Creating Forms
You can include a variety of different types of forms in your applications. You can include forms that enable users to update just a single row in a table or multiple rows at once. Application Builder includes several wizards you can use to create forms automatically, or you can create forms manually.
Topics:
Creating a Form Using a Wizard
The easiest way to create a form is to use a wizard. For example, the Form on Table or View Wizard creates one item for each column in a table. It also includes the necessary buttons and processes required to insert, update, and delete rows from the table using a primary key. Each region has a defined name and display position; all other attributes are items, buttons, processes, and branches.
To create a form using a wizard:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
-
Click Create Page.
-
Select Form and click Next.
-
Under Forms, select a type of form page as described in Table 10-1.
Form Page Type Description Builds a form based on stored procedure arguments. Use this approach when you have implemented logic or data manipulation language (DML) in a stored procedure or package.
Creates a form that enables users to update a single row in a database table.
Creates two pages. One page displays a report. Each row provides a link to the second page to enable users to update each record.
Note: This wizard does not support tables having more than 127 columns. Selecting more than 127 columns generates an error.
Creates a form that displays a master row and multiple detail rows within a single HTML form. With this form, users can query, insert, update, and delete values from two tables or views.
See Also: "Creating a Master Detail Form"
Creates a form in which users can update multiple rows in a database.
See Also: "Creating a Tabular Form"
Creates a form based on the columns returned by a SQL query such as an
EQUIJOIN.Creates a read-only version of a form. Typically used to provide a confirmation page at the end of a wizard.
Creates a page with items based on a Web service definition. This wizard creates a user input form, a process to call the Web service, and a submit button.
See Also: "Creating a Form on a Web Service"
Creates a page with items based on a Web service definition. This wizard creates a user input form, a process to call the Web service, a submit button, and displays the results returned in a report.
See Also: "Creating an Input Form and Report on a Web Service"
-
Follow the on-screen instructions. To learn more about a specific field, click the item label.
When help is available, the cursor changes to an arrow and question mark when you pass the cursor over an item. See "About Field-Level Help".
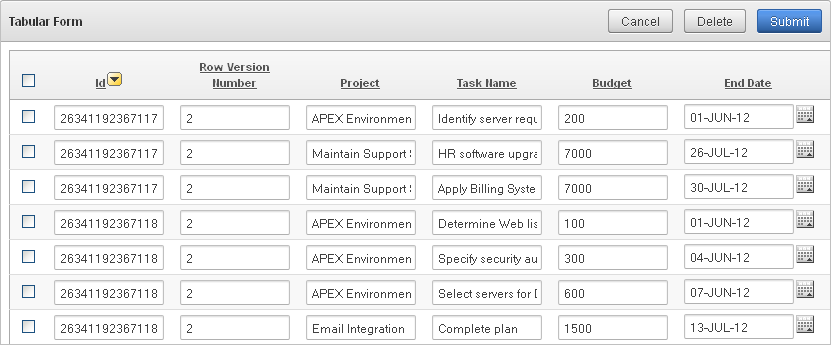
Creating a Tabular Form
A tabular form enables users to update multiple rows in a table at once from a single page. If created using a wizard, a tabular forms enables you to perform update, insert, and delete operations on multiple rows in a database table. This form includes a built-in multiple row update process that performs optimistic locking behind the scenes to maintain the data integrity.
Topics:
About Tabular Forms
There are two primary methods for creating tabular forms:
-
Create Application Wizard
-
Create Page Wizard
Tabular forms created using these wizards include automatic DML processes. These wizards create a form that performs update, insert, and delete operations on multiple rows in a database table. Alternatively, you can build a tabular form manually either by creating a updatable report region or standard report region with updatable columns with custom PL/SQL page processes to process the tabular form data.
Oracle does not recommend modifications of the select list of a SQL statement of a tabular form after it has been generated using a wizard. If you do modify the query, make sure the values of the updatable columns are not altered after being queried from the database by the Application Express engine.
Running a Tabular Form
When running a tabular form, data is rendered as a report having updatable columns shown using various form elements (including text fields, text areas, date pickers, select lists, radio groups, and so on).
