Modeling Communications Entities Using Seeded Item Metadata Libraries
This chapter covers the following topics:
- Modeling Communications Entities
- Modeling Billing Products
- Modeling Billing Discounts
- Modeling Service Bundles
- Modeling Commercial Bundles
- Modeling Promotions
Modeling Communications Entities
Communications businesses can use Oracle Product Hub to standardize product specifications across multiple applications. For example, create the following bundle of products in Oracle Product Hub (OPH) by creating items and structures:
Bundle for Text Messaging Service
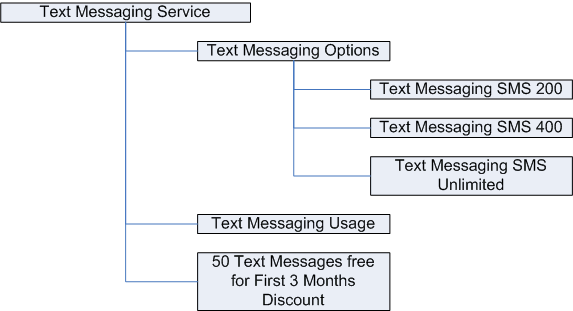
Publish bundles of products to other applications, such as Siebel Customer Relationship Management (Siebel) and Oracle Billing and Revenue Management (BRM). Publishing from a central hub such as OPH ensures consistent product data across applications. To define the product data needed by these other applications, use seeded item attributes provided in the following libraries by Oracle Product Hub:
-
Sellable Product Information Library - Horizontal, Oracle Product Hub Implementation Guide
-
Product Management Library - Horizontal, Oracle Product Hub Implementation Guide
-
Communications Services Billing Library - Vertical, Oracle Product Hub Implementation Guide
-
Communications Product Details Library - Vertical, Oracle Product Hub Implementation Guide
Other applications use communications entities known by names such as billing products, billing discounts, service bundles, commercial bundles, and promotions. You can define items and structures and use seeded item and component attributes from the above libraries to model these entities in Oracle Product Hub, then publish the items and structures to the other applications.
Related Topics
Modeling Billing Products
You can model billing products used in BRM and Siebel as items in Oracle Product Hub. In BRM, a billing product (also known as simply a product) might be a text messaging service or an IP dialup service. A billing event, such as a text message sent or connecting to the internet for one hour, is linked to a billing product.
When defining billing product items in Oracle Product Hub, you can use seeded item attributes to define billing product and pricing information for the item. Publish this pricing information with items defined as billing products by assigning the value "Billing" to the Pricing Code attribute (in the Product Details: Definitions attribute group). This enables billing product pricing information to synchronize with BRM. If you assign the value "Standard" to the Pricing Code attribute, the item pricing information is only published to a target system if a customized target application connector service maps the pricing information to the target application.
Before creating billing product items, associate the following seeded attribute groups with an item catalog category. Create the billing product items within this item catalog category.
-
Billing Products Attributes General
-
Billing Products Event Map
-
Rate Plan
-
Tier Group
-
Day Time Range
-
Days of the Week Range (Mapping only to the EBM)
-
Rate Data
-
Balance Impact
-
Additional Billing Information
Important: Specify values for all attributes within this attribute group when defining billing product items and billing discount items.
-
Additional Entity Details
-
Entity Type = "Product"
-
Internal Reference Code
Note: You must assign a value to this attribute when publishing to BRM.
-
-
Product Details: Definitions
-
Pricing Code = "Billing"
Note: Required when publishing to BRM.
-
-
Destination System Specification
-
Communications:Product Info
-
When publishing a billable product to Siebel CRM, ensure that the Billable attribute is set to 'Yes'.
-
Refer to AIA for Communications 2.4 - Building An Order To Activate Process - Whitepaper, Doc ID 843298.1, https://support.oracle.com/epmos/faces/ui/km/DocumentDisplay.jspx?id=843298.1, for information about setting the values of the following attributes:
-
Composition Type
-
Success Dependency
-
Fulfillment Item Code
-
-
Use the following attribute groups to define the pricing hierarchy for a billing product used in BRM:
-
Billing Products Event Map
-
Rate Plan
-
Tier Group
-
Day Time Range
-
Days of the Week Range
-
Rate Data
-
Balance Impact
Each of the above attribute groups models one of the following entities in BRM that creates the pricing hierarchy:
-
Event
-
Rate Plan
-
Tier
-
Day
-
Time
-
Rate Data
-
Balance Impact
-
-
-
-
-
-
Each of the above attribute groups that models the entities in BRM are multi-row attribute groups. Each billing product in BRM can have multiple associated billing events, each billing event can have multiple associated rate plans, and so on.
Defining Events or Charges
You can assign one or more billing events or charges to each billing product/item. For example, a billing product such as text messaging only has one associated event, a monthly fee for text messaging, but a billing product such as a wireless phone plan might have two associated events, a one-time activation fee or phone purchase and a monthly service charge. The following examples explain how to define events for four different billing scenarios.
