6 Managing Oracle Privileged Account Manager Auditing and Logging
This chapter describes how to configure and use Oracle Privileged Account Manager's auditing and logging functionality.
The topics in this chapter include:
-
Section 6.1, "Understanding Oracle Privileged Account Manager Auditing"
-
Section 6.2, "Understanding Oracle Privileged Account Manager Logging"
6.1 Understanding Oracle Privileged Account Manager Auditing
Oracle Privileged Account Manager audits all security events that occur under its purview, which gives you better visibility into how privileged accounts are used within your organization and enables you to effectively manage sensitive information.
Specifically, the Oracle Privileged Account Manager audit logger logs any events that modify entity states; such as when you add, modify, or remove new accounts, targets, or policies.
The following table describes all of the event categories and event types for which an audit can be generated:
| Event Category | Event Types | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Account Management |
Events related to managing principal accounts Note: A principal can be an end-user or a pseudo-user (a service within the system). |
|
|
Add Account |
Adding users, groups, or any other principal accounts |
|
|
Change Password |
Changes to user passwords |
|
|
Disable Account |
Disabling users, groups, or any other principal accounts |
|
|
Enable Account |
Enabling users, groups, or any other principal accounts |
|
|
Modify Account |
Modifying account attributes |
|
|
Query Account |
Queries to a user's account |
|
|
Remove Account |
Removing users, groups, or any other principal accounts |
|
|
Policy Management |
Events related to managing policies |
|
|
Create Policy |
Creating policies |
|
|
Delete Policy |
Deleting policies |
|
|
Modify Policy |
Modifying policies |
|
|
Query Policy |
Querying policies |
|
|
Target Management |
Events related to managing targets |
|
|
Add Target |
Adding targets |
|
|
Modify Target |
Modifying targets |
|
|
Query Target |
Querying targets |
|
|
Remove Target |
Removing targets |
Logging these audit events creates a processing history that allows reporting tools to gather statistics, as described in Section 6.1.2, "Understanding Oracle Privileged Account Manager Audit Reports."
6.1.1 Configuring Auditing in Oracle Privileged Account Manager
You can configure Oracle Privileged Account Manager to save audit events into a database or a file. When a database is not available, Oracle Privileged Account Manager saves its audit logs into this file,
DOMAIN_HOME/servers/<opamserver>/logs/auditlogs/opam#11.1.2.0.0
You can also configure Oracle Privileged Account Manager to deploy audit reports in BI Publisher (version 11.1.1.5.0 or higher), and you can use BI Publisher to view audit events in the database.
The following topics provide instructions for configuring auditing in Oracle Privileged Account Manager:
-
Configuring File-Based Auditing in Oracle Privileged Account Manager
-
Configuring Database-Based Auditing in Oracle Privileged Account Manager
-
Deploying Oracle Privileged Account Manager Audit Reports in BI Publisher
6.1.1.1 Configuring File-Based Auditing in Oracle Privileged Account Manager
Use the following steps to configure Oracle Privileged Account Manager:
Note:
These instructions assume you have already installed a WebLogic server.
-
Open a command window and change directory (
cd) toDOMAIN_HOME/config/fmwconfig/
-
Edit the
jps-config.xmlfile by changing theaudit.filterPresetparameter fromNonetoAll,Medium, orLowdepending on the type of events to be audited.Note:
See Section 6.1.1.4, "Setting the Audit Logging Levels" for more information.
For example,
<serviceInstance location="./audit-store.xml" provider="audit.provider" name="audit.db"> <property name="audit.filterPreset" value="All"/> <property name="audit.maxDirSize" value="0"/> <property name="audit.maxFileSize" value="104857600"/> <property name="audit.loader.jndi" value="jdbc/AuditDB"/> <property name="audit.loader.interval" value="15"/> <property name="audit.loader.repositoryType" value="File"/> <property name="auditstore.type" value="file"/> </serviceInstance> -
Restart the Oracle Privileged Account Manager server.
Note:
For detailed information about starting a Managed Server, see "Starting or Stopping the Oracle Stack" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle Identity and Access Management.
After the server restarts, audit logs will start appearing in this location:
DOMAIN_HOME/servers/<opamserver>/logs/auditlogs/opam#11.1.2.0.0
6.1.1.2 Configuring Database-Based Auditing in Oracle Privileged Account Manager
This section describes how to configure database-based auditing in Oracle Privileged Account Manager.
If you want to generate audit reports from a database and BI Publisher, then you must install
-
A database
-
The Oracle Repository Creation Utility application, which is used to create a schema and load a repository into the database.
