1 Governance Infrastructure
This chapter describes Oracle's service oriented architecture (SOA) governance infrastructure and Oracle's SOA Governance Suite components, such as the Oracle Service Registry (OSR) which is the runtime interface for the repository, Oracle Web Services Manager (OWSM) for security policy management, SOA Suite Runtime MetaData Store (MDS) for design-time tooling, and Oracle's Business Intelligence (BI) Publisher for reporting.
This chapter contains the following sections:
1.1 Overview of Governance Infrastructure
The governance infrastructure includes the following components of Oracle's SOA Governance Suite:
-
Oracle Enterprise Repository (OER)
-
Oracle Service Registry (OSR)
-
Runtime security policy enforcement (OWSM)
-
Service monitoring (Oracle Enterprise Manager SOA Management Pack Enterprise Edition)
Figure 1-1 Components of Oracle's SOA Governance Suite
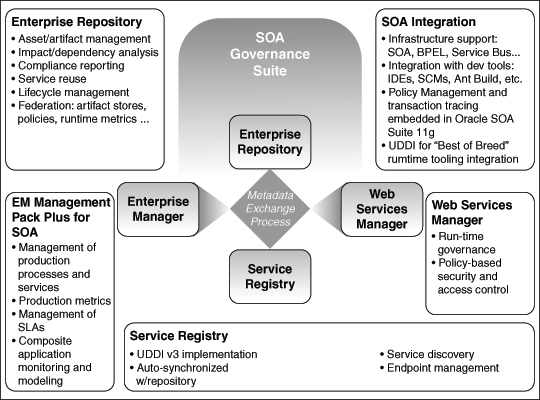
Description of "Figure 1-1 Components of Oracle's SOA Governance Suite"
Figure 1-1 illustrates the components of Oracle's SOA Governance Suite.
Oracle's Governance Suite is a loose bundle, meaning that Oracle does not require you to purchase all of the components. As a matter of fact, some of the Governance components are also included in Oracle's SOA Suite.
The Governance Infrastructure can interoperate with the following design-time tooling:
-
Version Control Systems
-
IDEs
-
Document repositories and File Stores
-
Design-time policy validation tooling
The Governance Infrastructure can also interoperate with the following runtime tooling:
-
MetaData Store (MDS)
-
Testing tools
-
Build Tools/Scripts
-
Defect tracking systems
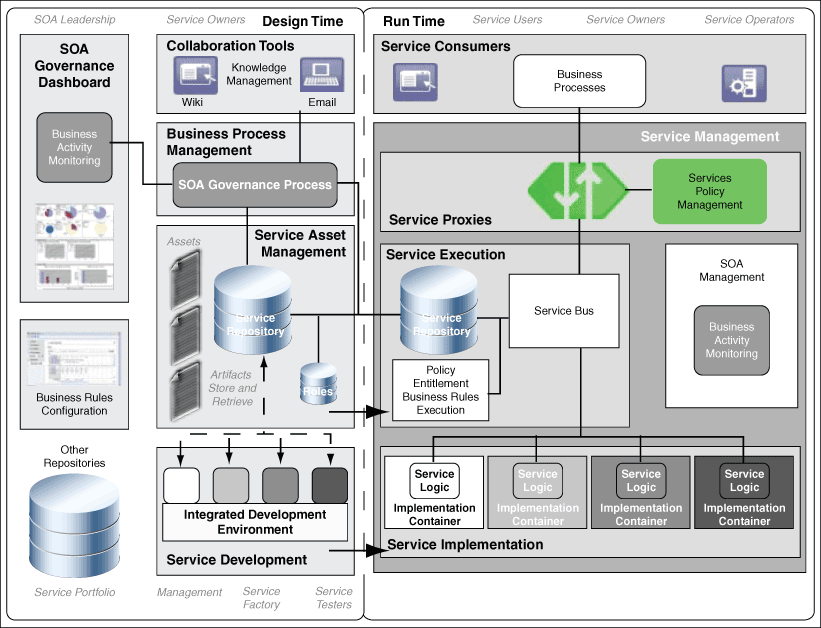
Figure 1-2 shows the governance infrastructure within Service Oriented Architecture. This guide describes the governance role for each of these tools and how you can install, connect, and configure all the pieces.
Note:
You need not install all of the governance infrastructure, especially when first starting out. Organizations should select the components most relevant to their use cases.
