| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Directory Server Enterprise Edition 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.7.0) Part Number E28972-01 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Directory Server Enterprise Edition 11g Release 1 (11.1.1.7.0) Part Number E28972-01 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
Directory Service Control Center (DSCC) is a console that enables you to manage Directory Servers and Directory Proxy Servers using a web browser. This chapter includes the following topics:
See the Deployment Planning Guide for Oracle Directory Server Enterprise Edition for information on the role of the DSCC in the ODSEE administration model and how the DSCC works.
You must have administrator privileges to log into DSCC. The following table compares the various DSCC administrators and their privileges.
Table 29-1 Comparison of Administrators
| Administrator | Description | Privileges |
|---|---|---|
|
Directory Manager |
The LDAP superuser for a Directory Server. The Directory Manager account is established within a directory server at the time of instance creation, and is stored in the local |
|
|
Directory Administrators Group |
|
Has the same privileges as the Directory Manager but is subject to access controls, password policies, and authentication requirements. |
|
Directory Service Manager |
|
Has the privileges assigned to the Directory Administrators Group. |
|
Administrative User |
|
Privileges must be defined using ACIs. |
The Directory Service Managers page contains a list of administrators who can manage Oracle Directory Servers and Oracle Directory Proxy Servers in the DSCC registry. To view the Directory Service Managers page, go to Settings > Directory Service Managers.
When you install DSCC, a default Directory Service Manager is automatically created for you and defined in the DSCC registry. By default, this Directory Service Manager is named admin(default) and has unlimited access on the Directory Server. The following figure displays admin(default) and its DN:
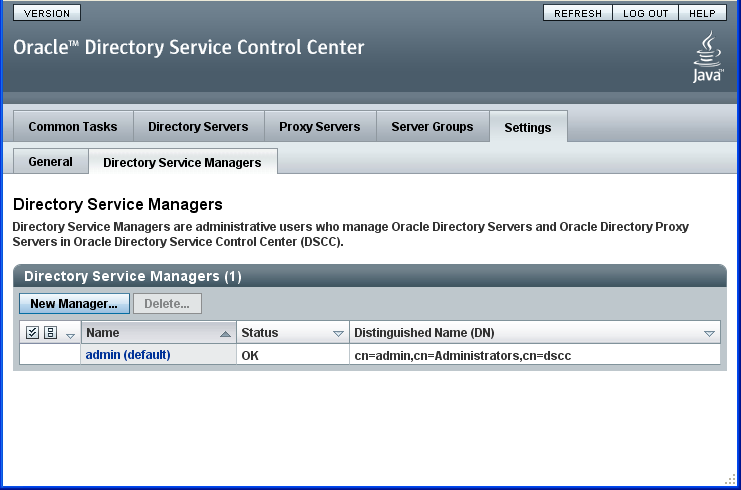
The DN for admin(default) is cn=admin,cn=Administrators,cn=dscc. As soon as you register a server instance in DSCC, admin(default) can manage the newly registered server instance.
The Directory Service Manager named admin(default) is not related to any user located in the Directory Server.
A Directory Service Manager logs into DSCC using a Directory Server Manager DN and password. A Directory Service Manager password can be configured by only another Directory Service Manager using the Settings > Directory Service Manager page.
You can create more than one Directory Service Manager that has the same unlimited server access as the admin(default). This is useful when you want more than one administrator to have unlimited access to all Directory Servers and Directory Proxy Servers, but you want each Directory Service Manager to know and to use a different password at login.
In the DSCC, go to Settings > Directory Service Managers > New Manager.
In the New Directory Service Manager page, provide the following information:
Type a username the administrative user will use to log into DSCC. This is the name that will be displayed in DSCC.
Choose "Create a Directory Service Manager" to create a Directory Service Manager that has privileges identical to privileges of the admin(default) that is already registered with the DSCC on the local machine.
Click OK.
The new Directory Service Manager is automatically created with default privileges, and added to the Directory Administrators Group.
To reset the Directory Service Manager password, use DSCC, as described in this procedure.
Access DSCC as described in Accessing DSCC.
Click the Settings tab, then choose Directory Service Managers.
Click the name of the Directory Service Manager for which you want to change the password.
In the properties screen, enter the new password.
Confirm the new password by typing it again in the Confirm Password field. Click OK to save your changes.
You can designate a specific user, whose entry is contained in the Directory Server, to act as a Directory Service Manager. A user who acts as a Directory Service Manger is called an Administrative User.
When you designate an Administrative User, you must configure the server to give this individual the appropriate privileges to change server configuration. For example, through ACIs, you can give the Administrative User the same unlimited access as the Directory Service Manager named admin (default).
The new Administrative User can then log in to DSCC using his or her own username or DN.
Note:
Unlike the Directory Service Manager, an Administrative User does not have access to Directory Proxy Server nor to any server group (which may contain a mix of Directory Server and Directory Proxy Server instances).
You must enable the Administrative User feature before you can make DSCC accessible to Administrative Users.
Before You Begin. You must create and register a DSCC agent before you can enable the Administrative Users feature. See "Set Up the Administration (DSCC) Host" in the Installation Guide for Oracle Directory Server Enterprise Edition.
