| ナビゲーションリンクをスキップ | |
| 印刷ビューの終了 | |
|
Oracle Solaris Studio 12.3: スレッドアナライザユーザーズガイド Oracle Solaris Studio 12.3 Information Library (日本語) |
| ナビゲーションリンクをスキップ | |
| 印刷ビューの終了 | |
|
Oracle Solaris Studio 12.3: スレッドアナライザユーザーズガイド Oracle Solaris Studio 12.3 Information Library (日本語) |
3.4.3.1 スレッドアナライザを使用したデッドロック検出実験結果の表示
3.4.3.2 er_print を使用した、デッドロック検出実験結果の表示
潜在的デッドロックと実デッドロックを取り除くには、哲学者は食事しようとする前にトークンを受け取る必要があるとするトークンのシステムを使用した方法があります。使用可能なトークンの数は、テーブルの哲学者の人数より少なくする必要があります。哲学者はトークンを受け取ると、テーブルのルールに従って食事できます。それぞれの哲学者は食事が終わればトークンを返し、プロセスを繰り返します。次の擬似コードは、トークンシステムを使用したときの、各哲学者のロジックを示します。
while (there is still food on the table)
{
get token
grab right fork
grab left fork
eat some food
put down left fork
put down right fork
return token
}
以降の節では、トークンのシステムの 2 つの異なる実装について詳しく説明します。
次のリストは、トークンシステムを使用する修正バージョンの食事する哲学者プログラムを示します。このソリューションには 4 つのトークン (食事する人数より 1 少ない) が組み入れられ、したがって同時に 4 人の哲学者しか食事できません。このバージョンのプログラムは din_philo_fix1.c と呼ばれます。
ヒント - サンプルアプリケーションをダウンロードした場合、din_philo_fix1.c ファイルを SolarisStudioSampleApplications/ThreadAnalyzer/din_philo ディレクトリからコピーできます。
1 /*
2 * Copyright (c) 2006, 2010, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
3 * @(#)din_philo_fix1.c 1.3 (Oracle) 10/03/26
4 */
5
6 #include <pthread.h>
7 #include <stdio.h>
8 #include <unistd.h>
9 #include <stdlib.h>
10 #include <errno.h>
11 #include <assert.h>
12
13 #define PHILOS 5
14 #define DELAY 5000
15 #define FOOD 100
16
17 void *philosopher (void *id);
18 void grab_chopstick (int,
19 int,
20 char *);
21 void down_chopsticks (int,
22 int);
23 int food_on_table ();
24 void get_token ();
25 void return_token ();
26
27 pthread_mutex_t chopstick[PHILOS];
28 pthread_t philo[PHILOS];
29 pthread_mutex_t food_lock;
30 pthread_mutex_t num_can_eat_lock;
31 int sleep_seconds = 0;
32 uint32_t num_can_eat = PHILOS - 1;
33
34
35 int
36 main (int argn,
37 char **argv)
38 {
39 int i;
40
41 pthread_mutex_init (&food_lock, NULL);
42 pthread_mutex_init (&num_can_eat_lock, NULL);
43 for (i = 0; i < PHILOS; i++)
44 pthread_mutex_init (&chopstick[i], NULL);
45 for (i = 0; i < PHILOS; i++)
46 pthread_create (&philo[i], NULL, philosopher, (void *)i);
47 for (i = 0; i < PHILOS; i++)
48 pthread_join (philo[i], NULL);
49 return 0;
50 }
51
52 void *
53 philosopher (void *num)
54 {
55 int id;
56 int i, left_chopstick, right_chopstick, f;
57
58 id = (int)num;
59 printf ("Philosopher %d is done thinking and now ready to eat.\n", id);
60 right_chopstick = id;
61 left_chopstick = id + 1;
62
63 /* Wrap around the chopsticks. */
64 if (left_chopstick == PHILOS)
65 left_chopstick = 0;
66
67 while (f = food_on_table ()) {
68 get_token ();
69
70 grab_chopstick (id, right_chopstick, "right ");
71 grab_chopstick (id, left_chopstick, "left");
72
73 printf ("Philosopher %d: eating.\n", id);
74 usleep (DELAY * (FOOD - f + 1));
75 down_chopsticks (left_chopstick, right_chopstick);
76
77 return_token ();
78 }
79
80 printf ("Philosopher %d is done eating.\n", id);
81 return (NULL);