Note:
For information about installing and working with the Repository Creation Utility, refer to Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository Creation Utility User's Guide available at
http://www.oracle.com/technology/documentation/index.htmlFor information about installing and configuring BI Publisher, refer to "Configuring Oracle Business Intelligence Publisher" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Identity Navigator.
To configure database-based auditing:
-
Download the Repository Creation Utility
.zipfile from Oracle Technology Network (OTN): -
Run
./rcuto load the audit schema into the database.By default, this step creates the
dev_iauuser in the database and loads tables under this user. -
Log in to the WebLogic Server Administrative Console to configure WebLogic.
http://adminserver_host:adminserver_port/console
-
Navigate to Services > Data Sources.
Click New to create a new data source.
-
Enter the following information to create a JDBC data source.
-
Type
jdbc/AuditDBin the Name field. -
Leave the JNDI Name field blank.
-
Select Oracle's Driver (Thin) for instance connections that are Versions 9.0.1 and later.
-
Leave Transaction Options set to the default setting.
-
Specify the DB name, host, and listener port.
-
Specify the Audit DB user (for example,
dev_iau) and apply it to both the Admin and Managed servers. -
Test the connection and apply it to both the Admin and Managed Servers.
Note:
Refer to "Create JDBC Data Sources" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help for more information about creating a JDBC data source and deploying it on a server.
-
-
Edit the
jps-config.xmlfile, located in
DOMAIN_HOME/config/fmwconfig/jps-config.xml, as follows:-
Change the
<property value="File" name="audit.loader.repositoryType"/>parameter to<property value="Db" name="audit.loader.repositoryType"/>. -
Change the
audit.filterPresetparameter fromNonetoAll,Medium, orLowdepending on the type of events to be audited.Note:
See Section 6.1.1.4, "Setting the Audit Logging Levels" for more information.
For example,
<serviceInstance location="./audit-store.xml" provider="audit.provider" name="audit"> <property name="audit.filterPreset" value="All"/> <property name="audit.maxDirSize" value="0"/> <property name="audit.maxFileSize" value="104857600"/> <property name="audit.loader.jndi" value="jdbc/AuditDB"/> <property name="audit.loader.interval" value="15"/> <property name="audit.loader.repositoryType" value="Db"/> <property name="auditstore.type" value="file"/> </serviceInstance>
-
-
Restart the Oracle Privileged Account Manager server.
6.1.1.3 Deploying Oracle Privileged Account Manager Audit Reports in BI Publisher
This section describes how to deploy Oracle Privileged Account Manager audit reports in BI Publisher, a component used to manage and deliver reports.
Use the following steps:
-
Install and configure Oracle Business Intelligence Publisher (BI Publisher) version 11.1.1.5.0 or higher if it is not already installed.
Refer to "Configuring Oracle Business Intelligence Publisher" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Identity Navigator for instructions.
-
After installing BI Publisher, locate the following directory in the WebLogic domain:
Note:
BI Publisher can be deployed on the same host or in a different domain.
BI_DOMAIN_HOME/config/bupublisher/repository/Reports -
Locate the
opam_product_BIP11gReports_11_1_1_6_0.zipfile in the following directory:ORACLE_HOME/opam/reportsUnzip this file into the
Reportsfolder noted in step 2. -
To set up the catalog and configure data sources, open a browser window and enter the URL for BI Publisher.
The format for this URL is
http://hostname: port/xmlpserver/
For example
http:/localhost:7001/xmlpserver/
-
When the BI Publisher login page displays, log in as a user with WebLogic privileges and click Sign In.
-
Set up the catalog as follows:
-
Select Administration > System Maintenance > Server Configuration.
-
Open the Catalog dialog, select the BI Publisher - File System from the Catalog Type menu, and enter the following path in the Path field:
BI_DOMAIN_HOME/config/bupublisher/repository/Reports -
Log in as an administrator.
-
Click Catalog to open the
Shared Folder/ Oracle Privileged Account Managerfolder.Note:
If this folder does not display, restart the application from the WebLogic console.
-
-
One JDBC (Oracle Privileged Account Manager JDBC) connection is required for Oracle Privileged Account Manager reports. Use the following steps to define an Oracle Privileged Account Manager JDBC connection and define the data sources:
-
Click the Administration link found on the right side of the BI Publisher page.
The BI Publisher Administration page displays. (Note the Data Sources section on this page.)
-
Click the JDBC Connection link found in the Data Sources section.
-
When the Data Sources page displays, click Add Data Source in the JDBC section to create a JDBC connection to your database.
-
On the Add Data Source page, enter the following information:
Data Source Name
Oracle Privileged Account Manager JDBC
Driver Type
Select a driver type to suit your database (for example, Oracle 10g or Oracle 11g).
