Export Data
Click here for aggregate storage version
Export all data, level-0 data, or input-level data, which does not include calculated values. Export files are stored in the ARBORPATH/app directory on the server unless an absolute path is specified. To use Report Writer, export the data using a report file.
Minimum permission required: Read. This statement requires the database to be started.
Syntax
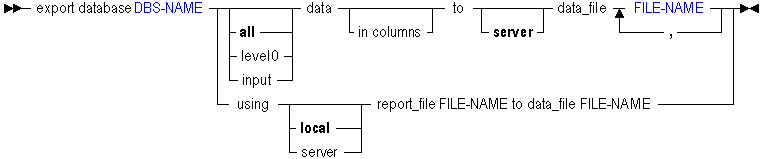
You can export data from a database in the following ways using export data.
| Keyword | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
export database <dbs-name> all data... | Export all data in the specified database to the $ARBORPATH/app directory on the server.
| ||
export database <dbs-name> level0 data... | Export level-0 data blocks only (blocks containing only level-0 sparse member combinations. Note that these blocks may contain data for upper level dense dimension members.) A level-0 block is created for sparse member combinations when all of the members of the sparse combination are at the bottom of dimension branches.
| ||
export database <dbs-name> input data... | Export only blocks of data where the block contains at least one data value that was loaded (imported), rather than created as the result of a calculation. | ||
export database <dbs-name> ... data in columns | Export data in columns, to facilitate loading the exported data into a relational database. In each row, the columnar format displays a member name from every dimension. Names can be repeated from row to row. Columnar format provides a structure to the exported data, so that it can be used for further data processing by applications other than Essbase tools. In non-columnar format, sparse members identifying a data block are included only once for the block. Because the export file in non-columnar format is smaller than in columnar format, reloading a file in non-columnar format is faster. | ||
export database <dbs-name> ...using...report_file... | Run a stored report script, exporting a subset of the database. |
Notes
To export data in parallel, specify a comma-separated list of export files. The number of threads Essbase uses depends on the number of file names you specify.
If the data for a thread exceeds 2 GB, Essbase may divide the export data into multiple files with numbers appended to the file names.
The naming convention for additional export files is as follows: _1, _2, etc. are appended to the additional file names. If the specified output file name contains a period, the numbers are appended before the period. Otherwise, they are appended at the end of the file name.
For example, if the given file name is /home/exportfile.txt, the next additional file is /home/exportfile_1.txt. If the file name is /home/exportfile, the next additional file is /home/exportfile_1.
To export data in column format, use the optional "in columns" grammar.
During a data export, the export process allows users to connect and perform read-only operations.
When MaxL exports data from a Unicode-mode application, the export file is encoded in UTF-8. You cannot use UTF-8-encoded export files from a Unicode-mode application to import data to a non-Unicode-mode application. For more information about file encoding, see the Unicode section of the Oracle Essbase Database Administrator's Guide.
MaxL cannot export databases with names containing hyphens (-). To export databases with names containing hyphens, use Administration Services.
Example
export database sample.basic data to data_file 'D:\\fileout','D:\\fileout2','D:\\fileout3';
Exports data concurrently to a list of file names.
export database sample.basic input data to data_file 'exp_input.exp'; export database sample.basic using report_file "'$ARBORPATH/App/Sample/Basic/asym.rep'" to data_file 'home/month2.rpt';
Note: | In the path to the report file in the above UNIX example, double quotation marks are used to allow variable expansion in the single-token FILE-NAME, and single quotation marks are required because there are special characters (see MaxL Syntax Notes) in the file name. |
export database sample.basic using report_file 'EssbaseServer\\App\\Sample\\Basic\\asym.rep' to data_file 'c:\\home\\month2.rpt';
Note: | In the file paths in the above Windows example, single quotation marks are required because there are special characters(see MaxL Syntax Notes) in the file name. Two backslashes ( \\ ) are required by the MaxL Shell to indicate one backslash, because the backslash has a special meaning to the MaxL Shell. |