By default, date columns are created using the Date Picker item type. If user interface defaults are defined, other columns can be automatically created as select lists based on lists of values, or numeric fields and large text areas.
"Managing User Interface Defaults" in Oracle Application Express SQL Workshop Guide
For numeric and date fields, you can also pre-define date and number format masks, or apply those format masks after generating the initial form.
Each report also includes a check box column (called a row selector). Users use this row selector to select one or more columns and update or delete data. To add a row, users click Add Row.
How Tabular Forms Work
Tabular forms are based on a SQL query in which the query columns are tied to the underlying table columns. Unlike a single record from, tabular forms do not store data in session state. When a tabular form page is submitted, the tabular form data is processed using built-in data manipulation language (DML), or a custom PL/SQL page processes.
A tabular form with automatic DML has two processes for multi-row operations:
-
A Multi Row Update (MRU) process performs create and update operations
-
Multi Row Delete (MRD) process deletes requests on one or more rows
MRU and MRD processes reference the underlying table name and the primary key columns. The primary key columns must be part of the tabular form SQL query, and the report columns must be either hidden or display-only (save state) in order for the DML processes to be able to identify the correct records. For new records, the primary key values must be NULL to be identified as new records. Delete operations are performed by referencing row number of the row to be deleted. Users can check one or more rows on the current page and when they click the Delete button, the row numbers identify the corresponding primary key value(s) and the matching rows are deleted.
Wizard generated tabular forms built-in DML, include a checksum column to prevent lost updates. Using a method called optimistic locking, a checksum is computed for each row when rendering a tabular form. This checksum is stored in an extra hidden tabular form column. Upon submission of the form for update, an additional set of checksums is computed on the then current data stored in the database. The new checksums are compared to those built when the tabular form was first rendered, and if there are any mismatches, the update is rejected, because the data in the database was either modified by another user or anther process in the time between the tabular form was rendered and the time the data was submitted.
Wizard generated tabular forms also automatically create validations for some columns. Validations are created for columns that are set to NOT NULL in the underlying table and columns of type NUMBER, DATE or TIMESTAMP. Note that validations are not created for columns if the column is set to read-only, either based on the user's selection, or defined user interface defaults.
Creating a Tabular Form Using the Create Application Wizard
The Create Application Wizard is designed to quickly create a basic Oracle Application Express application consisting of multiple pages and components. For that reason, this wizard uses general best practices to generate the application and does not include several advanced options included in the Create Page Wizard.
When creating a tabular form, Oracle recommends using a generic column template and avoiding column report templates. See "Report Templates".
To create a tabular form using the Create Application Wizard:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Click the Create button.
-
For Method, select Database and click Next.
-
For Name:
-
Application - Enter a unique integer value to identify the application. Application IDs between 3000 to 9000 are reserved for internal use by Oracle Application Express.
-
Name - Enter a name to identify the application.
-
Schema - Each application obtains its privileges by parsing all SQL as a specific database schema. Identify the database schema owner.
-
Create Options:
-
Start from scratch - Enables you to manually add all pages.
-
Include Home page - Includes a blank page, which automatically acts as the parent of any new pages added. A list region is also created on the home page, providing navigation to the additional pages.
-
Use previously created application model - Reuses an existing application definition. Using an existing application definition enables you to run this wizard without reentering application property values.
Note that you still have to define all other application attributes, or you can choose to copy some attributes by choosing to copy shared components from another application.
-
-
User Interface - Select a user interface for the application. For application primarily designed for desktop use, select Desktop.
-
Click Next.
-
-
Under Add Page:
-
Select Page Type - Select Tabular Form.
-
Subordinate to Page - If applicable, select a subordinate page. To learn more, see item Help.
-
Table Name - Select a table.
-
Click Add Page.
The new page appears at the top of the page.
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Shared Components, indicate whether to copy shared components from another application. Select Yes or No. If you select Yes, select where to copy them from and which components to import.
Shared components are common application elements that can be displayed or applied across multiple pages in an application. To save time or maintain consistency between applications, copy the shared components from an existing application. The types of shared components you can copy include: user interface themes, lists of values, navigation bar entries, authorization schemes and authentication schemes.