Billing Scenario 1
To create a single event billing product (for example, a billing product, such as text messaging, with one associated event, a monthly fee for text messaging), associate only one rate plan with the event. Similarly, for a billing product with more than one event (for example, a wireless phone plan with two events, a one-time activation fee and a monthly service charge), associate only one rate plan with each event.
Attributes Values for a Single Rate Plan per Event
-
Rate Plan Structure = Single Rate Plan
-
Rate Plan ID = the corresponding ID of the rate plan
Billing Scenario 2
Alternatively, use a rate plan selector to calculate a rate based on various item attribute values. When using a rate plan selector, you must further define the rate plan selector in BRM after synchronization.
Attribute Values for a Rate Plan Selector
-
Rate Plan Structure = Rate Plan Selector
-
Rate Plan ID = null
-
Rate Plan Selector ID = the corresponding ID of the rate plan selector
-
Rate Plan Selector Name = specify a name
-
Rate Plan Selector Description = specify a description
Billing Scenario 3
You can also assign multiple single rate plans to one event or charge. For example, a billing product, such as text messaging, with one associated event, a monthly fee for text messaging, can be billed at either the standard rate or the corporate rate. The monthly fee event then has two associate rate plans, standard or corporate. To assign more than one rate plan to the event, specify the following attribute values for the event:
Attribute Values for Multiple Single Rate Plans per Event
-
Rate Plan Structure = Custom Event Analysis
-
Rate Plan ID = null (specify the Rate Plan ID for each single rate plan associated with the event using multiple rows of the Rate Plan attribute group)
Billing Scenario 4
For billing events based on usage (for example, text messaging billed at 10 cents per message), use a pipeline rate plan. When using a pipeline rate plan, you must further define the rate plan in BRM after synchronization.
Attribute Values for a Pipeline Rate Plan
-
Rate Plan Structure = Pipeline Rate Plan
-
Rate Plan ID = the corresponding ID of the rate plan
Defining Rate Plans
Define each rate plan using the Rate Plan attribute group. Each defined rate plan except for rate plan selectors must use a unique Rate Plan ID and Rate Plan Name. When using a rate plan selector, assign attribute values as follows:
-
Rate Plan ID = Rate plan unique identifier.
-
Rate Plan Name = null.
-
Rate Plan Selector ID = Rate plan selector unique identifier.
Defining Rate Tiers
Use rate tiers in the scenario where the rate changes depending on the time, day, or frequency of usage. For example, a rate plan for internet access charges $1 per hour for dialup access on weekdays, with free access on weekends. This rate plan uses two tiers, one for weekdays and one for weekends.
The following list explains how to set various attribute values for the Tier Group attribute group:
-
If no day or time restrictions apply to a rate tier, then set the attribute Time Day Restrictions to 'No Restrictions'.
-
If the rate tier has both day and time restrictions, then set the attribute Time Day Restrictions to 'Day Restrictions' and set the attribute Use Time of Day Ranges in the attribute group Day Time Range to 'Yes'.
-
Effectivity Mode indicates whether the rate tier is effective during a certain specified date range (absolute) or during a certain number of days relative to the purchase date (relative). For a rate plan with internet access charges that differ on weekdays and weekends, set the Effectivity Mode to Absolute. For a rate plan that offers unlimited internet access for $20/month for the first six months, then the rate increases, set the Effectivity Mode to Relative. The value of the Effectivity Mode indicates how to set the values of other attributes in the Rate Tiers attribute group:
-
Effectivity Mode = Absolute: Specify values for the Start Date Time and End Date Time attributes.
-
Effectivity Mode = Relative: Specify values for the Relative Start, Relative Start UOM, Relative End, and Relative End UOM attributes.
-
Defining the Day Time Range
For each rate tier, specify the day and, optionally, the time ranges that apply to that tier. You can assign multiple time ranges per day range. In this case, the day range repeats for every time range associated with it. If you choose to associate a time range with a day range, then you must set the attribute Use Time of Day Ranges to Yes. If you choose not to associate a time range with a day range, then the rate applies to the entire day for all days within the day range. When specifying day and time ranges that spans across multiple months, Oracle recommends including a day and time range for each month.
Defining Days of the Week Range
You can use the attribute group Days of the Week Range as an alternative to the attribute group Day Time Range, depending on the day/time restrictions of the rate tier. The same rules for modeling day/time restrictions apply to both attribute groups. However, the attribute values from Days of the Week Range are not automatically synchronized with any target application. You must extend the target application connector services to map the Days of the Week Range information to target applications.
You can assign multiple time ranges per week range. In this case, the week range repeats for every time range associated with it. If you choose to associate a time range with a week range, then you must set the attribute Use Time in Day of the Week to Yes. If you choose not to associate a time range with a week range, then the rate applies to the entire day for all days within the week range. You can define time range without a week range where the rate applies to the time range for all the days when the rate tier is valid.
