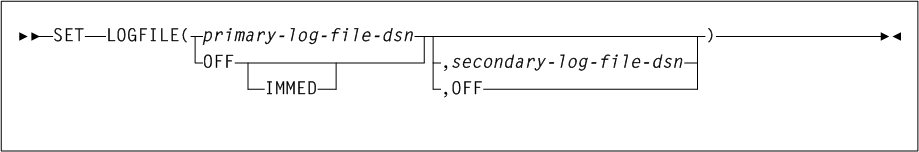
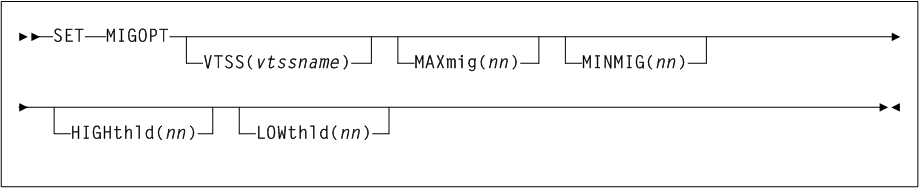
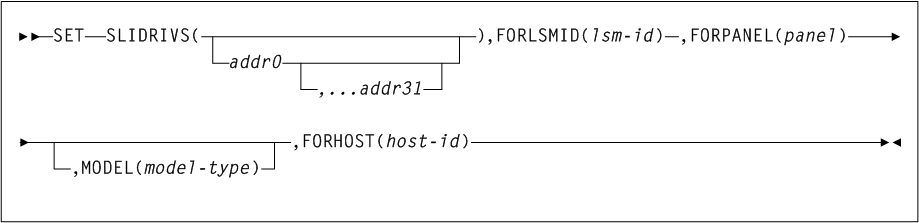
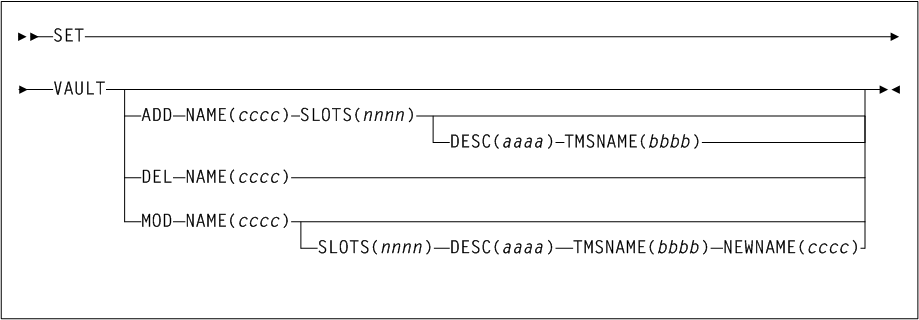
3 HSC Commands, Utilities, and Control Statements
This chapter contains reference information about HSC and VTCS commands and control statements.
Note:
-
Control statements that are loaded by an operator command are described along with that command. Other control statements, including those specified in the
PARMLIBdata set, are described independently. -
Certain HSC and VTCS commands are described in the ELS Legacy Interfaces Reference. These commands were introduced in a pre-ELS software release and their functionality has been replaced in ELS. These commands are supported by ELS, however, this support will end in a future release.
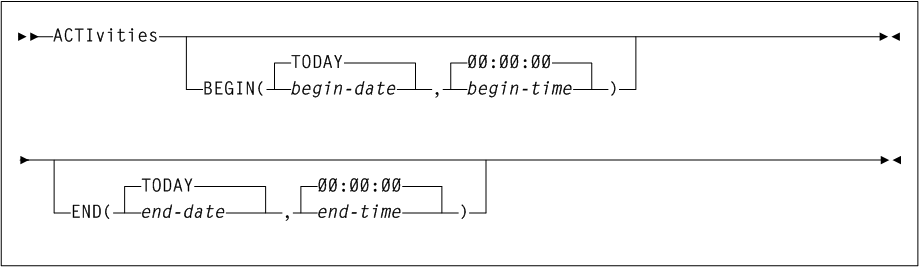
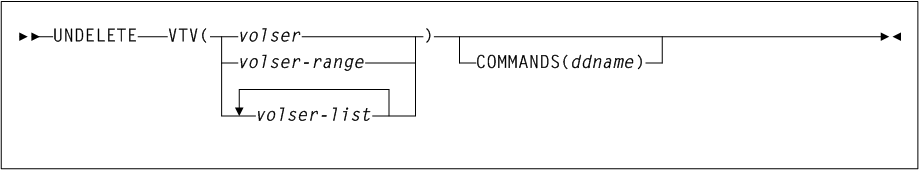
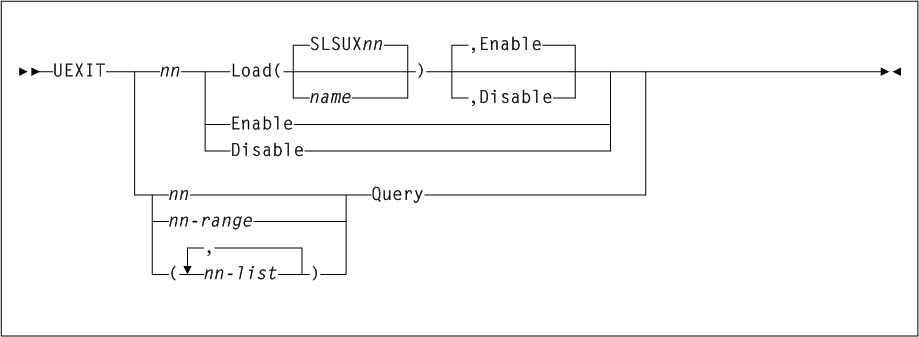
ACTIvities
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The ACTIvities command generates a statistical report of library resource loading by volume groups (for example, scratch compared to nonscratch, pass-thru activity, mounts, dismounts, entered, and ejected). This report provides information to help you monitor library resources and usage.
