Overview
This chapter covers the following topics:
- Introduction to Oracle Trading Community Architecture
- Oracle Customer Data Management
- Using Oracle Trading Community Architecture
Introduction to Oracle Trading Community Architecture
Oracle Trading Community Architecture (TCA) is a data model that allows you to manage complex information about the parties, or customers, who belong to your commercial community, including organizations, locations, and the network of hierarchical relationships among them.
This information is maintained in the TCA Registry, which is the single source of trading community information for Oracle E-Business Suite applications. These applications, as well as TCA itself, provide user interfaces, batch data entry functionality, and other features for you to view, create, and update Registry information. See: Using Oracle Trading Community Architecture.
The key entities in TCA include:
-
Parties: Entities of type Person or Organization that can enter into business relationships. Parties can also be of type Relationship. For example, Joe as himself is a party of type Person, but Joe as a contact for Vision Corporation is a party of type Relationship. Every party in the TCA Registry has a unique Registry ID.
TCA includes an extensive variety of information for parties, for example party name, addresses, contacts, and contact points. Joe as a person can have a personal phone number that differs from the phone number for the relationship of Joe as a contact.
-
Party sites: Addresses that parties use for specific purposes, or uses.
-
Customers: Parties with whom you have a selling relationship.
-
Customer accounts: The business relationships between you and your customers.
-
Customer account sites: Party sites used in the context of customer accounts for specific purposes, or uses, for example ship-to and bill-to account sites.
-
Locations: Geospatial points, usually defined by an address.
-
Contacts: People who have a contact or employment relationship with an organization or person.
-
Contact points: Means of contact, for example, phone and e-mail address.
TCA also includes conceptual functionality that helps you manage and understand your trading community. For example, you can use relationships to model the roles that parties play with respect to one another, and classifications to classify entities.
Entities and Attributes Details
Entities in the TCA Registry consist of logical groups of descriptive, related attributes. For example, the Person Profile entity contains attributes, such as last name and date of birth, that describe parties of type Person. Likewise, the Organization Profile entity consists of attributes that describe parties of type Organization, the Address entity has address-related attributes, and so on.
An entity corresponds to one or more tables in TCA. For example, attribute values for a party record are stored in the HZ_PARTIES table.
Related Topics
Oracle Customer Data Management
Customers Overview
Use the Customers set of pages to manage customer information in Oracle Receivables.
You create customers so that you can properly record and account for sales transactions, as well as all other attributes of your selling relationships. Recording a sales transaction requires that a customer, stored as a party in Oracle Trading Community Architecture, has an account as well as an account site. Consequently, to understand the role of a customer in the context of your trading community, you should also understand other concepts such as party, customer account, and account site.
-
Party: An entity that can enter into a business relationship, such as buying and selling, and can be of the type Organization or Person. A party exists separately from any business relationship that it enters into with another party. For example, Vision Distribution could be a party within your trading community.
-
Customer: A party, either an organization or person, with whom you have a selling relationship. This selling relationship can result from the purchase of products and services or from the negotiation of terms and conditions that provide the basis for future purchases. For example, a division of Vision Distribution could become one of your customers.
-
Customer Account: A customer account represents the attributes of the business relationship that a party can enter into with another party. The account has information about the terms and conditions of doing business with the party. For example, you could open a commercial account for purchases made by Vision Distribution for its internal use and a reseller account for purchases made by Vision Distribution for sales of your products to end-users.
You can create multiple customer accounts for a party, to maintain information about different categories of business activities. For example, to track invoices for different types of purchases, you can maintain an account for purchasing office supplies and another account for purchasing furniture.
You can also maintain multiple customer accounts for a customer that transacts business with more than one line of business in your organization.
Information about a party such as profile, addresses, and contacts can be shared across a party's customer accounts. In addition, you can also maintain separate profiles and contacts, along with the contacts' contact addresses and contact points, for each customer account.
-
Sites/Addresses:
-
A location is a point in space described by an address.
-
A party site is the location where a party is physically located. Every party has only one identifying address, but a party can have multiple party sites.
-
An account site is a party site that is used in the context of an account. An account can have multiple account sites.
-
A customer address is an account site that is used for billing, shipping, or other purposes.
-
-
Relationship:
-
A party relationship is a party's role in the context of another party. Party relationships can be either seeded or user defined. Examples include, affiliate, subsidiary, partner, employee of, or contact of.
-
An account relationship is established between different accounts of a party to allow sharing of billing, shipping, and pricing information.
-
-
Contact: A person who communicates for or acts on behalf of a party or customer account. A contact can exist for a customer at the account or address level. A person usually acts as a contact for an organization, but can also be a contact for another person. For example, an administrative assistant could be the contact for an executive.