Defining Rate Data
The Rate Data attribute group enables the grouping of actual rates and prices (stored in the Balance Impact attribute group) for each tier. Certain discount brackets and proration details that apply to rates and prices are defined by using this attribute group.
You can reuse the same rate data attribute values for different rate tiers and day time ranges. As long as the quantity discount bracket and override credit limit attributes stay the same, you can use the same rate data across multiple balance impacts (prices), too. Set the proration information (Purchase Proration Information, Cancel Proration Information) only if you plan to associate the rate data with recurring charges.
Defining Balance Impact
BRM uses Balance Impact entities to store an actual rate or price for a billable event. For example, for a certain rate plan, rate tier, day time range, and rate data combination, the price of a billing product is a certain amount of money. You then can associate this price structure for a certain rate plan to a billable event in the Billing Products Event Map attribute group.
If billing product information is sent to both BRM and Siebel, the billing connector service for BRM ignores the following attributes:
-
Promotional Price
-
Service Pricing Method
-
Service Price Percent
If needed, you can extend the connector service to map these values to the target billing application.
Modeling Billing Discounts
Model Oracle Billing and Revenue Management (BRM) billing discounts in Oracle Product Hub by creating items, similarly to how you model billing products (see: Modeling Billing Products). BRM uses discounts when charging for billable events. For example, you might want to offer real-time discounts based on the number of accounts. If a company has more than 100 dialup accounts, you can offer a 10% discount.
Before creating billing discount items, associate the following seeded attribute groups with an item catalog category. Create the billing discount items within this item catalog category.
-
Billing Discount Attributes
-
Billing Discount Event Map
-
Additional Billing Information
Important: Specify values for all attributes within this attribute group when defining billing product items and billing discount items.
-
Additional Entity Details
-
Entity Type = "Product"
-
Internal Reference Code
Note: You must assign a value to this attribute when publishing to BRM.
-
-
Product Details: Definitions
-
Pricing Code = None
Caution: The Pricing Code value can change based on the customer implementation.
-
-
Destination System Specification
-
Communications:Product Info
Important: When publishing a billable discount to Siebel, ensure that the Billable attribute is set to 'Yes'.
If you plan to implement the product MDM Integration PIP to co-exist with the Order to Bill or Order to Activate PIP, then you must set the following attributes for billing discount items:
-
Additional Billing Information
-
Billing Entity Type = Discount
-
Billing Service Type = Set this value based on the service to which the discount belongs to.
-
-
Communications:Product Info
Tip: Refer to AIA for Communications 2.4 - Building An Order To Activate Process - Whitepaper, Doc ID 843298.1, https://support.oracle.com/epmos/faces/ui/km/DocumentDisplay.jspx?id=843298.1, for information about setting the values of the following attributes.
-
Composition Type
-
Success Dependency
-
Fulfillment Item Code
-
Once you create discounts by publishing Oracle Product Hub billing discount items to BRM, then you can create and associate a discount model to a discount within BRM. The discount model name must be associated with the billing discount item in Oracle Product Hub. You can choose from two ways to accomplish this:
-
Specify the discount model name in Oracle Product Hub. After publishing the discount to BRM, the product administrator in BRM can create a discount model with the same name, then associate the discount model to the billing discount.
-
Create the discount model in BRM. Associate the discount model name with the discount in Oracle Product Hub.
Modeling Service Bundles
Siebel uses service bundles to sell a related group of services as a package. A service bundle for text messaging might look like this:
Service Bundle for Text Messaging Service

To create a service bundle in Oracle Product Hub (OPH), create an item (such as Text Messaging Service), then associate a structure to the item. The components in the structure become components of the service bundle. The components can consist of simple service bundles (such as Text Messaging Usage), nested service bundles, and options (such as Text Messaging Options).
When creating a service bundle, the top service bundle item (Text Messaging Service) must have a BOM Item Type of 'Model'. Any nested components can have BOM Item Types of Model (for nested service bundles), Option Class (for modeling product options, such as Text Messaging Options shown above), and Standard. Publishing the service bundle from Oracle Product Hub to Siebel creates the service bundle in Siebel. Do not publish service bundles to Oracle Billing and Revenue Management (BRM).
Important: Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) requires creation of a primary structure/bill of material (BOM) before creating alternate BOMs. Primary structures are date effective and alternate (which include Model and Option Class) structures are revision effective. If you plan to publish service bundles to EBS, you must first create a primary (date effective) structure for each item structure in OPH, then publish it to EBS. Next, you can create the necessary Model and Option Class structures in OPH and publish them to EBS.
Simple Service Bundles
A simple service bundle is defined as a service, but with no associated structure. A simple service bundle consists of a service-oriented billing product with one or more associated billing events. For example, a billing product such as Text Messaging Usage might have a billing event of Text Message Sent/Received.
Friends and Family Lists
You can offer a special rate class to customers when they call certain phone numbers. Create this special rate class by defining simple billing products, then offering them as product options within a service bundle. For example, when selling wireless voice service, you can offer special rates to friends, family, and colleagues as shown below.