The utility also requires the SMF data for the time period requested (see "SET SMF"). It is assumed that you elect to have cartridge movement SMF records recorded in the time period specified. It is also assumed that the SMF records are in sequence by:
-
SMF ID
-
date
-
time, from earliest to latest.
Duplicate or out of sequence records cause the utility to terminate and to display a message indicating that the SMF records are not sorted. See "Additional Sort Control Cards" for sort statements you can specify to avoid this situation.
Note:
Periodic performance statistics are not available for the SL8500 library. Volume movement statistics, including enter, eject, mount, dismount, and move, are produced for all library types.Parameters
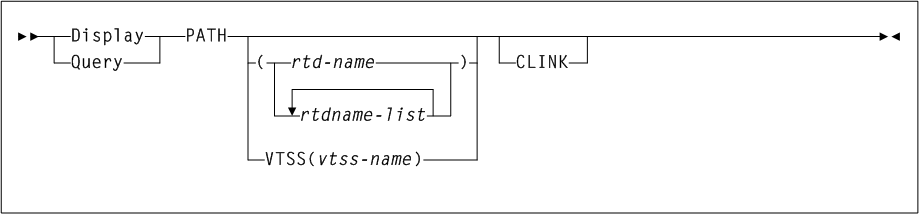
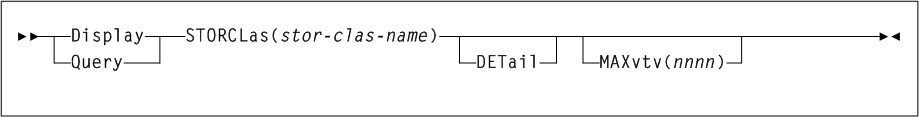
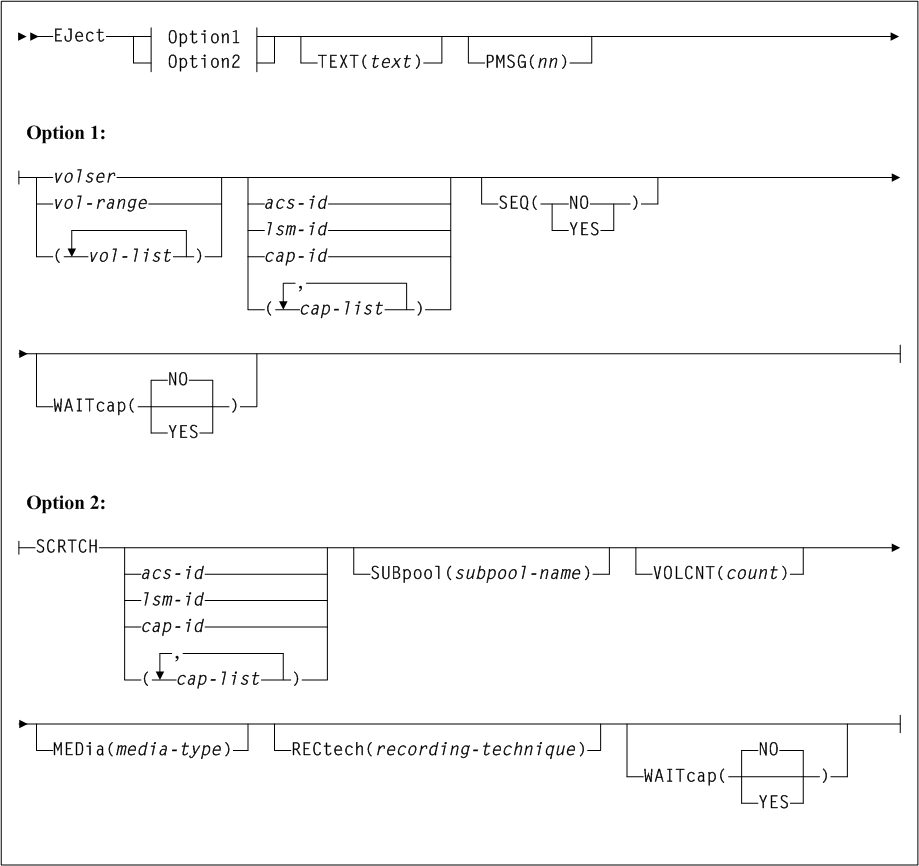
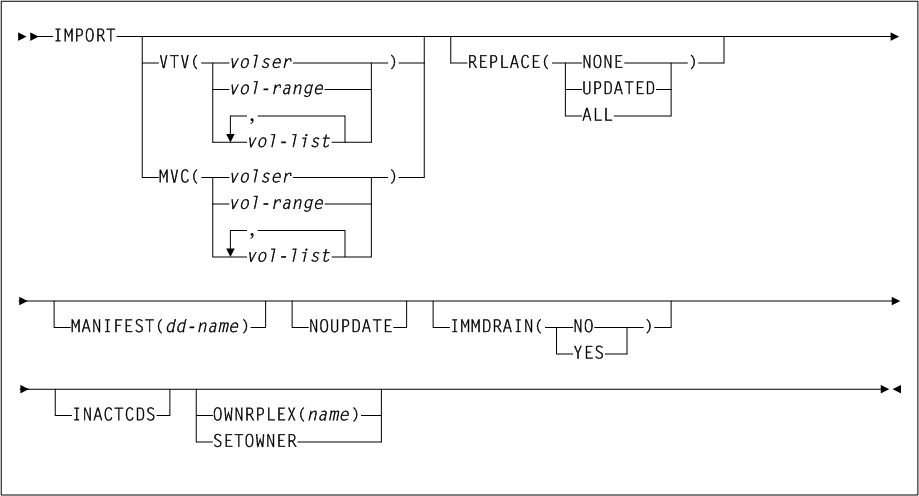
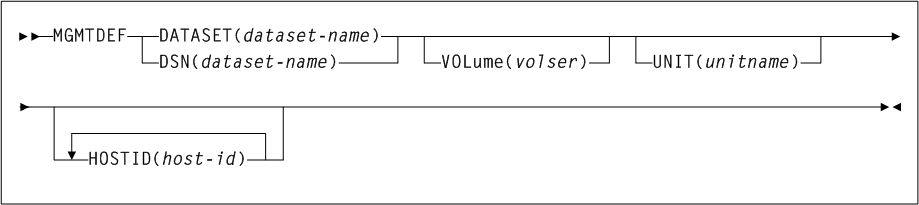
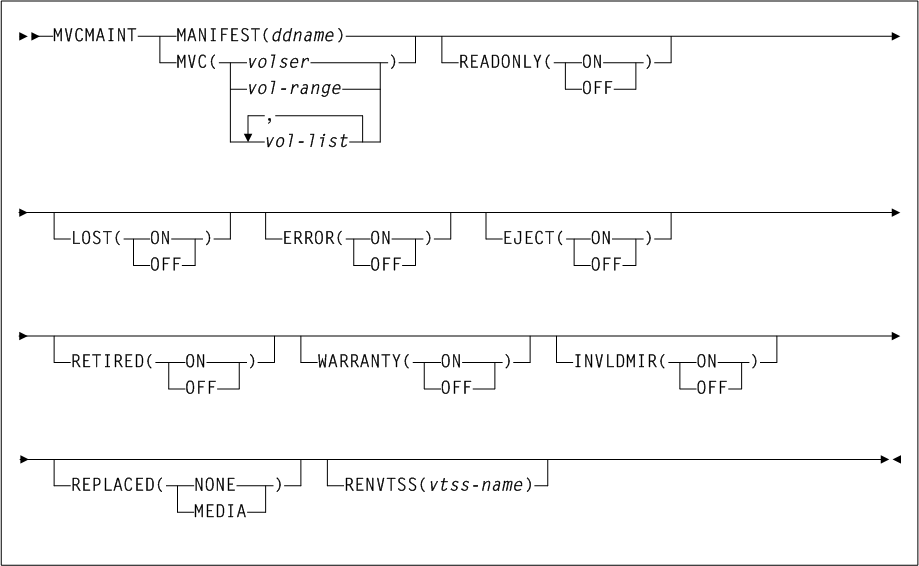
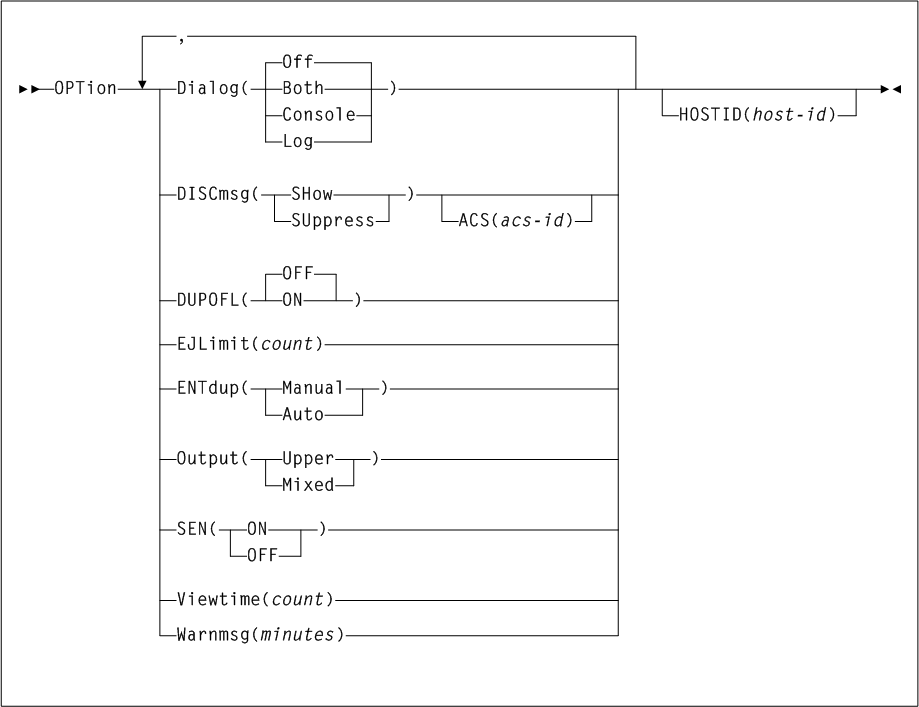
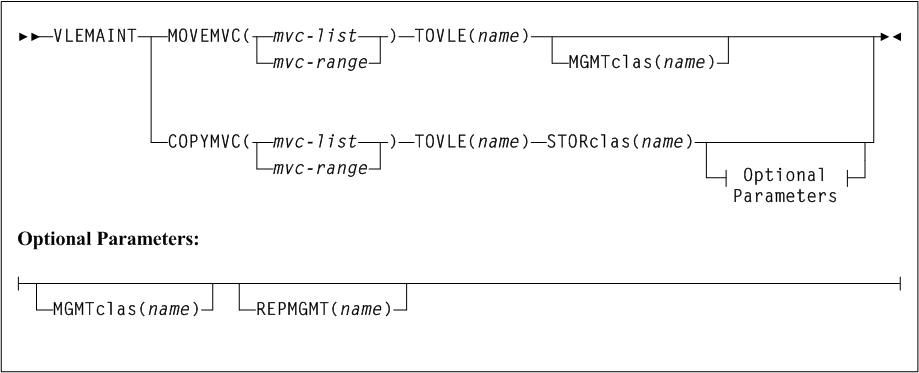
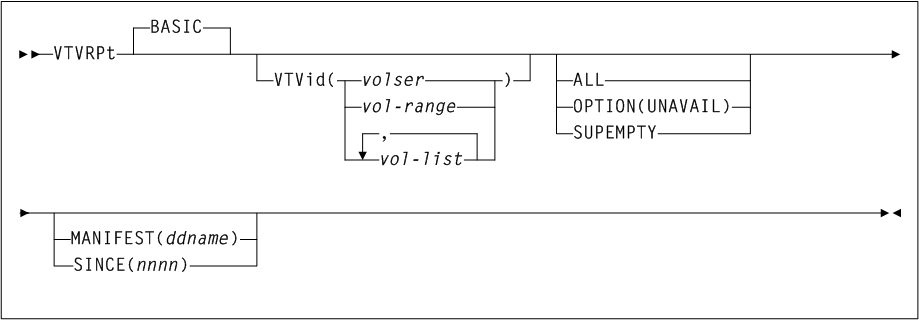
As shown in Figure 3-1, the ACTIvities command includes the following parameters:
- BEGIN(begin-date or TODAY),begin-time)
-
optionally, specifies the beginning of the period for the activities analysis.