-
For Attributes:
-
Authentication Scheme - Determines how to establish user identity before accessing an application. Options include:
-
Application Express - Uses the user account credentials created and maintained with the Application Express Service Administration application. These are the accounts you use to log in to the Application Express development environment. You can also create accounts in this user account repository for end users of your applications.
-
Database Account - Requires users logging into your application to enter a database schema name (or user name) and a password in order to authenticate. This account information is managed entirely within the Oracle database.
-
No Authentication - Also known as Database Account Credentials. This option enables users to access your application using the account credentials stored in the
mod_plsqlDAD definition. In most cases this results in users not having to login when accessing your application. This is the quickest way to create a “public" application.
To learn more, see "Establishing User Identity Through Authentication"
-
-
Tabs - Select whether to include tabs in your application. You can create one level tabs, two level tabs, or no tabs at all. To learn more, see "Creating Tabs"
This attribute identifies the language in which an application is developed. This language is the base language from which all translations are made.
-
Language - Select the primary language for this application.
This attribute identifies the language in which an application is developed. This language is the base language from which all translations are made.
-
User Language Preference Derived From - Specifies how the engine determines the application language. The application primary language can be static (that is, derived from the web browser language) or determined from a user preference or item. The database language setting determines date display and sorting characteristics. To learn more, see item Help.
You can alter the Language and User Language Preference Derived From attributes later on the Edit Globalization attributes page. See "Configuring Globalization Attributes".
-
Date Format - Specifies the date format to be used in the application.
This date format is used to alter the
NLS_DATE_FORMATdatabase session setting before showing or submitting any page within the application. This value can be a literal string containing a valid Oracle date format mask or an item reference through substitution syntax. If no value is specified, the default date format is derived from the database session at runtime. If supplied, this is also used as the date format for any items resulting from columns of typeDATE. -
Date Time Format - Specifies the date time format to be used in the application.
This date time format can be referenced in an application using the substitution reference
&APP_DATE_TIME_FORMAT., or in PL/SQL using the functionv('APP_DATE_TIME_FORMAT'). This attribute does not alter any NLS settings. This value can be a literal string containing a valid Oracle date format mask or an item reference using substitution syntax. If this attribute value is not specified, then a reference toAPP_DATE_TIME_FORMATreturns the NLS database session date format and the NLS time format. -
Timestamp Format - Specifies the timestamp format to be used in your application.
This timestamp format is used to alter the
NLS_TIMESTAMP_FORMATdatabase session setting before showing or submitting any page within the application. This value can be a literal string containing a valid Oracle timestamp format mask or an item reference through substitution syntax. If no value is specified, the default timestamp format is derived from the database session at runtime. -
Timestamp Time Zone Format - Specifies the timestamp with time zone format to be used in your application.
This timestamp with time zone format is used to alter the
NLS_TIMESTAMP_TZ_FORMATdatabase session setting before showing or submitting any page within the application. This value can be a literal string containing a valid Oracle timestamp with time zone format mask or an item reference through substitution syntax. If no value is specified, the default timestamp with time zone format is derived from the database session at runtime. -
Click Next.
-
-
For User Interface Theme, select a theme and click Next.
Themes are collections of templates that you can use to define the layout and style of an entire application. See "Managing Themes".
-
Confirm your selections and click Create.
"Managing User Interface Defaults" in Oracle Application Express SQL Workshop Guide
Creating a Tabular Form Using the Create Page Wizard
Use the Create Page Wizard to add a tabular form to an existing application. Once you provide a table name on which to build the tabular form, the wizard reads the table columns from the database data dictionary.
Tabular forms perform insert, update and delete operations on table rows. Unlike with the Create Application Wizard, when you create a tabular form using the Create page Wizard you determine how rows are identified. You can either specify a primary key defined on the table, or a ROWID pseudo column, which uniquely identifies a row in a table. If you choose to select a primary key, you can choose between three different primary key source types: trigger, PL/SQL function, and sequence.
When creating a tabular form, Oracle recommends using a generic column template and avoiding column report templates. See "Report Templates".
To create a tabular form using the Create Page Wizard:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
-
Click Create Page.
-
Select Form and click Next.
-
Select Tabular Form and click Next.
The Create Tabular Form Wizard appears.