To enable the User Directory Service Manager, run the following command:
# install-path/bin/dsccsetup enable-admin-users
To disable the User Directory Service Manager, run the following command:
# install-path/bin/dsccsetup disable-admin-users
When you create an administrative user, you specify an actual person in the Directory Server. You can then create ACIs to give the new administrative user select Directory Service Manager rights and privileges.
In the DSCC, go to Settings > Directory Service Managers > New Manager.
In the New Directory Service Manager page, provide the following information:
Type a username the administrative user will use to log into DSCC. This is the name that will be displayed in DSCC.
Choose "Create an Administrative User" to choose a user from the Directory Server, and to assign that user limited Directory Service Manager privileges.
Note:
The User Directory Service Manager feature must be enabled before you can create an administrative user. See Section 29.1.3, "To Enable the Administrative Users Feature" for more information.
Provide the following information, then click OK.
Host. Choose the hostName:portNumber of the Directory Server that contains the entry for the user you want to designate as a Directory Service Manager.
User DN. Specify the user DN as it exists in the Directory Server. You can type the user DN, or click Browse to locate the user DN in the DIT.
Configure the administrative user privileges.
The administrative user must already be created. See Section 29.1.4, "To Create an Administrative User."
In DSCC, on the Directory Servers tab, click the hostName:portNumber of the Directory Server that contains the user entry specified when the administrative user was created.
Click Entry Management > Access Control.
In the Access Control Settings page, click "New ACI From Wizard."
Use the ACI Wizard to create an ACI for the administrative user.
You can base the administrative user ACI on an existing ACI, or your can create a new ACI. In this example, the user abarnes is given the same privileges as the Directory Service Manager named admin(default).
Click Directory Servers > hostname:portnumber > Entry Management > Access Control.
In the Access Control Settings list, click the name of the ACI upon which you will base the ACI for the Administrative User.
For this example, click the ACI named "Enable full access for Directory Services Managers." The allow(all) component of this ACI provides full access to Directory Server. Copy the contents of the ACI Syntax field, then click Cancel.
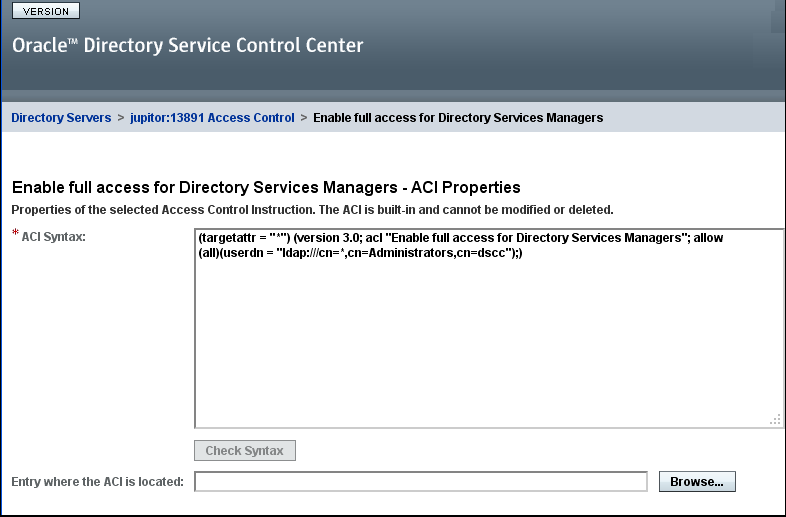
In the Access Control Settings list, click New ACI from syntax.
Use the ACI Wizard to create a new ACI for the administrative user. In this example, the Directory Service ACI from the previous step is pasted into the ACI Syntax field.
Modify the ACI to work for the Administrative User.
In this example, the ACI name and the user DN were customized for the user abarnes.
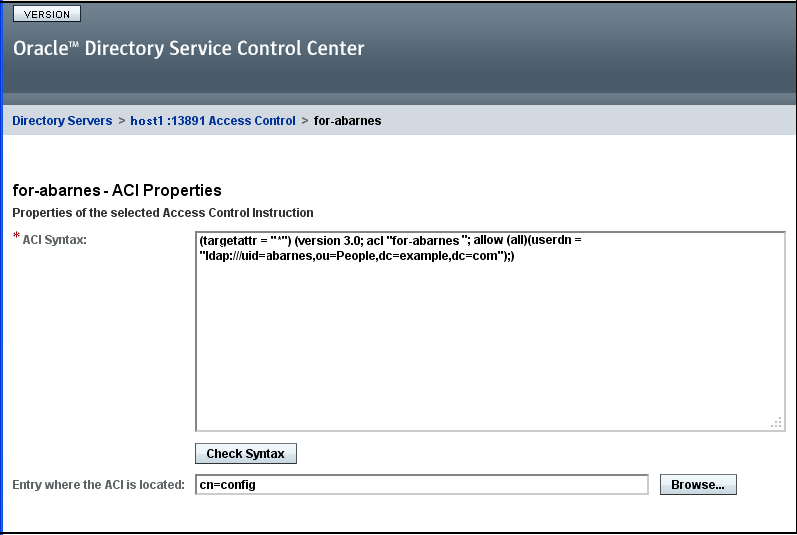
For more examples of ACIs you can create, see Section 6.2, "Access Control Usage Examples."
