 Understanding Enterprise Integration Technology
Understanding Enterprise Integration Technology
This chapter provides overviews of enterprise integration technology, integration with PeopleSoft HCM, PeopleSoft Campus Solutions or third-party HR data and data integrations. It also discusses how to:
Set up defaults for integrating customer and contact information.
Market-enable Company, Consumer, Site, and Contact enterprise integration points (EIPs).
Establish master ID databases.
Map message data to PeopleSoft CRM records and fields.
 Understanding Enterprise Integration Technology
Understanding Enterprise Integration Technology
This section discusses:
EIPs in PeopleSoft CRM.
PeopleSoft CRM foundation EIPs.
Application messages.
Data mapping for application messages.

 EIPs in PeopleSoft CRM
EIPs in PeopleSoft CRM
PeopleSoft CRM applications collaborate to manage and share data across your enterprise—from managing customers and workers to tracking inventory. They use EIPs primarily to integrate with:
PeopleSoft applications outside of CRM.
Third-party applications.
This diagram illustrates how PeopleSoft CRM works with other PeopleSoft applications to manage and share data across your enterprise:
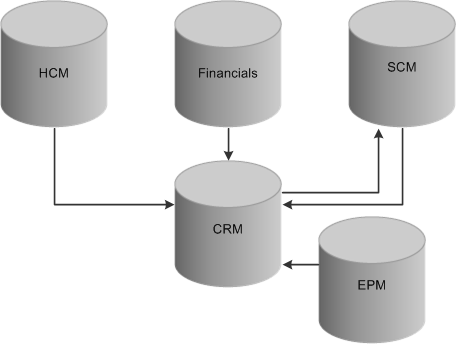
Integration between PeopleSoft databases
PeopleSoft CRM integrates with:
PeopleSoft HCM, which publishes employee and workforce data to the CRM database.
PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft Supply Chain Management (PeopleSoft SCM) for customer, contact, and product information.
This is a two-way integration.
PeopleSoft Enterprise Performance Management (PeopleSoft EPM), which publishes the data mining results from Customer Behavior Modeling for use in PeopleSoft CRM.
By taking advantage of the integration technology that PeopleSoft software provides and the existing integrations with PeopleSoft HCM, PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions, and PeopleSoft SCM, you can integrate with other third-party systems. PeopleSoft CRM achieves integration using Application Messaging, Business Interlinks, and the PeopleTools Integration Broker technology.
PeopleSoft CRM offers many ways of integrating with third-party applications. For example, if you send or publish a message to a third-party system, the system structures the data into a message and automatically delivers it to the destination location. You can also accept or subscribe to messages from third-party systems. The system validates incoming data, checking for errors before updating the system of record.
You can also send a synchronous request or reply transaction to a third-party system for processing and receive a real-time response.
Note. There is no CRM LOCATION_SYNC_EFF, LOCATION_FULLSYNC_EFF, DEPT_SYNC_EFF and DEPT_FULLSYNC_EFF message in CRM. The LOCATION_SYNC, LOCATION_FULLSYNC, DEPT_SYNC, and DEPT_FULLSYNC messages contain both the SYNC and EFF message structures.
See Also
PeopleTools 8.52: PeopleSoft Integration Broker PeopleBook
PeopleTools 8.52: PeopleSoft Integration Broker Testing Utilities & Tools PeopleBook