Wireless Voice Service Bundle
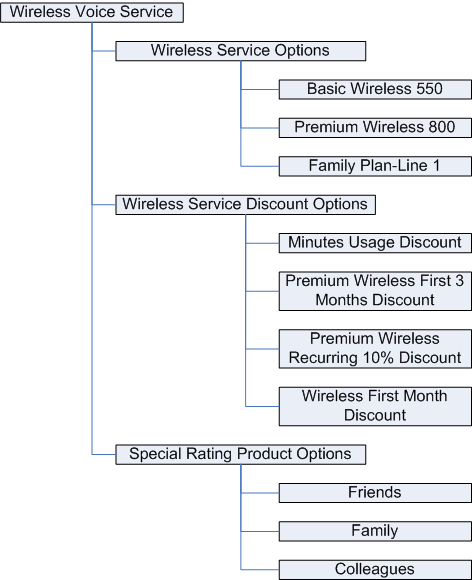
When defining a simple billing product, do not associate a billing event with the product. The billing products Friends, Family, and Colleagues shown above do not have an associated billing event. Define seeded attribute values as listed below when creating friends and family items:
Seeded Attributes and their Values
-
Billing Entity Type = Special Rating
-
Billing Service Type = null
-
Special Rating Type = Phone Number (or another applicable rating type)
-
Special Rating Max Items = specify the number of phone numbers allowed.
-
Internal Reference Code = used to uniquely identify the entity (for example, Friends).
-
Version: Structure attribute group - you must specify values for the following attributes when the item is an immediate component of a structure.
-
Relationship Name
-
Domain Type
-
Product Class (define only if the Domain Type = Class)
-
Default Product (define only if the Domain Type = Class)
-
Attributes Available for Customized Mapping
The following seeded attributes are not mapped to any target application, but you can create your own map. They are available in the integration layer, but are ignored in the target application services.
-
Format (in the Product Details: Definitions attribute group): Siebel uses this attribute, which is dependent on rules. Review the rules in Siebel and set the value accordingly.
-
Supplier Tax ID (in the Billing Products Attributes General attribute group): BRM automatically generates the Supplier Tax ID, so this attribute is unnecessary when publishing to BRM. When publishing to other billing applications where the Supplier Tax ID is used, consider specifying a value for this attribute.
Attributes Available for Order Provisioning and Order Fulfillment Systems
Use the following attributes in the Communications: Product Info attribute group based on your individual requirements. You must specify these attributes if you plan to implement the product MDM Integration PIP to co-exist with the Order to Bill or Order to Activate PIP.
-
Special Rating Type: Use only when modeling Friends and Family lists.
-
Special Rating Max Items: Use only when modeling Friends and Family lists.
-
Composition Type: For use with Order Provisioning systems.
-
Success Dependency: For use with Order Provisioning systems.
-
Service Instance Enabled: Used to identify a simple service bundle.
-
Fulfillment Item Code: For use with Order Fulfillment systems.
Operational Attributes for Order Submission Systems
Use the following operational attributes based on your individual requirements. You must specify these attributes if you plan to implement the product MDM Integration PIP to co-exist with the Order to Bill or Order to Activate PIP.
-
Orderable: Flag that indicates orders can be placed for this item.
-
Track as Asset: Flag that identifies an item as an asset.
More Attributes Available for Customized Mapping
The following seeded attributes are not mapped to any target application, but you can create your own map. They are not mapped to the integration layer, but you can use these attributes in a customized integration solution that includes friends and family items.
-
Sales Product
-
Product Line: Use to define a primary product line with this product in Siebel. Any subsequent updates to the product will not override the values originally set in Siebel.
-
Service Product: This is a redundant attribute. Use the operational attribute Service instead.
-
Lead Time: This is a redundant attribute. Use the operational attribute Processing instead.
-
Model Product
-
Track as Asset
-
Network Element Type: Used by the Communications industry item entity. If you are using this entity, you must map this attribute.
-
MSISDN Required: Used by the Communications industry item entity. If you are using this entity, you must map this attribute.
To create a service bundle
-
Create an item catalog category with the following associated seeded attribute groups:
-
Additional Entity Details
-
Product Details: Definitions
-
Destination System Specification
-
Additional Billing Information*
-
Communications:Product Info*
Note: You only need to associate the attribute groups with asterisks (*) if you plan to implement the product MDM Integration PIP to co-exist with the Order to Bill or Order to Activate PIP. Refer to AIA for Communications 2.4 - Building An Order To Activate Process - Whitepaper, Doc ID 843298.1, https://support.oracle.com/epmos/faces/ui/km/DocumentDisplay.jspx?id=843298.1, for information about setting the values of the attributes in the Communications:Product Info attribute group.
-
-
Create a structure type and a structure name. Associate the seeded component attribute group 'Version: Structure'. See: Defining Structures, Oracle Product Hub Implementation Guide and Associating Component Attribute Groups with a Structure Type, Oracle Product Hub Implementation Guide.