Database Driver Class
oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver(Define a driver class to suit your database.)Connection String
Provide the database connection details.
For example, hostname:port:sid.User name
Provide the Oracle Privileged Account Manager Audit DB user name.
Password
Provide the Oracle Privileged Account Manager Audit DB user password.
If the connection to the database is established, a confirmation message is displayed indicating the success.
-
Click Apply.
You should see this newly defined connection (Oracle Privileged Account Manager JDBC) in the list of JDBC Data Sources.
-
Navigate to Oracle Privileged Account Manager Audit Reports.
The Catalog page is displayed as a tree structure on the left side of the page with details on the right.
-
Expand
Shared Foldersand select theOracle Privileged Account Managerfolder to view all of the objects in that folder.
-
-
Use Oracle Identity Navigator to configure a connection to the BI Publisher server.
Refer to "Creating a Connection to BI Publisher" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Identity Navigator for the necessary instructions.
When you configure the connection successfully, the My Reports section of the Oracle Identity Navigator Dashboard page will contain the link, Click here to create reports. In addition, users with the Security Auditor role can now perform the following tasks:
-
View Oracle Identity Management BI Publisher reports and audit reports
Note:
Oracle Privileged Account Manager provides a set of out-of-the box audit reports that are integrated with BI Publisher 11g and the Oracle Fusion Middleware Audit Framework. Oracle Privileged Account Manager generates these reports based on audit events logged in the audit store. Refer to Section 6.1, "Understanding Oracle Privileged Account Manager Auditing" for more information.
-
Select and add reports to the My Reports list
-
View and run any reports for which you have access privileges
You can now navigate in BI Publisher and use the Oracle Privileged Account Manager 11g BI reports.
6.1.1.4 Setting the Audit Logging Levels
To change the amount of audit logging provided by Oracle Privileged Account Manager, use the following steps:
-
Open a command window and change directory (
cd) toDOMAIN_HOME/config/fmwconfig/ -
Change the
audit.filterPresetparameter fromNoneto one of the following settings:-
All: Logs all event types. -
Medium: Logs all event types in thePolicyManagementandTargetManagementcategories, and the following event types in theAccountManagementcategory:-
ChangePassword -
CheckinAccount -
CreateAccount -
DeleteAccount -
DisableAccount -
EnableAccount -
ModifyAccount -
QueryAccount
-
-
Low: Logs the following event types-
In the
AccountManagementcategory:ChangePassword,CheckinAccount,CreateAccount,DeleteAccount,DisableAccount,EnableAccount, andModifyAccount -
In the
PolicyManagementcategory:CreatePolicy,DeletePolicy, andModifyPolicy
-
-
In the
TargetManagementcategory:CreateTarget,DeleteTarget, andModifyTarget
For example,
<serviceInstance location="./audit-store.xml" provider="audit.provider" name="audit"> <property value="All" name="audit.filterPreset"/> <property value="0" name="audit.maxDirSize"/> <property value="104857600" name="audit.maxFileSize"/> <property value="jdbc/AuditDB" name="audit.loader.jndi"/> <property value="15" name="audit.loader.interval"/> <property value="File" name="audit.loader.repositoryType"/> <property value="file" name="auditstore.type"/> </serviceInstance> -
-
Restart the Oracle Privileged Account Manager server.
Note:
For detailed information about starting a Managed Server, see "Starting or Stopping the Oracle Stack" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle Identity and Access Management.
After the server restarts, audit logs will start appearing in the following location:
DOMAIN_HOME/servers/<opamserver>/logs/auditlogs/opam#11.1.2.0.0
6.1.2 Understanding Oracle Privileged Account Manager Audit Reports
Oracle Privileged Account Manager supplies a set of default audit reports that are integrated with BI Publisher 11g and the Oracle Fusion Middleware Audit Framework. Oracle Privileged Account Manager generates these reports based on the audit events logged in the audit store.
The default audit report types include:
-
Error and Exception reports, such as authentication and authorization failures
-
User Activities reports, including account check-out and check-in history
-
Operational reports, including grantee assignments and any targets, accounts, and policies that have been added, edited, or removed
-
All Events reports, including all audit events that have been logged in the audit store
Oracle Privileged Account Manager audit reports can show who checked out an account and on which system it was checked out, justifications, requests for a system that is already checked out, and requests for a system to which a user does not have privileges.