-
For Table and Columns, specify the following:
-
Table/View Owner - Select the table or view owner on which to base the tabular form.
-
Table/View Name - Select the table or view which contains the columns to be included in the tabular form region.
-
Select Columns - Select one or more columns to be included in the tabular form. In the pages that follow you define which columns should be updatable.
-
Allowed Operations - Select the operations to be performed on the table (for example, Update, Insert and Delete).
-
User Interface Defaults - Select whether to use user interface defaults. See item Help for more information and "Managing User Interface Defaults" in Oracle Application Express SQL Workshop Guide.
-
Click Next.
Next, define a primary key. Tabular forms perform insert, update and delete operations on table rows in the database. You identify the rows by using either a primary key defined on the table, or the ROWID pseudo column, which uniquely identifies a row in a table.
-
-
For Primary Key, select one of the following:
-
Managed by Database (ROWID) - The tabular form uses the ROWID pseudo column to identify rows to update and delete.
-
Select Primary Key Column(s) - The tabular form uses the source table's primary key column(s).
-
-
If you select Managed by Database (ROWID), click Next to continue.
-
If you select Select Primary Key Column(s):
-
Primary Key Column 1 - Select the first column of the primary key.
-
Primary Key Column 2 - If you have a compound primary key, specify the second primary key column in this attribute. This attribute is optional.
-
Click Next.
-
For Source Type, select the method by which the primary key is populated:
-
Existing trigger - Select this option if a before-insert trigger populates the primary key. You can also select this option if you plan on specifying the primary key column source later after completing the form.
-
Custom PL/SQL function - Select this option to provide a PL/SQL function to generate returning key value.
-
Existing sequence - Select this option to pick the sequence from a list of sequences available in the selected schema.
-
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Updatable Columns:
-
Updatable Columns - Select the updatable columns to include in the form.
You can modify the column order or your SQL query after you create the page.
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Page and Region Attributes:
-
Page - Select a page to contain the new updatable report, or enter a new page number.
-
Page Name - If you are creating a new page, enter a name.
-
Region Title - Enter a name for the region in which the updatable report appears.
-
Region Template - Select a region template for the updatable report region.
-
Report Template - Select a report template.
-
Breadcrumb - Select whether you want to use a breadcrumb navigation control on your page, and which breadcrumb navigation control you want to use.
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Tab Options, select an option that describes how tabs display on the page and click Next.
-
For Buttons and Branching:
-
Cancel Button Label - Enter text to display on the Cancel button.
-
Branch to Page - Specify the page number to branch to when the user clicks Cancel.
-
Submit Button Label - Enter text to display on the Submit button.
-
Branch to Page - Specify the page number to branch to when the user clicks Submit.
-
Delete Button Label - Enter text to display on the Delete button.
-
Add Row Button Label - Enter text to display on the Add Row button label.
-
Click Next.
-
-
Click Create.
A success message appears.
Synchronizing Tabular Form Column Order with Region Source
To synchronize a classic report's column order with the column order defined in the region source query:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select the application.
-
Select a page containing the tabular form.
The Page Definition appears.
-
To access the Report Attributes page:
-
Tree view - Right-click Tabular Form region and select Edit Report Attributes.
-
Component view - Click the Report link next to the Tabular Form region.
-
-
From Tasks, select Synchronize Column Order with Region Source.
-
Click Synchronize.
Creating a Master Detail Form
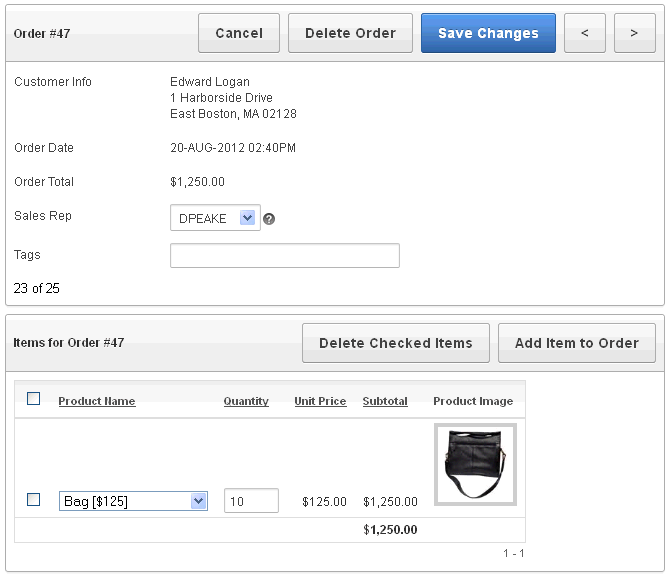
A master detail form reflects a one-to-many relationship between two tables in a database. Typically, a master detail form displays a master row and multiple detail rows within a single HTML form. With this form, users can insert, update, and delete values from two tables or views.