-
Create an item that represents the top service bundle item, associate the item catalog category created above, and specify the main attributes of the item.
Important: You must set the BOM Item Type attribute value to Model.
-
Set the values for the item's seeded attributes as described below.
Refer to the Seeded Item Metadata Libraries appendix in the Oracle Product Hub Implementation Guide for information about how to set the attributes within the associated seeded attribute groups listed above. The following list provides some information about how to set some attributes specifically for service bundles.
-
Product Details: Definition
-
Pricing Code =None
Note: The value of this attribute can change depending upon the particular implementation.
-
-
Additional Billing Information
-
Entity Type = Product
-
You only need to set the following attributes as described if you plan to implement the product MDM Integration PIP to coexist with the Order to Bill or Order to Activate PIP:
-
Additional Billing Information
-
Billing Entity Type = Service Bundle
-
Billing Service Type = Set this attribute equal to the same Billing Service Type as its components, unless the component is another service bundle.
-
-
Communications:Product Info
-
Composition Type = Whole Item
-
Success Dependency*
-
Fulfillment Item Code*
Note: For the attributes with an asterisk (*), refer to AIA for Communications 2.4 - Building An Order To Activate Process - Whitepaper, Doc ID 843298.1, https://support.oracle.com/epmos/faces/ui/km/DocumentDisplay.jspx?id=843298.1, for information about setting the values.
-
-
-
Create a structure for the top service bundle item using the structure type you created above.
See: Creating Structures.
-
Update the seeded component attribute values within the attribute group Version: Structure for each of the component items.
-
Relationship Name - enter the name of the component item.
-
Domain Type
For the Domain Type attribute, assign a value of 'Class' to all items with a BOM Item Type value of 'Option Class'. Assign a value of 'Product' to all other items. The Domain Type 'Class' and BOM Item Type 'Option Class' together identify an item that represents the product options.
Warning: The item catalog category associated with the item that represents the product options (Text Messaging Options in the above example) and with the product option item's components must be the same.
-
Product Class - if the component has a Domain Type of 'Class', then enter the same name as the component's item catalog category. If the component has a Domain Type of 'Product, then leave this attribute blank.
-
Default Product - If the Domain Type is 'Class', then the domain for that component has more than one product. Enter the default product from among the set of products.
-
Max Cardinality
-
Min Cardinality
-
Default Cardinality - set this between the min and max cardinality values.
-
-
You can now publish the service bundle.
To create a simple service bundle
-
Create a billing product with one or more associated billing events as described in Modeling Billing Products.
-
Set the following attributes for the billing product:
-
Service Instance Enabled = Y
-
Entity Type = Product
-
Pricing Code = Billing
Note: This value can change based on differences in implementation.
If you implement the Product MDM Integration PIP to co-exist with the Order to Bill or Order to Activate PIP, then set the following attributes:
-
Billing Entity Type = Subscription
-
Billing Service Type = Set this to the service type associated with the product.
-
Composition Type = WholeItem
Values of the following attributes depend on individual implementation requirements. Refer to the AIA for Communications 2.4 - Building An Order To Activate Process - Whitepaper, Doc ID 843298.1, https://support.oracle.com/epmos/faces/ui/km/DocumentDisplay.jspx?id=843298.1, for information.
-
Success Dependency
-
Fulfillment Item Code
-
To exclude a component within a bundle
You can exclude a component of a service bundle. The exclusion only applies to the structure of the top service bundle item, not to a nested structure. For example, if you exclude Text Messaging SMS 200 from the structure for Text Messaging Service, the exclusion does not apply to the structure for Text Messaging Options.
Important: Do not use component exclusions within a service bundle when publishing to Siebel. Siebel can only accept component exclusions for items with an Entity Type = Promotion.
For information on how to exclude a component within a service bundle, see: Excluding Structures.
To override a component attribute value
You can override a component attribute value for a service bundle. The override only applies to the structure of the top service bundle item, not to a nested structure. For example, if you override a component attribute value for Text Messaging SMS 200 from the structure for Text Messaging Service, the override does not apply to the structure for Text Messaging Options.
Important: Do not use component overrides within a service bundle when publishing to Siebel. Siebel can only accept component overrides for items with an Entity Type = Promotion.
For information on how to override a component attribute value within a service bundle, see: Overriding Component Attribute Values.
To delete a component within a bundle
After publishing a service bundle to Siebel, you can delete a component from the bundle, if necessary. For example, you might want to remove the component Text Messaging SMS 200 from the list of product options. Refer to 'Deleting or Disabling Components' within Editing Structure Information. If the parent item of the deleted component is a component of another item, then the deleted component is removed from all multi-level structures (such as a nested service bundle) containing the parent item.