1.2 Oracle's Governance Suite
This section describes the components in the Governance Suite. It contains the following topics:
1.2.1 Oracle Enterprise Repository
Oracle Enterprise Repository provides design-time governance support for the service lifecycle, enabling storage and management of extensible metadata for composites, services, business processes, and other IT-related assets. Oracle Enterprise Repository acts as the central source of SOA information, allowing you to find planned, existing and retired services.
Oracle Enterprise Repository provides vital information to service producers, providers, and consumers who enhance applications or deliver new service capabilities. In addition, portfolio managers and business architects use the repository to understand business capabilities and to assist with strategic planning.
Oracle Enterprise Repository provides role-based links to asset artifact stores and links to design documents, justification documents, test plans, support plans, policies, and so on. Approvers in the lifecycle process can reference and upload documentary evidence to support their approvals, and consumers can reference information to support their service choices. Oracle Enterprise Repository features that help automate service lifecycle governance include:
-
An Asset Harvester that automatically populates OER with SOA assets and tracks updates to artifacts automatically.
-
Direct integration with IDEs, allowing prescription of assets for new projects and easy browsing and consumption of existing assets.
-
Reporting on reuse, compliance, and other portfolio management metrics.
-
A built-in process engine with a set of standard but modifiable processes to meet an organization's governance process workflows.
-
Built-in automated notification about a selection of lifecycle events, plus discretionary notification of asset subscribers.
-
An event engine that can publish repository events to any process service endpoint.
-
A bi-directional registry exchange feature that keeps information synchronized between the enterprise repository and the service registry.
-
A rich SOAP-based API that allows organizations to programmatically update the repository, keeping it synchronized with the IT and business environment that it describes.
In addition, Oracle Enterprise Manager SOA Management Pack Enterprise Edition provides Oracle Enterprise Repository with a summary of runtime performance metrics. These metrics help service providers judge portfolio performance and service consumers judge runtime performance.
Oracle Enterprise Repository also tracks asset usage and provides robust reports that help organizations determine the ROI on asset reuse. Oracle Enterprise Repository's interface integrates with JDeveloper and other integrated development environments, and with source code management tools, to promote developer adoption.
The following resources can help you when installing the Enterprise Repository:
-
Size Oracle Enterprise Repository
For more information, see http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/repository/overview/oer11gsizingguidelines-130307.pdf.
-
Choose a platform from the Oracle Enterprise Repository Supported Platforms
For more information, see http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/ias/downloads/fusion-certification-100350.html.
-
Download the Oracle Enterprise Repository from the Oracle Enterprise Repository page at http://www.oracle.com/technology/products/soa/repository/index.html
-
Install the Oracle Enterprise Repository
For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
-
Upgrade from previous Oracle Enterprise Repository versions
For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Upgrade Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
-
Run Oracle Enterprise Repository in a clustered environment
For more information, see "Install Oracle Enterprise Repository into a Clustered Environment" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
Oracle Enterprise Repository can also use common authentication mechanisms. Oracle Enterprise Repository supports:
-
LDAP/Active Directory
For more information, see "LDAP/Active Directory" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
-
eTrust Siteminder
For more information, see "eTrust Single Sign-On" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
-
Container-managed authentication
For more information, see "Container Managed Setup" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
Oracle Enterprise Repository uses Oracle's Business Process Management (BPM) Tool to run the out-of-the-box automated workflows. While organizations can use the workflow engine of their choice, the Oracle Enterprise Repository includes a limited use license of Oracle BPM. For more information about Oracle BPM, see
-
http://www.oracle.com/us/technologies/bpm/index.html to download Oracle BPM.
-
https://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E13154_01/bpm/docs65/installguide/index.html to install Oracle BPM.
Oracle Enterprise Repository uses Oracle's Business Intelligence (BI) Publisher as its reporting engine. The Oracle Enterprise Repository includes a limited use license of Oracle BI Publisher. For more information about Oracle BI Publisher, see
-
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/bi-publisher/downloads/index.html to download Oracle BI Publisher.
-
https://download.oracle.com/docs/html/B25825_01/toc.htm to install Oracle BI Publisher.