For a detailed discussion of these Oracle Trading Community Architecture concepts and examples of how to model your customers using the Customers set of pages, see: Oracle Trading Community Best Practices Setting Up Customer and Prospect Data (Note 269124.1 on My Oracle Support).
Process Flow
This diagram shows the process flow for managing, searching, creating, and updating customer information.
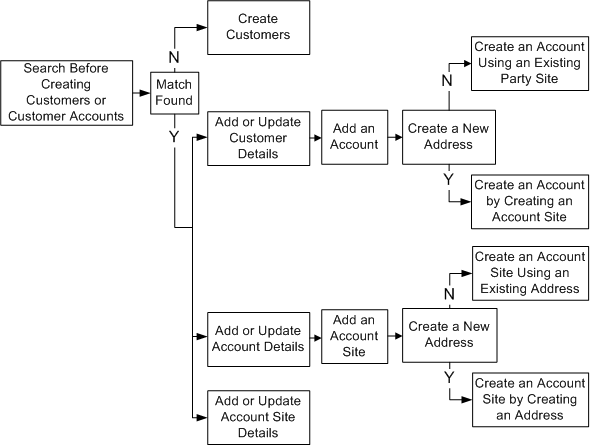
Oracle Customer Data Management
Oracle Trading Community Architecture is the foundation not only for the Oracle E-Business Suite, but also specifically for the product family that it belongs to: Oracle Customer Data Management (CDM). CDM includes:
-
Oracle Customers Online (OCO): Oracle Customers Online lets you view, create, maintain, and enrich your central repository of customer data.
See: Oracle Customers Online User Guide and Oracle Customers Online Implementation Guide.
-
Oracle Customer Data Librarian (CDL): Oracle Customer Data Librarian lets you establish and maintain an accurate, duplicate free, and complete customer database. This application includes all of the features from Oracle Customers Online.
See: Oracle Customer Data Librarian User Guide and Oracle Customer Data Librarian Implementation Guide.
-
Oracle Customer Data Hub (CDH): Oracle Customer Data Hub lets you centralize customer data from various source systems, providing an single view of your customers. The links between each source system and the Hub are operational and real-time. CDH includes all the TCA features, for example to maintain source systems, and cleanse and enrich data, and also includes Oracle Customers Online.
For reference material that supplements not only TCA but CDM product documentation, see Oracle Trading Community Architecture Reference Guide.
Related Topics
Introduction to Oracle Trading Community Architecture
Using Oracle Trading Community Architecture
Various applications in the Oracle E-Business Suite can view, create, and update the TCA Registry data. Because this information is shared, any change made in one application is reflected in all applications.
TCA itself provides the Trading Community Manager responsibility, which includes these features that you can use to maintain, enrich, and cleanse the TCA Registry.
-
Bulk Import: Import batches of party data in bulk from external source systems into the TCA Registry. See: Bulk Import Overview.
-
Customer Interface: Import customer account and party data leveraging row-by-row API's from external source systems into the TCA Registry. See: Customer Interface.
-
Customers: Enter and maintain party and customer account information. See: Entering and Updating Customer Information, Oracle Receivables User Guide and Defining Customer Profile Classes, Oracle Receivables Implementation Guide.
Run these reports for customer account information:
See: Listing Reports, Oracle Receivables User Guide.
-
Third Party Data Integration: Enrich the data for organizations and persons with D&B information. See: Third Party Data Integration Overview.
-
Locations: Generate longitude and latitude coordinates for addresses through an eLocations Spatial Data Integration, and generate time zones for locations. See: Locations Overview.
-
Phones: Generate time zones for phones. See: Generate Time Zone for Phone Numbers.
-
Relationship Manager: Create and manage relationships among existing parties in the TCA Registry. See: Relationship Manager Overview.
-
Batch duplicate identification: Create batches of potentially duplicate parties to merge. See: Batch Duplicate Identification Overview.
-
Party Merge: Cleanse the TCA Registry by merging duplicate parties and duplicate sites within a party. See: Party Merge Overview.
-
Customer Account Merge: Cleanse the TCA Registry by merging duplicate customer accounts and duplicate sites within an account. See: Merging Customers.
Note: If you have Oracle Customer Data Librarian, the data librarian can permanently purge parties from the TCA Registry. See: Party Purge Overview, Oracle Customer Data Librarian User Guide.
The Trading Community Manager responsibility also provides features for administering and implementing TCA. See: Introduction to Administration, Oracle Trading Community Architecture Administration Guide.
Related Topics