- begin-date or TODAY
-
the starting date of the analysis.
-
Specify a date in
mm/dd/yyoryyyymmddformat.When using this format, specify a
yyvalue of 71 or greater to indicate a 20th century (19xx) date. Specify ayyvalue of 70 or less to indicate a 21st century (20xx) date. To avoid confusion, you are encouraged to use theyyyymmdddate format. -
Specify
TODAYfor the default date.
-
- begin-time
-
the beginning timeofday (24hour value), expressed in
hh:mm:ssformat.The allowable range for
begintimeandendtimeparameters is 00:00:00 to 24:00:00. The default value is 00:00:00.In each of the following examples, activity reporting begins on October 27, 2008 at midnight:
BEGIN(10/27/08,00:00:00) BEGIN(20081027,00:00:00) BEGIN(TODAY,00:00:00) BEGIN(,00:00:00)
- END(end-date or TODAY),end-time)
-
optionally, specifies the beginning of the period for the activities analysis.
- end-date or TODAY
-
the ending date of the analysis.
-
Specify a date in
mm/dd/yyoryyyymmddformat.When using this format, specify a
yyvalue of 71 or greater to indicate a 20th century (19xx) date. Specify ayyvalue of 70 or less to indicate a 21st century (20xx) date. To avoid confusion, you are encouraged to use theyyyymmdddate format.If
begindateis specified,enddatemust be in the same format. -
Specify
TODAYfor the default date.
-