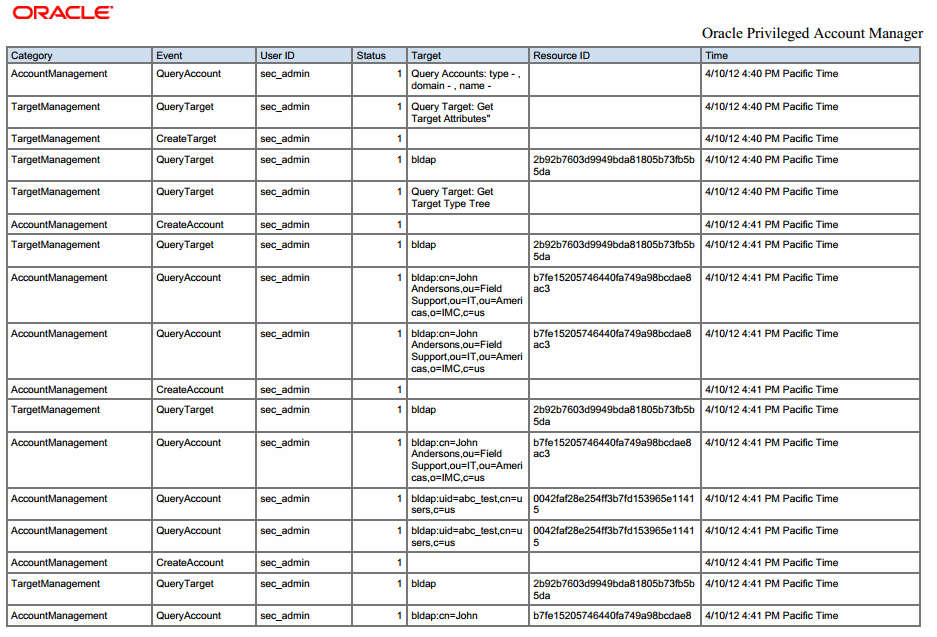
For example, the following figure shows a typical Oracle Privileged Account Manager audit report as viewed in BI Publisher.
Note:
You can view Oracle Privileged Account Manager audit reports in BI Publisher.
Notice that this report provides the following information:
-
Category: Event category
-
Event: Type of event that occurred
-
User ID: User that initiated the event
-
Status: Event results, where 1 is success and 0 is a failure
-
Target: Target on which the event occurred
-
Resource ID: Resource identifier
-
Time: Date and time the event occurred
6.2 Understanding Oracle Privileged Account Manager Logging
The Oracle Privileged Account Manager generic logger takes care of all logs not recorded by the audit logger, which includes debugging statements and exception messages. Processing tools can use these logs to diagnose problems that occur within the Oracle Privileged Account Manager server.
Oracle Privileged Account Manager-related log files are stored in the following locations:
DOMAIN_HOME/servers/adminserver/logs DOMAIN_HOME/servers/opamserver/logs
6.2.1 Configuring Basic Logging
To change the out-of-the-box logging for Oracle Privileged Account Manager,
-
Manually edit the
opam-logging.xmlfile, which is located in the following directory:DOMAIN_HOME/config/fmwconfig/opam -
Restart the OPAM server (usually the Managed Server).
Note:
For more information about implementing logging functionality and setting log levels, refer to "Logging Custom WLST Commands" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware WebLogic Scripting Tool Command Reference and "Managing Log Files and Diagnostic Data" in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
6.2.2 Example Logging Data
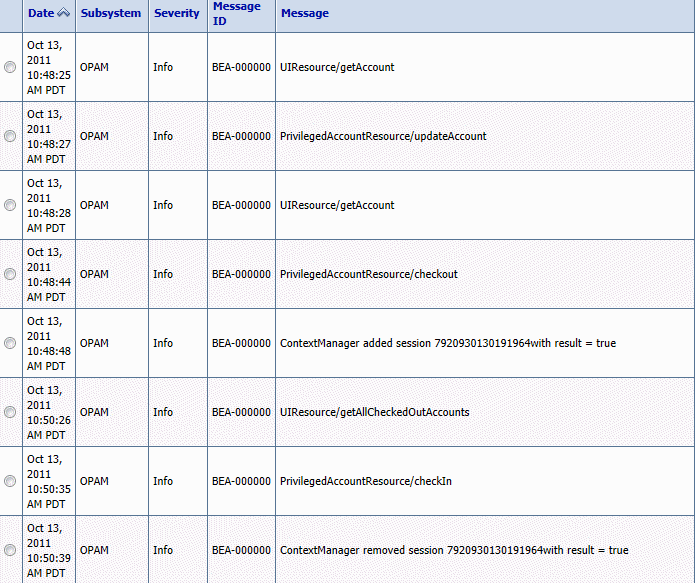
This figure shows some example logging data as viewed from the WebLogic console.
Notice that this report provides the following information:
-
Date and timestamp when the event occurred
-
Subsystem on which the event occurred
-
Message severity
-
Message ID
-
Message describing the operation that was performed