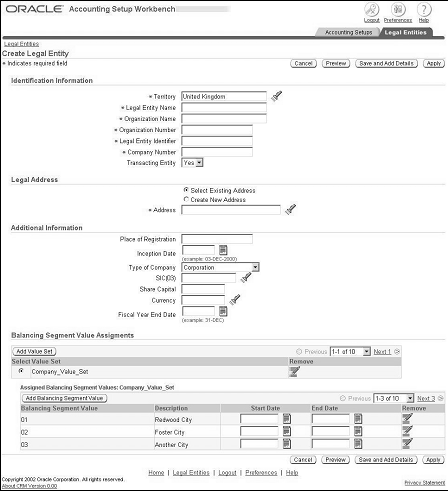
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites are required only if planning to assign balancing segment values to legal entities:
-
define a chart of accounts
-
define segment values for the balancing segment
To Create Legal Entities:
-
Navigate to the Legal Entities page.
-
Click Create Legal Entity.
-
Enter all relevant fields for the Identification Information, Legal Address, Additional Information, and Balancing Segment Value Assignments.
-
Click Apply or click Save and Add Details to enter additional information for the legal entity that includes the following:
-
registrations
-
establishments
Note: Adding this additional information is not required for creating an accounting setup.
Note: You can quickly create legal entities when creating an accounting setup.
-
-
In the Balancing Segment Value Assignments region, click Add Value Set.
-
Select a value set from the list of values.
Only value sets that use the balancing segment value qualifier are displayed.
-
To assign balancing segment values for the value set, click Add Balancing Segment Value.
-
Select one or more balancing segment values to assign to this legal entity. You cannot assign parent values.
Note: Be sure to assign unique balancing segment values to each legal entity. You cannot complete the accounting setup if multiple legal entities assigned to the same accounting setup have overlapping balancing segment values assigned or only some of the legal entities have balancing segment values assigned.
-
To make this value available for a limited time, enter a start date and/or an end date.
Note: Start and end dates can be changed at any time.
-
Click Apply.
Note: Once you add a legal entity to an accounting setup and complete the accounting setup, you cannot remove balancing segment values from legal entities. You can only disable balancing segment values by entering an end date.
Updating Balancing Segment Values
Update the balancing segment value assignments for the legal entity in one of the following pages:
-
Legal Entities tab
-
Accounting Options page after assigning legal entities to accounting setups
Add value sets and balancing segment values to legal entities at any time
Prerequisites
-
Define a legal entity.
-
Assign a legal entity to an accounting setup to automatically assign the value set associated with the legal entity's ledger.
To update balancing segment values for legal entities:
-
Navigate to the Legal Entities page and search for a legal entity.
-
Select the Balancing Segment Value Assignments sub-tab.
-
To update the balancing segment value assignment, click Update.
-
Add one or more value sets.
Once assigned, you cannot remove the value set.
If you accidentally assign the wrong value set that is not associated with any of the legal entity's ledgers, the invalid value set will be ignored during transaction processing.
-
Add or remove balancing segment values.
If the legal entity is assigned to a complete accounting setup, you cannot remove its balancing segment values. You can disable them by entering an end date.
-
Click Apply.
To update balancing segment values for legal entities that are assigned to accounting setups:
-
Navigate to the Accounting Options page for an accounting setup.
-
In the Legal Entities region, select the Update Balancing Segment Values icon for a legal entity.
The value set associated with one or more of the legal entity's ledgers will be automatically assigned.
-
Add or remove balancing segment values for the appropriate value set.
If multiple value sets are assigned to the legal entity, assign the same balancing segment value across value sets.
Creating Accounting Setup Structures
The accounting setup structure defines the framework or skeleton of an accounting setup.
Accounting Setup Manager Prerequisites Checklist
The following table lists the prerequisites for accounting setup manager.
| Step | Required | Description | Application or Feature Name | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Review Oracle Financials Implementation Guide | Required | Carefully consider the number of accounting setups that you need. | Accounting Setup Manager | Oracle Financials Implementation Guide |
| 2. Define chart of accounts | Required | Define at least one chart of accounts. For ease in assigning balancing segment values to legal entities, it is recommended that all charts of accounts should share the same value set for the balancing segment. | General Ledger | Oracle E-Business Suite Flexfields Guide, Oracle General Ledger User Guide |
| 3. Define accounts | Required | Define the following natural accounts that will be used to create your ledgers:
|
General Ledger | Oracle General Ledger User Guide |
| 4. Define cross-validation rules | Optional | You can define multiple cross-validation rules per chart of accounts to prevent invalid combinations when entering accounts during setup and data entry. | General Ledger | Oracle General Ledger User Guide |
| 5. Define chart of accounts mapping | Conditionally Required | If you plan to use a secondary ledger that uses a different chart of accounts from the primary ledger, define a chart of accounts mapping. The mapping provides instructions on how to transfer data between disparate charts of accounts. | General Ledger | Oracle General Ledger User Guide |
| 6. Define period types | Optional | If you want to use period types that are not installed with General Ledger, define the period types that you will use for your accounting calendar. | General Ledger | Oracle General Ledger User Guide |
| 7. Define accounting calendars | Required | Define one or more accounting calendars. | General Ledger | Oracle General Ledger User Guide |
| 8. Define transaction calendars | Conditionally Required | If you plan to use average balance processing, define a transaction calendar to specify valid business days used by your organization. | General Ledger | Oracle General Ledger User Guide |
| 9. Define or enable currencies | Required | Define or enable one or more currencies. | General Ledger | Oracle General Ledger User Guide |
| 10. Define currency conversion rate types and rates | Required | If you plan to enter foreign currency transactions, define conversion rate types and conversion rates. | General Ledger | Oracle General Ledger User Guide |
| 11. Define journal reversal criteria | Optional | Define a journal reversal criteria set that you will assign to each ledger to have journals for that ledger automatically reversed. | General Ledger | Oracle General Ledger User Guide |
| 12. Define jurisdictions | Optional | If you do not want to use the jurisdictions that are seeded, define a jurisdiction. The jurisdiction is used to assign a territory to a legal entity. | Legal Entity Configurator | Oracle Financials Implementation Guide |
| 13. Define legal entities | Optional | Create a complete definition of your legal entity. It is recommended that you assign specific balancing segment values to legal entities to help you secure and identify transactions by legal entity. | Legal Entity Configurator or Accounting Setup Manager | Oracle Financials Implementation Guide |
| 14. Define subledger accounting methods | Optional | If you do not want to use Standard Accrual or Standard Cash as your ledger's default accounting method, define subledger accounting methods using Oracle Subledger Accounting. | Oracle Subledger Accounting | Oracle Subledger Accounting Implementation Guide |
Creating an Accounting Setup
Creating an accounting setup includes the following steps:
Assigning Legal Entities
Assigning legal entities to accounting setups is optional. Assign legal entities if you are planning to use Oracle financial subledgers that require a legal entity context for transaction processing. Also, assign legal entities if you are planning to use legal entity specific features, such as intercompany accounting.
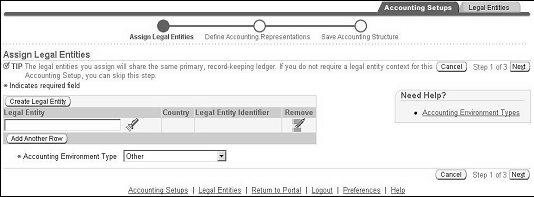
To assign legal entities:
-
In the Assign Legal Entities page, assign legal entities.
If creating legal entities from the Assign Legal Entities page, you are not creating a complete definition of your legal entity. Complete the definition of the legal entity later from the Legal Entities tab.
Defining Accounting Representations
Specify the ledger attributes for the primary ledger. The primary ledger acts as the primary accounting representation. Optionally specify the ledger attributes for one or more secondary ledgers to represent primary ledger transactions in a different chart of accounts, calendar, currency, subledger accounting method, and/or ledger processing options.
To maintain additional currency representations of primary or secondary ledgers, assign reporting currencies to them.
Note: Add secondary ledgers and reporting currencies to accounting setups at any time. Before completing the accounting setup, you can delete secondary ledgers and reporting currencies. After completing the accounting setup, you can only disable the conversion of reporting currencies and secondary ledgers.
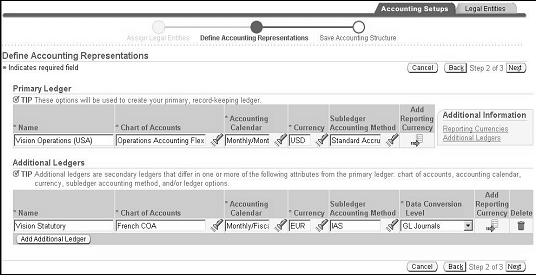
To define accounting representations:
-
Navigate to the Define Accounting Representations page from the Assign Legal Entities page.
-
Specify primary ledger attributes for the required fields.
Note: You cannot assign a calendar if it contains gaps between periods or it does not have a full fiscal year defined.
-
Optionally assign a subledger accounting method if planning to use Subledger Accounting to integrate data from Oracle financial subledgers or external feeder systems.
Note: Once you assign a subledger accounting method, you must always have a subledger accounting method assigned. You can change the subledger accounting method at any time.
-
Optionally, specify the following secondary ledger attributes:
-
name
-
chart of accounts
-
accounting calendar
-
currency
-
subledger accounting method
Note: To define a subledger level secondary ledger, assign a subledger accounting method to both the primary ledger and to this secondary ledger.
Note: To define an adjustments only secondary ledger, the chart of accounts, accounting calendar, and currency must be the same as the primary ledger. If you only want to use the Adjustments Only secondary ledger for manual adjustments in General Ledger, do not assign a subledger accounting method. To use the Adjustments Only secondary ledger for both manual and automated adjustments from Subledger Accounting, assign a subledger accounting method to both the primary and secondary ledger.
-
-
Specify a Data Conversion Level.
Additional Information: Data Conversion Levels
If assigning a balance level secondary ledger that uses a different currency from the primary ledger, a balance level reporting currency is automatically assigned to the primary ledger if you did not create one. For example, if the primary ledger's currency is EUR and you assign a balance level secondary ledger whose currency is CAD, the system automatically creates a balance level reporting currency for the CAD currency. This reporting currency is used as the source representation when transferring CAD balances to this secondary ledger.
-
Optionally, select the Add Reporting Currency icon.
-
In the Add Reporting Currency page, enter a currency and one of the following currency conversion levels:
-
Balance: maintains translated balances
Note: The currency of the balance level reporting currency cannot be the same currency as its source ledger.
-
Journal: maintains journals and balances in the reporting currency using the General Ledger Posting program
-
Subledger: maintains a currency representation of the source ledger's subledger journals, General Ledger journals, and balances using both Subledger Accounting and the General Ledger Posting program.
Note: The subledger level reporting currency requires a subledger accounting method to be assigned to the primary ledger.
Note: You cannot assign subledger level reporting currencies to secondary ledgers.
-
-
Click Apply.
Additional Information: Reporting Currencies
Saving the Accounting Structure
Carefully review and save the accounting setup structure to finish creating the framework of the accounting setup before proceeding to the Accounting Options.
Once you save the accounting setup structure, you cannot change the following:
-
chart of accounts, accounting calendar, or currency of the primary ledger and secondary ledger
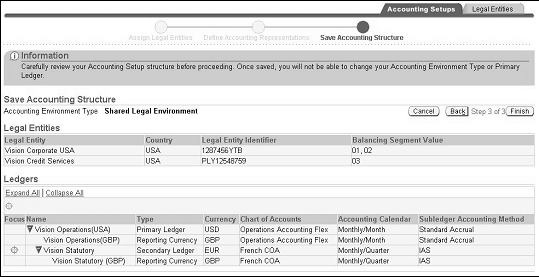
To save the accounting structure:
-
Navigate to the Save Accounting Structure page from the Define Accounting Representations page.
