C Dual TCP/IP Overview
Dual TCP/IP provides two separate connections between the library host (ACSLS or ELS) and the HBC/HBCR controller card using primary port 2B and secondary port 2A. Dual TCP/IP prevents a loss of connection between the library and host by automatically avoiding a failing communication path.
-
ACSLS or ELS documentation.
Minimum Requirements for Dual TCP/IP
-
ACSLS 7.1 with PUT0701 for Solaris or AIX. Oracle recommends ACSLS 8.1 or above.
-
NCS 6.2 with the following PTFs for HSC/MVS/VM: SOS620 L1H168G, SMS620 L1H168F, and MSP: MSP PTF LF620DL.
-
The switch or router ports must be configured to auto negotiate. The SL3000 ports are configured to auto negotiate by default and support 10/100 Mbps speeds.
Using a Shared Network
Note:
Oracle recommends a private network for maximum throughput, minimum resource contention, and higher security.If you must use a shared network:
-
Directly connect the library to a switch or router that filters out undirected (broadcast) traffic.
-
Place the library on its own subnet. This may protect the library from receiving broadcast messages.
-
Use a managed switch or router to:
-
Set priorities on ports to supply the host and library with higher priority.
-
Provide dedicated bandwidth between the host and library.
-
Create a virtual local area network (VLAN) between the host and library.
-
-
Use a virtual private network (VPN) to insulate host-to-library traffic from other interference, such as irrelevant broadcasts.
Network Broadcast Issues on a Shared Network
Broadcasts sent to all network nodes may be directed to the library. The library cannot efficiently process requests while it is receiving these irrelevant broadcasts. As a result, the host may determine the connection to the library is lost.
Heavy network traffic can also overwhelm the Ethernet controller on the HBC/HBCR card. As a result, the controller continuously resets.
ARP Floods on a Shared Network
The SL3000's processor can be overwhelmed by floods of address resolution protocol (ARP) broadcasts. You should connect the library behind a switch or router.
Dual TCP/IP Configuration Examples
-
See also "Redundant Electronics Configuration Examples" for an example of RE and dual TCP/IP
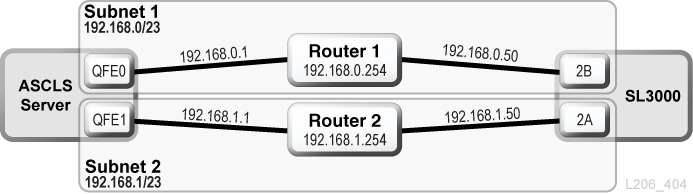
ACSLS Dual TCP/IP and Shared Subnets Example
In this example, the ACSLS server and the library share two separate subnets. The SL3000 uses a one-to-one relationship with the network interfaces on the ACSLS server. The network interface card on subnet 192.168.0/23 connects to port 2B and the network interface card on subnet 192.168.1/23 connects to port 2A.
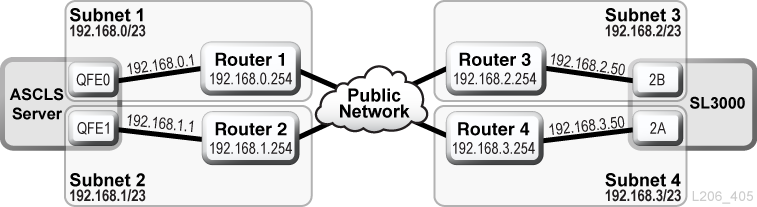
ACSLS Dual TCP/IP Through a Public Network Example
In this example, the ACSLS server contains two network interfaces that reside on two separate subnets. Both interfaces pass through a public network and into two different subnets before connecting to the SL3000 library. This configuration uses the same commands as in the first example.
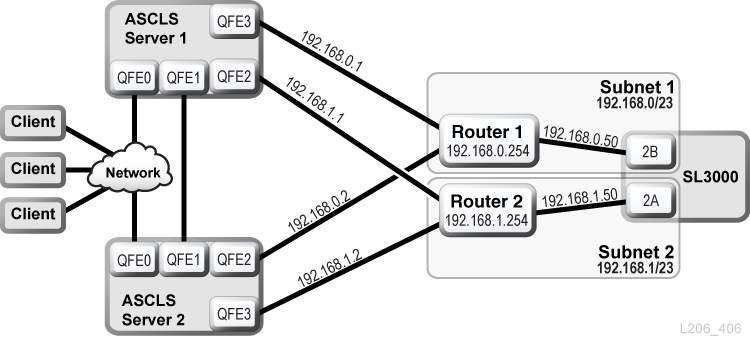
ACSLS High Availability Dual TCP/IP Example
The following example is an ACSLS High Availability (HA) environment that requires dual TCP/IP. The purpose of the HA environment is to have two ACSLS servers, one active and one standby. In this configuration, two ACSLS servers connect six network interfaces (three on each server) to two separate subnets. A third subnet connects the two ACSLS servers through a public network.
For more information on ACSLS HA and dual TCP/IP, see the ACSLS Administrator's Guide.
Routing
You should separate the SL3000 network interfaces over two different subnets when using ACSLS HA. The two different ACSLS servers use different network interfaces; therefore, you should add custom route entries to both ACSLS HA servers. Add the IP addresses for both servers to the SL3000 configuration.
Routing Tables
Add custom entries to the routing tables on the ACSLS server; however, any customized routing table entries will be lost after a restart of the ACSLS server. To maintain custom routing table entries, create scripts to add custom routes. Place the scripts in the rc directory structure for automatic execution at boot time.
For more information, refer to the ACSLS Administrator's Guide.
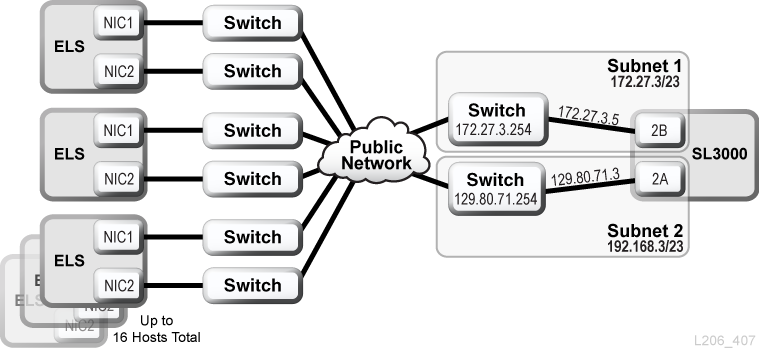
ELS/HSC and Dual TCP/IP Example
The following example shows a preferred configuration for mainframe systems using dual TCP/IP. The mainframe host contains two network interfaces residing on two separate subnets. Each connection travels through a public network, then connects to two different subnets before reaching the SL3000 library.
For more information, refer to the ELS documentation.