 PeopleSoft CRM Foundation EIPs
PeopleSoft CRM Foundation EIPsThis table lists the EIPs that are provided with PeopleSoft software for foundation PeopleSoft CRM:
|
EIP Name |
Description |
Message Name |
Direction of Integration |
Technology |
|
CUSTOMER |
Customer information is retrieved to PeopleSoft CRM from other external systems. |
CUSTOMER_SYNC CUSTOMER_FULLSYNC_EFF |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ SCM/external system |
Application Message |
|
CUSTOMER_COMPANY |
Synchronizes company information with other systems. |
CUST_COMPANY_FULLSYNC CUST_COMPANY_FULLSYNC_EFF CUST_COMPANY_SYNC CUST_COMPANY_SYNC_EFF |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ SCM/external system |
Application Message |
|
CUSTOMER_CONSUMER |
Synchronizes consumer information with other systems. |
CUST_CONSUMER_FULLSYNC CUST_CONSUMER_FULLSYNC_EFF CUST_CONSUMER_SYNC CUST_CONSUMER_SYNC_EFF |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ SCM/external system |
Application Message |
|
CUSTOMER_SITE |
Synchronizes site information with other systems. |
CUST_SITE_FULLSYNC CUST_SITE_FULLSYNC_EFF CUST_SITE_SYNC CUST_SITE_SYNC_EFF |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ SCM/external system |
Application Message |
|
WORKER |
Synchronizes worker information with other systems. |
WORKER_FULLSYNC WORKER_FULLSYNC_EFF WORKER_SYNC WORKER_SYNC_EFF |
PeopleSoft CRM –>external system |
Application Message |
|
CUSTOMER_CONTACT |
Synchronizes contact information with other systems. |
CONTACT_SYNC CONTACT_SYNC_EFF CONTACT_FULLSYNC CONTACT_FULLSYNC_EFF |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ SCM/external system |
Application Message |
|
PARTNER_PROFILE |
Synchronizes partner program information with other systems. |
PARTNER_PROFILE_SYNC PARTNER_PROFILE_FULLSYNC |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ SCM/external system |
Application Message |
|
BUSINESS UNIT TABLE FS |
Synchronizes financial business unit data. |
BUS_UNIT_FS_FULLSYNC BUS_UNIT_FS_SYNC |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ SCM |
Application Message |
|
TABLE SET CONTROL |
Synchronizes setID data. |
SETID_INITIALIZE |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ SCM |
Application Message |
|
COUNTRY TABLE |
Synchronizes country codes and address data to an external system. |
COUNTRY_FULLSYNC COUNTRY_SYNC |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ SCM/HCM/External system |
Application Message |
|
STATE TABLE |
Synchronizes state name, description, and abbreviation information with an external system. |
STATE_FULLSYNC STATE_SYNC |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ SCM/HCM/external system |
Application Message |
|
UNIT OF MEASURE |
Synchronizes units of measure. |
UOM_FULLSYNC UOM_SYNC |
PeopleSoft SCM/HCM/external system –> CRM |
Application Message |
|
CURRENCY CODE TABLE |
Transmits currency code data. |
CURRENCY_FULLSYNC CURRENCY_SYNC |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ SCM/external system |
Application Message |
|
MARKET RATES DATA |
Imports and synchronizes updated market rates. |
CURR_QUOTE_MTHD_FULLSYNC CURR_QUOTE_MTHD_SYNC MARKET_RATE_DEFN_FULLSYNC MARKET_RATE_DEFN_SYNC MARKET_RATE_FULLSYNC MARKET_RATE_SYNC MARKET_RATE_LOAD MARKET_RATE_INDEX_FULLSYNC MARKET_RATE_INDEX_SYNC MARKET_RATE_TYPE_FULLSYNC MARKET_RATE_TYPE_SYNC |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ SCM/HCM/external system |
Application Message |
|
DEPARTMENT TABLE |
Synchronizes departments across the enterprise. |
DEPT_FULLSYNC DEPT_SYNC |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ SCM/HCM/external system |
Application Message |
|
LOCATION TABLE |
Synchronizes location table data across the enterprise. |
LOCATION_FULLSYNC LOCATION_SYNC |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ SCM/HCM/external system |
Application Message |
|
PRODUCT |
Synchronizes product information with PeopleSoft SCM or third-party external systems. |
PRODUCT_FULLSYNC PRODUCT_SYNC PRODUCT_GROUP_FULLSYNC PRODUCT_GROUP_SYNC PRODUCT_SYNC_EFF |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ SCM/external system |
Integration Broker |
|
COMPETENCY TYPE |
Receives competency information from PeopleSoft HCM. |
CM_TYPE_FULLSYNC CM_TYPE_SYNC |
PeopleSoft CRM ← HCM |
Application Message |
|
COMPETENCY TABLE |
Receives competency and accomplishment details from PeopleSoft HCM. |
COMPETENCY_FULLSYNC1 COMPETENCY_SYNC1 |
PeopleSoft CRM ← HCM |
Application Message |
|
PERSON COMPETENCY |
Receives a person's competency data from PeopleSoft HCM. |
PERSON_COMPETENCY_FULLSYNC PERSON_COMPETENCY_SYNC |
PeopleSoft CRM ← HCM |
Application Message |
|
RATING MODEL |
Receives rating model data from PeopleSoft HCM. |
RATING_MODEL_FULLSYNC RATING_MODEL_SYNC |
PeopleSoft CRM ← HCM |
Application Message |
|
PERSONAL DATA |
Synchronizes personal data from PeopleSoft HCM. |
PERSON_BASIC_FULLSYNC PERSON_BASIC_SYNC |
PeopleSoft CRM ← HCM |
Application Message |
|
WORKFORCE DATA |
Synchronizes workforce data from PeopleSoft HCM. |
WORKFORCE_FULLSYNC WORKFORCE_SYNC |
PeopleSoft CRM ← HCM |
Application Message |
|
PERSON OF INTEREST DATA |
Synchronizes persons of interest (POIs) that do not have a job record from PeopleSoft HCM. POIs with a job record are synchronized in the WORKFORCE DATA EIP. |
PERS_POI SYNC |
PeopleSoft CRM ← HCM |
Application Message |
|
CALENDAR/TASK |
Fully synchronizes the calendar with Outlook, Lotus Notes, or other personal information manager (PIM). |
PIM_CONTACT_SYNC |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ Outlook/PIM |
Application Message |
|
CUSTOMER GROUP |
Synchronizes customer groups. |
CUSTOMER_GROUP_FULLSYNC CUSTOMER_GROUP_SYNC |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ SCM |
Application Message |
|
REPRESENTATIVE |
Synchronizes representative data with PIM. |
PIM_CONTACT_SYNC REP_SYNC |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ Personal Information Manager (PIM) |
Application Message |
|
PS GETID |
Retrieves customer IDs and contact IDs from other PeopleSoft systems. |
PSGETID |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ SCM |
XML link |
|
GET CUSTOMER VALUE |
Retrieves customer value/KPI information from PeopleSoft EPM and updates the BC (Business Contact) and the RB_CLAF_EPM_KIP (Key Performance Indicator) tables in the PeopleSoft CRM database. |
KP_KPI_ASMT_FACTS |
PeopleSoft CRM ↔ EPM |
Application Message |
|
GET BILLS FOR 360 DEGREE VIEW |
|
|
|
|
|
GET ACCOUNT RECEIVABLES FOR 360 DEGREE VIEW |
|
|
|
|
EIPs that support particular business processes and applications are documented in other PeopleSoft CRM PeopleBooks. The online EIP Catalog database lists, with technical details, the EIPs that PeopleSoft CRM uses.
See Also
Integrating with Fulfillment and Billing Systems
Integrating with PeopleSoft Applications

 Application Messages
Application MessagesEIPs that publish data to another database are available as both FULLSYNC and SYNC messages. FULLSYNC messages are designed for use at implementation time for setup information. Once a table has been set up, the SYNC messages allow for updates to that data.
Important! Some FULLSYNC messages are designed to fully replace the data through the use of the header message. To avoid losing existing data, turn off the header—the message refreshes the data by updating the existing data and adding any missing data.
As delivered, PeopleSoft EIP application messages are inactive.
To set up a delivered application message:
Activate the application message.
For inbound messages, activate the message subscription PeopleCode.
Set the associated message channel to Run mode.
Configure an existing message node or define a new message node.
Define asynchronous or synchronous transactions on the message node.
Define relationships to reconcile transaction parameters for routing, transmission type, message structure, or message content, if necessary.
See PeopleTools 8.52: PeopleSoft Integration Broker PeopleBook

 Data Mapping for Application Messages
Data Mapping for Application Messages
PeopleSoft CRM has the capability of subscribing to other PeopleSoft-application or third-party-application messages. Before PeopleSoft CRM can subscribe to a PeopleSoft EPM message or any third-party message, data mapping must occur between the source format and the destination format. To accommodate this data mapping, PeopleSoft CRM created a Data Mapping component. Using this component, you can perform data mapping for any single-level hierarchical message.
The integration between PeopleSoft EPM and CRM is currently the one place that uses this data mapping component. Before PeopleSoft CRM can receive key performance indicator (KPI) information through the KP_KPI_ASMT_FACTS application message from EPM, the application message data must be mapped to data fields that the CRM system recognizes. To assist with this integration, PeopleSoft provides a predefined data mapping structure sample.
Alternatively, data is inserted into RB_CLAF_EPM_KPI table via the KP_KPI_EPM terms subscription. This subscription creates terms for the Active Analytics Framework.
This table shows the predefined data mapping structure sample provided with PeopleSoft software to assist with integration between PeopleSoft CRM and EPM:
|
Message Name |
Record to Update |
Fields to Update Field/XML Tag |
Record Identification Field/XML Tag |
Message Row Identification XML Tag Name/XML Tag Value |
|
KP_KPI_ASMT_FACTS |
BC |
|
CUST_ID/OBJ_ID |
PF_OBJECT_TYPE/CUSTOMER MASTER |
See Also
Mapping Message Data to PeopleSoft CRM Records and Fields
 Integration with PeopleSoft HCM, PeopleSoft Campus Solutions or Third-Party
HR Data
Integration with PeopleSoft HCM, PeopleSoft Campus Solutions or Third-Party
HR Data
This section discusses:
Person Basic Fullsync and Person Basic Sync.
Workforce Fullsync and Workforce Sync.
Campus Solutions EIPs.
Pers POI Sync.
Customer Data Model EIP.
Implementation using Fullsyncs.
PeopleSoft CRM employs a number of EIPs to integrate the CRM Customer Data Model (CDM) with PeopleSoft HCM, PeopleSoft Campus Solutions, or another third-party system. The interdependent nature of these EIPs makes it very important that they are used correctly and in the proper sequence to ensure data quality.