Topics:
About Master Detail Forms
When running a master detail form, data is rendered as a report using various form elements (including text fields, text areas, date pickers, select lists, radio groups, and so on). By default, date columns are created using the Date Picker item type. If user interface defaults are defined, other columns can be automatically created as select lists based on lists of values, or numeric fields and large text areas.
On the Master Detail, the master record displays as a standard form and the detail records display in a tabular form at the bottom of the page. Click Add Item to Order to add a new row.
"Managing User Interface Defaults" in Oracle Application Express SQL Workshop Guide
For numeric and date fields, you can also pre-define date and number format masks, or apply those format masks after generating the initial form. Wizard generated master detail forms also automatically create validations for some columns. Validations are created for columns that are set to NOT NULL in the underlying table and columns of type NUMBER, DATE or TIMESTAMP. Note that validations are not created for columns if the column is set to read-only, either based on the user's selection, or defined user interface defaults.
Creating a Master Detail Form Using the Create Application Wizard
The Create Application Wizard is designed to quickly create a basic Oracle Application Express application consisting of multiple pages and components. This wizard uses general best practices to generate the application and does not include several advanced options included in the Create Page Wizard.
To create a master detail form using the Create Application Wizard:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Click the Create button.
-
For Method, select Database and click Next.
-
For Name:
-
Application - Enter a unique integer value to identify the application. Application IDs between 3000 to 9000 are reserved for internal use by Oracle Application Express.
-
Name - Enter a name to identify the application.
-
Schema - Each application obtains its privileges by parsing all SQL as a specific database schema. Identify the database schema owner.
-
Create Options:
-
Start from scratch - Enables you to manually add all pages.
-
Include Home page - Includes a blank page, which automatically acts as the parent of any new pages added. A list region is also created on the home page, providing navigation to the additional pages.
-
Use previously created application model - Reuses an existing application definition. Using an existing application definition enables you to run this wizard without reentering application property values.
Note that you still have to define all other application attributes, or you can choose to copy some attributes by choosing to copy shared components from another application.
-
-
User Interface - Select a user interface for the application. For application primarily designed for desktop use, select Desktop.
-
Click Next.
To create an instant application consisting of just a login page and blank page, click the Create Application button.
Next, add pages to your application.
-
-
For Pages:
-
Select Page Type - Select Master Detail.
-
Subordinate to Page - If applicable, select a subordinate page. To learn more, see item Help.
-
Master Table Name - Select the table or view to be used as your master table. This table is used to create a report page and a master form on the master detail page.
-
Detail Table Name - Select the table or view to be used as your detail table.
Only tables and views that are associated to your selected Master Table using a foreign key are displayed.
-
Click Add Page.
The new pages appear at the top of the page.
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Shared Components, indicate whether to copy shared components from another application. Select Yes or No. If you select Yes, select where to copy them from and which components to import.
Shared components are common application elements that can be displayed or applied across multiple pages in an application. To save time or maintain consistency between applications, copy the shared components from an existing application. The types of shared components you can copy include: user interface themes, lists of values, navigation bar entries, authorization schemes and authentication schemes.
-
For Attributes:
-
Authentication Scheme - Determines how establish user identity before accessing an application. Options include:
-
Application Express - Uses the user account credentials created and maintained with the Oracle Application Express Service Administration application. These are the accounts you use to log in to the Application Express development environment. You can also create accounts in this user account repository for end users of your applications.
-
Database Account - Requires users logging into your application to enter a database schema name (or user name) and a password in order to authenticate. This account information is managed entirely within the Oracle database.