- end-time
-
the ending timeofday (24hour value), expressed in
hh:mm:ssformat.The allowable range for
begintimeandendtimeparameters is 00:00:00 to 24:00:00. The default value is 23:59:59.For example:
END(10/27/08,18:00:00) END(20081027,11:30:00) END(TODAY,23:29:00) END(,23:59:59)
Additional JCL Requirements
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statements apply to the ACTIvities JCL:
- SLSSMF
-
SMF data which the utility reports against. This may be a number of data sets concatenated from oldest to newest. This is an off-loaded copy of the active SMF data sets, created by the SMF dump utility
IFASMFDP.The SMF record type defined to HSC is the only SMF record used by
ACTIvities. To reduce theACTIvitiesrun time, use theIFASMFDPutility to create a new SMF data set containing only the SMF record type defined to HSC. The following example can be used to create the HSC only SMF data set://jobcard //SMFCOPY EXEC PGM=IFASMFDP //MAN DD DISP=SHR,DSN=input.smf.data //DUMPOUT DD DISP=(NEW,CATLG,DELETE),UNIT=your_esoteric, // SPACE=(CYL,(500,500),RLSE),DSN=hsc.only.data //SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=* //SYSIN DD * INDD(MAN,OPTIONS(DUMP)) OUTDD(DUMPOUT,TYPE(your_HSC_SMF_record_number)) . Note - A DISPLAY CDS command can be issued to find your_HSC_SMF_record_number.