 Person Basic Fullsync and Person Basic Sync
Person Basic Fullsync and Person Basic SyncThe Person Basic EIPs form the foundation of the CDM integrations. They are responsible for creating the Person object that is the building block of the CDM. Additional duties include the populating and updating of personal biographical data, National ID, and names. Finally, all creation and maintenance of contact methods (address, email, phone) are processed through the Person Basic EIPs.
Person Basic Fullsync versus Person Basic Sync
Person Basic Fullsync is designed as an initial load program to be used during system implementation to create new persons in the CDM. While it is possible to run Person Basic Fullsync more than once, it will not perform updates on existing person data or contact methods. Any existing person found in the fullsync message is skipped and written to a log file for review.
Once Person Basic Fullsync has been used for initial customer population creation, it should be deactivated and the incremental Person Basic Sync message activated. Person Basic Sync handles the creation of persons going forward as well as any subsequent updates to personal biographical data, National ID, names, and contact methods.
Search Match
Search Match is a utility that validates whether a new person being added to the CDM via an import or EIP actually already exists in CRM in order to avoid data duplication. The matching is based on a set of predefined criteria set in the Search Match configuration. Person Basic Sync is compatible with Search Match and, if enabled, will perform the matching function. Person Basic Fullsync, however, is not compatible with Search Match.
See Using Search/Match with PERSON_BASIC_SYNC.
Contact Methods and Person Start Date
When the Person Basic EIPs create a new Person object, the new person is given the default Individual role type. It is important for data integrity that any contact methods created for the person do not have a start date that is earlier than the start date of the individual role. The possibility of this issue often arises in instances of a legacy data conversion where an extensive history of person data is being loaded into CRM for the first time. To handle this scenario, a comparison algorithm is performed using the inbound data so that the start date of the person object is set to the earliest of these three dates: the effective date of the PERSON_DATA_EFFDT record, the original hire date, and the earliest contact method effective date.
Example:
|
Person_Data_Effdt.Effdt |
Person_Data_Effdt.Orig_Hire_Dt |
Earliest Contact Method Effdt |
Person Object, Individual Role Start Date |
|
6/20/2010 |
5/01/2010 |
5/02/2010 |
05/01/2010 |
|
6/20/2010 |
Null |
04/01/2010 |
04/01/2010 |
|
6/20/2010 |
6/15/2010 |
07/01/2010 |
06/15/2010 |
Note. The audit Date Stamp on the CDM entry will reflect the day and time that the Person Basic message is processed by CRM and the record is added to the database. The Date Stamp may not match the Person Role Start Date if the Person Role Start Date is adjusted as in the above examples. This may also occur if there is an extended processing delay between the time the message is published from HCM and ultimately received and processed by CRM.
Adding Contact Methods Across Roles
Person Basic EIPs provide only the Individual role when a person is created. Additional roles such as Worker or Consumer are added to persons later by the other CDM EIPs that rely on the Person object having already been created. Despite this, Person Basic Sync is responsible for the subsequent contact method maintenance across all roles held by the person.
When Person Basic Sync receives a request to add a new contact method of a particular contact method type (address, email, phone) for an existing person, it uses the configuration on the Contact Method Type definition to determine which roles the contact method will be added to if they exist for the person. Available roles are Individual Consumer, Worker, and POI (person of interest).
When a new contact method is created, it cannot have a start date that predates the established role to which it is to be associated. The start date of the contact method will be adjusted accordingly upon creation if necessary. This table lists several examples:
|
Person Basic Sync Run Date |
Inbound Contact Method Start Date |
Role Exists? |
Role Start Date |
Resulting Contact Method Start Date |
|
5/30/2010 |
5/01/2010 |
Yes |
1/1/2010 |
5/01/2010 |
|
5/30/2010 |
5/01/2010 |
Yes |
5/15/2010 |
5/15/2010 |
|
5/30/2010 |
5/01/2010 |
No |
5/30/2010 |
5/30/2010 |
|
5/30/2010 |
7/01/2010 |
Yes |
1/1/2010 |
7/01/2010 |
Note. Contact methods that are entered manually into CRM are not maintained by Person Basic Sync.
See Modifying Contact Method Types.
Person Basic Message Logging
During Person Basic EIP processing, some informational messages will be written to the message log. It happens, for example, when existing persons are skipped by Person Basic Fullsync or when there are issues with the Search Match configuration issues that need to be addressed. Additionally, the log can be used to debug integration issues should a Person Basic message go to error status. Users can access the log file after a run is completed through the Service Operations Monitor under this navigation: PeopleTools, Integration Broker, Service Operations Monitor, Monitoring, Asynchronous Services.
Select the completed PBS or PBS_FS message details.
Select the Error Messages link and the log will be displayed.

 Workforce Fullsync and Workforce Sync
Workforce Fullsync and Workforce SyncThe Workforce EIPs are another important part of the CDM EIP structure. They are responsible for importing job and employment data for persons from PeopleSoft HCM or PeopleSoft Campus Solutions into CRM. Workforce is dependent on the Person Basic EIPs having already created the Person object for which the job and employment data is being synchronized. Workforce Fullsync is for initial load of job data and the incremental Workforce Sync handles updates and additions going forward.
Besides importing POI data, Workforce EIPs affect the CDM in two ways. First, they create the Worker role for the Person object if it does not already exist. Second, when the Worker role is added, any existing contact methods for that person are cloned and added to the Worker role. This is the only contact method interaction for Workforce EIPs; all subsequent changes or additions are processed through Person Basic Sync.
For import of employee job data from non-PeopleSoft third-party systems, the Worker Sync EIP is used.
Job Code Data
PeopleSoft CRM subscribes to all job information for worker and for POI. All fields (except for Physical Location) in the Worker component are updated from PeopleSoft HCM.
See Also
Worker Data Integration with Third-Party Systems

 Campus Solutions EIPs
Campus Solutions EIPsPeopleSoft Campus Solutions maintains multiple EIP integrations with CRM to add and maintain student and prospective student data. Not all of these EIPs interact with the CDM, though a select few do (see the CDM Message Summary session below). These messages are dependent on the Person Basic EIPs having already created the Person object for which the data is being synchronized.
The Campus Solutions EIPs create the Consumer role for the Person object if it does not already exist. Also, when the Consumer role is added, any existing contact methods for that person are cloned and added to the Consumer Role. This is the only contact method interaction for Campus Solutions EIPs; all subsequent changes or additions are processed through Person Basic Sync.
See Also
Oracle's PeopleSoft CRM for Higher Education Preface

 Pers POI Sync
Pers POI SyncThe Pers POI EIP is an important part of the CDM EIP structure. It is responsible for importing POI data for persons from PeopleSoft HCM or PeopelSoft Campus Solutions into CRM. Pers POI Sync is dependent on the Person Basic EIPs having already created the Person object for which the data is being synced.
Pers POI Sync creates the POI role for the Person object if it does not already exist. Also, when the POI role is added, any existing contact methods for that person are cloned and added to the POI role. This is the only contact method interaction for Pers POI Sync; all subsequent changes or additions are processed through Person Basic Sync.