Modeling Commercial Bundles
Siebel uses commercial bundles to sell a related group of services, discounts, and products as a package. Commercial bundles differ from service bundles because they include products. A commercial bundle for a wireless service plan might look like this:
Commercial Bundle for a Wireless Service Plan
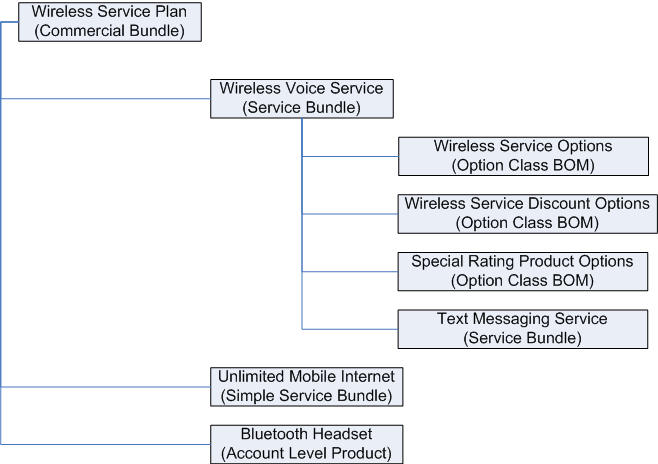
To create a commercial bundle in Oracle Product Hub (OPH), create an item (such as a Wireless Service Plan), then associate a structure to the item. The components in the structure become components of the commercial bundle. The components can consist of simple service bundles (such as Unlimited Mobile Internet), other commercial or service bundles (such as Wireless Voice Service), and items that represent account level products (such as a Bluetooth Headset).
When creating a commercial bundle, the top item (Wireless Service Plan) must have a BOM Item Type of 'Model'. Any nested components can have BOM Item Types of Model (for nested commercial or service bundles), Option Class (for modeling product options, such as Special Rating Product Options shown above), and Standard. Publishing the commercial bundle from Oracle Product Hub to Siebel creates the commercial bundle in Siebel. Do not publish commercial bundles to Oracle Billing and Revenue Management (BRM).
Important: Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) requires creation of a primary structure/bill of material (BOM) before creating alternate BOMs. Primary structures are date effective and alternate (which include Model and Option Class) structures are revision effective. If you plan to publish commercial bundles to EBS, you must first create a primary (date effective) structure for each item structure in OPH, then publish it to EBS. Next, you can create the necessary Model and Option Class structures in OPH and publish them to EBS.
To create a commercial bundle
-
Create an item catalog category with the following associated seeded attribute groups:
-
Additional Entity Details
-
Product Details: Definitions
-
Destination System Specification
-
Additional Billing Information*
-
Communications:Product Info*
Note: You only need to associate the attribute groups with an asterisk (*) if you plan to implement the product MDM Integration PIP to co-exist with the Order to Bill or Order to Activate PIP. Refer to AIA for Communications 2.4 - Building An Order To Activate Process - Whitepaper, Doc ID 843298.1, https://support.oracle.com/epmos/faces/ui/km/DocumentDisplay.jspx?id=843298.1, for information about setting the values of the attributes in the Communications:Product Info attribute group.
-
-
Create a structure type and a structure name. Associate the seeded component attribute group 'Version: Structure'. See: Defining Structures, Oracle Product Hub Implementation Guide and Associating Component Attribute Groups with a Structure Type, Oracle Product Hub Implementation Guide.
-
Create an item that represents the top commercial bundle item, associate the item catalog category created above, and specify the main attributes of the item.
Important: You must set the BOM Item Type attribute value to Model.
-
Set the values for the item's seeded attributes as described below.
Refer to the Seeded Item Metadata Libraries appendix in the Oracle Product Hub Implementation Guide for information about how to set the attributes within the associated seeded attribute groups listed above. The following list provides some information about how to set some attributes specifically for commercial bundles.
-
Product Details: Definition
-
Pricing Code =None
Note: The value of this attribute can change depending upon the particular implementation.
-
-
Additional Billing Information
-
Entity Type = Bundle
-
You only need to set the following attributes as described if you plan to implement the product MDM Integration PIP to coexist with the Order to Bill or Order to Activate PIP:
-
Additional Billing Information
-
Billing Entity Type = null
-
Billing Service Type = null
-
-
Communications:Product Info
-
Composition Type = WholeItem
-
Success Dependency*
-
Fulfillment Item Code*
Note: For the attributes with an asterisk (*), refer to AIA for Communications 2.4 - Building An Order To Activate Process - Whitepaper, Doc ID 843298.1, https://support.oracle.com/epmos/faces/ui/km/DocumentDisplay.jspx?id=843298.1, for information about setting the values.
-
-
-
Create a structure for the top commercial bundle item using the structure type you created above.
See: Creating Structures.
-
Update the seeded component attribute values within the attribute group Version: Structure for each of the component items.
-
Relationship Name - enter the name of the component item.
-
Domain Type
For the Domain Type attribute, assign a value of 'Class' to all items with a BOM Item Type value of 'Option Class'. Assign a value of 'Product' to all other items. The Domain Type 'Class' and BOM Item Type 'Option Class' together identify an item that represents the product options.