-
Review the accounting setup structure.
-
Click Finish.
Completing Accounting Options
The Accounting Options page is displayed in a checklist format to complete the relevant setup steps to make the accounting setup ready for entering transactions and journals.
Before entering transactions, complete all of the required setup steps for each accounting setup. If using secondary ledgers, complete all of the required setup steps for the primary ledger before completing the setup steps for the secondary ledgers
Navigate to the Accounting Options page in one of the following ways:
-
After saving the accounting setup structure, click Define Accounting Options.
-
Query an existing accounting setup from the Accounting Setups page, and then select the Update Accounting Options icon.
The name of the Accounting Options page is named after the primary ledger, such as Accounting Options: <Name of primary ledger>
Related Topics
Updating Legal Entities
The Legal Entities region of the Accounting Options page allows you to do the following:
-
view legal entities and make changes
-
update legal entities
-
add legal entities
-
remove legal entities from one accounting setup and assign them to another accounting setup
Once the accounting setup is complete, you cannot remove any of its legal entities. To disable a legal entity, end-date it.
Once you end-date a legal entity, you cannot enter new subledger transactions against the legal entity. You can use the legal entity's balancing segment values to enter manual journal entries in General Ledger. This allows you to enter adjusting entries during the accounting close.
If you end-date a legal entity, end date its balancing segment value to prevent the use of the balancing segment value for journal entries.
-
assign unique balancing segment values to legal entities
Note: If you use balancing segment values to represent legal entities, do not assign the same balancing segment values to multiple legal entities that are assigned to different accounting setups. Accounting Setup Manager will not prevent you from assigning the same values to legal entities in different accounting setups.
-
remove balancing segment values
You can only remove balancing segment values before the accounting setup is complete. A balancing segment value removed from one legal entity can be assigned to another legal entity within the same or different accounting setup
Note: If the accounting setup is complete, you cannot remove any balancing segment values from the accounting setup's legal entities. To disable the balancing segment value, end-date it.
You can query historical transactions and report on the end-dated balancing segment value
-
end-date balancing segment values
You can end-date balancing segment values at any time. If you end-date a balancing segment value, you cannot enter new transactions with dates after the end-date. You can query historical transactions and report on the end-dated balancing segment value.
Note: If you end-date a legal entity, end-date the balancing segment values that are assigned to the legal entity. This prevents users from entering transactions using a balancing segment value that is associated with an inactive legal entity.
Additional Information: Legal Entities Overview
Primary Ledger Setup Steps
The primary ledger setup steps are as follows:
-
Ledger Options, required
-
Reporting Currencies, conditionally required
Additional Information: Accounting Setup Manager Checklist
Secondary Ledger Setup Steps
The same setup steps for the primary ledger also apply to secondary ledgers. The following setup step applies only to secondary ledgers:
-
Primary to Secondary Ledger Mapping, required
Note: Add secondary ledgers at any time after completing the ledger options for the primary ledger by clicking Add Secondary Ledgers.
Ledger Options
A ledger determines the chart of accounts, accounting calendar, currency, subledger accounting method, and ledger processing options for each company, legal entity, or group of companies and legal entities.
Each accounting setup requires a primary ledger that acts as the main record-keeping ledger for none or one or more legal entities that use your main chart of accounts, accounting calendar, subledger accounting method, and currency to record and report on all of your financial transactions.
To maintain an additional accounting representation, use secondary ledgers.
To maintain an additional currency representation, use reporting currencies.
Ledger Overview
Reporting Currencies
To report on account balances in multiple currencies, assign reporting currencies to ledgers.
Reporting currencies can only differ by currency from their source ledger and must share the same chart of accounts, accounting calendar/period type combination, subledger accounting method, and ledger processing options as their source ledger.
Reporting currencies can be maintained at one of the following currency conversion levels:
-
Subledger
-
Journal
-
Balance
Additional Information: Reporting Currencies
Assigning Ledgers to Accounting Setups
When creating an accounting setup structure, specify the ledger attributes for the primary ledger and optionally one or more secondary ledgers.
The ledgers assigned when creating the accounting setup structure are not completely defined; complete the ledger options for each ledger to complete the ledger definition.
Using Ledgers to Perform Accounting
To use ledgers to perform accounting, complete the following:
-
Complete the ledger options for each ledger using the Accounting Options page.
-
Complete the accounting setup.
-
Assign the ledger to the GL Ledger Name profile option for each Subledger responsibility to grant access to ledgers used by Oracle Subledgers.
-
Assign the appropriate data access set to the profile option GL: Data Access Set for each General Ledger responsibility to grant access to ledgers used by General Ledger.
Additional Information: Setting General Ledger Profile Options, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
Enabling Average Balance Processing
If enabling average balance processing for the ledger, General Ledger tracks and maintains average and end–of–day balances.
Note: You can only enable average balances or average balance consolidation for your secondary ledger if average balances or average balance consolidation is also enabled for its primary ledger
Note: You cannot enable average balances if your ledger is enabled for secondary segment tracking.
Additional Information: Overview of Average Balancing Processing, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
Completing Ledger Options
This section describes the ledger options that must be completed.
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites are needed to complete the ledger options for ledgers:
-
(Required) assign one or more ledgers to an accounting setup
-
define the following accounts:
-
(Required) Retained earnings account
-
Suspense account to enable suspense posting
-
Cumulative Translation Adjustment account to translate balances
-
(Recommended for Subledger Accounting) Rounding Differences account to use a specific account to track small currency differences during currency conversion
-
(Required for Average Balances) Non-Postable Net Income account to use average balance processing
This account captures the net activity of all revenue and expense accounts when calculating the average balance for retained earnings.
-
Reserve for Encumbrance account to use Encumbrance Accounting
-
(Recommended for Subledger Accounting) Entered Currency Balancing Account to use Subledger Accounting to balance foreign currency subledger journals by the entered currency and balancing segment value
-
Ledger Currency Balancing Account to use Subledger Accounting to balance subledger journals by the ledger currency and balancing segment value
-
-
(Required for Average Balances) Define transaction calendars to use average balance processing. Transaction calendars ensure journal entries created in General Ledger and Oracle Subledger Accounting, if used, are only booked on valid business days.
-
Define Journal Reversal Criteria to automatically reverse journals in General Ledger
To complete ledger options:
-
Navigate to the Accounting Options page in one of the following ways:
-
After saving the accounting setup structure, click Define Accounting Options.
-
Query an existing accounting setup from the Accounting Setups page and then choose the Update Accounting Options icon.
-
-
Click the Update Ledger Options icon.
-
Enter all relevant fields for the following pages:
-
Ledger Definition
The following table provides descriptions for selected fields in the Ledger Definition page.
Ledger Definition Page Field Description Short Name Ledger short name; appears in the title bar of windows and in some lists of values; can be changed at any time. Currency Main transaction currency for this ledger. Note: If the ledger's currency does not match the functional currency as defined by FASB #52 (U.S.) and you need to report financial results in your functional currency, consider using General Ledger Translation or Reporting Currencies.
Additional Information: Reporting Currencies and Reporting Currencies, Oracle General Ledger User Guide.
First Ever Opened Period First period that can be opened for this ledger. This cannot be changed after you open the first period. Number of Future Enterable Periods Number of future periods to allow for journal entry within this ledger. General Ledger automatically assigns a status of Future Entry to accounting periods following the latest open period in the calendar based on the number of future enterable periods defined here. If you change the number of future enterable periods for the ledger, General Ledger does not change additional periods to the Future Enterable status until a new period is opened. Note: You can enter journal batches for a future enterable period, but you cannot post the batches until a period is opened.
Tip: Minimize the number of future enterable periods to prevent users from accidentally entering journal entries in an incorrect period.
Subledger Accounting Method Subledger accounting method for this ledger; defined in Subledger Accounting. Entered Currency Balancing Account Posts differences from out-of-balance foreign currency journals in subledgers. Use Cash Basis Accounting This option pertains only to Oracle Payables. Payables uses this option for its Mass Additions Create program for determining expense account information. Note: The option cannot be changed after the Accounting setup is complete. Also, this option is not available for selection for Secondary Ledgers.
Additional Information: Payables Options, Oracle Payables User Guide
Balance Subledger Entries by Ledger Currency Enables balancing of subledger journal entries by ledger currency and balancing segment value Ledger Currency Balancing Account Posts out-of-balance subledger journal entries to this account. This account is only required if the Balance Subledger Entries by Ledger Currency option is selected. Additional Information Stores descriptive information about this ledger if the descriptive flexfield for this page has been enabled. -
Ledger Options
The following table provides descriptions for selected fields in the Ledger Options page.
Ledger Options Page Field Description Retained Earnings Account Net balance of all income and expense accounts from the prior year are posted against the retained earnings account when the first period of a fiscal year is opened in General Ledger.
The balancing segment and the segment nominated as the secondary tracking segment act as placeholders for this account. General Ledger automatically inserts the appropriate value when calculating retained earnings.Track by Secondary Segment If you assigned the Secondary Tracking Segment qualifier to a segment in your chart of accounts, you can enable this option to track more detail when General Ledger performs year-end closing, translation, and revaluation activities. Note: You cannot enable both the Track by Secondary Segment and Average Balances options.
Additional Information: Secondary Tracking Segment, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
Suspense Account Allows suspense posting of out-of-balance journal entries.
If you have multiple companies or balancing entities within a ledger, General Ledger automatically creates a suspense account for each balancing entity.
You can also define additional suspense accounts to balance journal entries from specific sources and categories using the Suspense Accounts window.
Note that if you update the suspense account for the ledger, the default suspense account is updated in the Suspense Accounts window. Likewise, if you update the default account in the Suspense Accounts window, the account will be updated for the ledger.
If you do not enter a suspense account, you can only post journal entries that are balanced.Additional Information: Suspense Accounts, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
Rounding Differences Tracking Account In General Ledger, this account tracks rounding differences that occur during currency conversions. If you do not enter an account, General Ledger will post rounding differences to the journal line with the largest amount.
In Subledger Accounting, this account tracks currency conversion rounding differences that cause unbalanced journal entries. Subledger Accounting will issue an error if it encounters a subledger journal entry that is unbalanced because of rounding differences and an account is not specified.
If your foreign currency transactions include different balancing segment values to represent multiple companies, General Ledger and Subledger Accounting will automatically create a rounding differences account for each balancing segment value.Note: A rounding differences account is recommended for Subledger Accounting.
Note: Subledger Accounting offers features for controlling how the accounting program deals with rounding differences. For more details see Oracle Subledger Accounting Implementation Guide.
Enable Intracompany Balancing Posts out-of-balance intracompany journals (debits do not equal credits for a particular company or balancing segment value within the same ledger)
If you enable this option, you must define Intracompany Balancing Rules when you complete your Accounting Options to provide instructions on how to automatically balance intracompany journals against balancing accounts you specify.
If you do not choose to enable intracompany balancing, you can only post intracompany journals that balance by balancing segment.Note: For accounting setups with multiple legal entities, enabling intracompany balancing enables both intercompany and intracompany balancing for a journal that includes multiple legal entities.
-
Intercompany Balancing, Oracle Financials Implementation Guide
-
Intracompany Balancing Rules, Oracle Financials Implementation Guide
Enable Journal Approval Use General Ledger's Journal Approval feature for the ledger.