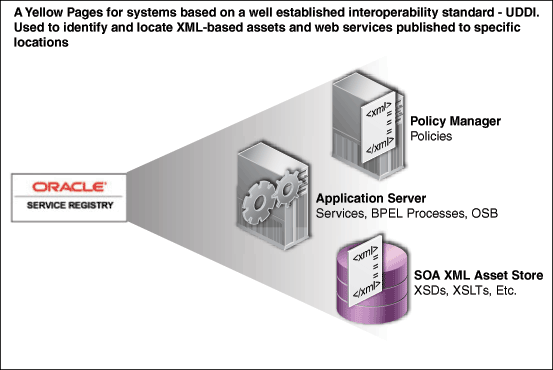
1.2.2 Oracle Service Registry
Oracle Service Registry is a feature rich UDDI version 3 compliant service registry that provides standards-based interoperability and forms the runtime interface of the Repository. It provides service binding and runtime location transparency, federation of runtime metrics for closed loop governance, and access to an appropriate service version based on the environment. You can look up services published to the registry at runtime for dynamic service location. For more information, see http://www.oracle.com/technology/products/soa/registry/index.html.
Oracle Service Registry also serves as an integration point for runtime tooling:
-
Oracle Service Bus subscribes to new or modified assets.
-
Composite applications can discover updated endpoints and WSDL locations.
-
Runtime monitoring tooling, such as Amberpoint, can publish metrics to Oracle Service Registry, which are then propagated back to Oracle Enterprise Repository.
Note:
Oracle Enterprise Manager SOA Management Pack Enterprise Edition provides runtime metrics directly to the Enterprise Repository.
Registries can also be federated. System configurations with a single logical repository, and multiple registries (one for each major environment or stage in the lifecycle) are common, as shown in Figure 1-3.
The following resources can help you when installing the Service Registry:
-
For information about downloading the Oracle Service Registry, see http://www.oracle.com/technologies/soa/service-registry.html.
-
For information about installing the Oracle Service Registry into each major environment or stage in the lifecycle, see https://download.oracle.com/otndocs/tech/soa/OSR11gR1ProductDocumentation.pdf.
-
For information about running Oracle Service Registry in a clustered environment, see http://www.oracle.com/technology/tech/soa/uddi/osr_cluster_config.pdf.
-
The Oracle Enterprise Repository and the Oracle Service Registry are tightly integrated. The Oracle Registry Repository Exchange Utility synchronizes Oracle Enterprise Repository and Oracle Service Registry bi-directionally so metadata can flow in either direction through the utility.
1.2.3 Oracle Web Services Manager
Oracle Web Services Manager (OWSM) allows IT management to centrally define security policies that govern Web services operations (such as access policy, logging policy, and load balancing). Those policies can be applied to Web services in a heterogeneous environment without modification. In addition, Oracle Web Services Manager collects and monitors statistics to ensure quality of service, uptime, and security and displays them in a Web dashboard.
OWSM provides end-to-end security between the service consumer and the service provider by deploying client and server agents within the container itself. The OWSM Policy Manager provides client and server agents with central policy information, ensuring that the consumer can apply the correct policies even when the service security measures are updated.
The Oracle Web Services Manager is part of Oracle's SOA Suite. If you have installed Oracle SOA Suite, then OWSM is also installed.
-
For more information about downloading the Oracle Web Services Manager, see http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/testcontent/index-085253.html.
-
For more information about installing the Oracle Web Services Manager, https://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E12524_01/web.1013/e12576/toc.htm.
-
For more information about configuring the Oracle Web Services Manager, https://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E12839_01/web.1111/b32511/toc.htm.
1.2.4 Oracle Enterprise Manager Grid Control
Oracle Enterprise Manager SOA Management Pack Enterprise Edition builds upon the core Oracle Enterprise Manager Grid Control (Grid Control) product and provides operational management of complex SOA environments.
Grid Control is a Web-based system for central management of Oracle products, host systems, and applications, as shown in Figure 1-4. It allows management of various Oracle products through packs and plug-ins. The Management Pack provides discovery and configuration management of deployed SOA artifacts.
Figure 1-4 Oracle Enterprise Manager Grid Control

Description of "Figure 1-4 Oracle Enterprise Manager Grid Control "
Grid Control also provides dynamic discovery and service-level monitoring of all artifacts deployed within a Java Application Server. Administrators can confirm that what is running in a particular SOA environment is exactly as defined at design time.
Grid Control collects statistics that include latency, invocation counts, and exceptions for each service component. It then aggregates and stores them to provide a rich dashboard of metrics presented across a user selected set of time-periods. You can establish service-level objectives at each SOA architecture layer. You can set cautionary and violation level thresholds, which when breached over a defined period trigger alerts sent over standard protocols.