Additional Sort Control Cards
You must specify several additional control cards in the SYSIN portion of the SYELSORT JCL to make sure SMF records are sorted.
//SYSIN DD# INCLUDE COND=(6,1,BI,EQ,X'xx') SORT FIELDS=(15,4,CH,A,11,4,PD,A,7,4,BI,A) SUM FIELDS=NONE
Note:
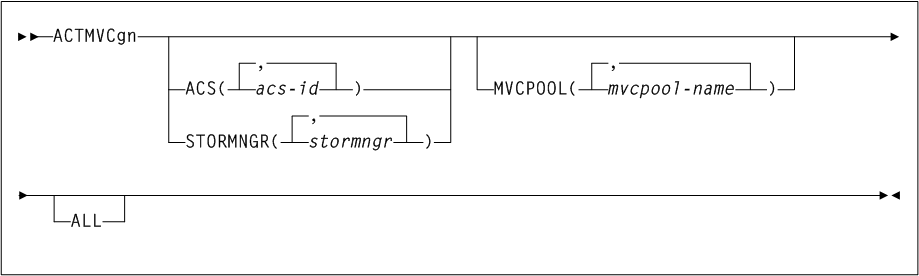
In theINCLUDE COND statement, the SMF type setting, shown as X'xx above, is supplied by the user. The default setting is FF (SMF type 255).ACTMVCgn
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC required only when specifying the MVCPOOL parameter
Description
The ACTMVCgn command is an optional command used in a VSM environment with the CDRT facility. ACTMVCgn produces two sets of MVCMAINT statements which are output to two files specified by the SLUSMVON and SLUSMVOF DD statements.
After ACTMVCgn executes:
-
SLUSMVONcontains a set ofMVCMAINTstatements with theREADONLY(ON)keyword. -
SLUSMVOFcontains a set ofMVCMAINTstatements with theREADONLY(OFF)keyword.
Successful execution of ACTMVCgn results in an equal number of MVCMAINT statements in both SLUSMVON and SLUSMVOF data sets.
Note:
Refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Disaster Recovery and Offsite Data Management Guide for examples of use of this utility function.Parameters
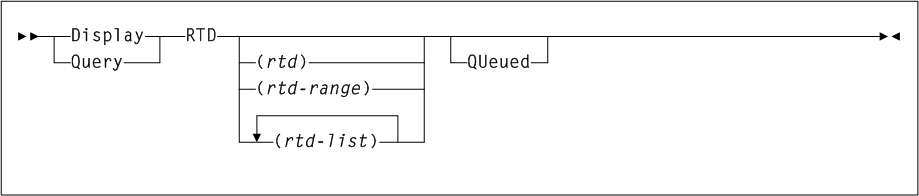
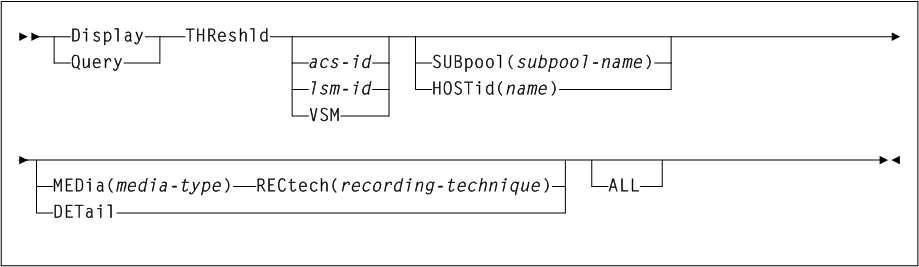
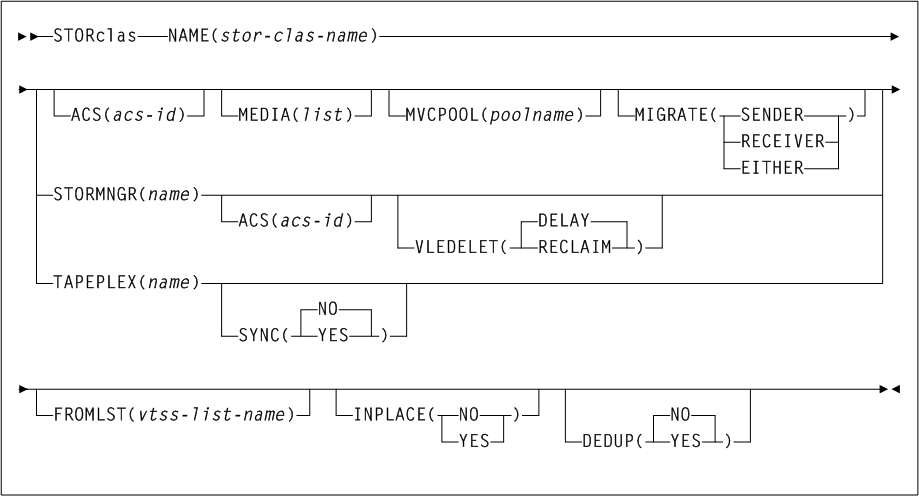
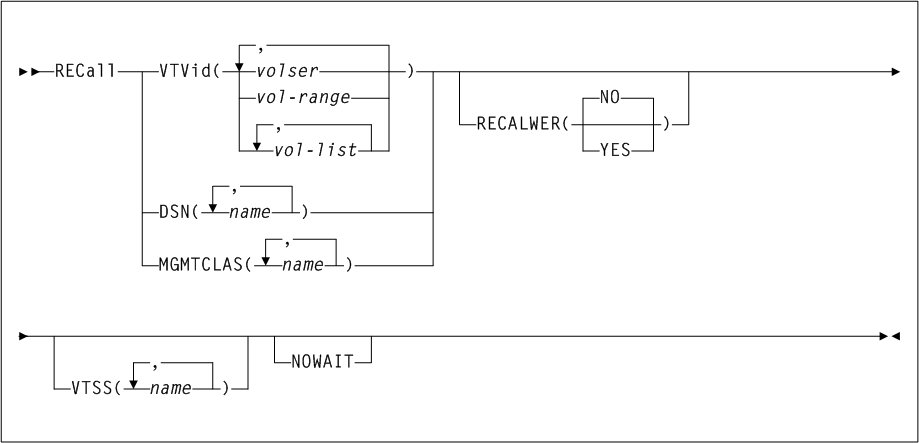
As shown in Figure 3-2, the ACTMVCgn command includes the following parameters:
- ACS(acs-id)
-
optionally, specifies an ACS that the CSV-based output is filtered against.