When Journal Approval is enabled and a journal entry's journal source requires approval, the journal must be approved by the appropriate level of management before any further action can be taken, such as posting. If Journal Approval is not enabled, approval is not required, even if the journal source requires approval.Note: When you enable Journal Approval, only journal entries that use actual amounts and the Manual journal source will automatically have Journal Approval enabled. To require journal approval for budget or encumbrance journals or for journals using a source other than Manual, you must select the Require Journal Approval check box for the appropriate journal source in the Journal Sources window in Oracle General Ledger.
Additional Information: Setting Up Journal Approval, Oracle General Ledger Implementation Guide
Journal Reversal Criteria Set Automatically reverses this ledger's journals based on the Journal Reversal Criteria Set assigned. Additional Information: Assigning Journal Reversal Criteria, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
Default Period End and Average Rate Types Used to translate actual account balances Note: The rate types specified for the ledger are used to assign default rate types for any balance level reporting currencies assigned to this ledger. You can override the default rate types for each balance level reporting currency.
Cumulative Translation Adjustment Account This account is necessary to translate the ledger's currency balances into a balance level reporting currency. For journal level reporting currencies, this account is used when revaluing foreign currency denominated balances.
General Ledger automatically posts any net adjustments resulting from currency translation to this account, in accordance with FAS 52 (U.S.) and IAS 21. If you have multiple companies or balancing entities within a ledger, General Ledger automatically creates a translation adjustment account for each company or balancing entity.
The difference in revaluation adjustments between the ledger and its journal level reporting currencies are recorded to the cumulative translation adjustment account.
The balancing segment and the nominated secondary tracking segment act as placeholders in this field. General Ledger automatically inserts the appropriate value when translation or revaluation is run.
Set the account type of your Cumulative Translation Adjustment account to Owner's Equity to create a translation adjustment on your balance sheet. Set the account type of this account to Revenue or Expense to create a translation gain/loss on your income statement.-
Translating Balances, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
-
-
Advanced Options
The following table provides descriptions for selected fields in the Advanced Options page.
Advanced Options Page Field Description Journal Reconciliation Allows you to reconcile transactions in accounts that should balance to zero, such as a suspense account, or a Value Added Tax control account. Additional Information: Entering Journals, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
Require Budget Journals Allows you to require budget journals for all budgets. If using budgetary control, General Ledger already requires you to create budget journals for your funding budget. If you want to require budget journals for all budgets, choose this option. Reserve for Encumbrance Account Allows encumbrance accounting for the ledger; required for budgetary control.
If you enter an out-of-balance encumbrance entry, General Ledger automatically posts the difference against the account you specify here. If you have multiple companies or balancing entities within a ledger, General Ledger automatically creates a Reserve for Encumbrance account for each balancing entity.
When you enter a Reserve for Encumbrance account without enabling budgetary control, you can still enter manual encumbrances via journal entry, but you cannot generate encumbrances from requisitions and purchase orders.Additional Information: Overview of Encumbrance Accounting, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
Mark Funding Budget as Commitment Budget This option is specific to Oracle Public Sector Financials (International) and is only displayed for the secondary ledger. This option determines the secondary ledger that accommodates the commitment budget. Enable Average Balances Allows you to use the ledger for average balance processing. In an average balances ledger, your standard and average balances are tightly linked. Each time you post a journal entry, Oracle General Ledger updates both the standard (period-based) balances and corresponding average balances for your balance sheet accounts.
If enabled, enter data in the following fields that are displayed:-
Net Income Account: Captures the net activity of all revenue and expense accounts when calculating the average balance for retained earnings
-
Rate Type: Enter any daily conversion rate type except User for translating average balances. General Ledger automatically translates period-average-to-date balances. You can also choose to have translation maintain end-of-day, quarter-average-to-date, and year-average-to-date balances by selecting the appropriate check boxes.
-
Transaction Calendar: Ensures that journal entries created in General Ledger and Subledger Accounting are posted only to valid business days; not required for average balance consolidation ledgers.
Note: You can only enable average balance processing for those ledgers that require it. This ensures that you incur no additional overhead unless you need average balance processing enabled.
Note: You can only enable average balances for a secondary ledger if its primary ledger has average balances or average balance consolidation enabled.
Note: You cannot enable average balances if your ledger is enabled for secondary segment tracking.
Additional Information: Overview of Average Balance Processing, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
Enable Average Balance Consolidation Select this option if you do not want to maintain a link between standard and average balances to allow you to update standard and average balances independently. Many users use this type of ledger for consolidation purposes to allow them to consolidate standard and average balances separately in order to make adjustments to those balances independently. Note: You can only enable average balance consolidation for a secondary ledger if its primary ledger has average balances or average balance consolidation enabled.
Additional Information: Consolidation, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
-
-
-
Click Next to review your ledger options and then click Finish to complete your ledger definition.
-
Defining Calendars, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
-
Defining Currencies, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
-
Opening and Closing Accounting Periods, Oracle General Ledger Implementation Guide
-
Using Budgetary Control and Online Funds Checking, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
-
Define Budgets, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
-
GL Ledger Name Profile Option, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
Updating Ledger Options
After the ledger has a complete status, you can only update some ledger options.
The following ledger options cannot be changed:
-
Currency
-
Chart of Accounts
-
Accounting Calendar
-
Period Type
-
Average Balance Processing
-
Net Income Account
-
Transaction Calendar
Note: The Track by Secondary Segment option cannot be changed once the Accounting Setup status is complete.
Note: The First Ever Opened Period cannot be changed once the first period is opened for the ledger.
Prerequisites
-
The ledger options must have a status of Complete.
To make changes to ledgers:
-
In the Accounting Setups page, search for accounting setups by ledger.
-
Navigate to the Accounting Options page.
-
To navigate to the ledger definition pages, click the Update icon for the ledger; or click the ledger name link and then the Update button.
-
Make changes to the ledger and then click Finish.
Reporting Currencies
Reporting currencies express the accounting in your primary and/or secondary ledgers in an additional currency representation. For example, the USD primary ledger balances can be expressed in CAD or Yen by assigning a balance level reporting currency to the primary ledger.
Unlike secondary ledgers, reporting currencies can only differ by currency from their source ledger. They must share the same chart of accounts, accounting calendar/period type combination, subledger accounting method, and ledger processing options as their source ledger (primary or secondary ledger).
Reporting currencies can be maintained at three different currency conversion levels:
-
Subledger: Maintains a currency representation of your subledger journals, General Ledger journal entries, and balances.
When using the subledger level reporting currency, you must define subledger accounting rules using Subledger Accounting. These rules provide instructions on how to convert subledger data entered into the source ledger to one or more subledger level reporting currencies.
You must also define journal conversion rules. General Ledger Posting uses the journal conversion rules to automatically replicate specific journals, such as manual journal entries, to one or more subledger level reporting currencies.
Note: Subledger level reporting currencies can only be assigned to primary ledgers, not secondary ledgers.
-
Journal: Maintains General Ledger journal entries and balances in another currency representation.
Journal level reporting currencies are maintained using the General Ledger Posting Program. Every time a journal is posted in the source ledger, the journal is automatically converted to the respective journal level reporting currency based on the journal conversion rules defined.
-
Balance: Maintains balances in another currency.
The General Ledger Translation program is used to convert balances from the source ledger to the balance level reporting currency. When you run Translation in your primary or secondary ledger and specify a target currency, the translated balances are reflected in the balance level reporting currency.
Note: If a balance level reporting currency is not assigned to the ledgers in the accounting setup, a balance level reporting currency is automatically created the first time Translation is run. The name of the balance-level reporting currency is the same as its source ledger except its currency code, such as (USD), is appended to the end of its name.
Note: The subledger level and journal level reporting currencies act similarly to ledgers. You must open and close the periods for these reporting currencies before you can enter transaction and journal entries. You can also enable journal approval for these reporting currencies if planning to enter manual journal entries directly to these reporting currencies.
Assigning Reporting Currencies to Ledgers
If reporting currencies are assigned to ledgers when creating an accounting setup structure, the status for the Reporting Currencies step is In Process. To complete the accounting setup, update the reporting currency and complete the conversion options for all reporting currencies that are assigned.
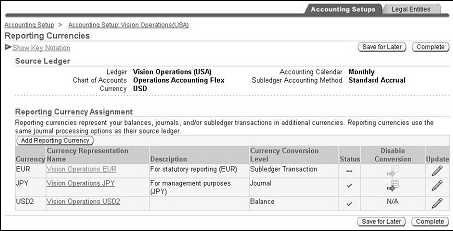
If no reporting currencies are assigned to the ledgers when creating the accounting setup structure, the Reporting Currencies step is not required and the status is Not Started.
Add reporting currencies to accounting setups at any time.
Additional Information: Adding Reporting Currencies
To complete reporting currencies:
-
In the Accounting Options page, click the Update icon for a reporting currency.
-
Update each reporting currency.
-
Enter all relevant fields for the reporting currency.
The following table describes selected options for balance level reporting currencies.
Selected Options for Balance Level Reporting Currency Field Description Currency Conversion Level Balance defaults to indicate that this is a balance level reporting currency; cannot be changed Period End Rate Type Translates actual account balances; defaults from the source ledger; can be changed Period Average Rate Type Translates actual account balances; defaults from the source ledger; can be changed The following table describes selected options for journal and subledger level reporting currencies.
Selected Options for Journal and Subledger Level Reporting Currencies Field Description Currency Conversion Level Indicates that this is a journal level or subledger level reporting currency Status If disabled, data is no longer automatically converted to the reporting currency. Additional Information: Disabling the Conversion of Reporting Currencies
First Ever Opened Period The first period that can be opened for this reporting currency; defaults from the source ledger Rounding Differences Tracking Account In General Ledger, this account tracks rounding differences that occur during currency conversions. If you do not enter an account, General Ledger will post rounding differences to the journal line with the largest amount.
If your foreign currency transactions include different balancing segment values to represent multiple companies, General Ledger will automatically create a rounding differences account for each balancing segment value.Warning: Any changes you make to the Rounding Differences Account in the source ledger will automatically be applied to all of its journal and subledger level reporting currencies. If you have a different rounding differences account assigned to your reporting currencies and you change the rounding differences account for the source ledger, such as removing one, changing one, or adding one, be sure to also update the rounding differences account for each of the reporting currencies.
Enable Journal Approval Use General Ledger's Journal Approval feature for this reporting currency.
When enabled, Journal Approval only applies to journals that are entered directly to the reporting currency, such as manually entered journals or journals loaded directly to the reporting currency. Journal Approval will not apply to journals that were automatically converted from the source ledger by General Ledger Posting.Note: When you enable Journal Approval, only journal entries that use actual amounts and the Manual journal source will automatically have Journal Approval enabled. To require journal approval for budget or encumbrance journals or for journals using a source other than Manual, you must mark the Require Journal Approval check box for the appropriate journal source in the Journal Sources window in Oracle General Ledger.
Additional Information: Setting Up Journal Approval, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
Rounding Differences Tracking Account In General Ledger, this account tracks rounding differences that occur during currency conversions. If you do not enter an account, General Ledger will post rounding differences to the journal line with the largest amount.
If your foreign currency transactions include different balancing segment values to represent multiple companies, General Ledger will automatically create a rounding differences account for each balancing segment value.Warning: Any changes you make to the Rounding Differences Account in the source ledger will automatically be applied to all of its journal and subledger level reporting currencies. If you have a different rounding differences account assigned to your reporting currencies and you change the rounding differences account for the source ledger, such as removing one, changing one, or adding one, be sure to also update the rounding differences account for each of the reporting currencies.
