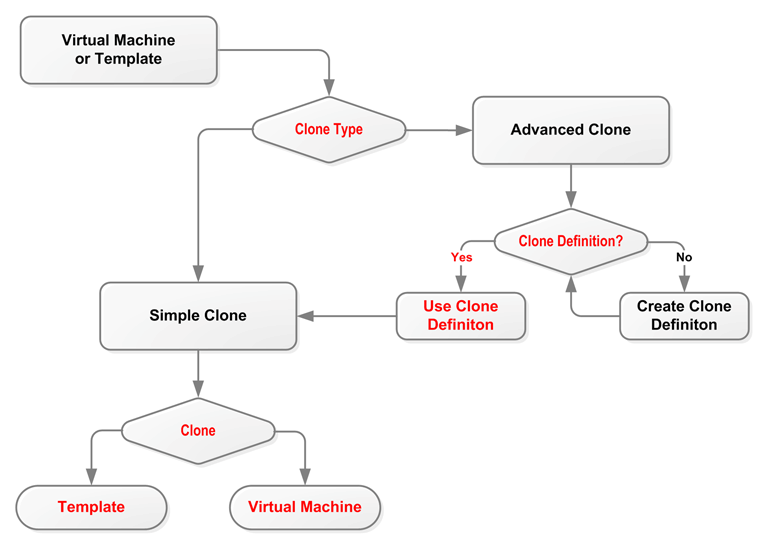
Cloning a virtual machine or template enables you to create multiple virtual machines or templates based on the original. There are two methods of cloning virtual machines; a simple clone, and an advanced clone. A simple clone sets up the clone with the same configuration information as the original. An advanced clone enables you to create and use a clone definition with differing configuration from the original. For example, you can change the cloned virtual machine or template to deploy to a different server pool or repository, with changed memory, virtual CPU number, network settings, and so on. Figure Figure 7.2, “Cloning a virtual machine or template” shows the process of creating a clone of a virtual machine or template.
To modify the clone parameters, such as virtual disks, network, memory, and so on, you should use a clone definition, and use that clone definition to perform cloning. See Section 7.8.1, “Creating a Clone Definition” to create a clone definition to during cloning.
A cold clone is a clone created from a stopped virtual machine. A cold clone performs a clone of the virtual machine, with safe and consistent virtual disk status. This is useful for creating a virtual machine or template from the original virtual machine. A hot clone is created from a running virtual machine. A hot clone creates a clone with inconsistent disk status, and should only be used as a snapshot or back up of a virtual machine, perhaps on a virtual machine that requires 100% uptime and cannot be shut down. If you want to use the hot-cloned virtual machine, you should first repair any virtual disks, using a disk repair utility such as fsck. Do not use hot cloning for virtual machines running an Oracle Database. Instead, you should use an Oracle Database backup strategy, such as the rman utility.
A thin clone means copies the virtual machine files and only take up the amount of disk space actually used, not the full specified disk size. Thin cloning can only be used when cloning from and to the same repository, and when the storage used for the storage repository is non-generic (for example, a Sun 7000 or NetApp Storage Connect plug in). Thin cloning is the fastest and most efficient cloning method.
A clone can also be performed using two other file copy methods: sparse copy, and non-sparse copy. These two cloning methods can be used when cloning from and to different repositories, and when the storage used for the storage repository uses a generic Storage Connect plug in. These cloning methods are slower than thin cloning, but more versatile.
To create a clone:
Select the virtual machine or template to clone and display the Clone Virtual Machine or Template dialog box. You display this dialog box from different locations, depending on whether you are cloning a virtual machine or a template.
Virtual Machine: In the Home view, select the virtual machine to clone in the navigation pane, right click and select Clone from the menu.
Virtual Machine Template: In the Home view click Server Pools in the navigation pane, then open the Templates tab in the management pane. Select the template to clone and click Clone
Select the clone type radio button, either Simple Clone or Advanced Clone. Select or enter the following:
Clone Definition: Click Search to find the clone definition to use, or to create a new one to use. See Section 7.8.1, “Creating a Clone Definition”. This field is only displayed if you select Advanced Clone.
TipIf you clone a virtual machine or template using the Simple Clone option, the storage repository is locked for the duration of the cloning job; this may be some time in some circumstances. To quickly create clones and not lock the storage repository, use the Advanced Clone option with a clone definition.
Target Clone Type: Select the clone type, either Template or Virtual Machine, to specify the object to create from the clone.
Name: A name for the virtual machine or template.
Description: A description for the virtual machine or template.
Target Repository: The repository to store the clone files, such as virtual disks. This field is only displayed if you select Advanced Clone.
Target Server Pool: The server pool on which the clone is to be deployed.
Click OK.