-
No Authentication - Also known as Database Account Credentials. This option enables users to access your application using the account credentials stored in the
mod_plsqlDAD definition. In most cases this results in users not having to login when accessing your application. This is the quickest way to create a “public" application.
To learn more, see "Establishing User Identity Through Authentication"
-
-
Tabs - Select whether to include tabs in your application. You can create one level tabs, two level tabs, or no tabs at all. To learn more, see "Creating Tabs"
This attribute identifies the language in which an application is developed. This language is the base language from which all translations are made.
-
Language - Select the primary language for this application.
This attribute identifies the language in which an application is developed. This language is the base language from which all translations are made.
-
User Language Preference Derived From - Specifies how the engine determines the application language. The application primary language can be static (that is, derived from the web browser language) or determined from a user preference or item. The database language setting determines date display and sorting characteristics. To learn more, see item Help.
You can alter the Language and User Language Preference Derived From attributes later on the Edit Globalization attributes page. See "Configuring Globalization Attributes".
-
Date Format - Specifies the date format to be used in the application.
This date format is used to alter the
NLS_DATE_FORMATdatabase session setting before showing or submitting any page within the application. This value can be a literal string containing a valid Oracle date format mask or an item reference through substitution syntax. If no value is specified, the default date format is derived from the database session at runtime. If supplied, this is also used as the date format for any items resulting from columns of typeDATE. -
Date Time Format - Specifies the date time format to be used in the application.
This date time format can be referenced in an application using the substitution reference
&APP_DATE_TIME_FORMAT., or in PL/SQL using the functionv('APP_DATE_TIME_FORMAT'). This attribute does not alter any NLS settings. This value can be a literal string containing a valid Oracle date format mask or an item reference using substitution syntax. If this attribute value is not specified, then a reference toAPP_DATE_TIME_FORMATreturns the NLS database session date format and the NLS time format. -
Timestamp Format - Specifies the timestamp format to be used in your application.
This timestamp format is used to alter the
NLS_TIMESTAMP_FORMATdatabase session setting before showing or submitting any page within the application. This value can be a literal string containing a valid Oracle timestamp format mask or an item reference through substitution syntax. If no value is specified, the default timestamp format is derived from the database session at runtime. -
Timestamp Time Zone Format - Specifies the timestamp with time zone format to be used in your application.
This timestamp with time zone format is used to alter the
NLS_TIMESTAMP_TZ_FORMATdatabase session setting before showing or submitting any page within the application. This value can be a literal string containing a valid Oracle timestamp with time zone format mask or an item reference through substitution syntax. If no value is specified, the default timestamp with time zone format is derived from the database session at runtime. -
Click Next.
-
-
For User Interface Theme, select a theme and click Next.
Themes are collections of templates that you can use to define the layout and style of an entire application. See "Managing Themes".
-
Confirm your selections and click Create Application.
Create a Master Detail Form Using the Create Page Wizard
The Create Page Wizard provides support for creating a master detail from two tables that do not have foreign key relationship defined in the database. Although Oracle recommends the use of foreign keys and properly defined relationships in the underlying database, developers do not always have the ability to modify their database model.
When created using a wizard, the master form on a master detail form page includes buttons that enable the user to move forward and backward within the master result set. While running the wizard, you choose which columns determine the navigation order. You also have the option to choose whether to create a two-page or three-page master detail form, with the detail records shown in a report with single-record editing on a separate page.
To create a master detail form using the Create Page Wizard:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
-
Click Create Page.
-
Select Form and click Next.
-
Select Master Detail Form and click Next.
The Master Detail Wizard appears.
-
On Define Master Table:
-
Table/View Owner - Select the schema that owns the master table.
-
Table/View Name - Select the table or view which contains the columns to be included in the master page.
The columns in that object display.
-
Click Next.
-
-
On Define Detail Table:
-
Show Only Related Tables - Specify whether to restrict the list of detail tables to only those tables related to the master table. Select Yes or No.
-
Table/View Owner - Select the table or view owner. The default selected owner for the table or view is the same owner as for your application. If the owner of your application has select privileges on tables or views in other schemas, you may select another schema.