Default Rate Type The conversion rate type used to retrieve exchange rates for converting transactions from the source ledger to this reporting currency
This differs from the conversion rate type specified when entering a transaction. Oracle E-Business Suite use the transaction conversion rate type to retrieve exchange rates for converting entered amounts from the transaction currency to the ledger currency. Alternatively, users can specify their own rate type.
The Default Rate Type works with the Retain Transaction Rate Type field. If you choose not to retain the same rate type used to convert the original transaction, the Default Rate Type is used instead.Additional Information: Defining Conversion Rate Types, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
Retain Transaction Rate Type Controls the conversion rate type that should be used to convert transaction currency amounts from the source ledger to this reporting currency. -
If Yes is selected, then the conversion rate type used to enter the transaction in the source ledger will be retained when converting the same transaction from the transaction currency amount to this reporting currency.
Note: If the original transaction rate type is User or EMU Fixed, the default rate type assigned to the reporting currency will always be used.
-
If No is selected, then the default rate type specified in the Default Rate Type field will be used to convert transactions to this reporting currency.
The Retain Transaction Rate Type option is ignored for the following reasons:
-
An EMU fixed rate relationship exists between the transaction currency and the currency of the reporting currency. In this case, the EMU Fixed conversion rate type is used.
-
The transaction currency is the same as the currency of the source ledger, such as the primary or secondary ledger. In this case, a conversion rate type does not exist for the transaction and the default rate type is used.
-
The transaction currency is the same as the currency of the reporting currency. In this case, the User conversion rate type is used with a default rate of 1.
-
A User rate is used for the transaction. In this case, the User conversion rate type is used. The reporting currency conversion is completed in two steps via the default rate type assigned to the reporting currency.
Note: If the Account Type Specific Conversion is enabled, you can determine whether Accounting Setup Manager should inherit the conversion type used in the source ledger.
-
Additional Information: Reporting Currency Account Type Specific Conversion, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
Missing Conversion Rate Controls what the system should do if it cannot find a conversion rate as of the conversion date -
If Report an Error is selected, the system will report an error and prevent a transaction or journal from being posted in the source ledger; a conversion rate will need to be specified to successfully convert data entered in the source ledger to this reporting currency.
-
If Use Last Rate is selected, the system will use the last rate defined for a particular rate type if it cannot find a currency conversion rate; if enabled, specify a number for the Number of Days to Find the Last Rate.
Number of Days to Find Last Rate Indicates how many days back in time the system should look to find a rate; enter a number from 1 to 999. Retain Journal Creator from Source Ledger Controls the Created By user information that can be viewed for each journal using Help > Record History -
Select Yes to retain the person who entered the journal in the source ledger as the Created By user.
-
Select No to indicate the person who posted the journal as the Created By user.
-
-
Click Apply.
Related Topics
Journal Source and Category Conversion
Subledger Level Reporting Currencies
Journal Conversion Rule Examples
Disabling the Conversion of Reporting Currencies
Journal Source and Category Conversion
General Ledger Posting uses the journal source and category conversion rules to determine the journals (based on journal source and category combinations) to automatically convert to this reporting currency.
Journal sources identify the origin of journal entry transactions, such as Purchasing or Payables. Journal categories describe the purpose of journal entries, such as purchase requisitions or purchase orders.
Specifying a journal source and category combination and selecting Yes in the Convert Journals to this Reporting Currency field instructs the General Ledger Posting program to automatically convert those journals to this reporting currency when they are posted in the source ledger.
The journal source and category Other represents all other journal sources and categories other than those explicitly defined.
-
To convert the majority of journals to this reporting currency, specify Yes for the Other journal source and category and then select No for the journal source and category combinations that you do not want converted.
-
If you do not want the majority of the journals to be automatically converted to this reporting currency, specify No for the Other journal source and category and then selectively add those journal source and category combinations that you do want converted.
Note: If the General Ledger Posting program cannot find a matching journal source/category combination, or if no conversion rules for a journal source/category combination are defined, the journal is not converted to the reporting currency.
The journal sources Move/Merge and Move/Merge Reversal are set to No because they are not converted to the reporting currency using General Ledger Posting. They are automatically converted to the reporting currency when performing a move/merge or move/merge reversal in the source ledger. This means that if you use Mass Maintenance to move or merge balances between accounts in the source ledger, the same accounts are moved or merged in the reporting currency.
Additional Information: Moving or Merging Account Balances, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
Subledger Level Reporting Currencies
For subledger level reporting currencies, the journal sources for all transaction sources that use Subledger Accounting must be set to No in the Convert Journals to this Reporting Currency field. Any journal source that uses Subledger Accounting to generate its accounting entries must not be converted to the reporting currency using General Ledger Posting because Subledger Accounting automatically performs the conversion for these subledger journals.
Warning: If you incorrectly choose Yes in the Convert Journals to this Reporting currency field for any transaction sources that use Subledger Accounting, the journal will be double counted; once by Subledger Accounting and once by General Ledger Posting. You will need to reverse the journal in General Ledger.
Note: To find all transaction sources that integrate with Oracle Subledger Accounting, query them in the Subledger Application form that is accessed from the Subledger Accounting Setup menu.
Note: If integrating with transaction sources that do not use Subledger Accounting and you want to maintain journals from these subledgers in the subledger level reporting currency, do not use Oracle's seeded journal sources. For example, if you use a non-Oracle Receivables application, you should create your own journal source for that application instead of using the seeded source Receivables that is reserved for Oracle sources. If you use the seeded source to import data from third party systems, those journals will not be converted to a subledger level reporting currency when you post them in the primary ledger.
Journal Conversion Rule Examples
This section describes examples that illustrate how journals are converted based on different journal conversion rules.
Example 1: Specific Journal Source and Journal Category Match
The following example shows a matching source/category combination. It also shows that no conversion takes place if there is not a match with any of the defined conversion rules.
Conversion rules are defined in the following table.
| Source | Category | Convert Journals |
|---|---|---|
| Other | Other | No |
| Manual | Adjustment | Yes |
| Consolidation | Consolidation | No |
| Manufacturing | Labor Cost | Yes |
The following table describes the results for journals converted to the reporting currency.
| Journal Number | Source/Category | Results |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Manual/Adjustment | Journal is converted using the defined conversion options for this combination. |
| 2 | Consolidation/Consolidation | Journal is not converted because the Convert option is set to No. |
| 3 | Manufacturing/Freight | Journal is not converted because there is no rule defining Journal Source Manufacturing and Category Freight. |
Example 2: No Specific Journal Source or Category
The following shows an example of matching a journal source but not a category; and another example of matching a journal category but not a source.
Conversion rules are defined in the following table.
| Source | Category | Convert Journals |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Other | Yes |
| Other | Adjustment | Yes |
| Manufacturing | Adjustment | No |
The following table describes the results for journals converted to the reporting currency.
| Journal Number | Source/Category | Results |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Manufacturing/Labor Cost | Journal is converted because the first rule only has a requirement to match to a source of Manufacturing with any category. |
| 2 | Manual/Adjustment | Journal is converted because a rule has a requirement to match to any source with the Adjustment category. |
| 3 | Spreadsheet/Adjustment | Journal is converted because a rule has a requirement to match any source with the Adjustment category. |
| 4 | Manufacturing/Adjustment | Journal is not converted because the Convert option is set to No for this source/category combination. |
Example 3: Journal Source and Journal Category Conflicting Rules
The following example shows what happens when you set up contradictory rules for journal source/category combinations. The rule for the source always overrides the rule for the category.
Conversion rules are defined in the table below.
| Source | Category | Convert Journal |
|---|---|---|
| Other | Adjustment | No |
| Manual | Other | Yes |
The following table describes the results for journals converted to the reporting currency.
| Journal Number | Source/Category | Results |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Manufacturing/Adjustment | Journal is not converted because it matches the first rule to not convert. |
| 2 | Manual/Adjustment | Journal is converted because the second rule requires conversion of all journals with the source Manual. The source rule overrides the category rule. |
Changing Conversion Rules
Change the journal source and category conversion rules at any time. For example, for any journal source/category combination, you can change the Convert Journals to this Reporting Currency option.
Note that the changes are effective immediately, but that they apply only to new journals.
Caution: It is strongly recommended that you do not change the conversion rules once you begin entering transactions. Doing so may result in inconsistent transaction amounts and account balances between your source ledger (primary or secondary ledger) and its reporting currencies.
Adding Reporting Currencies
Add reporting currencies to primary or secondary ledgers at any time. If adding journal level or subledger level reporting currencies to existing ledgers that have periods opened, you must initialize the beginning balances for your reporting currency and optionally choose to convert historical data from the source ledger to the reporting currency. Historical Conversion refers to converting the historical transactions of the source ledger to the journal level or subledger level reporting currency.
Note: Historical Conversion does not apply to reporting currencies that are assigned to new accounting setups.
Note: Before adding journal or subledger level reporting currencies, carefully review the information in the Implementation Considerations section of the Journal or Subledger-Level Reporting Currencies chapter of the Oracle General Ledger User Guide.
Note: If you allow users to make adjustments in Oracle Projects to expenditure items that represent receipts, receipt non-recoverable tax, or exchange rate variances, then Oracle Projects does not perform accounting for adjustments in reporting currencies and subledger level secondary ledgers if the secondary ledger currency differs from the primary ledger currency. Please review your business practices and ensure that the Oracle Projects profile options PA: Allow Adjustments to Receipt Accruals and Exchange Rate Variance are set appropriately. For additional information, see: Profile Restrictions to Supplier Cost Adjustments, Oracle Project Costing User Guide.
Note: Additional steps are required if adding a new subledger level secondary/reporting ledger to an existing primary ledger that already has final accounted subledger journal entries. For more information, see Please see the Conversion of Historical Data for Reporting Currencies and Secondary Ledgers section of Oracle Subledger Accounting Implementation Guide.
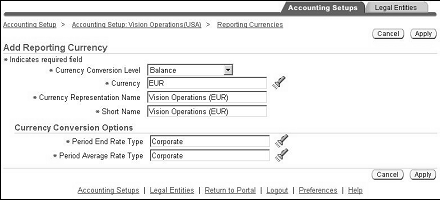
To add reporting currencies:
-
Navigate to the Accounting Options page.
-
Click the Update icon for the reporting currency.
-
In the Reporting Currency Assignment region, click Add Reporting Currency.
-
Select the Currency Conversion level.
-
You can only assign subledger level reporting currencies to primary ledgers that have subledger accounting methods assigned.
If assigning a reporting currency to a secondary ledger, the currency conversion level of the reporting currency must be equal to or less than the Data Conversion Level of the Secondary Ledger. The following table lists the types of reporting currencies that can be assigned to Secondary Ledgers.
Reporting Currencies that can be Assigned to Secondary Ledgers If the secondary ledger data conversion level is ... Then the type of reporting currency available is… Balance Balance level only Journal Balance or journal level Subledger Balance or journal level Note: : Secondary ledgers cannot have subledger level reporting currencies assigned.
Adjustments Only Balance level only
-
-
Enter all required fields.
-
To initialize beginning balances and convert historical transactions or journals to this reporting currency, enter Data Conversion Initialization options as described in the following table.
Data Conversion Initialization Options Option Description First Future Conversion Period The first period for which you want to convert transactions or journals to your reporting currency. The First Future Conversion Period is also the period in which account balances are initialized in your reporting currencies. It must be the first future-enterable period in your source ledger. Retain Original Conversion Rate Type To convert data from the source ledger to your reporting currency for periods prior to the First Future Conversion Period, this options determines whether the original rate type can be used to convert historical data. -
Select Yes to retain the conversion rate type used to enter the original transaction.