82 }
83
84 int
85 food_on_table ()
86 {
87 static int food = FOOD;
88 int myfood;
89
90 pthread_mutex_lock (&food_lock);
91 if (food > 0) {
92 food--;
93 }
94 myfood = food;
95 pthread_mutex_unlock (&food_lock);
96 return myfood;
97 }
98
99 void
100 grab_chopstick (int phil,
101 int c,
102 char *hand)
103 {
104 pthread_mutex_lock (&chopstick[c]);
105 printf ("Philosopher %d: got %s chopstick %d\n", phil, hand, c);
106 }
107
108
109
110 void
111 down_chopsticks (int c1,
112 int c2)
113 {
114 pthread_mutex_unlock (&chopstick[c1]);
115 pthread_mutex_unlock (&chopstick[c2]);
116 }
117
118
119 void
120 get_token ()
121 {
122 int successful = 0;
123
124 while (!successful) {
125 pthread_mutex_lock (&num_can_eat_lock);
126 if (num_can_eat > 0) {
127 num_can_eat--;
128 successful = 1;
129 }
130 else {
131 successful = 0;
132 }
133 pthread_mutex_unlock (&num_can_eat_lock);
134 }
135 }
136
137 void
138 return_token ()
139 {
140 pthread_mutex_lock (&num_can_eat_lock);
141 num_can_eat++;
142 pthread_mutex_unlock (&num_can_eat_lock);
143 }
この修正バージョンの食事する哲学者プログラムをコンパイルし、複数回それを実行してみます。トークンのシステムは、箸を使用して食事しようとする人の人数を制限し、これによって実デッドロックおよび潜在的デッドロックを回避します。
コンパイルするには、次のコマンドを使用します。
cc -g -o din_philo_fix1 din_philo_fix1.c
実験結果を収集する
collect -r deadlock din_philo_fix1 -o din_philo_fix1.1.er
トークンのシステムを使用するときでも、スレッドアナライザは、まったく存在していないのにこの実装の潜在的デッドロックを報告します。これが誤検知です。潜在的デッドロックについて詳しく説明した次のスクリーンショットを見てください。
図 3-5 潜在的デッドロックの誤検知レポート
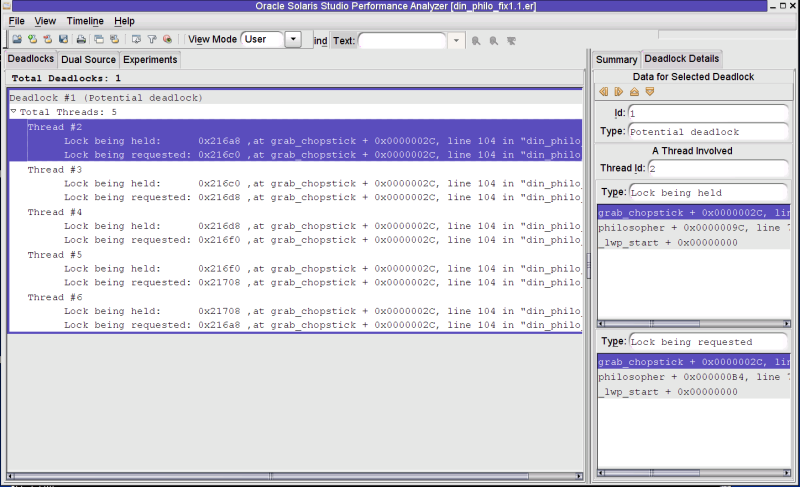
チェーンの最初のスレッド (スレッド #2) を選択し、「デュアルソース」タブをクリックして、スレッド #2 がアドレス 0x216a8 でロックを保持していたソースコード位置と、アドレス 0x216c0 でロックを要求したソースコードでの位置を確認します。次の図には、スレッド #2 の「デュアルソース」タブが示されています。
図 3-6 誤検知の潜在的デッドロックのソース

din_philo_fix1.c の get_token() 関数は、while ループを使用してスレッドを同期します。スレッドは、トークンの取得に成功するまで、while ループ外に出ません (これは、num_can_eat が 0 より大きいときに起こります)。while ループは同時に食事する人を 4 人に制限します。ただし、while ループによって実装された同期は、スレッドアナライザには認識されません。スレッドアナライザは、5 人の哲学者全員が同時に箸を掴んで食事しようとしていると想定しているので、潜在的デッドロックを報告します。次の節では、スレッドアナライザが認識する同期を使用することによって、同時に食事する人の人数を制限する方法について詳しく説明します。
次のリストには、トークンのシステムを実装する代替方法が示されています。この実装方法でも 4 つのトークンを使用するので、同時に 4 人しか食事しようとしません。ただし、この実装方法は、sem_wait() と sem_post() セマフォールーチンを使用して、食事する哲学者の人数を制限します。このバージョンのソースファイルは din_philo_fix2.c と呼ばれます。
ヒント - サンプルアプリケーションをダウンロードした場合、din_philo_fix2.c ファイルを SolarisStudioSampleApplications/ThreadAnalyzer/din_philo ディレクトリからコピーできます。
次のリストでは、din_philo_fix2.c について詳しく説明します。
1 /*
2 * Copyright (c) 2006, 2010, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
3 * @(#)din_philo_fix2.c 1.3 (Oracle) 10/03/26
4 */
5
6 #include <pthread.h>
7 #include <stdio.h>
8 #include <unistd.h>
9 #include <stdlib.h>
10 #include <errno.h>
11 #include <assert.h>
12 #include <semaphore.h>
13
14 #define PHILOS 5
15 #define DELAY 5000
16 #define FOOD 100
17
18 void *philosopher (void *id);
19 void grab_chopstick (int,
20 int,
21 char *);
22 void down_chopsticks (int,
23 int);
24 int food_on_table ();
25 void get_token ();
26 void return_token ();
27
28 pthread_mutex_t chopstick[PHILOS];