-
Table/View Name - Select the table or view which contains the columns to be included in the detail page.
The columns in that object appear.
-
Select columns for detail page - Select the columns to display in your detail page. You may add columns later.
-
Click Next.
Next, define a primary key. Forms perform insert, update and delete operations on table rows in the database. You identify the rows by using either a primary key defined on the table, or the ROWID pseudo column, which uniquely identifies a row in a table.
-
-
For Define Primary Key, select one for each table:
-
Managed by Database (ROWID) - Use the ROWID pseudo column to identify rows to update and delete.
-
Select Primary Key Column(s) - Use the source table's primary key column(s).
-
-
If you select Managed by Database (ROWID):
-
Click Next.
-
For Master Options, define the relationship between the Master and Detail tables. You may type in the column names (fully qualified with table names), or choose them from the list. Click Next.
-
Click Next.
-
-
If you select Select Primary Key Column(s):
-
On Define Primary Key, select the following for each table:
-
Primary Key Column 1 - Select the first column of the primary key.
-
Primary Key Column 2 - If you have a compound primary key, specify the second primary key column in this attribute. This attribute is optional
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Primary Key Source, select the method by which the primary key is populated and click Next.
-
Existing trigger - Select this option if a before-insert trigger populates the primary key. You can also select this option if you plan on specifying the primary key column source later after completing the form.
-
Custom PL/SQL function - Select this option to provide a PL/SQL function to generate returning key value.
-
Existing sequence - Select this option to pick the sequence from a list of sequences available in the selected schema.
-
-
For Master Options, specify whether to include master row navigation and click Next.
If you include master row navigation, define navigation order columns. If a navigation order column is not defined, the master update form navigates by the primary key column.
-
Click Next.
-
-
On Layout, specify how to build the master detail and click Next. Options include:
-
Edit detail as tabular form on same page creates a two page master detail. Edit detail on separate page creates a three page master detail.
-
Edit detail on separate page creates a three page master detail.
-
-
On Page Attributes:
-
Page Attributes - Review and edit the master page and detail page information.
-
Breadcrumb - Specify whether to create a breadcrumb. To create breadcrumbs entries:
-
Entry Name (Master Report) - Specify the name of the breadcrumb entry for the master report page.
-
Entry Name (Master Detail Page) - Specify the name of the breadcrumb entry for the master detail page.
-
Select Parent Entry - Select a parent entry for this breadcrumb entry.
-
Parent Entry - This item displays if you have chosen a parent entry.
-
-
Click Next.
-
-
On Tab Options, specify whether to include a tab set and click Next.
-
Click Create.
Creating a Form Manually
You can also create a form manually by performing the following steps:
-
Step 1 - Create an HTML region (to serve as a container for your page items).
-
Step 2 - Create items to display in the region.
-
Step 3 - Create processes and branches.
To create a form manually by creating an HTML region:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Create an HTML region. See "Creating a Region".
-
Start adding items to the page. "Creating Page-Level Items".
Processing a Form
Once you create a form, the next step is to process the data a user types by inserting into or updating the underlying database tables or views. There are three ways to process a form:
Creating an Automatic Row (DML) Processing Process
One common way to implement a form is to manually create an Automatic Row Processing (DML) process. This approach offers three advantages. First, you are not required to provide any SQL coding. Second, Oracle Application Express performs DML processing for you. Third, this process automatically performs lost update detection. Lost update detection ensures data integrity in applications where data can be accessed concurrently.
To implement this approach you must:
-
Add items, define the Item Source Type as Database Column, and specify a case-sensitive column name.
-
Select the option Always overrides the cache value.
To create an Automatic Row Processing (DML) process:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition"
-
Access the Create Page Process Wizard:
-
Tree view - Under the appropriate location, right-click and click Create Process.
-
Component view - Under Processes, click the Create icon.
-
-
Under Processes, click the Create icon.
-
Select the process Data Manipulation.
-
Select the process category Automatic Row Processing (DML).
-
Specify the following process attributes:
-
In the Name field, enter a name to identify the process.
-
In the Sequence field, specify a sequence number.
-
From the Point list, select the appropriate processing point. In most instances, select Onload - After Header.