Select No to use the rate type specified in the next field, Historical Conversion Rate Type.
Historical Conversion Rate Date Enter the date of the conversion rate to use to convert historical data to this reporting currency. Historical Conversion Rate Type If you entered No to retain the original transaction's conversion rate type, enter the conversion rate type to use for historical data conversion. Note: For more information about the previous four options, see the Implementation Considerations section of the Journal or Subledger-Level Reporting Currencies chapter of the Oracle General Ledger User Guide.
-
-
Click Apply.
Note: Reporting currencies can only be deleted before the accounting setup is complete. If the reporting currency acts as the source representation for a secondary ledger, delete the secondary ledger before deleting the reporting currency.
Disabling the Conversion of Reporting Currencies
After the accounting setup is complete, you cannot delete reporting currencies; you can disable the conversion of subledger and journal level reporting currencies. This prevents future transactions and journals from being converted to the reporting currency. You will still be able to use the disabled reporting currency to view historical data and enter manual journals.
If the reporting currency acts as the source representation for a secondary ledger, disable the conversion of the secondary ledger before disabling the conversion for the reporting currency.
Note: The source representation of the secondary ledger is displayed in the Source Representation field in the Primary to Secondary Ledger Mapping page.
Note: Balance level reporting currencies cannot be disabled. To stop the conversion of balances from the source ledger to the balance level reporting currency, stop running Translation.
Once the conversion of a reporting currency is disabled, the status of the reporting currency is changed to Disabled.
To disable the conversion of reporting currencies:
-
Navigate to the Reporting Currencies page.
-
In the Reporting Currency Assignment region, click the Disable Conversion icon.
Note: Once disabled, the conversion of a reporting currency cannot be enabled.
Ledger Balancing Segment Value Assignments
Optionally assign specific balancing segment values to ledgers to track non-legal entity-related transactions or adjustments using a specific balancing segment value.
Note: Assign specific balancing segment values to all legal entities in an accounting setup before assigning a specific balancing segment value to the ledgers in the accounting setup.
Balancing segment values can be added to ledgers at any time.
-
Before the accounting setup is complete, you can remove balancing segment values from ledgers.
-
After the accounting setup is complete, you can only disable the balancing segment value by entering an end date.
To assign balancing segment values to ledgers:
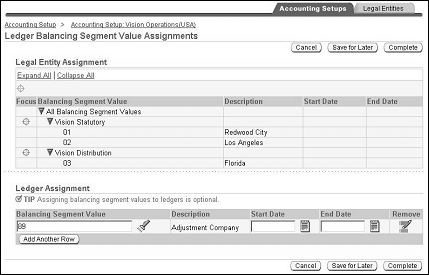
-
Navigate to the Accounting Options page.
-
Click the Update icon for the Balancing Segment Value Assignments step.
-
View the balancing segment values assigned to the legal entities associated with the accounting setup in the Legal Entity Assignment region.
Additional Information: Updating Balancing Segment Values
-
In the Ledger Assignment region, enter a balancing segment value.
Note: The value cannot be the same as the balancing segment values assigned to the legal entities.
-
Optionally, enter a start and end date to make the value effective for a limited time.
Note: This step does not have to have a status of Complete in order to complete the accounting setup.
To remove balancing segment values:
Balancing segment values can only be removed from ledgers before the accounting setup is complete.
-
Navigate to the Ledger Balancing Segment Value Assignments page. You access this page by updating the Balancing Segment Value Assignments step for the ledger.
-
To remove balancing segment values, click the Remove icon for each balancing segment value.
To disable balancing segment values:
Disable balancing segment values by entering an end date for the value. You cannot use the balancing segment value to enter new transactions or journals after the end date. You can only use the value for reporting and viewing historical data.
-
Navigate to the Ledger Balancing Segment Value Assignments page. You access this page by updating the Balancing Segment Value Assignments step for the ledger.
-
To disable a balancing segment value, enter an end date.
Subledger Accounting Options
If you assigned a subledger accounting method to your ledgers, the Subledger Accounting Options step will be displayed with a status of Complete.
If you did not assign a subledger accounting method to your ledger, then this step will not be displayed.
You can update this step at any time from the Accounting Options page. Subledger Accounting Options allow you to define how to generate the accounting entries from subledger transactions.
Note: All of the subledgers assigned to a ledger inherit its subledger accounting method from that ledger.
Additional Information: Oracle Subledger Accounting Implementation Guide
Operating Units
You can assign operating units to the primary ledger to partition subledger transaction data when multiple operating units perform accounting in the context of one or more legal entities.
If using an accounting setup that has legal entities assigned, the Operating Units step will be displayed. The status for this step will be Not Started.
You can update the Operating Units step at any time from the Accounting Options page.
Additional Information: You do not have to complete this step in order to complete your accounting setup.
Note: If you defined operating units in the Define Organization window in Oracle HRMS, then those operating units will be automatically assigned to the appropriate primary ledger in Accounting Setup Manager.
Additional Information: Multiple Organizations Overview, Oracle E-Business Suite Multiple Organizations Implementation Guide
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites are required if you plan to assign operating units to a primary ledger in the Accounting Setup Manager:
-
Define legal entities and assign them to accounting setups
-
Complete primary ledger setup steps
To Define and Assign Operating Units:
-
Navigate to the Operating Units page.
-
Click Add Operating Unit to both create and assign an operating unit to the primary ledger.
-
In the Add Operating Units page, enter the following:
-
Name: The name of the operating unit
-
Short Code: The short name of the operating unit
-
Business Group: The highest level in the organization structure, such as the consolidated enterprise, a major division, or an operation company that secures human resources information
-
Default Legal Context: One of the legal entities assigned to the accounting setup to act as the default legal context
-
-
Alternatively, you can create operating units by clicking Open Organization Form to open the Define Organization window in Oracle HRMS. When you define your operating unit and assign it to a primary ledger and default legal context, you will be able to view the operating unit assignment from Accounting Setup Manager.
-
Click Apply or Add Another to define and assign multiple operating units.
-
To mark the Operating Units step complete, click Complete.
Additional Information: Once you add an operating unit to a primary ledger, you cannot remove it. You can prevent the use of that operating unit by not assigning it to a Security Profile in Oracle HRMS. For more information on security profiles, see Implementing Multiple Organization Support, Oracle E-Business Suite Multiple Organizations Implementation Guide.
Intercompany Accounts
If using an accounting setup that has legal entities assigned and balancing segment values have been assigned to the legal entities, the Intercompany Accounts step will be displayed. The status for this step will be Not Started.
Update the Intercompany Accounts step to account for transactions across legal entities.
Note: You do not have to complete this step in order to complete your accounting setup. You can update this step at any time from the Accounting Options page.
Additional Information: Intercompany Balancing, Oracle Financials Implementation Guide
Intracompany Balancing Rules
If you enabled the Intracompany Balancing option for your ledger, the Intracompany Balancing step will be displayed. The status for this step will be Not Started.
Update the Intracompany Balancing step to define rules to balance journal entries between balancing segment values that are assigned to the same legal entity or ledger.
Note: You do not have to complete this step in order to complete your accounting setup. You can update this step at any time from the Accounting Options page.
Additional Information: Intracompany Balancing Rules, Oracle Financials Implementation Guide
Sequencing
Sequencing allows you to define accounting and reporting sequencing options for ledgers and reporting currencies. You can update this step at any time from the Accounting Options page.
Note: It is not necessary to complete this step in order to complete your accounting setup.
Additional Information: Sequencing
Secondary Ledgers
Secondary ledgers represent the primary ledger's accounting data in another accounting representation that differs in one or more of the following ways:
-
chart of accounts
-
accounting calendar/period type combination
-
currency
-
subledger accounting method
-
ledger processing options
Use secondary ledgers for supplementary purposes, such as consolidation, statutory reporting, or adjustments for one or more legal entities within the same accounting setup. For example, use a primary ledger for corporate accounting purposes that uses the corporate chart of accounts and subledger accounting method, and use a secondary ledger for statutory reporting purposes that uses the statutory chart of accounts and subledger accounting method. This allows you to maintain both a corporate and statutory representation of the same legal entity's transactions in parallel.
Assign one or more secondary ledgers to each primary ledger for an accounting setup.
The secondary ledgers assigned can only perform the accounting for the legal entities within the same accounting setup.
Note: If an additional ledger is needed to perform accounting across legal entities or ledgers in different accounting setups, use a ledger in an accounting setup with no legal entity assigned. This can be used for multiple purposes, such as performing management reporting or consolidation across multiple legal entities.
Note: If you allow users to make adjustments in Oracle Projects to expenditure items that represent receipts, receipt non-recoverable tax, or exchange rate variances, then Oracle Projects does not perform accounting for adjustments in reporting currencies and subledger level secondary ledgers if the secondary ledger currency differs from the primary ledger currency. Please review your business practices and ensure that the Oracle Projects profile options PA: Allow Adjustments to Receipt Accruals and Exchange Rate Variance are set appropriately. For additional information, see: Profile Restrictions to Supplier Cost Adjustments, Oracle Project Costing User Guide.
Related Topics
Data Conversion Levels
Secondary Ledgers can be maintained at one of the following data conversion levels:
Conversion Rules
The following conversion rules are used to convert data from the primary ledger to the secondary ledger:
-
Chart of Accounts Conversion: If the secondary ledger uses a different chart of accounts from the primary ledger, a chart of accounts mapping is used to provide instructions for mapping accounts or entire account segments from the primary ledger to the secondary ledger.
-
Calendar Conversion: If the secondary ledger uses a different accounting calendar from the primary ledger, the journal effective date determines the corresponding non-adjusting period in the secondary ledger.
-
Currency Conversion: If the secondary ledger uses a different currency from the primary ledger, currency conversion rules are required to instruct the system on how to convert data from the currency of the primary ledger to the currency of the secondary ledger.
-
Journal Conversion (Used by General Ledger Posting only): To select the journals for transfer to the secondary ledger based on journal source and category combinations. The General Ledger Posting program uses these rules to determine which journals to automatically transfer to the secondary ledger during posting.
Note: The above conversion rules do not apply to Adjustments Only level secondary ledgers because they must share the same chart of accounts, accounting calendar, and currency as the primary ledger.
Additional Information: Primary to Secondary Ledger Mapping
Subledger Level Secondary Ledgers
The subledger level secondary ledger maintains an additional accounting representation of the subledger journals, journal entries, and balances. The subledger level secondary ledger is maintained using both Subledger Accounting and the General Ledger Posting program.
By assigning two different subledger accounting methods to the primary and secondary ledger, you can use Subledger Accounting rules to simultaneously account for the same legal entity transaction in both ledgers. This allows you to maintain multiple accounting representations of a single subledger transaction and have the different subledger journals produced in each ledger.
Note: Subledger Accounting integrates data from both Oracle and non-Oracle transaction sources. For a list of transaction sources that integrate with Oracle Subledger Accounting, query them in the Subledger Application page available from the Subledger Accounting setup menu.
When entering subledger transactions using Oracle financial subledgers that integrate with Subledger Accounting, Subledger Accounting automatically generates the appropriate accounting entries to both the primary and secondary ledgers in General Ledger based on the accounting rules defined for a particular subledger accounting method.
Note: If using Oracle Assets, fixed asset transactions are transferred to specific ledgers based on the ledger you assigned to each Asset Book. For example, if you assigned the primary ledger to the Corporate Book and the secondary ledger to the Tax Book in Oracle Assets, the asset transactions for each book will only be reflected in the respective ledgers. Thus, the Corporate Book transactions will only be reflected in the primary ledger and the Tax Book transactions will only be reflected in the secondary ledger.