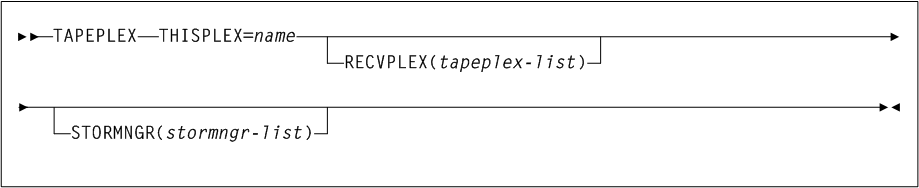
acs-idindicates the two-character ACS id. Blanks are not valid. To specify multiple ACSs, separate each ACS id with a comma. IfACSis not specified, the default is all ACSs. - STORMNGR(stormngr-name)
-
optionally, specifies a
STORMNGRthat the CSV-based output is filtered against.stormngr-nameindicates theSTORMNGRname. This name can include a maximum of 8 characters. Blanks are not valid. To specify multipleSTORMNGRnames, separate each name with a comma. - MVCPOOL(mvcpool-name)
-
optionally, specifies an
MVCPOOLthat the CSV-based output is filtered against.mvcpool-nameindicates theMVCPOOLname. This name can include a maximum of 13 characters. Blanks are not valid. To specify more than oneMVCPOOL, separate eachMVCPOOLname with a comma.Note:
If you specify theMVCPOOLparameter and the HSC subsystem is not active, the utility cannot complete and a return code of 8 is issued. - ALL
-
optionally, requests that
READONLY(ON)andREADONLY(OFF)control statements be generated for all non-empty MVCs. IfALLis not specified,READONLYcontrol statements are not generated for full MVCs.
Additional JCL Requirements
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statements apply to the ACTMVCGN JCL:
- SLUSMAUD
-
Output in the form of
SLUADMINutility control statements to audit selected MVCs. This statement is optional; if it is present, thenAUDITutility control statements are generated for all non-empty MVCs, except for those inEXPORTstatus. - SLUSMVON
-
ACTMVCGNoutput in the form ofMVCMAINTutility control statements with theREADONLY(ON)keyword. - SLUSMVOF
-
ACTMVCGNoutput in the form ofMVCMAINTutility control statements with theREADONLY(OFF)keyword.
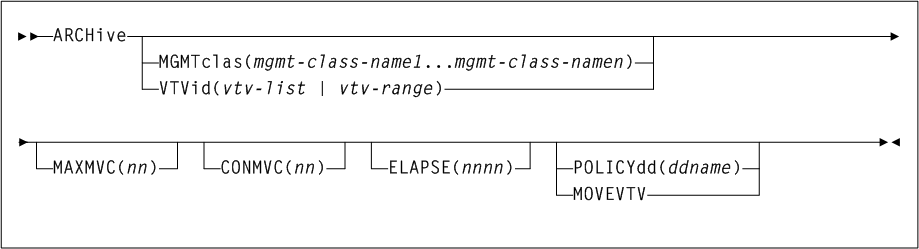
ARCHive
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
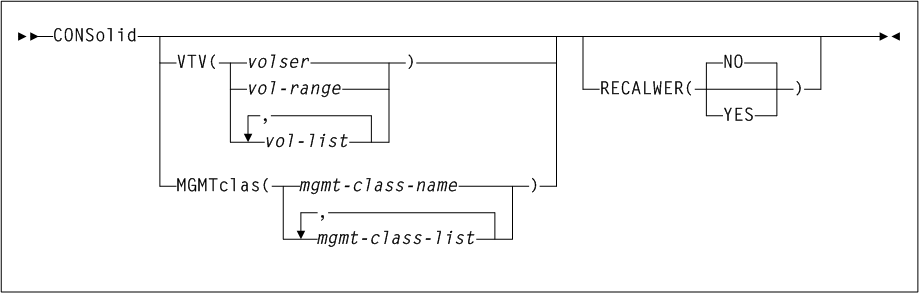
Parameters
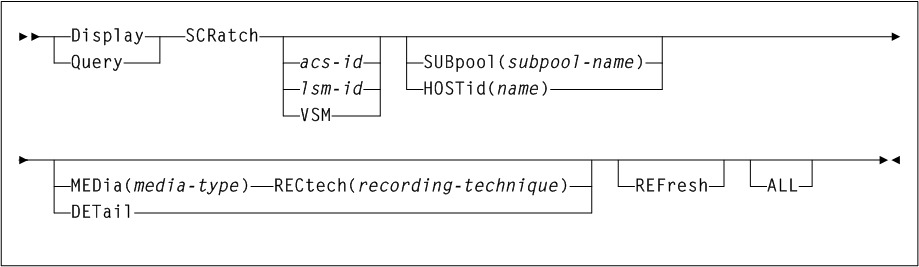
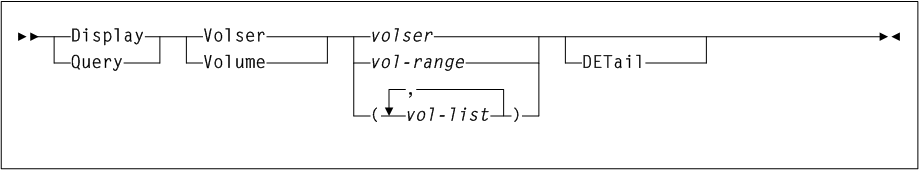
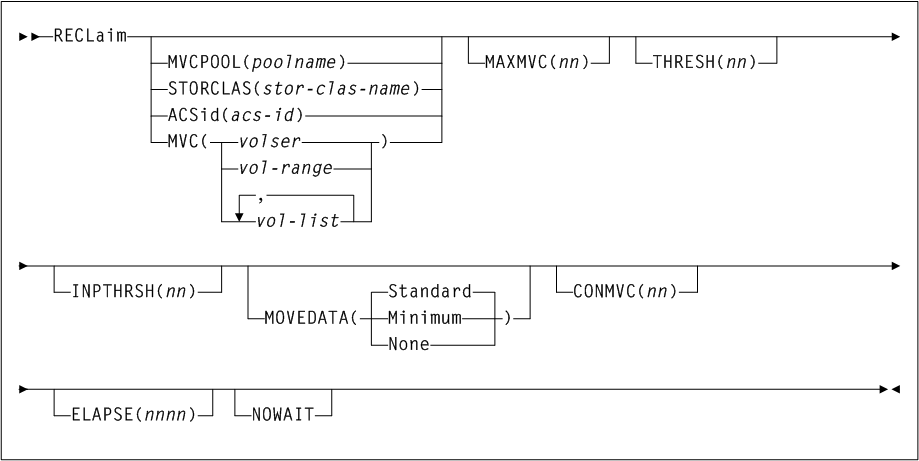
As shown in Figure 3-3, the ARCHive command includes the following parameters:
