| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Solaris Administration: IP Services Oracle Solaris 10 1/13 Information Library |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Solaris Administration: IP Services Oracle Solaris 10 1/13 Information Library |
Part I Introducing System Administration: IP Services
1. Oracle Solaris TCP/IP Protocol Suite (Overview)
2. Planning Your TCP/IP Network (Tasks)
3. Introducing IPv6 (Overview)
4. Planning an IPv6 Network (Tasks)
5. Configuring TCP/IP Network Services and IPv4 Addressing (Tasks)
6. Administering Network Interfaces (Tasks)
7. Configuring an IPv6 Network (Tasks)
8. Administering a TCP/IP Network (Tasks)
9. Troubleshooting Network Problems (Tasks)
10. TCP/IP and IPv4 in Depth (Reference)
IPv6 Addressing Formats Beyond the Basics
6to4-Derived Addressing on a Host
IPv6 Multicast Addresses in Depth
Oracle Solaris IPv6 Implementation
IPv6 Interface Configuration File
/etc/inet/ipaddrsel.conf Configuration File
ifconfig Command Extensions for IPv6 Support
netstat Command Modifications for IPv6 Support
snoop Command Modifications for IPv6 Support
route Command Modifications for IPv6 Support
ping Command Modifications for IPv6 Support
traceroute Command Modifications for IPv6 Support
in.ndpd Daemon, for Neighbor Discovery
in.ripngd Daemon, for IPv6 Routing
inetd Daemon and IPv6 Services
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol
ICMP Messages From Neighbor Discovery
Obtaining a Router Advertisement
Prefix Configuration Variables
Neighbor Solicitation and Unreachability
Duplicate Address Detection Algorithm
Comparison of Neighbor Discovery to ARP and Related IPv4 Protocols
Packet Flow Through the 6to4 Tunnel
Considerations for Tunnels to a 6to4 Relay Router
IPv6 Extensions to Oracle Solaris Name Services
Changes to the nsswitch.conf File
Changes to Name Service Commands
13. Planning for DHCP Service (Tasks)
14. Configuring the DHCP Service (Tasks)
15. Administering DHCP (Tasks)
16. Configuring and Administering the DHCP Client
17. Troubleshooting DHCP (Reference)
18. DHCP Commands and Files (Reference)
19. IP Security Architecture (Overview)
21. IP Security Architecture (Reference)
22. Internet Key Exchange (Overview)
24. Internet Key Exchange (Reference)
25. IP Filter in Oracle Solaris (Overview)
27. Introducing IPMP (Overview)
28. Administering IPMP (Tasks)
Part VI IP Quality of Service (IPQoS)
29. Introducing IPQoS (Overview)
30. Planning for an IPQoS-Enabled Network (Tasks)
31. Creating the IPQoS Configuration File (Tasks)
32. Starting and Maintaining IPQoS (Tasks)
33. Using Flow Accounting and Statistics Gathering (Tasks)
The term dual-stack normally refers to a complete duplication of all levels in the protocol stack from applications to the network layer. One example of complete duplication is a system that runs both the OSI and TCP/IP protocols.
Oracle Solaris is dual-stack, meaning that Oracle Solaris implements both IPv4 and IPv6 protocols. When you install the operating system, you can choose to enable the IPv6 protocols in the IP layer or use only the default IPv4 protocols. The remainder of the TCP/IP stack is identical. Consequently, the same transport protocols, TCP UDP and SCTP, can run over both IPv4 and IPv6. Also, the same applications can run over both IPv4 and IPv6. Figure 11-4 shows how the IPv4 and IPv6 protocols work as a dual-stack throughout the various layers of the Internet protocol suite.
Figure 11-4 Dual-Stack Protocol Architecture
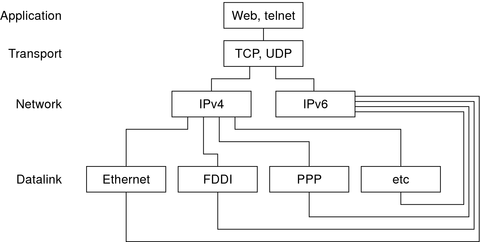
In the dual-stack scenario, subsets of both hosts and routers are upgraded to support IPv6, in addition to IPv4. The dual-stack approach ensures that the upgraded nodes can always interoperate with IPv4-only nodes by using IPv4.