If entering transactions using Oracle subledgers that do not use Subledger Accounting to generate their accounting entries, their journals will be imported through the GL Interface table of the primary ledger. When posting the journal in the primary ledger, the General Ledger Posting program automatically replicates the journal to the secondary ledger based on the conversion rules you specify.
Journal Conversion Rules
By default, the following types of journals are replicated to the secondary ledger using General Ledger Posting, not Subledger Accounting:
-
journals created by Oracle subledgers that do not use Subledger Accounting
-
manual journal entries entered in the primary ledger
-
journals from spreadsheets or non-Oracle systems that were entered via the primary ledger's GL Interface table
Each time you post these journals in the primary ledger, they are automatically propagated to the subledger level secondary ledger, unless you defined journal conversion rules to exclude these journal sources from being transferred to the secondary ledger.
By default, journals that use the following journal sources are not transferred to the subledger level secondary ledger:
-
Move/Merge
-
Move/Merge Reversal
-
Subledger sources that use Subledger Accounting
For the subledger level secondary ledger, the journal conversion of the Revaluation source can be enabled only if the primary ledger and secondary ledger have same ledger currency and subledger accounting method.
Additional Information: Primary to Secondary Ledger Mapping
'
The journal level secondary ledger is an additional accounting representation of the primary ledger journal entries and balances. This type of secondary ledger is maintained using the General Ledger Posting Program only.
Every time you post a journal in the primary ledger, the same journal is automatically replicated and maintained in the secondary ledger, depending on the journal conversion rules specified for the secondary ledger.
By default, journals that use the following journal sources are not transferred to the journal level secondary ledger:
-
Move/Merge
-
Move/Merge Reversal
For the journal level secondary ledger, the journal conversion of the Revaluation source can be enabled only if the primary ledger and secondary ledger have same ledger currency.
Additional Information: Primary to Secondary Ledger Mapping
Balance Level Secondary Ledgers
The balance level secondary ledger only maintains the primary ledger balances in another accounting representation. To maintain balances in this type of secondary ledger, use General Ledger Consolidation to transfer the primary ledger balances to this secondary ledger.
If the balance level secondary ledger uses a different currency from the primary ledger, use General Ledger Consolidation to transfer balances from the primary ledger's balance level reporting currency to the balance level secondary ledger. This balance level reporting currency uses the same currency as the secondary ledger and represents the translated balances of the primary ledger.
Adjustments Only Secondary Ledger
The adjustments only secondary ledger is an incomplete accounting representation that only holds adjustments and manual adjustments created by Subledger Accounting. Create adjustments as follows:
-
To create manual adjustments, enter manual journal entries directly in the secondary ledger.
Adjustments only secondary ledgers are useful if you do not need a complete ledger to perform management or statutory reporting. You can perform all of your daily transactions in the primary ledger and then book adjustments, such as management or statutory adjustments, in the adjustments only secondary ledger.
Note: Using a secondary ledger as an adjustments ledger is not sufficient for companies that operate in countries that require companies to have two complete ledgers, one for statutory reporting and another for corporate accounting.
By itself, this adjustments only secondary ledger does not represent the complete accounting picture; it only holds the adjustments for the transactions contained in its associated primary ledger. Use a ledger set to combine the adjustments only secondary ledger with the primary ledger to obtain a complete secondary accounting representation that includes both the transactional data and the adjustments. Then report on the ledger set using General Ledger's Financial Statement Generator (FSG), which automatically summarizes data across ledgers in a ledger set.
Note: Ledger Sets enable you to group multiple ledgers together (that share the same chart of accounts and accounting calendar/period type combination) to obtain processing efficiencies, such as opening and closing periods and reporting across multiple ledgers simultaneously.
Additional Information: Ledger Sets
Note: Adjustments only secondary ledgers must share the same chart of accounts, accounting calendar/period type combination, and currency as the associated primary ledger.
Using Secondary Ledgers for Consolidated Reporting
Use secondary ledgers for consolidated reporting to prevent the need to perform balance transfer consolidations, and to obtain a cross-company view of your enterprise. For example, assume the two accounting setups described in the following graphic and table are defined for the company's legal entities.
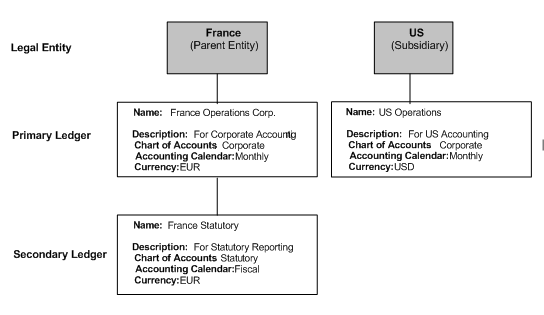
| Legal Entity | France (Parent Entity) | US (Subsidiary) |
|---|---|---|
Primary Ledger
|
France Operations Corporation
|
US Operations
|
Secondary Ledger
|
France Statutory (Subledger Level)
|
The France legal entity uses a primary ledger for corporate accounting purposes and a secondary ledger for statutory reporting purposes. Both ledgers use different charts of accounts and accounting calendars.
The US subsidiary uses its own chart of accounts and currency to account for its transactions in its main record-keeping ledger, the primary ledger.
For ease of consolidation, the US subsidiary can assign a secondary ledger to its primary ledger. The secondary ledger should use the same chart of accounts, accounting calendar, and currency as the parent entity, France. Then, by using a ledger set to group the secondary ledger of the US subsidiary with the primary ledger of the parent entity, consolidated results can be obtained by simply running an FSG report using the ledger set. This prevents the need to perform balance transfer consolidations every period.
The following graphic and table describe an example of the ledger configuration when a secondary ledger is added to the US subsidiary. The Consolidation Ledger Set is comprised of the primary Ledger for France and the secondary ledger for the US.
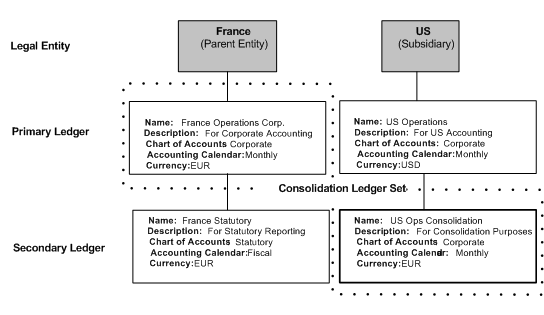
| Legal Entity | France (Parent Entity | US (Subsidiary) |
|---|---|---|
Primary Ledger
|
France Operations Corporation
|
US Operations
|
Secondary Ledger
|
France Statutory (Subledger Level)
|
US Operations Consolidation
|
Note: If the parent entity, France, needs to enter consolidation adjustments, such as intercompany eliminations, they can enter those adjustments in their primary ledger using a balancing segment value that is reserved for manual adjustments.
Using Ledgers for Consolidation
A ledger in an accounting setup with no entity assigned can be used as the parent consolidation ledger when performing fairly simple consolidations across multiple legal entities in different accounting setups. This allows users to keep consolidation adjustments completely separate from the ledgers that are used to maintain the day-to-day transactions for multiple legal entities.
For example, assume the legal entities and ledgers in three different accounting setups as described in the following figure and tables.
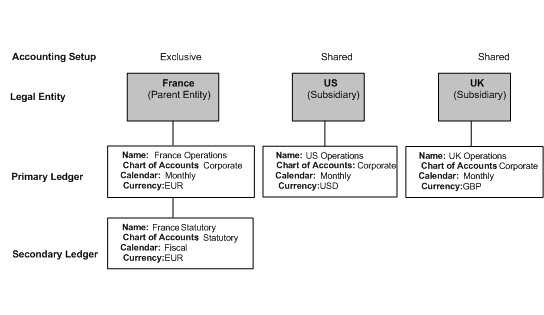
| Primary Ledger | Secondary Ledger |
|---|---|
| Name: France Operations Chart of Accounts: Corporate Calendar: Monthly Currency: EUR |
Name: France Statutory Chart of Accounts: Statutory Calendar: Fiscal Currency: EUR |
| Primary Ledger |
|---|
| Name: US Operations Chart of Accounts: Corporate Calendar: Monthly Currency: USD |
| Primary Ledger |
|---|
| Name: U.K. Operations Chart of Accounts: Corporate Calendar: Monthly Currency: GBP |
-
The France legal entity uses a primary ledger for corporate accounting purposes and a secondary ledger for statutory reporting purposes.
-
The US subsidiary uses its own chart of accounts and currency to account for its transactions in its primary ledger.
-
The U.K. Operations uses the corporate chart of accounts and calendar to account for its transactions, but it uses its own local currency.
Instead of assigning secondary ledgers to the US and U.K. operations to perform consolidation, the parent entity can define another accounting setup with no legal entity assigned to perform balance transfer consolidations from all three legal entities.
The primary ledger should share the same ledger attributes as the primary ledger of the parent entity, such as the same chart of accounts, accounting calendar, and currency.
The tables below describe an example of all of the accounting setups with the additional accounting setup added for consolidation purposes.
| Primary Ledger | Secondary Ledger |
|---|---|
| Name: France Operations Chart of Accounts: Corp. Calendar: Monthly Currency: EUR |
Name: France Statutory Chart of Accounts: Statutory Calendar: Fiscal Currency: EUR |
| Primary Ledger |
|---|
| Name: US Operations Chart of Accounts: Corporate Calendar: Monthly Currency: USD |
| Primary Ledger |
|---|
| Name: U.K. Operations Chart of Accounts: Corp. Calendar: Monthly Currency: GBP |
| Primary Ledger |
|---|
| Name: Consolidation Chart of Accounts: Corp. Calendar: Monthly Currency: EUR |
With this configuration, perform balance transfer consolidations as follows:
-
Assign balance level reporting currencies, using the euro currency (EUR), to both the primary ledgers for legal entities, US and U.K. Each balance level reporting currency maintains the translated balances for each respective legal entity.
-
Use GL Consolidation to transfer the balances directly from each of the balance level reporting currencies to the consolidation ledger in an accounting setup with no legal entity assigned.
-
For the parent entity, you can transfer its balances directly from its primary ledger to the consolidation ledger.
-
After all balances have been transferred to the consolidation ledger, enter any consolidation adjustments directly in the consolidation ledger.
Note: Using ledgers in an accounting setup with no legal entity assigned for consolidation purposes is not recommended if you have complex consolidation requirements. For example, if your organization performs frequent acquisitions, disposals, and reorganizations or has many partially owned subsidiaries, you should use Oracle Financial Consolidation Hub for your consolidation needs.
For more information on Oracle Financial Consolidation Hub, see the Oracle Financial Consolidation Hub User's Guide.
Completing Accounting Setup
If you assigned secondary ledgers when you created an accounting setup structure, complete the secondary ledger steps described in the table below in the Accounting Options page.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Ledger Options | Defines and updates the journal and transaction processing options for the ledger
Note: The Ledger Options for the primary ledger must be completed before completing the Ledger Options for the secondary ledger. |
| Primary to Secondary Ledger Mapping | To specify conversion options to transfer data from the primary ledger to the secondary ledger. |
Additional Information: To Complete Reporting Currencies
Adding, Deleting, and Disabling Secondary Ledgers
Adding Secondary Ledgers
Add secondary ledgers to accounting setups at any time in the Accounting Options page.
