When working with documents that contain data from an Oracle Hyperion data source, you can create XBRL maps that are associated with the data in the report or with the underlying data source. If you map data in an Office document derived from a Smart View report or query, you can create two types of maps:
Data Source Map—A data source map is achieved when metadata labels are mapped to XBRL taxonomy concepts. The XBRL taxonomy mapping is associated with the data source’s member and is stored in a Mapping repository, and can be then be reused in multiple reports. The advantage is you do not need to remap the concept when a new report is created with the same metadata or if the metadata appears elsewhere in the same document.
Data source level maps can be performed in:
Microsoft Office using Smart View, which includes dimensions of imported function grids from existing Financial Reporting reports, or data inserted in a function grid from a Smart Slice
Financial Reporting HTML client
Planning
Essbase
Financial Management
support for both Classic and Oracle® Hyperion Enterprise Performance Management
Note:
Smart View determines whether the document data pertains to a data source member.
Report Level Map—When you select actual data (such as a numeric value) from the Smart View report, manual data entry, or another system with Microsoft Office integration, a document level map is created. In this case, the mapped taxonomy concept is associated only with the Office document.
For example, assume the following table is derived from a function grid in a Smart View report:
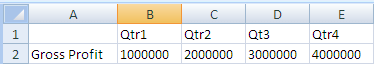
If you select cell A2 which contains the data source member “Gross Profit”, and then map it to the taxonomy concept GrossProfit; it becomes a data source map. In this case, all the data values in cells B2, C2, D2, and E2 become associated with the taxonomy concept GrossProfit. Additionally, all other function grids in the Smart View report or Financial Reporting grid that use the data source member Gross Profit are automatically associated with the XBRL taxonomy concept Gross Profit.
If you select cell B2 ( the data value 1000000) and map a taxonomy concept, it becomes a document level map.
If the member in cell A2 and the data in cell B2 have different taxonomy concept associations, the document level map supersedes the data source map (the map associated with cell B2).
If a data source map and a document level map are associated with the same data point, the document map supersedes the data source map.
If a document level map is removed, and there is a corresponding data source level map, the data source map is restored.
When an automatic taxonomy concept association is derived from a data source map, it is persisted only to an instance document when the map also has a context and unit association. For example in the table, if the member Gross Profit has a data source map, the data values in cells B2 and C2 are automatically associated with the mapped taxonomy concept. If you create a unit and context association with cell B2 only, cell C2 has an incomplete mapping. In this case, when an instance document is generated, the data from cell B2 is persisted, but the data from cell C2 is not.
All data source mappings are included into the resulting instance regardless of whether they have associated context or not. To eliminate a data source mapping from instance generation, use the “suppress” functionality. See Deleting and Suppressing Data Source Items.