-
From the Type list, select Automated Row Processing (DML).
-
-
Follow the on-screen instructions.
Creating a Process that Contains One or More Insert Statements
In this approach to form handling, you create one or more processes to handle insert, update, and delete actions. Instead of having the Application Express engine handling everything transparently, you are in complete control.
For example, suppose you have a form with three items:
-
P1_ID- A hidden item to store the primary key of the currently displayed row in a table. -
P1_FIRST_NAME- A text field for user input. -
P1_LAST_NAME- A text field for user input.
Assume also there are three buttons labeled Insert, Update, and Delete. Also assume you have a table T that contains the columns id, first_name, and last_name. The table has a trigger that automatically populates the ID column when there is no value supplied.
To process the insertion of a new row, you create a conditional process of type PL/SQL that executes when the user clicks the Insert button. For example:
BEGIN
INSERT INTO T ( first_name, last_name )
VALUES (:P1_FIRST_NAME, :P1_LAST_NAME);
END;
To process the updating of a row, you create another conditional process of type PL/SQL. For example:
BEGIN
UPDATE T
SET first_name = :P1_FIRST_NAME,
last_name = :P1_LAST_NAME
WHERE ID = :P1_ID;
END;
To process the deletion of a row, you create a conditional process that executes when the user clicks the Delete button. For example:
BEGIN
DELETE FROM T
WHERE ID = :P1_ID;
END;
Using a PL/SQL API to Process Form Values
For certain types of applications, it is appropriate to centralize all access to tables in a single or a few PL/SQL packages. If you created a package to handle DML operations, you can call procedures and functions within this package from an After Submit PL/SQL process to process insert, updates, and delete requests.
Populating Forms
Oracle Application Express populates a form either on load or when the Application Express engine renders the page. You can populate a form in the following ways:
-
Create a process and define the type as Automated Row Fetch.
-
Populate the form manually by referencing a hidden session state item.
To create an Automated Row Fetch process:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Access the Create Page Process Wizard:
-
Tree view - Under the appropriate location, right-click and click Create Process.
-
Component view - Under Processes, click the Create icon.
-
-
Select the process type Data Manipulation.
-
Select the process category Automatic Row Fetch.
-
Specify the following process attributes:
-
In the Name field, enter a name to identify the process.
-
In the Sequence field, specify a sequence number.
-
From the Point list, select the appropriate processing point.
-
From the Type list, select Automated Row Fetch.
-
-
Follow the on-screen instructions.
You can also populate a form manually by referencing a hidden session state item. For example, the following code in an Oracle Application Express process of type PL/SQL would set the values of ename and sal. The example also demonstrates how to manually populate a form by referencing a hidden session state item named P2_ID.
FOR C1 in (SELECT ename, sal
FROM emp WHERE ID=:P2_ID)
LOOP
:P2_ENAME := C1.ename;
:P2_SAL := C1.sal;
END LOOP;
In this example:
-
C1is an implicit cursor. -
The value of
P2_IDhas been set. -
The process point for this process would be set to execute (or fire) on or before Onload - Before Regions.
Validating User Input in Forms
You can use validations to check data a user enters before processing. Once you create a validation and the associated error message, you can associate it with a specific item. You can choose to have validation error messages display inline (that is, on the page where the validation is performed) or on a separate error page.
Creating an inline error message involves these steps:
-
Create a validation and specify error message text. To learn more, see "Creating Item and Page Validations".
-
Associate the validation with a specific item.
Topics:
Associating a Validation with a Specific Item
To associate an item with a validation and specify error message text:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Navigate to the Edit Page Validations page:
-
Tree view - Right-click the validation name and click Edit.
-
Component view - Under Validations, select the validation item you want to associate.
The attributes page for the validation appears.
-
-
Scroll down to Error Message:
-
Error message display location - Verify the display location.
-
Associated Item - Select the item you want to associate with this validation.
-
-
Click Apply Changes.
About Error Message
Error message display location identifies where a validation error message displays. Validation error messages can display on an error page or inline within the existing page. Inline error messages can display in a notification area (defined as part of the page template) or within the field label.
To create a hard error that stops processes, including any remaining validations, you must display the error on an error page.