If you add a balance level secondary ledger that uses a different currency from the primary ledger, a balance level reporting currency is generated for the primary ledger unless one already exists. This balance level reporting currency maintains the primary ledger's translated balances and is the source representation for the secondary ledger. In other words, when using GL Consolidation to transfer balances to the secondary ledger, transfer the balances from the source representation, the balance level reporting currency.
Note: The source representation is displayed on the Primary to Secondary Ledger Mapping page.
Note: Additional steps are required if adding a new subledger level secondary/reporting ledger to an existing primary ledger that already has final accounted subledger journal entries. For more information, see Please see the Conversion of Historical Data for Reporting Currencies and Secondary Ledgers section of Oracle Subledger Accounting Implementation guide.
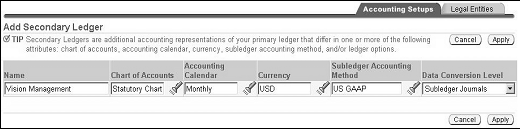
Prerequisite
-
The ledger options for the primary ledger must be completely defined.
To add secondary ledgers
-
Navigate to the Accounting Options page.
-
Click Add Secondary Ledger.
This button will only appear after the ledger options for the primary ledger have a complete status.
-
Enter all relevant fields.
The table below describes selected fields in the Add Secondary Ledger page.
Field Description Accounting Calendar General Ledger uses the calendar periods that have the period type specified for journal entry, budgeting, and reporting with this ledger. Note: Accounting Setup Manager reports an error if there are any gaps between periods in the accounting calendar or if any of the non–adjusting periods overlaps.
Subledger Accounting Method If defining a balance or journal level secondary ledger, do not assign a subledger accounting method.
If defining a subledger journals level secondary ledger, a subledger accounting method must be assigned to the secondary ledger and its primary ledger.Note: If defining an Adjustments Only secondary ledger for manual adjustments in General Ledger, do not assign a subledger accounting method. To use the Adjustments Only secondary ledger for both manual and automated adjustments from Subledger Accounting, assign a subledger accounting method to both the primary and secondary ledger.
Additional Information: Subledger Accounting Methods, Oracle Subledger Accounting Implementation Guide
Data Conversion Level To select Subledger, a subledger accounting method must be assigned to both the primary and secondary ledger.
To select Adjustments Only, the secondary ledger must share the same chart of accounts, accounting calendar, and currency as the primary ledger. The subledger accounting method, if used, can be different from the primary ledger. However, to assign a subledger accounting method to the adjustments only secondary ledger, you must also assign one to the primary ledger.Note: The data conversion level cannot be changed.
Note: After adding a secondary ledger, complete the Ledger Options step and the Primary to Secondary Ledger Mapping step to enable the secondary ledger for data entry.
Deleting Secondary Ledgers
You can only delete secondary ledgers before the accounting setup is complete. After the accounting setup is complete, you can disable the conversion of secondary ledgers. This prevents any journals that are entered in the primary ledger or source representation from being transferred to the secondary ledger.
Deleting a secondary ledger removes the ledger and all of its setup steps.
To delete secondary ledgers:
-
Navigate to the Accounting Options page.
-
Find the secondary ledger to delete and click the Remove Secondary Ledger icon.
Disabling the Conversion of Secondary Ledgers
Once you disable the conversion of secondary ledgers, it immediately prevents the propagation of journals from the primary ledger to the secondary ledger.
The disabled secondary ledger is still available for historical reporting and manual journal entries
Note: Balance level secondary ledgers cannot be disabled. To stop transferring balances from the source representation (primary ledger or balance level reporting currency) to the balances level secondary ledger, stop running consolidations.
Note: Adjustments only secondary ledgers cannot be disabled because journals are not automatically transferred to this secondary ledger.
To disable the conversion of secondary ledgers:
-
Navigate to the Accounting Options page.
-
In the Secondary Ledgers region, select the Disable Conversion icon for the secondary ledger to be disabled.
Note: Once the conversion of a secondary ledger is disabled, the status of the secondary ledger is changed to Disabled.
Note: Additional steps are required if adding a new subledger level secondary/reporting ledger to an existing primary ledger that already has final accounted subledger journal entries. For more information, see Please see the Conversion of Historical Data for Reporting Currencies and Secondary Ledgers section of Oracle Subledger Accounting Implementation Guide.
Primary to Secondary Ledger Mapping
The Primary to Secondary Mapping step specifies the conversion options to convert data from the primary ledger to the secondary ledger that may use a different chart of accounts, currency, and calendar from the primary ledger.
Note: If using an adjustments only secondary ledger, the Primary to Secondary Ledger Mapping step is not displayed. No conversion rules are required because the adjustments only secondary ledger must share the same chart of accounts, accounting calendar, and currency as the primary ledger.
Primary to Secondary Ledger Mapping Conversion Options
This section describes the following conversion options:
Chart of Accounts Conversion
In order to convert data between the charts of accounts of the primary and secondary ledgers, assign a chart of accounts mapping. A chart of accounts mapping is a set of instructions for mapping accounts or entire account segments from your primary ledger's chart of accounts to your secondary ledger's chart of accounts. This is particularly important if the primary and secondary ledgers use different charts of accounts.
Note: If a chart of accounts mapping is not assigned when the primary and secondary ledgers use different charts of accounts, errors are caused with Subledger Accounting and General Ledger posting.
If the primary and secondary ledgers use the same chart of accounts, the chart of accounts mapping is not required but can be assigned to the journal level and balance level secondary ledgers. This allows more flexibility to utilize different rollup rules when transferring journals or balances from the primary ledger to the secondary ledger. For example, you can maintain more detailed information in the primary ledger but maintain more summarized information in the secondary ledger, depending on the rollup rules defined for the chart of accounts mapping.
Note: You cannot change the chart of accounts mapping that is assigned to the secondary ledger once the accounting setup is complete.
Additional Information: Mapping Charts of Accounts, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
Calendar Conversion
If the primary and secondary ledgers use different accounting calendars, the journal effective date is used to determine the corresponding non-adjusting period in the secondary ledger. If the secondary ledger does not share the same calendar as the primary ledger, each primary ledger journal is transferred to the secondary ledger's non-adjusting period that includes the journal's effective date.
Journal Conversion
In order to transfer journals to the secondary ledger, specify journal conversion rules. Choose the journals to transfer to the secondary ledger by specifying journal source and category combinations. The General Ledger Posting program uses these journal conversion rules to determine which journals it should automatically transfer to the secondary ledger during posting.
Note: Journal conversion rules are only applicable if the data conversion level of the secondary ledger is subledger or journal.
Journal sources identify the origin of journal entry transactions, such as Purchasing or Payables. Journal categories describe the purpose of journal entries, such as purchase requisitions or purchase orders.
Specifying a journal source and category combination and selecting Yes to Transfer Journals to this Secondary Ledger, instructs the General Ledger Posting program to automatically transfer those journals to this secondary ledger when they are posted in the source representation.
The journal source and category Other represents all other journal sources and categories other than those explicitly defined.
-
To transfer the majority of journals to this secondary ledger, specify Yes for the Other journal source and category and then selectively choose No for the journal source and category combinations that you do not want transferred.
-
If you do not want the majority of journals to be automatically transferred to this secondary ledger, specify No for the Other journal source and category and then selectively add those journal source and category combinations that you do want transferred.
By default, journals using the journal sources described in the following table are not automatically converted to the secondary ledger using General Ledger Posting.
Journal Source Journal Category Transfer Journals to Secondary Ledger Move/Merge Other No Move/Merge Reversal Other No
This means that if you use Mass Maintenance to move or merge balances between accounts in the source representation, such as the primary ledger, the resulting journals are not transferred to the secondary ledger.
For example, if moving or merging account balances in the primary ledger, the resulting journal entries that use the source Move/Merge are not automatically converted to the secondary ledger. The same rule applies if reversing the Move/Merge journal entry. You must perform the Move/Merge operation and Move/Merge reversal in the secondary ledger separately.
By default, all other journal sources and categories are converted to the secondary ledger as indicated by the Other journal source and category.
Special Note for Subledger Level Secondary Ledgers
For subledger level secondary ledgers, the journal sources for transaction sources that use Subledger Accounting must be set to No in the Transfer Journals to this Secondary ledger field. Any journal source that uses Subledger Accounting to generate its accounting entries must not be converted to the secondary ledger using General Ledger Posting because Subledger Accounting automatically performs the conversion for these subledger journals.
Note: To find all transaction sources that integrate with Subledger Accounting, query them in the Subledger Application form that is accessed from the Subledger Accounting Setup menu.
Additional Information: Subledger Accounting Options
Note: If integrating with transaction sources that do not use Subledger Accounting and you want General Ledger posting to maintain journals from these subledgers in the subledger level secondary ledger, do not use Oracle's seeded journal sources. For example, if you use a non-Oracle Receivables application, you can create your own journal source for that application instead of using the seeded source Receivables that is reserved for Oracle sources. If you use the seeded source to import data from third party systems, those journals will not be transferred to a subledger level secondary ledger when you post them in the primary ledger.
Currency Conversion
If the primary and secondary ledger use different ledger currencies, currency conversion rules are required to instruct the system on how to convert data from the currency of the primary ledger to the currency of the secondary ledger.
Note: If both the primary and secondary ledgers use the same currency, the currency conversion rules are not applicable.
For information on the Default Rate Type and Retain Transaction Rate Type options, see the Journal and Subledger Level Reporting Currencies table.
This section includes the following topics:
Primary Ledger as Source Representation
A secondary ledger receives its data from its source representation.
When the source representation is the primary ledger, it means that the primary ledger's data is transferred directly to the secondary ledger.
When the source representation is a reporting currency that is assigned to the primary ledger, then the data is transferred directly from the reporting currency to the secondary ledger.
By default, the primary ledger is the source representation for all secondary ledgers, except the balance level secondary ledger that uses a different currency from the primary ledger. In this case, the source representation will always be the balance level reporting currency of the primary ledger whose currency matches the balance level secondary ledger.
When the source representation is the primary ledger, this is referred to as a one-step conversion from the primary ledger.
Example
Assume you have a primary ledger and a journal level or subledger level secondary ledger. The primary ledger's currency is CAD; the secondary ledger's currency is GBP; and the Default Rate Type is Reporting.
An SGD foreign currency journal is entered in the primary ledger using the transaction rate type of Spot.
The journal is first converted to the currency of the primary ledger using the transaction rate type, Spot. When the journal is posted in the primary ledger, the Secondary Ledger's Default Rate Type and Retain Transaction Rate Type settings determine how the SGD entered journal is converted.
-
If Retain Transaction Rate Type is set to Yes, then the journal is converted from SGD to GBP (the currency of the secondary ledger) using the transaction rate type, Spot.
-
If Retain Transaction Rate Type is set to No, then the journal is converted from SGD to GBP (the currency of the secondary ledger) using the Default Rate Type, Reporting.
This example is shown in the figure below.
One-Step Conversion from Primary Ledger to Secondary Ledger
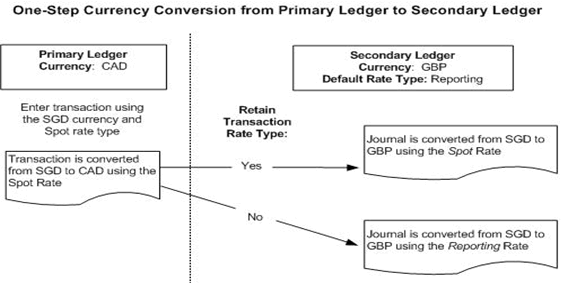
Reporting Currency as Source Representation
For journal level secondary ledgers only, you can choose to make the source representation a journal level reporting currency that is assigned to the primary ledger. For example, the source representation for a journal level secondary ledger can be a journal level reporting currency.