 Customer Data Model EIP Sequence
Customer Data Model EIP SequenceDue to the interdependent nature of the EIPs which are creating and modifying CDM information, it is vital that CRM receives and processes them in the correct order. Because the Person Basic EIPs create the foundation Person object, those messages must always be received and processed before subsequent Workforce or Campus EIPs for that same person. Failure to do so can result in data loss, inconsistent data between the CRM and the source system, or both.
To ensure that the messages are received and processed in the correct order, the EIPs are delivered in a single ordered message queue. Messages should not be removed from this queue.
CDM Message Summary
This table lists the delivered CDM messages:
|
Message Name |
Publishing Product(s) |
Creates Role |
Message Queue |
|
PERSON_BASIC_SYNC |
PeopleSoft HCM or Third-Party |
1 – Individual |
PERSON_DATA |
|
PERSON_BASIC_FULLSYNC |
PeopleSoft HCM or Third-Party |
1 – Individual |
PERSON_DATA |
|
WORKFORCE_SYNC |
PeopleSoft HCM |
4 – Worker |
PERSON_DATA |
|
WORKFORCE_FULLSYNC |
PeopleSoft HCM |
4 – Worker |
PERSON_DATA |
|
PERS_POI_SYNC |
PeopleSoft HCM |
88 – Person of Interest |
PERSON_DATA |
|
CS_TESTSCORES_FULLSYNC |
PeopleSoft Campus Solutions |
9 - Consumer |
PERSON_DATA |
|
CS_ADM_APPL_ DATA_FULLSYNC |
PeopleSoft Campus Solutions |
9 – Consumer |
PERSON_DATA |
|
CS_ADM_PRSPCT_DATA_FULLSYNC |
PeopleSoft Campus Solutions |
9 - Consumer |
PERSON_DATA |
|
SAD_ADM_APPL_DATA_SYNC |
PeopleSoft Campus Solutions |
9 - Consumer |
PERSON_DATA |
|
SAD_ADM_PRSPCT_DATA_SYNC |
PeopleSoft Campus Solutions |
9 - Consumer |
PERSON_DATA |
|
SAD_TEST_SCORES_SYNC |
PeopleSoft Campus Solutions |
9 - Consumer |
PERSON_DATA |
|
RC_EBS_PERSON_INC_SERVICE |
Oracle E-Business Suite |
1 – Individual |
PERSON_DATA |
|
RC_EBS_WORKFORCE_INC_SERVICE |
Oracle E-Business Suite |
4 – Worker |
PERSON_DATA |

 Implementation Using Fullsyncs
Implementation Using Fullsyncs
You should perform FULLSYNC messages at implementation time to set up your PeopleSoft CRM database correctly.
To set up your database with FULLSYNC messages (recommended sequence):
Before you run the main EIPs, run these common EIPs:
Country
State
Currency
SetID Initialization
Table Set Control Initialization
Location
Business Unit
Run the Person Basic Sync EIP.
Run the Workforce EIP group.
Department
Job Code
Workforce
Run the Person Competencies EIP group.
CM_TYPE
Rating Model
Competency
Person Competency
Inactivate the FULLSYNC messages and activate the corresponding SYNC messages.
SYNC messages always originate in PeopleSoft HCM or a third-party system and publish to PeopleSoft CRM. Thus, any field in PeopleSoft CRM that an EIP populates must be maintained from the originating source database, whether it is PeopleSoft HCM or a third-party system.
Note. If you create workers within PeopleSoft CRM, you must maintain these workers in CRM until you create them in an HR or third-party database.
 Data Integrations
Data IntegrationsThis section discusses:
Customer and contact data integration with PeopleSoft FSCM.
Worker data integration with third-party systems.
Product data integration.
Bill and payment data integration.
Other integration considerations.

