A manufacturer of jet engine turbines has an order to produce 50 turbines. Since about 20% of the turbines do not make it past the high-velocity spin test, the manufacturer will actually have to produce more than 50 turbines.
Matching these conditions with the negative binomial distribution:
These conditions match those of the negative binomial distribution.
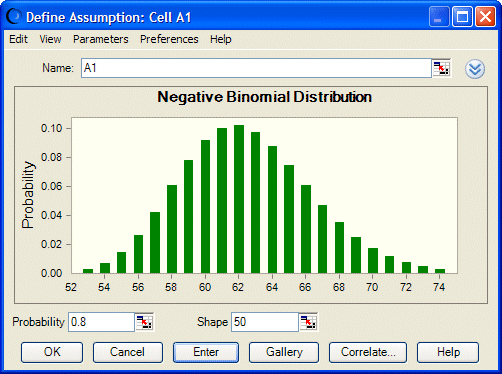
The negative binomial distribution has two parameters: Probability and Shape. The Shape parameter specifies the r th successful occurrence. In this example you would enter 0.8 for the Probability parameter (80% success rate of the spin test) and 50 for the Shape parameter (Figure 104, Negative Binomial Distribution).
Some characteristics of the negative binomial distribution:
When Shape = 1, the negative binomial distribution becomes the geometric distribution.
The sum of any two negative binomial distributed variables is a negative binomial variable.
Another form of the negative binomial distribution, sometimes found in textbooks, considers only the total number of failures until the r th successful occurrence, not the total number of trials. To model this form of the distribution, subtract out r (the value of the shape parameter) from the assumption value using a formula in the worksheet.