- MGMTclas(mgmtclas-name1...mgmtclas-namen)
-
optionally, specifies one or more Management Classes that define Archive Management Policies.
mgmtclas-name1...mgmtclas-namenindicates one or more Management Classes. - VTVid(vtv-list or vtv-range)
-
optionally, specifies a list or range of VTVs. This parameter is mutually exclusive with
MGMTclas.Note:
If you do not specify a value forMGMTclasorVTV, VTCS scans (or processes) all VTVs. - MAXMVC(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum number of MVCs that will be processed by a single archive task.
nnindicates the maximum number of MVCs. - CONMVC(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum number of MVCs (
nn) that VTCS concurrently processes during subsequent recall and migrate operations.Valid values are 1 to 99. If not specified the
CONFIG RECLAIMvalue (or default) is used. This parameter is ignored ifMOVEVTVis not specified. - ELAPSE(nnnn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum time for the archive in minutes (
nnnn). If the maximum time expires, VTCS issues messageSLS6682I. If there are no MVCs currently mounted, archive stops when theELAPSEvalue is reached. If any MVCs are currently mounted when theELAPSEvalue is reached, archive processes the mounted MVCs and then stops.Valid values are 1 to 1440. If not specified, there is no time limit on the archive process. This parameter is ignored if
MOVEVTVis not specified. - POLICYdd(ddname)
-
optionally, specifies the
ddnameof a file containing an alternateMGMTclasstatement. This parameter is mutually exclusive withMOVEVTV. - MOVEVTV
-
optionally, archive VTVs per the currently active Management Policies as specified by the
MGMTclasstatements that apply to the VTVs specified byMGMTclasorVTV. If you do not specifyMOVEVTV, only a report is generated (no VTVs are moved). This parameter is mutually exclusive withPOLICYdd.
Examples
The following examples provide examples of the following ARCHive reports:
ARCHive Report (MOVEVTV not specified)
The following example shows an example of an ARCHive report (MOVEVTV not specified).