 Customer and Contact Data Integration with
PeopleSoft FSCM
Customer and Contact Data Integration with
PeopleSoft FSCM
In PeopleSoft CRM, a customer can be either a company, a partner company, a consumer, or a site that is associated with a company or consumer. A contact is any person who performs transactions on a customer's behalf.
Company, Consumer, Site, and Contact EIPs
Use the CUSTOMER_COMPANY, CUSTOMER_CONSUMER, and CUSTOMER_SITE EIPs to synchronize customer information with other systems. When you implement these EIPs, application messages are published whenever a company, partner company, consumer, or site record in the PeopleSoft CRM system is added or modified. PeopleSoft CRM can also subscribe to these EIP application messages that are published when these records are modified in another system.
Note. CRM cannot publish a company with grandparent companies
to SCM, because SCM only supports a two-level customer hierarchy, whereas
CRM can support multi-level customer hierarchies. If you have implemented
the CUSTOMER_COMPANY EIP and a company with grandparent companies is added
in the Company component, this online message is issued:
SCM doesn't allow multi-level customer hierarchy, No message will be
published
The PARTNER_PROFILE EIP is triggered when you update data for a company that has the Partner role. It publishes an application message whenever a partner record is added or modified. The data in this EIP contains only information that is specific to the Partner role. The CUSTOMER_COMPANY EIP is also published to synchronize the basic company information.
The CUSTOMER_CONTACT EIP enables you to synchronize customer contact information with another system. When you implement the CUSTOMER_CONTACT EIP, application messages are published when a contact record in the PeopleSoft CRM system is added or modified. CRM can also subscribe to CUSTOMER_CONTACT EIP application messages that are published when these records are modified in another system.
Important! You must market-enable the Company, Consumer, Site, Partner Profile, and Contact EIPs before PeopleSoft CRM can send customer (company, partner profile, consumer, and site) and contact data to other databases. Market-enabling enables you to specify what data the PeopleSoft CRM system sends to other systems for a specific market. For example, you might opt not to publish certain customer and contact data to an external system for the FSI market. At the minimum, you must specify a global market to interface all non-market specific data.
See Market-Enabling Company, Consumer, Site, and Contact EIPs.
Partner Profile EIP
This EIP is triggered when you update data for a company that has the Partner role.
See PeopleSoft Partner Relationship Management 9.1 PeopleBook.
Site Considerations
Only CRM sites that are flagged with the bill-to or sold- to purchasing options are integrated as customers with PeopleSoft SCM. If a site is flagged as Ship To only then the site is integrated with PeopleSoft SCM as an address to the company with which the site is associated.
When you add the bill-to or sold-to flag to a ship-to site, the system publishes the site message to create a new customer in PeopleSoft SCM. However, if a customer already exists in PeopleSoft SCM, removing the bill-to and sold-to options from the site does not remove the customer information for that site in PeopleSoft SCM.
Specifying Customer ID and Contact ID Default Values
You must specify the system that owns the customer ID and contact ID and verify the automatic numbering for ID generation for each setID.
See Managing Enterprise Integration for PeopleSoft CRM.
See Setting Up Automatic Numbering.
Customer and Contact Integration with Other PeopleSoft Applications
Unlike PeopleSoft CRM, PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM do not distinguish between company, consumer, and site records. CUSTOMER_COMPANY, CUSTOMER_CONSUMER, and CUSTOMER_SITE EIP application messages to which these systems subscribe are all mapped to customer records with unique customer IDs in the PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM systems.
When customer records are added or modified in PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM, the system publishes application messages using the Customer EIP. These messages are mapped to companies in the PeopleSoft CRM system.
When a record that is created in PeopleSoft CRM is modified in PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM, the system uses the record key information (customer ID and setID) that is included in the application message that's reporting the change to derive the record's original business object ID in PeopleSoft CRM. This enables CRM to apply the changes that are reported in the application message to the corresponding company, consumer, or site record.
To ensure uniqueness of customer ID and contact ID between multiple PeopleSoft CRM databases, you must specify the system that owns the customer ID and contact ID and verify the automatic numbering for ID generation for each setID.
See Establishing Master ID Databases.
Note. The CUSTOMER_COMPANY, CUSTOMER_CONSUMER, CUSTOMER_CONTACT, and CUSTOMER_SITE EIPs enable you to maintain customer information in multiple databases. However, to simplify integration of customer information, choose one database as the system of record for customer maintenance, and use PeopleTools Applications Portal technology to support customer information inquiries from the other systems. If you maintain customer and contact information in multiple databases, you must consider additional design, planning, and integration steps.
Customer and Contact EIP Application Messages Processing Order
In PeopleSoft CRM, because contacts can be associated with a company, consumer, or site, the company, consumer, or site record should be created before the contact record. When you implement the CUSTOMER_COMPANY, CUSTOMER_CONSUMER, CUSTOMER_CONTACT, and CUSTOMER_SITE EIPs, make sure that the application messages from the CUSTOMER_COMPANY, CUSTOMER_CONSUMER, and CUSTOMER_SITE EIPs are processed before application messages from the CUSTOMER_CONTACT EIP when performing a FULLSYNC process.
Maintaining Customer and Contact Information in Different Databases
In PeopleSoft, customers exist in PeopleSoft CRM, PeopleSoft SCM, and PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions. There are a number of ways to design the system to integrate between PeopleSoft CRM, PeopleSoft SCM, and PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions. The simplest way to integrate customer master information is to manage all customer maintenance out of one database and support inquiry only on the other databases. Then you can use PeopleTools Applications Portal technology to access either system.
You might have a compelling business reason to maintain customer and contact information in different databases. For example, you may elect to have your front office users create customers in the PeopleSoft CRM database but want to use the Receivables payment processing options that are available only in Financial Management Solutions.
If you choose to maintain customer (company, consumer, and site) and contact information in different databases, you must:
Define which database owns the customer and contact ID number assignment on the Master ID DB Setup page.
By specifying an owner, the system will be consistent in assigning a unique customer or contact ID for a particular customer or contact across different databases.
Set up defaulting for the CRM Name Type field on the Name Type Defaults page.
You cannot add new contacts or customers to the PeopleSoft CRM database through the CUSTOMER_COMPANY, CUSTOMER_CONSUMER, CUSTOMER_CONTACT, and CUSTOMER_SITE EIPs unless you complete this step.
Set up at least one PeopleSoft CRM market control code for interfacing CRM customer and contact data to other databases.
Evaluate whether you plan to define customers as bill-to customers in PeopleSoft CRM.
In PeopleSoft SCM and PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions, customers that you define as bill-to customers must also have a defined collector and credit analyst. To ensure that PeopleSoft CRM passes these required fields to PeopleSoft SCM and PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions, select the Collector/Credit Analyst Req (collector/credit analyst required) check box on the Installation Setup table. This ensures that PeopleSoft CRM satisfies the required field edit that is needed to populate PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM. Set up defaulting of these values on the Interface Defaults page under Define Integration Rules.
Manually keep the Collector and Credit Analyst table in PeopleSoft CRM in sync with the PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM Collector and Credit Analyst table.
Establish a default support team code in PeopleSoft CRM for each setID to be used in when creating a customer.
In PeopleSoft SCM and PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions, a default support team code is required for each customer. To satisfy the required field edit, PeopleSoft CRM enables you to set up a default value on the Interface Defaults page under Define Integration Rules. In addition, ensure that the value set up on the Default page also exists on the PeopleSoft SCM and PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions system.
PeopleSoft FSCM Customer-Related Pages That Are Unavailable in PeopleSoft CRM
These pages in the PeopleSoft SCM or PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions Customer component are not available in CRM:
Vendor Info.
Credit Profile - General.
Credit Profile - Credit Check.
Region Code Info.
Subcustomer Info.
Customer Group Info.
Customer VAT Info (customer value-added tax information).
Customer Notes Info.
Attachments.
Messages.
User-Defined 1.
User-Defined 2.
Payment Options.
Write-Off Info.
Hierarchy.
Product Catalog.
Product Aliases.
Additional Ship To Options.
Ship Exception Dates.
Carrier Acct Number (carrier account number).
Note. If the PeopleSoft CRM installation is integrated with either PeopleSoft SCM or PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions, you can access these pages through those applications.
The Products component in PeopleSoft SCM and PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions uses these customer components, which are not available in CRM:
Dun & Bradstreet.
MICR Information.
Corporate Customer Tree.
Vendor Information.
Corporate Tree Messages.
Customer EFT Name (customer electronic funds transfer name).
Quick Customer Create.
Note. You can access these pages through PeopleSoft SCM or PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions if the PeopleSoft CRM installation is integrated with those systems.
See Also
Defining Purchasing Options for Companies, Consumers, and Sites
PeopleSoft 9.1 PeopleBook: Enterprise Components

 Worker Data Integration with Third-Party
Systems
Worker Data Integration with Third-Party
SystemsUse the Worker EIP to synchronize worker information with another system. In PeopleSoft CRM, workers are people who work for you. When you implement the Worker EIP, application messages are published when a worker record in the PeopleSoft CRM system is added or modified. PeopleSoft CRM can also subscribe to Worker EIP application messages that are published when these records are modified in another system. The Worker EIP enables PeopleSoft CRM to accept and create future dated workers that were created in another system and to which CRM subscribed.