Note: The currency of the journal level reporting currency must match the currency of the secondary ledger.
This is referred to as a two-step conversion from the primary ledger. When data is entered in the primary ledger, the data is first converted to the journal level reporting currency and then transferred to the journal level secondary ledger, as described in the figure below.
Two-Step Conversion from the Primary Ledger
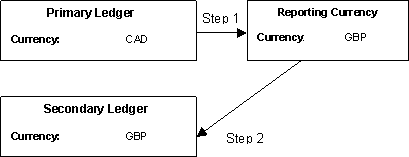
This is useful if you are already using a journal level reporting currency for reporting purposes. By using a journal level reporting currency as the source representation, you can enter additional journal entries directly in the reporting currency to have them propagated to the secondary ledger.
Note: The two-step conversion method is most suitable for companies that require a reporting currency level of detail for the primary ledger.
When choosing a journal level reporting currency as the source representation, the Default Rate Type and Retain Transaction Rate Type settings for the reporting currency control the currency conversion of transactions to the secondary ledger. In other words, the secondary ledger inherits the same settings as the reporting currency.
Two-Step Currency Conversion from Primary to Secondary Ledger
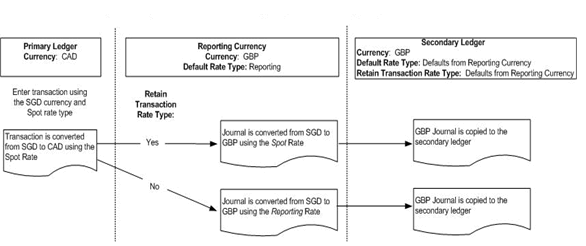
Example
Assume you have a primary ledger, a journal level reporting currency that is assigned to the primary ledger, and a journal level secondary ledger. The primary ledger's currency is CAD and the currency for both the secondary ledger and reporting currency is GBP. The source representation for the secondary ledger is the reporting currency.
An SGD foreign currency journal is entered in the primary ledger using the transaction rate type, Spot.
The following table lists the conversion rates for different currencies used in this example.
| From Currency | To Currency | Rate Type | Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| SGD | CAD | Spot | 1.50 |
| SGD | CAD | Reporting | 1.65 |
| SGD | GBP | Spot | 1.70 |
| SGD | GBP | Reporting | 1.75 |
The journal is first converted to the currency of the primary ledger, CAD, using the transaction rate type, Spot, as described in the following table.
| Account | Entered Debit (SGD) | Entered Credit (SGD) | Converted Debit (CAD) | Converted Credit (CAD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01.6110 | 1000.00 | 1500.00 | ||
| 01.2110 | 1000.00 | 1500.00 |
Upon posting the journal described in the preceding table, the same journal is converted to the reporting currency based on the reporting currency's Default Rate Type and Retain Transaction Rate Type settings.
If Retain Transaction Rate Type is set to Yes, then the journal is converted from SGD to GBP using the transaction rate type, Spot.
The following table describes the journal entry that appears in both the reporting currency and the secondary ledger.
| Account | Entered Debit (SGD) | Entered Credit (SGD) | Converted Debit (GBP) | Converted Credit (GBP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01.6110 | 1000.00 | 1700.00 | ||
| 01.2110 | 1000.00 | 1700.00 |
If Retain Transaction Rate Type is set to No, then the journal is converted from SGD to GBP using the default rate type, Reporting.
The following table describes the journal entry that appears in both the reporting currency and the secondary ledger if the default rate type is used.
| Account | Entered Debit (SGD) | Entered Credit (SGD) | Converted Debit (GBP) | Converted Credit (GBP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01.6110 | 1000.00 | 1750.00 | ||
| 01.2110 | 1000.00 | 1750.00 |
Journals Entered Directly in the Reporting Currency
If entering a journal directly in the reporting currency, the same journal may or may not be copied exactly as is to the secondary ledger. It depends on the Default Rate Type and the Retain Transaction Rate Type settings for the secondary ledger.
-
If Retain Transaction Rate Type is set to Yes, then the journal entered in the reporting currency is copied directly from the reporting currency to the secondary ledger.
The entered amounts and the converted amounts are exactly the same for the reporting currency and the secondary ledger.
-
If Retain Transaction Rate Type is set to No, then the journal is converted to the secondary ledger using the Default Rate Type.
Example
Assume you have a journal level reporting currency that is the source representation for a journal level secondary ledger. The default rate type assigned to the secondary ledger is Reporting. The currency for both the reporting currency and secondary ledger is GBP.
The following table lists the conversion rates for different currencies used in this example.
| From Currency | To Currency | Rate Type | Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| SGD | GBP | Spot | 1.70 |
| SGD | GBP | Reporting | 1.75 |
The SGD foreign currency journal described in the following table is entered in the reporting currency using the transaction rate type, Spot
| Account | Entered Debit (SGD) | Entered Credit (SGD) | Converted Debit (GBP) | Converted Credit (GBP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01.6110 | 1000.00 | 1700.00 | ||
| 01.2110 | 1000.00 | 1700.00 |
Upon posting the journal in the journal level reporting currency, the same journal is converted to the secondary ledger based on the secondary ledger's Default Rate Type and Retain Transaction Rate Type settings.
-
If Retain Transaction Rate Type is set to Yes, then the journal is copied directly to the secondary ledger.
-
If Retain Transaction Rate Type is set to No, then the journal is converted using the Default Rate Type, Reporting.
The following table describes the journal entry that appears in the secondary ledger if Retain Transaction Rate Type is set to No.
| Account | Entered Debit (SGD) | Entered Credit (SGD) | Converted Debit (GBP) | Converted Credit (GBP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01.6110 | 1000.00 | 1750.00 | ||
| 01.2110 | 1000.00 | 1750.00 |
Using Reporting Currencies as Source Representations
To use a journal level reporting currency as the source representation for a journal level secondary ledger, perform the following tasks:
-
Define a journal level reporting currency for the primary ledger.
Note: A journal level secondary ledger can only have the primary ledger or a journal level reporting currency as its source representation.
-
Choose the reporting currency to be the source representation in the Primary to Secondary Ledger Mapping page.
-
Specify currency conversion rules.
-
Specify journal conversion rules.
The journal conversion rules specified for the secondary ledger should be the same as the journal level reporting currency, but you can change them for the secondary ledger in the Primary to Secondary Ledger Mapping page.
You can choose to transfer selected journals that use different sources or categories from the reporting currency to the secondary ledger. For example, you can choose to transfer only a subset of journals from the reporting currency to the secondary ledger by making the journal conversion rules more restrictive for the secondary ledger.
Completing the Primary to Secondary Ledger Mapping

Prerequisites
The following prerequisites are required to complete the primary to secondary ledger mapping step:
-
A chart of accounts mapping must be defined in General Ledger if the secondary ledger uses a different chart of accounts
Additional Information: Mapping Charts of Accounts, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
-
A secondary ledger must be assigned to a primary ledger.
-
The reporting currencies assigned to the primary ledger must be completely defined.
Additional Information: Assigning Reporting Currencies to Ledgers
-
The ledger options for the secondary ledger must be completely defined.
Additional Information: Completing Ledger Options
To complete the primary to secondary ledger mapping
Note: This step is required to complete the accounting setup.
-
In the secondary ledger regions of the Accounting Options page, click the Update icon for the Primary to Secondary Ledger Mapping step.
-
Specify the following:
-
Chart of Accounts Mapping
This mapping is used to convert data from the primary ledger's chart of accounts to the secondary ledger's chart of accounts. If a mapping is not defined, click Create Mapping.
Note: You must assign a mapping if your primary and secondary ledgers use different charts of accounts.
Note: You cannot change the mapping assigned after the accounting setup is complete.
Additional Information: Mapping Charts of Accounts, Oracle General Ledger User Guide
-
currency conversion rules
The options in the following table pertain to balance level secondary ledgers only.
Balance Level Secondary Ledgers Currency Conversion Options Options Description Source Representation When transferring balances using GL Consolidation, the source representation acts as the source of the balances.
If the secondary ledger's currency is different from the primary ledger, the name of the primary ledger's balance level reporting currency defaults and cannot be changed.Currency Currency of the source representation defaults Period End and Period Average Rate Type The period end and period average rate types are used by General Ledger's Translation program. These rate types are used to translate balances from the primary ledger's currency to the balance level reporting currency that is used as the source representation for the secondary ledger. These rate types should be the same as the source representation. -
journal conversion rules for subledger level and journal level secondary ledgers
The following table describes currency conversion options for journal and subledger level secondary ledgers that use a different currency from the primary ledger.
Journal and Subledger Level Secondary Ledgers Currency Conversion Options Option Description Source Representation Acts as the source of the data that is transferred to the secondary ledger. The primary ledger defaults. For journal level secondary ledger the source representation can be a journal level reporting currency that is assigned to the primary ledger. Note: The source representation cannot be changed after completing the accounting setup.
Default Rate Type The conversion rate type to use to retrieve exchange rates for converting transactions from the primary ledger to this secondary ledger. The Default Rate Type works with the Retain Transaction Rate Type field. If you choose not to retain the same rate type that was used to convert the original transaction, then the Default Rate Type is used instead.
For the default rate type, specify your own conversion rate type or choose one of the predefined rate types. To specify your own, first define it in General Ledger.Additional Information: Defining Conversion Rate Types, Oracle General Ledger User's Guide
Retain Transaction Rate Type Controls the conversion rate type the system should use to convert transaction currency amounts from the source representation to this secondary ledger. -
If you select Yes, then the conversion rate type used to enter the original journal is used to convert the same journal to this secondary ledger.
-
If you select No, then the default rate type assigned in the Default Rate Type field is the one used to convert journals to this secondary ledger.
The Retain Transaction Rate Type option is ignored if the following conditions exist:-
An EMU fixed rate relationship exists between the transaction currency and the currency of the secondary ledger.
In this case, the EMU Fixed conversion rate type is used.
-
The transaction currency is the same as the currency of the source representation, such as the primary ledger.
In this case, a conversion rate type does not exist for the transaction and the default rate type is used.
-
The transaction currency is the same as the currency of the secondary ledger.
In this case, the User conversion rate type is used with a default rate of 1.
-
A User rate is used for the transaction.
In this case, the User conversion rate type is used. The secondary ledger conversion is done in two steps using the default rate type assigned to the secondary ledger.
If Missing Conversion Rate Controls what the system should do if it cannot find a conversion rate as of the conversion date -
If Report an Error is selected, the system reports an error and prevents journals from being posted in the source representation.
Specify a rate to successfully convert journals entered in the source representation to this secondary ledger.
-
If Use Last Rate is selected, the system uses the last rate that was defined for a particular rate type if it cannot find a currency conversion rate.
If enabled, specify a number for the Number of Days to Find the Last Rate.
Number of Days to Find Last Rate If Use Last Rate is selected, enter a number from 1 to 999. This number indicates how many days back in time the system should look to find a rate. Note: If a number is not entered, it adversely affects system performance.
Post Journals Automatically from Source Ledger Controls the automated posting of journals. -
If Yes is selected, journals will be automatically posted in the secondary ledger when posted in the source representation.
-
If No is selected, you must post journals separately in the secondary ledger.
Retain Journal Creator from Source Ledger Controls the Created By user information that can be viewed for each journal using Tools > Examine. -
If Yes is selected, the person who entered the journal in the source representation is retained as the Created By user.
-
If No is selected, the person who posted the journal is saved as the Created By user.
-
-