 PeopleSoft Activity-Based Management Overview
PeopleSoft Activity-Based Management Overview
This chapter provides an overview of Activity-Based Management and discusses:
Business processes.
Integrations.
Implementation.
Tools for building models.
 PeopleSoft Activity-Based Management Overview
PeopleSoft Activity-Based Management Overview
Building Activity-Based Management models is an investment that you make to better understand costs and profitability. Strategic analysis, incisive cost and profitability analysis, and reliable decision support are the foundation of critical business decisions that keep you ahead of the competition. Accurate, well-managed costing information can affect pricing of goods and services, budget outlays, profitability analysis, and other business processes.
Activity-Based Management enables managers to analyze the real costs of business processes for better cost and profitability management. Without it, managers are forced into a guessing game to determine where they make money and how much things really cost.
Activity-Based Management was developed in tandem with leading academics and goes beyond traditional accounting methods to deliver tools to support strategic and operational decision making. It provides the business intelligence that you need to answer pressing business questions about your organization's activities, such as:
What are the costs of serving my customers?
Which customers, products, or channels are the most profitable?
Where are the best opportunities to reduce costs?
In what products or services should we divest or invest?
Activity-Based Management does not arbitrarily allocate costs. It traces overhead based on the cause and effect of business activities. An Activity-Based Management model maintains the relationship of activities to costs. This model is a complete set of rules used to define individual activity-based costing model objects and their relationship to your organization's financial management systems. Activity-Based Management enables you to define models, process them, and then analyze the results to assess your organization's profitability.
The system assigns ledger amounts (from your general ledger, for example) to resources. Resources are the economic elements used in the performance of activities. They can be people, facilities, or any other expenses such as supplies or travel.
Ledger mappers provide a process by which you relate expense data from a ledger to resource objects. Activities consume resources and drive costs to cost objects. Activities are the lowest-level definition of what you do as an organization; they serve as the foundation for measuring activity costs.
Cost objects represent cost information grouped by profitability dimensions such as products, customers, and channels. They are the final result of the activities performed by your organization.
Drivers are the means of assigning monetary amounts from one object to another throughout the model. Resource drivers link expenses as captured in the ledger to the activities performed. Activity drivers distribute the activity costs to cost objects.
Activity-Based Management is part of the Performance Management business process.
 PeopleSoft Activity-Based Management Business Processes
PeopleSoft Activity-Based Management Business Processes
The following process flow illustrates the Activity-Based Management business processes:
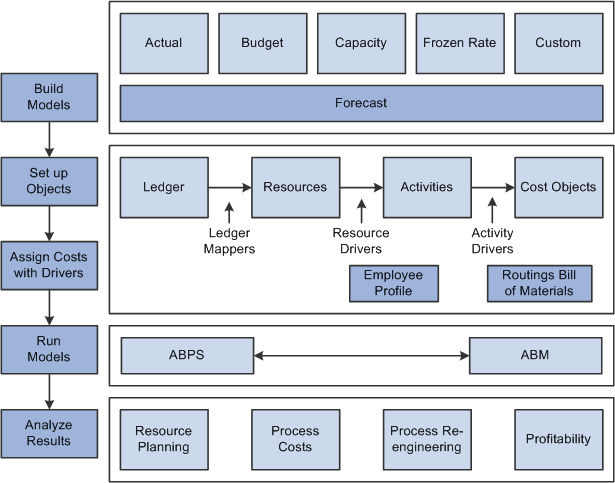
Activity-Based Management business process
Activity-Based Management is an analytical application that supports the measurement and management of your organization's current costs today and enables you to better plan for the future. It successfully integrates the proven computational power, leading-edge technology, and operational and financial information available with Activity-Based Costing/Management (ABC/M,) and Activity-Based Budgeting (ABB) theories and practices. This combination provides unrivaled strategic cost management and overcomes data integrity, transformation, and repeatability issues that troubled earlier cost management efforts. PeopleSoft Activity-Based Management aligns advanced cost management techniques with multidimensional profitability analysis and reporting and supports business process reengineering efforts. It provides a flexible, object-based solution that can easily adjust to your organization's unique business processes, activities, and data sources.
Activity-Based Management models are highly integrated with operational and financial information. They are flexible and easily adjusted to your organization's unique business processes, activities, and data sources. Activity Based Management can calculate five model types: Budget, Actual, Capacity, Frozen and Combination.
These model options enable you to:
Calculate variances from actual costs such as spending, volume, and capacity variances.
Attribute dollar amounts to entities that operate at greater or less than their capacity.
Maintain a more constant consumption pattern over time.
Link strategic choices with their operational impact.
Use a mix of rates, budget, actual, capacity, or frozen as necessary for your organization.
Perform unlimited 'what if' planning and simulation.
Activity-Based Management offers the following features to follow the general activity-based management business processes:
Understanding Activity-Based Management models, modeling components, and rate types
Using trees with Activity-Based Management
Setting up Activity-Based Management models and scenarios
Setting up attributes, cost of capital, resources, and ledger mapping rules
Setting up activities
Setting up cost objects
Setting up pointers, implicit pointers, and transaction pointers
Setting up drivers
Generating and maintaining models
Processing in Real-Time Activity-Based Management
Processing batch models
Reconciling your model and analyzing engine output
Using employee profile
Using reciprocal allocation looping
Using Activity-Based Planning and Simulation
Modeling for service-related industries
We discuss these business processes in the business process chapters in this PeopleBook.
 PeopleSoft Activity-Based Management Integrations
PeopleSoft Activity-Based Management Integrations
We discuss integration considerations in the implementation chapters in this PeopleBook.
Supplemental information about third-party application integrations is located on the My Oracle Support web site.
 PeopleSoft Activity-Based Management Implementation
PeopleSoft Activity-Based Management Implementation
PeopleSoft Setup Manager enables you to generate a list of setup tasks for your organization based on the features that you are implementing. The setup tasks include the components that you must set up, listed in the order in which you must enter data into the component tables, and links to the corresponding PeopleBook documentation.
Other Sources of Information
In the planning phase of your implementation, take advantage of all PeopleSoft sources of information including the installation guides, table-loading sequences, data models, and business process maps. A complete list of these resources appears in the preface in the PeopleBooks and the Online Library, with information about where to find the most current version of each.
See Also
PeopleBooks and the Online Library
PeopleTools PeopleBook: PeopleSoft Setup Manager
PeopleTools PeopleBook: PeopleSoft Component Interfaces
Enterprise Performance Management Fundamentals 9.1 PeopleBook

 Tools for Building Models
Tools for Building Models
Activity-Based Management also provides tools that let you quickly create a prototype model using the following engines:
Model Generator: Automates the setup of filter and constraint metadata as well as Activity-Based Management objects, drivers, and pointers.
Ledger Mapper Generator: Automates the setup of the ledger mapping rules for the resources.
The following table lists the model-building steps:
|
Step |
Reference |
|
1. Set up EPM Foundation. |
See Setting Up EPM Infrastructure, Business Rules, and Security. |
|
2. Set up the Model Generation Definition. |
|
|
3. Set up the Ledger Maps Generation Definition. |
|
|
4. Set up your Activity-Based Management model and specify the Ledger Maps Generation and Model Generation IDs. |
|
|
5. Start Activity-Based Management Model Generator. |
|
|
6. Start the Ledger Mapper Generator. |