 Product Data Integration
Product Data Integration
Integrate product data using the PeopleTools 8.5 Integration Broker. This technology enables both synchronous and asynchronous messages to be transmitted using one technology. The PRODUCT_SYNC and PRODUCT_FULLSYNC messages are used to both publish and subscribe to data between PeopleSoft CRM and PeopleSoft SCM or a third-party system.
Integrating from PeopleSoft SCM to PeopleSoft CRM
PeopleSoft CRM subscribes asynchronously to the PRODUCT_SYNC message that is coming from PeopleSoft SCM. This data is processed directly into the PeopleSoft CRM product tables using Component Interfaces (CIs).
A product package header record is added for any kit components that are received from PeopleSoft SCM.
Integrating from PeopleSoft CRM to PeopleSoft SCM
PeopleSoft CRM publishes the PRODUCT_SYNC message whenever product data is added, changed, or deleted through the Product Definition (PROD_DEFN), Product Package (PRODKIT_SUMMARY), Pricing (PROD_PRICE), Package Pricing (PRODKIT_COMPS_PRICE), Notes (PROD_NOTE), Relationships (PROD_RELATIONS_CMP), and Product Attributes by UOM (product attributes by unit of measure; PROD_UOM) pages.
The Integration Broker processes the message and applies a transformation to remove the PRODKIT_HEADER.
Any package components that are themselves packages are also stripped from the message.
Because PeopleSoft SCM does not allow packages within packages, package components that are themselves packages are also stripped from the message.
This table shows how an order represents packages to PeopleSoft SCM:
|
Type |
Line Display |
Line Data Model/EIP |
|
0-Static Package (1-level static quantity) PROD_ITEM.PROD_KIT=Y PROD_KIT_HEADER.LT_CONFIG_FLAG=N |
Display all components of the package as multiple lines. |
Store and publish parent line. |
|
1-Package (Kit) (multilevel dynamic quantity) PROT_ITEM.PROD_KIT=Y PROD_KIT_HEADER.LT_CONFIG_FLAG=Y |
Display all components of the package as multiple lines. |
Store all components as multiple lines, and publish as multiple lines. |
|
2-Configured Package(Kit) PROD_ITEM.PROD_KIT=Y PROD_ITEM.CFG_KIT=Y |
Display all components of the package as multiple lines. |
Store all components as multiple lines, and publish as multiple lines. |
|
3-Configured Product MASTER_ITEM_TBL.DIST_CFG_FLG=Y |
Display high level parent line. |
Store and publish parent line plus configuration. |
Integrating from PeopleSoft CRM to a third-party SCM database
PeopleSoft CRM publishes the PRODUCT_SYNC message whenever product data is added, changed, or deleted through the Product Definition, Product Package, Pricing, Package Pricing, Notes, Relationships, and Product Attributes by UOM components. Integration Broker passes the message to the subscribing system.

 Bill and Payment Data Integration
Bill and Payment Data Integration
PeopleSoft CRM integrates with Billing and Receivables to obtain billing information—invoices—and payments that are associated with a company, consumer, or contact. If a person is a contact of a company and that role is selected in the Role field in 360-Degree View, then the 360-Degree View EIPs retrieve invoices and payments for the company and not for the contact.
The PeopleSoft CRM 360-Degree View can display invoices and payments under those nodes in the 360-Degree View tree. When you define these types of nodes on the Define Node page in PeopleSoft CRM, you specify all of the necessary EIP details that are associated with that node.
To request invoices from PeopleSoft Billing, and for Billing to respond to the request, use the GET BILLS FOR 360 DEGREE VIEW EIP. This EIP consists of two application messages:
BI_EIP360_REQ (request message)
BI_EIP360_RSP (response message)
To request payments from PeopleSoft Receivables and for Receivables to respond to the request, use the GET ACCOUNT RECEIVABLES FOR 360 DEGREE VIEW EIP. This EIP consists of two application messages:
AR_CRM_REQUEST (request message)
AR_CRM_RESPONSE (response message)
All of the application messages that are used for integrating with 360-Degree View are synchronous.
PeopleSoft CRM passes the request parameters for the request application message using an application class method. This table lists the application classes that PeopleSoft CRM uses to pass the request parameters to Billing and Receivables:
|
PeopleSoft Application |
Class ID |
Class Path |
Method Name |
|
PeopleSoft Billing |
EIP |
RB_TD_360 |
PopulateBillRequestMsg |
|
PeopleSoft Receivables |
EIP |
RB_TD_360 |
PopulatePaymentRequestMsg |
See Also
PeopleSoft CRM 9.1 Industry Application Fundamentals PeopleBook

 Performance Considerations
Performance ConsiderationsWhen you integrate large amounts of data with other systems, system performance is slowed. The following tips might help.
Data Maintenance in Multiple Systems
If you have both PeopleSoft CRM and PeopleSoft SCM databases, PeopleSoft recommends that you:
Synchronize tables (such as Customer and Contacts) by running the FULLSYNC EIPs to perform a full batch publish to the subscribing system.
Note. In general, FULLSYNC messages first delete all existing data in the target record and then load a copy of the source record. For Company, Consumer, Contact, and Site FULLSYNC messages that come into PeopleSoft CRM, no delete occurs; the data is merged into the existing data instead. This ensures data integrity within the PeopleSoft CRM system.
Update databases in the subscribing system by running SYNC EIPs to perform incremental updates.
SYNC messages modify, delete, or add only the data that a user affected while performing an individual transaction.
Cascading Addresses
You can set a system option that automatically updates addresses on related business objects whenever you update an address on a parent business object. When you enable this option, each update that occurs also triggers an EIP to publish the address change to PeopleSoft SCM.
See Maintaining Contact Information for Business Objects.
See Also
Establishing Master ID Databases
Setting Up Defaults for Integrating Customer and Contact Information
Market-Enabling Company, Consumer, Site, and Contact EIPs
 Setting Up Defaults for Integrating Customer
and Contact Information
Setting Up Defaults for Integrating Customer
and Contact InformationTo set up defaults for integrating customer and contact information, use the Collector (COLLECTOR_TABLE), Credit Analyst (CR_ANALYST_TABLE), and General Options (RB_INSTALLATION) components.
This section discusses how to define default values for integrating customer and contact information.

 Pages Used to Set Up Default Values for
Integrating Customer and Contact Information
Pages Used to Set Up Default Values for
Integrating Customer and Contact Information|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
COLLECTOR_TABLE |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Customer, Collector |
Create and maintain collector codes, which are required on customer and site records in systems that are integrated with PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM. |
|
|
CR_ANALYST_TABLE |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Customer, Credit Analyst |
Create and maintain credit analyst codes, which are required on customer and site records in systems that are integrated with PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM. |
|
|
TEAM_CODE_TBL |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Codes and Auto Numbering, Support Team Codes, Support Team Code |
Create and maintain support team codes, which are required on customer and site records in systems that are integrated with PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM. |
|
|
RB_EIP_DEFAULTS |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Integration Rules, Integration Defaults, Interface Defaults |
Specify default values on customer records for fields that are required for integration with PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM. |
|
|
RB_NM_TYPE_DFLT |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Integration Rules, Integration Defaults, Name Type Options |
Specify default name type values to use on company and contact records that are received from PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM. |
|
|
RB_INSTALLATION |
Set Up CRM, Install, Installation Options, General Options |
Specify default exchange rate codes to use on company and contact records that are received from PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM and ensure that required codes are available to the EIP. |

 Creating and Maintaining Collector Codes
Creating and Maintaining Collector Codes
Access the Collector page (Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Customer, Collector).
Important! To ensure successful integration with PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM, you must synchronize collector codes manually between PeopleSoft CRM and PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM. Customer (company, consumer, and site) EIP application messages that include codes that are not available in the subscribing system will fail.