1.2.5 Oracle Enterprise Gateway (OEG)
Oracle Enterprise Gateway (OEG) is designed to secure SOA deployments on-premise, across domain boundaries, or in the cloud. It does this by providing an easier way to secure, accelerate, and integrate XML and other types of data. As a result it can significantly lower integration costs, lower costs of ownership, and reduce deployment risks. Oracle Enterprise Gateway also offers rich integration with many identity and access management platforms, and helps streamline regulatory compliance through authentication, authorization, and audit capabilities. OEG offers the following capabilities:
-
DMZ-class security and comprehensive threat defense system for SOA and cloud environments
-
Ultrafast XML processing, allowing SOA and cloud applications to offload resource-intensive, XML-based operations
-
Open and standards-based, certified on Oracle Fusion Middleware and non-Oracle technologies
1.3 Design-time Tooling
You can configure the Governance infrastructure to interoperate with design-time tooling. This section contains the following topics:
1.3.1 Version Control Systems
Oracle Enterprise Repository is not a Version Control system; it is a metadata management system. However, Oracle Enterprise Repository can be tightly integrated with existing version control systems. When developers need access to the physical artifact (such as an XSD or WSDL file) of an asset, Oracle Enterprise Repository delivers a copy of the code from the version control system.
This benefits your organization in several ways:
-
When no behavioral change is required, the organization maintains its existing version control practices.
-
When Oracle Enterprise Repository serves as a single broker for all SCMs, the developers do not need access to multiple version control systems.
You can also connect to several Version Control Systems or Source Control Management Systems.
For more information about connectors, see "Oracle Enterprise Repository Connectors" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Integration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
-
The supported Version Control Systems or Source Control Management Systems are as follows:
-
ClearCase
-
Download the connector
-
Access the documentation
For more information about ClearCase, see "ClearCase Integration" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Integration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
-
-
Harvest-HTTP
-
Download the connector
-
Access the documentation
For more information about Harvest-HTTP, see "Harvest-HTTP Repository Host Integration" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Integration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
-
-
Serena ChangeMan
-
Download the connector
-
Access the documentation
For more information about ChangeMan, see "Serena ChangeMan Integration" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Integration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
-
-
1.3.2 Integrated Development Environments (IDE)
Oracle Enterprise Repository makes governance as invisible as possible to developers through tight integration with the development environment (IDE). Through the IDE, developers can search for relevant assets, evaluate asset metadata, and select assets that they would like to reuse. Oracle Enterprise Repository can then harvest their completed work, automatically generating assets and relationships.
Integrating with Supported IDEs:
-
JDeveloper (new in Oracle Enterprise Repository 11g)
-
Download the plug-in
-
Access the documentation
For more information about Oracle JDeveloper, see "Configuring Oracle JDeveloper" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Integration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
-
-
Eclipse
-
Download the plug-in
-
Access the documentation
For more information about Eclipse, see "Configuring Eclipse" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Integration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
-
-
VS. NET
For more information about VS .NET, see "Configuring VS .NET" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Integration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
1.3.3 Document Repositories and File Stores
Sometimes developers need additional information to understand an asset's functions and behaviors. This information might be in use case documents, architecture documents, test cases, test results, and so on. Such documents are typically stored in version control systems, repositories, and file stores. However, you can create a link from the Enterprise Repository asset to the associated documents so developers can seamlessly access them.
This feature requires no connector or plug-in. For more information, see "Configure Artifact Stores" in Oracle Fusion Middleware User's Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
1.3.4 Design-time Policy Validation
Oracle offers OWSM for runtime security policy management and enforcement. In addition, Oracle Enterprise Repository offers native policies to communicate design-time and development requirements to development teams. Policies might include:
-
Corporate quality standards and guidelines
-
Asset naming conventions
-
Performance targets
Policies applied to assets communicate design and development requirements and help administrators enforce compliance with governance, architecture, and other organizational standards. For example, a policy might articulate corporate quality standards, identifying the platforms that an asset should run on and acceptable defect density rates.
Oracle Enterprise Repository's native policies can be validated manually by a Subject Matter Expert or programmatically through third-party tooling, such as Parasoft and WebLayers.
To use Oracle Enterprise Repository's native policies:
-
Activate the Policy Management Feature
-
Create a Policy Type
-
Add the Policy Assertion Element to the Policy Type
-
Create a Policy
-
Add the Applied Asset Policies Element to a Type
-
Apply a Policy to an Asset
-
View Policy Status
-
Validate Policy Assertions
For more information about configuring Oracle Enterprise Repository's native policies, see "Configuring Policy Management" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
For more information about validating Oracle Enterprise Repository native policies using third-party tooling, see http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/middleware/repository/.