Warning: The item catalog category associated with the item that represents the product options and with the product option item's components must be the same.
-
Product Class - if the component has a Domain Type of 'Class', then enter the same name as the component's item catalog category. If the component has a Domain Type of 'Product, then leave this attribute blank.
-
Default Product - If the Domain Type is 'Class', then the domain for that component has more than one product. Enter the default product from among the set of products.
-
Max Cardinality
-
Min Cardinality
-
Default Cardinality - set this between the min and max cardinality values.
-
-
You can now publish the commercial bundle.
To exclude a component within a bundle
You can exclude a component of a commercial bundle. The exclusion only applies to the structure of the top commercial bundle item, not to a nested structure. For example, if you exclude Text Messaging Service from the structure for Wireless Service Plan, the exclusion does not apply to the structure for Wireless Voice Service.
Important: Do not use component exclusions within a commercial bundle when publishing to Siebel. Siebel can only accept component exclusions for items with an Entity Type = Promotion.
For information on how to exclude a component within a commercial bundle, see: Excluding Structures.
To override a component attribute value
You can override a component attribute value for a commercial bundle. The override only applies to the structure of the top commercial bundle item, not to a nested structure. For example, if you override a component attribute value for Text Messaging Service from the structure for Wireless Service Plan, the override does not apply to the structure for Wireless Voice Service.
Important: Do not use component overrides within a commercial bundle when publishing to Siebel. Siebel can only accept component overrides for items with an Entity Type = Promotion.
For information on how to override a component attribute value within a commercial bundle, see: Overriding Component Attribute Values.
To delete a component within a bundle
After publishing a commercial bundle to Siebel, you can delete a component from the bundle, if necessary. For example, you might want to remove the component Text Messaging Service from the list of product options. Refer to 'Deleting or Disabling Components' within Editing Structure Information. If the parent item of the deleted component is a component of another item, then the deleted component is removed from all multi-level structures (such as a nested service bundle) containing the parent item.
Modeling Promotions
Siebel uses promotions to represent the marketing definition of a product. Product promotions are time-sensitive, and they state discounted prices and contractual terms. Oracle Product Hub uses items with an associated structure to represent promotions. The immediate components can consist of service or commercial bundles or items that represent billing discounts.
When creating a promotion, the top item must have a BOM Item Type of 'Model'. Any immediate components must also have BOM Item Types of Model. Subcomponents (contained within an immediate component service or commercial bundle) can have any BOM Item Type. Publishing the promotion item from Oracle Product Hub to Siebel creates the promotion in Siebel. Do not publish promotions to Oracle Billing and Revenue Management (BRM).
When publishing a promotion item to target applications, first publish the item without attribute values entered in the attribute groups Subject Compatibility Rules and Promotion: Upgrade. Next, update the promotion item with the attribute values for the attribute groups Subject Compatibility Rules and Promotion: Upgrade and update the promotion in the target applications by publishing again.
Excluding or Overriding Components of Bundles within the Promotion
When publishing to Siebel, use the Version: Structure attribute group to specify whether or not to require a component, exclude a component, or include the component as an option in the promotion. You can only exclude or override components that are components of a service or commercial bundle. The Cardinality attributes control this:
-
Required: Max Cardinality = 1, Min Cardinality = 1, Default Cardinality = 1.
-
Optional: Max Cardinality = 1, Min Cardinality = 0, Default Cardinality = 0 or 1.
-
Excluded: Max Cardinality = 0, Min Cardinality = 0, Default Cardinality = 0.
Specifying Promotion Upgrade and Downgrade Rules
You can define promotion rules for upgrading or downgrading services. For example, a double play promotion, where a customer must purchase both VOIP and Broadband services, can be upgraded to a triple play promotion, where a customer must purchase VOIP, Broadband, and Wireless services. Alternatively, the double play promotion can be downgraded to either a single VOIP or a single Broadband promotion. In this scenario, you must define three rules:
-
Upgrade to the triple play promotion.
-
Downgrade to the Broadband promotion.
-
Downgrade to the VOIP promotion.
Use the multi-row attribute group "Promotion: Upgrade" to associate these three rules with the double play promotion item. When specifying a rule for upgrading from the double play to the triple play promotion, enter the Original Promotion attribute value as Triple Play. When specifying a rule for downgrading from the double play to the Broadband promotion, enter the Original Promotion attribute value as Broadband.
Specifying Price and Discount Overrides for Promotions
You can override a price or a discount for any component or subcomponent in the context of a promotion. To specify an override for an immediate component of a promotion, use the attribute group Product Promotions: Pricing: Components. To specify an override for a subcomponent of a promotion, use two attribute groups, Product Promotions: Pricing: Components (for the item that is the immediate component to the promotion and the parent to the subcomponent where you want to specify an override) and Product Promotions: Pricing: Components: Adjustments (for the subcomponent item where you want to specify an override). Use these attribute groups when publishing to Siebel. When publishing to other systems, refer to Overriding Component Attribute Values.