29 pthread_t philo[PHILOS];
30 pthread_mutex_t food_lock;
31 int sleep_seconds = 0;
32 sem_t num_can_eat_sem;
33
34
35 int
36 main (int argn,
37 char **argv)
38 {
39 int i;
40
41 pthread_mutex_init (&food_lock, NULL);
42 sem_init(&num_can_eat_sem, 0, PHILOS - 1);
43 for (i = 0; i < PHILOS; i++)
44 pthread_mutex_init (&chopstick[i], NULL);
45 for (i = 0; i < PHILOS; i++)
46 pthread_create (&philo[i], NULL, philosopher, (void *)i);
47 for (i = 0; i < PHILOS; i++)
48 pthread_join (philo[i], NULL);
49 return 0;
50 }
51
52 void *
53 philosopher (void *num)
54 {
55 int id;
56 int i, left_chopstick, right_chopstick, f;
57
58 id = (int)num;
59 printf ("Philosopher %d is done thinking and now ready to eat.\n", id);
60 right_chopstick = id;
61 left_chopstick = id + 1;
62
63 /* Wrap around the chopsticks. */
64 if (left_chopstick == PHILOS)
65 left_chopstick = 0;
66
67 while (f = food_on_table ()) {
68 get_token ();
69
70 grab_chopstick (id, right_chopstick, "right ");
71 grab_chopstick (id, left_chopstick, "left");
72
73 printf ("Philosopher %d: eating.\n", id);
74 usleep (DELAY * (FOOD - f + 1));
75 down_chopsticks (left_chopstick, right_chopstick);
76
77 return_token ();
78 }
79
80 printf ("Philosopher %d is done eating.\n", id);
81 return (NULL);
82 }
83
84 int
85 food_on_table ()
86 {
87 static int food = FOOD;
88 int myfood;
89
90 pthread_mutex_lock (&food_lock);
91 if (food > 0) {
92 food--;
93 }
94 myfood = food;
95 pthread_mutex_unlock (&food_lock);
96 return myfood;
97 }
98
99 void
100 grab_chopstick (int phil,
101 int c,
102 char *hand)
103 {
104 pthread_mutex_lock (&chopstick[c]);
105 printf ("Philosopher %d: got %s chopstick %d\n", phil, hand, c);
106 }
107
108 void
109 down_chopsticks (int c1,
110 int c2)
111 {
112 pthread_mutex_unlock (&chopstick[c1]);
113 pthread_mutex_unlock (&chopstick[c2]);
114 }
115
116
117 void
118 get_token ()
119 {
120 sem_wait(&num_can_eat_sem);
121 }
122
123 void
124 return_token ()
125 {
126 sem_post(&num_can_eat_sem);
127 }
この新しい実装方法は、セマフォー num_can_eat_sem を使用して、同時に食事できる哲学者の人数を制限します。セマフォー num_can_eat_sem は、哲学者の人数より 1 少ない 4 に初期化されます。食事しようとする前に、哲学者は get_token() を呼び出し、続いてこれが sem_wait(&num_can_eat_sem) を呼び出します。sem_wait() の呼び出しは、呼び出した哲学者をセマフォーの値が正になるまで待機させ、続いてセマフォーの値を 1 を引いて変更します。哲学者は食事を終えると、return_token() を呼び出し、続いてこれが sem_post(&num_can_eat_sem) を呼び出します。sem_post() は 1 を追加してセマフォーの値を変更します。スレッドアナライザは、sem_wait() および sem_post() の呼び出しを認識し、哲学者全員が同時に食事しようとしているわけではないと判断します。
注 - 適切なセマフォールーチンとリンクするように、-lrt を付けて din_philo_fix2.c をコンパイルする必要があります。
din_philo_fix2.c をコンパイルするには、次のコマンドを使用します。
cc -g -lrt -o din_philo_fix2 din_philo_fix2.c
プログラム din_philo_fix2 のこの新しい実装方法を複数回実行すると、どの場合も通常どおり終了し、ハングアップしないことがわかります。
この新しいバイナリで実験を作成する
collect -r deadlock -o din_philo_fix2.1.er din_philo_fix2
次の図に示すように、din_philo_fix2.1.er の実験から、スレッドアナライザが実デッドロックも潜在的デッドロックも報告していないことがわかります。
図 3-7 din_philo_fix2.c で報告されないデッドロック

スレッドアナライザが認識するスレッドおよびメモリー割り当て API のリストについては、付録 A スレッドアナライザで認識される APIを参照してください。