 Creating and Maintaining Credit Analyst
Codes
Creating and Maintaining Credit Analyst
Codes
Access the Credit Analyst page (Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Customer, Credit Analyst).
Important! To ensure successful integration with PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM, you must synchronize credit analyst codes manually between PeopleSoft CRM and PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM. Customer (company, consumer, and site) EIP application messages that include codes that are not available in the subscribing system will fail.

 Creating and Maintaining Support Team Codes
Creating and Maintaining Support Team Codes
Access the Support Team Code page (Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Codes and Auto Numbering, Support Team Codes, Support Team Code).
Important! To ensure successful integration with PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM, you must synchronize support team codes manually between PeopleSoft CRM and PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM. Customer (company, consumer, and site) EIP application messages that include codes that are not available in the subscribing system will fail.

 Specifying Interface Defaults
Specifying Interface Defaults
Access the Interface Defaults page (Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Integration Rules, Integration Defaults, Interface Defaults).
When you create a customer or site record using the Company, Consumer, and Site components in PeopleSoft CRM, the system automatically populates the record with the values that you enter on the Interface Defaults page. Users can select alternate values for these fields using the Bill Options view of the Customer Roles page, which is available in each of the components.

 Specifying Name Type Defaults
Specifying Name Type Defaults
Access the Name Type Options page (Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Integration Rules, Integration Defaults, Name Type Options).
PeopleSoft CRM requires name type codes to create all business object records; however, PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM do not require name codes. To ensure that records that are received from PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM are populated with name types that are valid in CRM, you specify default name type values here.
See Defining Business Object and Name Types.
|
Company Name Type |
Enter the default value to use for name type on company records that are received from PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM. The system uses this value on customer records that are received through Customer (company, consumer, site) EIP application messages. |
|
Person Name Type |
Enter the default value to use for name type on contact records that are received from PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM. The system uses this value on contact records that are received through Contact EIP application messages. |

 Specifying Default Exchange Rates
Specifying Default Exchange Rates
Access the General Options page (Set Up CRM, Install, Installation Options, General Options).
Important! You must manually synchronize exchange rate codes between PeopleSoft CRM and PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM. Customer (company, consumer, and site) EIP Application messages that include codes that are not available in the subscribing system will fail.

 Ensuring Required Code Availability
Ensuring Required Code Availability
Access the General Options page (Set Up CRM, Install, Installation Options, General Options).
Select the Collector/Credit Analyst Req check box. This prevents Customer (company, consumer, and site) EIP application message failures in PeopleSoft Financial Management Solutions and PeopleSoft SCM that are due to missing collector or credit analyst field values.
 Market-Enabling Company, Consumer, Site,
and Contact EIPs
Market-Enabling Company, Consumer, Site,
and Contact EIPs
To market-enable company, consumer, site, and contact EIPs, use the Market Control Codes (RB_MKT_CTL_DFN) and Market Installation Options (RB_MKT_CTL_TBL) components.
This section discusses how to specify the markets that PeopleSoft CRM integrates with.

 Pages Used to Market-Enable Company, Consumer,
Site, and Contact EIPs
Pages Used to Market-Enable Company, Consumer,
Site, and Contact EIPs|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
RB_MKT_CTL_DFN |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Codes and Auto Numbering, Market Control Codes |
Define market control codes for market-enabling the Customer (company, consumer, and site) and Contact EIPs. |
|
|
RB_MKT_CTL_TBL |
Set Up CRM, Install, Market Installation Options |
Specify market options for a specific market or use with the Customer (company, consumer, and site) and Contact EIPs. |
|
|
RB_INT_BUILD |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Integration Rules, Integration Utilities, Request Processes, Build CDM Interface Records |
Run the Build CDM Interface Records Application Engine process (RB_INT_BUILD). |

 Defining Market Control Codes
Defining Market Control Codes
Access the Market Control Codes page (Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Codes and Auto Numbering, Market Control Codes).
Enter a market control code name and a description. Use the Comments field to add any more information. These control codes are used on the Market Installation Options page.

 Specifying Market Installation Options
Specifying Market Installation Options
Access the Market Installation Options page (Set Up CRM, Install, Market Installation Options).
|
Market Control Code |
Select the market control code. Note. CDMINTFC is the market control code for CDM interface records. |
|
Option Activated |
Select to activate the code. |
Note. Use this page for market-enabling credit card information as well.

 Building Business Object Relationship Model
Interface Records
Building Business Object Relationship Model
Interface Records
Access the Build CDM Interface Records page (Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Integration Rules, Integration Utilities, Request Processes, Build CDM Interface Records).
Click Run to run the Build CDM Interface Records process, which populates the interface records.
 Establishing Master ID Databases
Establishing Master ID Databases
This section lists prerequisites and discusses how to set up master ID databases.

 Prerequisites
PrerequisitesYou must first set up number type codes that relate object IDs to databases.
See Setting Up Automatic Numbering Rules.

 Pages Used for Establishing Master ID Databases
Pages Used for Establishing Master ID Databases|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
RB_IDMASTER |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Integration Rules, Remote Data Access, Master ID Owner, Master ID DB Setup |
Designate which systems have the source (or master) object IDs. |
|
|
RB_XML_TEST |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Integration Rules, Remote Data Access, XML Test Utilities, XML Test Utility |
Test calls between remote databases. |

 Designating the Systems That Have Master
Object IDs
Designating the Systems That Have Master
Object IDs
Access the Master ID DB Setup page (Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Integration Rules, Remote Data Access, Master ID Owner, Master ID DB Setup).
Important! Use the Master ID DB Setup page to indicate the location of the master database that is responsible for issuing identifiers for customers, contacts, and so on. You must do this on all databases in the community except the master. Failure to do so may result in duplicate customer and contact identifiers.
|
Number Type |
Select the objects whose IDs will be generated by the master database that appears in the Master Database URL (uniform resource locator) field. You can select the database for generating IDs for customers, contacts, products, sales orders, and quotes. |
|
Master Database URL |
Enter the database URL for the master database. When an application must obtain an identifier, it checks this field to see if there is a value. If there is no value, then the system issues the identifier itself, because it is assumed that the database is the master. If there is a value, the system contacts the remote master database for the identifier. |

 Testing Calls
Testing Calls
Access the XML Test Utility page (Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Integration Rules, Remote Data Access, XML Test Utilities, XML Test Utility).
|
Transaction |
Enter the identifier for the object whose ID generation you want to test. Enter 1 for customers, 2 for contacts, 3 for sales orders, 4 for quotes, and 5 for products. When you press Tab to exit the field, the system enters default values in the first three unlabeled text boxes. The first unlabeled text box displays the setID or business unit for which the autonumber is to be generated; modify this if you like. Do not modify the other fields. The second text box displays the next number to be generated. This is always NEXT by default; do not change the value. The third field displays the zero padding indicator: Y (yes) to suppress leading zeros or N (no) to include leading zeros. You can modify this if you like. The last two unlabeled fields are not used when testing autonumber generation. |
|
Test |
Click the Test button to fetch the next ID number from the external system. The result appears in the Text field. If the object's autonumbers come from the PeopleSoft CRM system (and not an external ID master), the Text field displays the word Local. Note. This test increments the number in the external system's database. |
 Mapping Message Data to PeopleSoft CRM Records
and Fields
Mapping Message Data to PeopleSoft CRM Records
and Fields
This section discusses how to map message data to PeopleSoft CRM records and fields.

