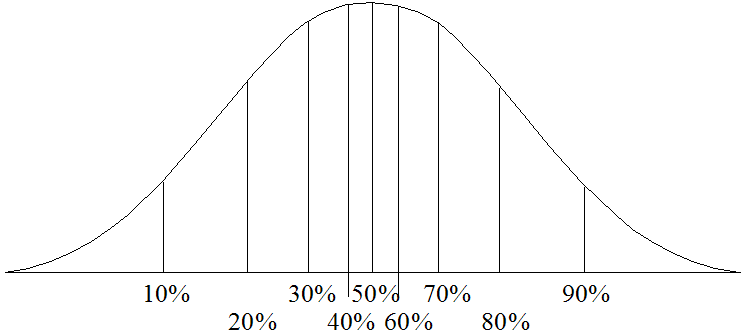
A percentile is a number on a scale of 0–100 that indicates the percent of a distribution that is equal to or less than a value (by default). Standardized tests usually report results in percentiles. If you are in the 95th percentile, then 95 percent of test takers had either the same score or a lower score. This number does not mean that you answered 95 percent of the questions correctly. You might have answered only 20 percent correctly, but your score was better than, or as good as, 95 percent of the other test takers' scores.
Crystal Ball calculates percentiles of forecast values using an interpolation algorithm. This algorithm is used for both discrete and continuous data, resulting in the possibility of having real numbers as percentiles for even discrete data sets. If an exact forecast value corresponds to a calculated percentile, Crystal Ball accepts that as the percentile. Otherwise, Crystal Ball proportionally interpolates between the two nearest values to calculate the percentile.
When calculating medians, Crystal Ball does not use the proportional interpolation algorithm; it uses the classical definition of median, described in Median. |
Percentiles for a normal distribution look like the following figure (Figure 6, Normal Distribution with Percentiles).