Ensure that DSCC has been correctly installed, as described in Chapter 2, Installing Directory Server Enterprise Edition, in Installation Guide for Oracle Directory Server Enterprise Edition.
Access DSCC directly in your preferred application server by typing the DSCC host URL. DSCC host URL can be any of the following depending on the configuration of your application server.
https://hostname:8181/dscc7
or
http://hostname:8080/dscc7
where hostname is the system on which you installed the DSCC software.
Log in to DSCC.
You are now logged into DSCC and at the Common Tasks tab.
If you experience any difficulty accessing DSCC, see Chapter 8, Troubleshooting DSCC Problems, in the Troubleshooting Guide for Oracle Directory Server Enterprise Edition.
Navigate by using the tabs.
The Common Tasks tab contains shortcuts to commonly used windows and wizards.
The Directory Servers tab displays all Directory Servers managed by DSCC. To see more options for managing and configuring a particular server, click the server name.
The Proxy Servers tab displays all Directory Proxy Servers managed by DSCC. To see more options for managing and configuring a particular server, click the server name.
Figure 29-2 List of Directory Servers On the Servers Sub Tab
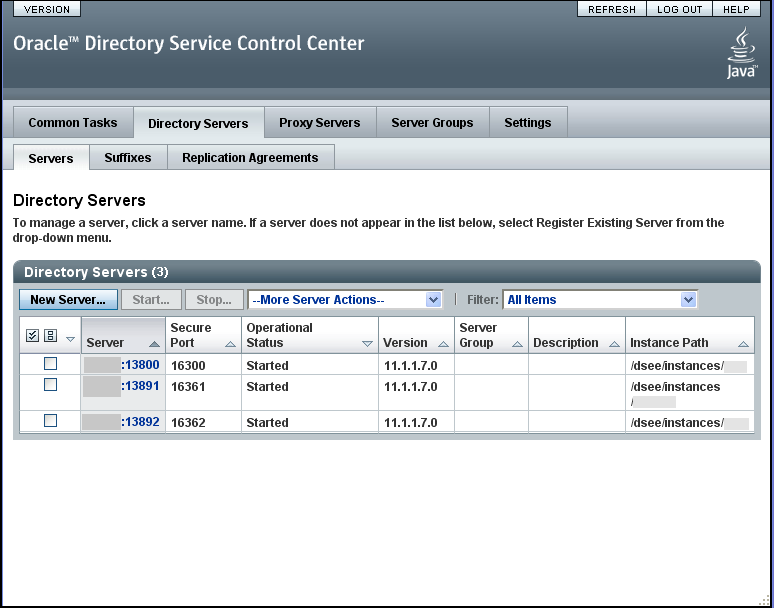
The following tab interfaces comprise the DSCC console:
The Common Tasks tab is the first interface that you see when opening DSCC. It contains links to commonly used administrative tasks, such as searching directory data, checking logs, and managing servers.
The Directory Servers tab lists all directory servers registered in DSCC. For each server, you can see the server status and instance path, which shows where the instance is located.
When you click a server name, you see another window with a different set of tabs that relate only to that server.
Figure 29-4 List of Directory Servers On the Servers Sub Tab

The Proxy Servers tab lists all the directory proxy servers that are registered in DSCC. For each server, you can see the server status and the server instance path, which shows where the instance resides.
When you click a server name, you see another window with a different set of tabs that relate only to that server.
The Server Groups tab enables you to assign servers to groups, to make server management easier. If you have numerous servers, you can use filters to display only the servers in a certain group. You can also copy the server configuration (for example index or cache settings) from one server to all other servers in a group.
This tab displays DSCC port numbers and allows you to create and delete Directory Service Managers.
Following are the commands that help you work with DSCC.
With the dsccagent command, you can create, start, manage DSCC agent instances. For more info, see dsccagent in the man pages.
Note:
DSCC agent daemon always runs in the JVM delivered by ODSEE. Setting the JAVA_HOME property does not change the JVM used by the daemon.
The dsccsetup command helps in setting up DSCC. When used with appropriate subcommands, the dsccsetup command performs the operations such as creating the DSCC registry, initializing DSCC after installation, and registering local agents of the administration framework.For more information, see dsccsetup in the man pages.
The dsccreg command handles registering, de-registering, and listing registered Directory Server instances within a target DSCC.
For more information, see dsccreg in the man pages.
The ODSEE online help model is changed from previous releases. This release provides the following online help resources:
Context-sensitive help for the page you are currently using.
From within a wizard, click the Help tab.
Direct link to the Oracle Directory Server Enterprise Edition Documentation Library online at Oracle Technology Network.
Click the Help button on the top right corner of the screen. You can also click Documentation link on the Common Tasks tab.
For information about troubleshooting DSCC, see Chapter 8, Troubleshooting DSCC Problems, in the Troubleshooting Guide for Oracle Directory Server Enterprise Edition.