1.4 Runtime Tooling
You can configure the Governance infrastructure to interoperate with runtime tooling. This section contains the following topics:
1.4.1 SOA Suite Runtime MetaData Store (MDS)
MDS stores runtime metadata and configuration information used by Oracle Fusion Middleware, including Oracle SOA Suite. Oracle Enterprise Repository can harvest and display metadata from MDS. Oracle Enterprise Repository provides Oracle SOA Suite with visibility into the service endpoints. Oracle Enterprise Repository maintains references to externally hosted artifacts that reside in an HTTP server, Web based Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WEBDAV), or repository such as MDS.
The best practice is hosting all shared runtime metadata on a single MDS instance for access by all SOA infrastructures.
For more information about harvesting assets and metadata from MDS, see "Configuring and Using Automated Harvesting in Design-time and Runtime Environments" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
1.4.2 Testing Tools
Because of the number of Web Service testing tools on the market, there is no single out-of-the-box testing tool connector. Instead, use the Repository Extensibility Framework (REX) to integrate with the testing tool of your choice. REX is a Web Services API for programmatic integration into Oracle Enterprise Repository. It is based on accepted industry standards, and designed with a focus on interoperability and platform independence. REX uses Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Web Services described by the Web Services Description Language (WSDL v1.1). This allows clients to interact with Oracle Enterprise Repository using any platform and any implementation language that supports Web Services.
When integrating with testing tools, the following approach is recommended:
-
When a Web Service asset in Oracle Enterprise Repository reaches a particular lifecycle stage, an event is triggered.
-
The event initiates retrieval of the Web Service code from the location indicated in Oracle Enterprise Repository.
-
The testing tool runs the appropriate tests for the lifecycle stage.
-
The test results are posted to Oracle Enterprise Repository as metadata or as a document link attached to the Web Service asset.
To view the REX API calls that can be used to execute the previous sequence, see "Repository Extensibility Framework" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Integration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
1.4.3 Build Tools/Scripts
One of the goals of governance is visibility into assets as they move throughout the lifecycle. To harvest information about assets at build time, integrate the Oracle Enterprise Repository Harvester into build tools and scripts, including Ant and the WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST). WLST is a command-line scripting interface that manages WebLogic Server instances. WLST supports Oracle Service Bus and SOA Suite.
For more information about WLST, see Oracle Fusion Middleware WebLogic Scripting Tool Command Reference.
You can invoke Oracle Enterprise Repository Harvester from WLST to ensure that all deployment information is stored in Oracle Enterprise Repository at deployment time. For more information about embedding the Harvester into Build Tools and Scripts, see "Configuring and Using Automated Harvesting in Design-time and Runtime Environments" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
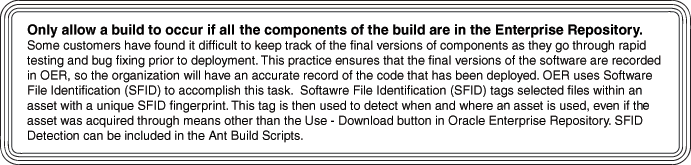
Governance practices can also be enforced at build time. Figure 1-5 shows an example of an Oracle customer's governance practices.
For more information about SFID, see "Configuring Automated Usage Detection" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
1.4.4 Defect Tracking Systems
Defect Tracking Systems track problems with assets after they are deployed to the runtime environment. When a developer considers whether to reuse an asset, it is helpful to view all of the defects associated with that asset.
Oracle Enterprise Repository can integrate with defect tracking systems and has an adapter that supports integration with ClearQuest. You can use a ClearQuest store in Oracle Enterprise Repository. For more information about integration with ClearQuest, see "ClearQuest Integration" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Integration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.
1.4.5 Federation
Oracle Enterprise Repository can be logically federated: the repository's Role Based Access controls can ensure that different groups across the organization have access to their assets, and that everyone can see enterprise-wide assets. Oracle Enterprise Repository does not have any out-of-the-box support for physical federation: individual instances of Oracle Enterprise Repository serve the needs of individual groups. While it is possible to build a federated structure using Oracle Enterprise Repository, Oracle does not recommend it.
For more information about setting up your Oracle Enterprise Repository instance to support logical federation, see "Advanced Role-based Access Control" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Guide for Oracle Enterprise Repository.