-
You must specify a current price or discount for an item first before you can override it.
-
When specifying a price or discount override for a product with multiple events or charges (for example, specifying a price override for a wireless service bundle that includes many voice and text messaging options and bundles), apply the override to the first item with a recurring charge (such as basic wireless usage). If there is no item with a recurring charge, then apply the override to the first item with a non-usage based charge (such as a charge for a certain limited number of text messages).
-
Specify only one price or discount override per promotion.
-
Do not delete overrides that are no longer applicable. Specify an end date for the override instead.
To create a promotion
-
Create an item catalog category with the following associated seeded attribute groups:
-
Additional Entity Details
-
Product Details: Definitions
-
Destination System Specification
-
Additional Billing Information*
-
Communications:Product Info*
-
Subject Compatibility Rules
-
Promotion:More Information
-
Promotion:Charge Plan:Non Recurring Charge Details
-
Promotion:Charge Plan:Recurring Charge Details
-
Promotion:Charge Plan: Charges,Adjustment, Usage Plan Details
-
Promotion:Commitment:Charges Credits
-
Promotion:Commitment:Terms
-
Promotion:Upgrade
Note: You only need to associate the attribute groups with an asterisk (*) if you plan to implement the product MDM Integration PIP to co-exist with the Order to Bill or Order to Activate PIP. Refer to AIA for Communications 2.4 - Building An Order To Activate Process - Whitepaper, Doc ID 843298.1, https://support.oracle.com/epmos/faces/ui/km/DocumentDisplay.jspx?id=843298.1, for information about setting the values of the attributes in the Communications:Product Info attribute group.
-
-
Create a structure type and a structure name. Associate the following seeded component attribute groups:
-
Product Promotions:Components (Specify only for immediate components.)
-
Component Pricing (Specify only for immediate components. Specify the values as overrides.)
-
Product Promotions: Pricing: Components: Adjustments (Specify only for immediate components.)
-
Version: Structure (Specify only for subcomponents, not for the immediate components of the item representing a promotion.)
See: Defining Structures, Oracle Product Hub Implementation Guide and Associating Component Attribute Groups with a Structure Type, Oracle Product Hub Implementation Guide.
-
-
Create an item that represents the promotion, associate the item catalog category created above, and specify the main attributes of the item.
Important: You must set the BOM Item Type attribute value to Model.
-
Set the values for the item's seeded attributes as described below.
Refer to the Seeded Item Metadata Libraries appendix in the Oracle Product Hub Implementation Guide for information about how to set the attributes within the associated seeded attribute groups listed above. The following list provides some information about how to set some attributes specifically for promotions.
-
Product Details: Definition
-
Pricing Code =None
Note: The value of this attribute can change depending upon the particular implementation.
-
-
Additional Billing Information
-
Entity Type = Promotion
-
You only need to set the following attributes as described if you plan to implement the product MDM Integration PIP to coexist with the Order to Bill or Order to Activate PIP:
-
Additional Billing Information
-
Billing Entity Type = null
-
Billing Service Type = null
-
-
Communications:Product Info
-
Composition Type = WholeItem
-
Success Dependency*
-
Fulfillment Item Code*
Note: For the attributes with an asterisk (*), refer to AIA for Communications 2.4 - Building An Order To Activate Process - Whitepaper, Doc ID 843298.1, https://support.oracle.com/epmos/faces/ui/km/DocumentDisplay.jspx?id=843298.1, for information about setting the values.
-
-
-
Create a structure for the promotion item using the structure type you created above, then associate the structure to the promotion item.
See: Creating Structures.
-
Update the seeded component attribute values within the attribute group Version: Structure for each of the component items.
-
Relationship Name - enter the name of the component item.
-
Domain Type
For the Domain Type attribute, assign a value of 'Class' to all items with a BOM Item Type value of 'Option Class'. Assign a value of 'Product' to all other items. The Domain Type 'Class' and BOM Item Type 'Option Class' together identify an item that represents the product options.
Warning: The item catalog category associated with the item that represents the product options and with the product option item's components must be the same.
-
Product Class - if the component has a Domain Type of 'Class', then enter the same name as the component's item catalog category. If the component has a Domain Type of 'Product, then leave this attribute blank.
-
Default Product - If the Domain Type is 'Class', then the domain for that component has more than one product. Enter the default product from among the set of products.
-
Max Cardinality
-
Min Cardinality
-
Default Cardinality - set this between the min and max cardinality values.
Important: Use the cardinality attributes to exclude or override bundle components when publishing to Siebel. To exclude the components when publishing to other target systems, see: Excluding Structures. Do not delete subcomponents for the purpose of a promotion. Deleting a subcomponent permanently deletes it from the bundle as well as from the promotion.
If you want to exclude a component of the promotion, not of a component bundle, then you must delete the component from the promotion's structure.
-
-
Optionally, specify promotion upgrade and downgrade rules by specifying attribute values within the Promotion: Upgrade attribute group.
-
You can now publish the promotion.