| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Solaris Cluster Geographic Edition System Administration Guide Oracle Solaris Cluster 4.1 |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Solaris Cluster Geographic Edition System Administration Guide Oracle Solaris Cluster 4.1 |
1. Introduction to Administering the Geographic Edition Software
3. Administering the Geographic Edition Infrastructure
4. Administering Access and Security
5. Administering Cluster Partnerships
7. Administering Protection Groups
8. Monitoring and Validating the Geographic Edition Software
9. Customizing Switchover and Takeover Actions
Introduction to Geographic Edition Script-Based Plug-Ins
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Script-Based Plug-Ins
Script-Based Plug-In Architecture
Property Descriptions for Script-Based Plug-Ins
Protection Group Properties - Overview
Replicated Component Properties - Overview
Protection Group Property Descriptions
start_replication_script Property
stop_replication_script Property
Internals for Script-Based Plug-Ins
Plug-In Script Functional Requirements
Plug-In Script Argument Validation
Standardized Script Command-Line Arguments
Script-Based Plug-In Replication Resource Groups and Resources
Protection Group Status Mapped from Replication Resource Status
How Geographic Edition Handles Password Properties
A. Standard Geographic Edition Properties
B. Legal Names and Values of Geographic Edition Entities
C. Disaster Recovery Administration Example
E. Troubleshooting Geographic Edition Software
F. Deployment Example: Replicating Data With MySQL
Geographic Edition supports Availability Suite software, EMC Symmetrix Remote Data Facility (SRDF), and Sun ZFS Storage Appliance. However, the creation of these modules requires detailed knowledge of both the replication software and the internals of the Geographic Edition product. Geographic Edition uses the common agent container with a number of Java management beans (MBeans) that form the interface for the Geographic Edition monitoring and management infrastructure and the replication control software. For more information about Availability Suite, see the dscfg(1M) man page.
By providing a more generic interface module analogous to the Oracle Solaris ClusterGeneric Data Service (GDS), the Geographic Edition script-based plug-In enables you to rapidly integrate additional replication technologies by supplying a few interface scripts to fulfill the necessary control functions. This capability frees you from needing to learn the internals of Geographic Edition or needing any knowledge of Java technology or MBeans. Instead, you can focus on the replication technology you need to protect your enterprise data. For more information on the Generic Data Service, see Chapter 10, Generic Data Service, in Oracle Solaris Cluster Data Services Developer’s Guide.
For simplicity, the term script is used throughout this document to represent any compiled binary or script-based executable.
This section provides the following information:
The main advantage of using the script-based plug-in comes from reducing the barriers to implementing new replication mechanisms. Rather than spending time learning about the Java, JMX, MBeans, or common agent container technologies, you can focus on the critical logic needed, for example, to set up a replicated configuration or change the direction of the replication flow.
The disadvantage of this approach stems from the very generic nature of the plug-in that makes it so easy to use. Generic plug-ins lack some of the tight integration that a custom module can offer. For example, the arguments that you supply on the command line to a script-based plug-in configuration are at the script argument level rather than the highly specific replication variable level. So, whereas the Geographic Edition Oracle Data Guard module has separate, specific arguments for properties like standby_type and replication_mode, an equivalent script-based plug-in version would pass these properties and their value as part of a single, anonymous bundle to a script. The script would need to determine the arguments and whether each argument is valid.
The disadvantage of this approach stems from the very generic nature of the plug-in that makes it so easy to use. Generic plug-ins lack some of the tight integration that a custom module can offer. For example, the arguments that you supply on the command line to a script-based plug-in configuration are at the script argument level rather than the highly specific replication variable level. So, whereas the Geographic Edition SRDF module has built-in arguments for the Symmetrix ID that the Geographic Edition browser interface prompts for separately, an equivalent script-based plug-in version would pass the value as one of a bundle of arguments to a script. The script would need to determine the arguments and whether each argument is valid.
Unlike other replication modules, the script-based plug-in is generic and capable of supporting a wide range of replication technologies. Consequently, the script-based plug-in does not contain a specific set of scripts to control a particular piece of replication software. Instead, it provides a framework for integrating a set of scripts or programs that you, the developer, write and that a system administrator will later use.
This flexibility means that the script-based plug-in cannot directly enforce the inclusion or exclusion of application resource groups in a protection group. Furthermore, the script-based plug-in cannot even restrict the node lists of these entities, nor the relationship with the replication resource group that contains the replication resource needed to supply the replication status, or indeed any other resource group that is required.
The following figure outlines the relationships between the various components within the Geographic Edition system. Commands issued through the command-line interface (CLI) call the Geographic Edition modules through their relevant common agent container modules. These modules then call out to shell scripts to perform specific tasks. Once a protection group has been instantiated, the replication resource, representing a particular replicated object entity, reports its status back to the module through the event framework. This process enables the overall replication status to be reflected in the Geographic Edition output on the command line.
Figure 10-1 Script-Based Plug-Ins Framework
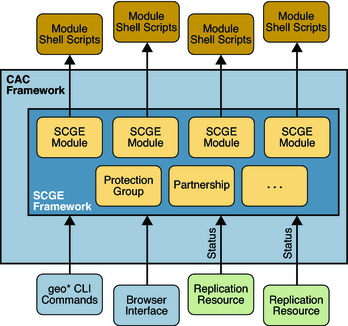
The script-based plug-in developer therefore is free to govern the relationships between any or all of these entities: application resource group, data replication resource group, and replication status resource group. As the following figure shows, the only constraints are the requirements to have a named replication resource group per protection group and a named replication resource per device group or replicated component.
Figure 10-2 Script-Based Plug-In Replication Resource Group
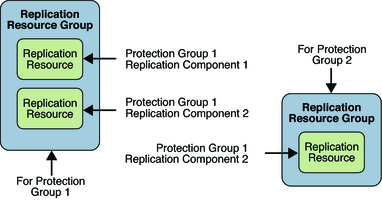
The consequence of these requirements is that the administrator must provide script-based plug-in configuration file for each protection group that is accessible from all cluster nodes and that details which nodes pertain to each script-based plug-in configuration. The purpose of this configuration file is to ensure that any subsequent developer-written scripts are called on one or more nodes on which the service is present.
In addition to the standard protection properties, the script-based plug-in enables the developer to name one or more scripts to perform the actions required by the Geographic Edition framework. These actions fall into two separate groups: those actions that operate at a per protection level and those actions that operate at a per replicated component level.
There are no inherent restrictions regarding what you can do when creating script-based plug-in modules. However, using the script-based plug-in does not enable you to circumvent or overcome any inherent limitations present in the replication technology you intend to use.
The preferred method for creating a script-based plug-in module is to use the Generic Data Service (GDS) toolkit, which contains the extensions for the script-based plug-in.
Alternatively, the scripts can be written using an integrated development environment (IDE), such as the NetBeans IDE. For more information on NetBeans IDE, see NetBeans IDE.