 Page Used to Map Message Data to PeopleSoft
CRM Records and Fields
Page Used to Map Message Data to PeopleSoft
CRM Records and Fields|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
RB_CLAF_MAP |
Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Process Automation, Message Mapping, Message Data Mapping |
Map source fields to destination fields in PeopleSoft CRM. |

 Mapping Message Data to PeopleSoft CRM Records
and Fields
Mapping Message Data to PeopleSoft CRM Records
and Fields
Access the Message Data Mapping page (Set Up CRM, Common Definitions, Process Automation, Message Mapping, Message Data Mapping).
Note. You can define message mapping for message with single-level hierarchy only.
|
Message Name |
Displays the message against which you want to perform data mapping. |
|
Record To Update |
Enter the record that needs to be updated upon receiving the message into the PeopleSoft CRM system. |
Fields to Update
|
Record Field to Update and XML Tag Name |
Select the fields to update along with the corresponding XML tags from the message that you plan to receive. The system updates the record fields with the value of the XML tag element from the received message. |
Record Identification
|
Record Field Name and XML Tag Name |
Select a record field and corresponding XML tag. This criteria identifies the rows that must be updated when PeopleSoft CRM receives the message from another system. The system uses these fields to construct the where condition depending on the record fields and values of the corresponding XML tags. |
Message Row Identification
|
XML Tag Name and XML Tag Value |
Select the XML tags and XML tag values for the given message. This determines whether the message row qualifies with the given criteria to update the information into PeopleSoft CRM. In a message that you plan to receive, you may not want all of the rows to go to PeopleSoft CRM. Using these fields, you can sparse (filter) those rows from the received message. |
Here is an example of a message:
<?xml version="1.0"?> <KP_KPI_ASMT_FACTS> <Fieldpiece> <KP_KPI_PUBL_TBL class="R"> <BUSINESS_UNIT type="CHAR"/> <PF_SCENARIO_ID type="CHAR"/> <FISCAL_YEAR type="NUMBER"/> <ACCOUNTING_PERIOD type="NUMBER"/> <KPI_ID type="CHAR"/> <OBJ_ID type="CHAR"/> <TRGT_RULE_TYPE type="CHAR"/> <PF_OBJECT_TYPE type="CHAR"/> <RESOLVED_VALUE type="NUMBER"/> <ASSESS_ID type="CHAR"/> <ASSESS_IMAGE_ID type="CHAR"/> <ASSESS_DESCR type="CHAR"/> <PERIOD_END_DT type="DATE"/> <PCT_OF_TARGET type="NUMBER"/> <STRETCH_GOAL type="NUMBER"/> <CURRENT_TARGET type="NUMBER"/> <CURRENCY_CD type="CHAR"/> <RESOLVED_IND type="CHAR"/> <KPI_CALCDTTM type="DATETIME"/> <KP_TREND_IND type="CHAR"/> <QTD_VALUE type="NUMBER"/> <YTD_VALUE type="NUMBER"/> <YEAR_OVER_YEAR_PCT type="NUMBER"/> <MONITOR_ONLY type="CHAR"/> <DESCR type="CHAR"/> <KP_USER_FLD1 type="CHAR"/> <KP_USER_FLD2 type="CHAR"/> <PS_OWNER type="CHAR"/> </KP_KPI_PUBL_TBL> <PSCAMA class="R"> <LANGUAGE_CD type="CHAR"/> <AUDIT_ACTN type="CHAR"/> <BASE_LANGUAGE_CD type="CHAR"/> <MSG_SEQ_FLG type="CHAR"/> <PROCESS_INSTANCE type="NUMBER"/> <PUBLISH_RULE_ID type="CHAR"/> <MSGNODENAME type="CHAR"/> </PSCAMA> </FieldTypes> <MsgData> <Transaction> <KP_KPI_PUBL_TBL class="R"> <BUSINESS_UNIT>FSI01</BUSINESS_UNIT> <PF_SCENARIO_ID>1</PF_SCENARIO_ID> <FISCAL_YEAR>1998</FISCAL_YEAR> <ACCOUNTING_PERIOD>1</ACCOUNTING_PERIOD> <KPI_ID>1</KPI_ID> <OBJ_ID>200022</OBJ_ID> <TRGT_RULE_TYPE/> <PF_OBJECT_TYPE>CUSTMASTER</PF_OBJECT_TYPE> <RESOLVED_VALUE>11</RESOLVED_VALUE> <ASSESS_ID>11</ASSESS_ID> <ASSESS_IMAGE_ID>PS_COMPANY_ICN</ASSESS_IMAGE_ID> <ASSESS_DESCR>Green</ASSESS_DESCR> <PERIOD_END_DT/> <PCT_OF_TARGET>11</PCT_OF_TARGET> <STRETCH_GOAL>0</STRETCH_GOAL> <CURRENT_TARGET>0</CURRENT_TARGET> <CURRENCY_CD>USD</CURRENCY_CD> <RESOLVED_IND/> <KPI_CALCDTTM/> <KP_TREND_IND/> <QTD_VALUE>4670</QTD_VALUE> <YTD_VALUE>4670</YTD_VALUE> <YEAR_OVER_YEAR_PCT>0</YEAR_OVER_YEAR_PCT> <MONITOR_ONLY/> <DESCR/> <KP_USER_FLD1>KPI</KP_USER_FLD1> <KP_USER_FLD2/> <PS_OWNER/> </KP_KPI_PUBL_TBL> <PSCAMA class="R"> <LANGUAGE_CD>ENG</LANGUAGE_CD> <AUDIT_ACTN/> <BASE_LANGUAGE_CD>ENG</BASE_LANGUAGE_CD> <MSG_SEQ_FLG/> <PROCESS_INSTANCE>0</PROCESS_INSTANCE> <PUBLISH_RULE_ID/> <MSGNODENAME/> </PSCAMA> </Transaction> </MsgData> </KP_KPI_ASMT_FACTS>
From this message and the mapping that is provided, you can determine the:
Message name - KP_KPI_ASMT_FACTS
Record to update
This message updates the BC table.
Fields to update
The BC table fields ASSESS_DESCR, ASSESS_ID, ASSESS_IMAGE_ID, KPI_ID, and PCT_OF_TARGET are updated with the values of XML tags <ASSESS_DESCR>, <ASSESS_ID>, <ASSESS_IMAGE_ID>, <KPI_ID>, and <PCT_OF_TARGET> in the message.
Record identification
Subscription code updates the row in the BC table if the CUST_ID field value equals the value of the XML tag <OBJ_ID> in the message.
Message row identification
Message rows qualify if the value of the XML tag <PF_OBJECT_TYPE> is equal to CUSTOMERMASTER; otherwise, the message rows are ignored.