Example 3-1 ARCHive report (MOVEVTV not specified)
SLUADMIN (7.2.0) STORAGETEK ENTERPRISE LIBRARY SOFTWARE UTILITY SSYS=HSCI PAGE 00002 TIME 15:50:09 ARCHIVE VTV REPORT DATE 2012-06-17 VTV SIZE %COMP <------------CREATION------------> MGMT VOLSER (MB) DATE TIME CLASS MVC1 MVC2 MVC3 MVC4 Y00001 1.62 39 2008JAN15 04:11:18 MJ4 02250 02251 02252 02253 Y00002 1.62 39 2008JAN15 04:03:57 MJ4 02250 02251 02252 02253 Y00003 1.62 39 2008JAN15 03:50:59 MJ3 02254 02255 Y00004 1.62 39 2008JAN15 03:45:04 MJ2 02256 02257 02268 Y00005 0.01 0 2008JAN17 23:56:00 MJ1 02259 Y00006 0.01 0 2008JAN17 23:41:37 MJ1 02259 Y00007 1.62 39 2008JAN05 06:15:46 MJ4 02250 02251 02252 02253 TOTAL VTVS=23 TOTAL SIZE=29.32MB TIME 15:50:09 ARCHIVE MVC REPORT DATE 2012-06-17 MVC MEDIA MEDIA STORAGE LOCATION CANDIDATE TOTAL VTV VOLSER TYPE SIZE(MB) CLASS (ACS ID) VTVS SIZE(MB) 022550 9840 20000 SC1 00 3 4.86 Y00001 Y00002 Y00007 022551 9840C 40000 SC3 3 4.86 Y00001 Y00002 Y00007 022559 9940A 60000 SC4 17 18.50 Y00005 Y00006 Y00015 Y00027 Y00042 Y00048 Y00053 Y00059 Y00061 Y00067 Y00073 Y00078 Y00084 Y00088 Y00101 Y00123
Fields
The following list describes the ARCHive VTV report fields. This section of the report is followed by a total line showing the number of candidate VTVs and the size in MB to be recalled and re-migrated.
- VTV Volser
-
the VTV volser.
- Size (MB)
-
the uncompressed size of the VTV (MB).
<MOUNT>indicates that the VTV was mounted when the report ran.<FENCED>indicates that the VTV's state is unknown. If<FENCED>appears, contact Oracle StorageTek Software Support. - Comp %
-
the VTV compression percentage achieved. This is the difference between the uncompressed and compressed VTV size expressed as a percentage of the uncompressed VTV size. For example if a 100 MB VTV compresses to 40 MB then the compression% will be given as 60%. A compression of 0% indicates that no compression was possible on the VTV.
- Creation Date and Time
-
the date and time that the VTV was created.
- MGMT Class
-
the name of the Management Class for the VTV specified.
- MVC1, MVC2, MVC3, MVC4
-
the MVC(s) that contain the VTV. If all of these fields are empty, the VTV has not been migrated or consolidated. If 1 or more of these fields list an MVC volser, the VTV was migrated to each of these MVCs.
Fields (MVC Report)
The following list describes the ARCHive MVC report fields. The data for each MVC is followed by one or more VTV volsers with copies on the MVC. This section of the report is followed by a total line showing the number of candidate MVCs and the size in MB to be recalled and re-migrated.
- MVC volser
-
the MVC volser.
- MVC Media Type
-
the MVC type.
- Media Size (MB)
-
the size of the MVC (MB). This will only be determined after VTCS has used an MVC.
UNKNOWNappears in this field until VTCS migrates a VTV to the MVC. - Storage Class
-
the MVC's Storage Class.
- Candidate VTVs
-
the number of candidate VTVs on the MVC.
- Total VTV Size (MB)
-
the size of all candidate VTVs on the MVC in MBs.
- Location (ACS ID)
-
the ACS where the MVC resides. If blank, the MVC is not currently in an ACS.
ARCHive MOVEVTV Report (MOVEVTV specified)
The following example shows an example of an ARCHive MOVEVTV report.
Example 3-2 ARCHive MOVEVTV report
SLUADMIN (7.2.0) StorageTek Enterprise Library Software Utility PAGE 0001 TIME 10:07:10 ARCHIVE MOVEVTV REPORT DATE 2015-03-31 Move VTV - MVC 022705 ignored, MAXMVC reached Move VTV - VTV X04898 ignored, all MVC copies rejected Move VTV - 4 MVCs selected for processing Move VTV - 5 VTVs selected for processing Move VTV - 5 VTV copies to be processed Move VTV - 0 VTV copies not matched to request Move VTV - 1 VTV copies rejected by MAXMVC limit Move VTVs - MVC 023484 selected and contains 1 VTVs Move VTVs - MVC 022628 selected and contains 1 VTVs Move VTVs - MVC 022631 selected and contains 2 VTVs Move VTVs - MVC 022608 selected and contains 1 VTVs Recall from MVC 022628 to VTSS HBVTSS17 SLS6683I Bulk recall of 1 VTVs issued to MVC 022628 SLS6644I VTV X99909 recalled from MVC:022628 Block:25401431 SLS6637I Recall from MVC 022628 completed Recall from MVC 023484 to VTSS HBVTSS17 SLS6683I Bulk recall of 1 VTVs issued to MVC 023484 SLS6644I VTV X04897 recalled from MVC:023484 Block:02402581 SLS6637I Recall from MVC 023484 completed Recall from MVC 022608 to VTSS HBVTSS16 SLS6683I Bulk recall of 1 VTVs issued to MVC 022608 SLS6637I Recall from MVC 022608 completed Migrate to storage class HBVTSS16 from VTSS HBVTSS17 SLS6681I VTV X99909 migrated to MVC:022589 Block:01400025 StorCl:HBVTSS17 MgmtCl:SIMPLEX SLS6636I Demand migration to MVC 022589 completed Recall from MVC 022631 to VTSS HBVTSS16 SLS6683I Bulk recall of 2 VTVs issued to MVC 022631 SLS6644I VTV X99910 recalled from MVC:022631 Block:03400141 SLS6644I VTV X99908 recalled from MVC:022631 Block:05400281
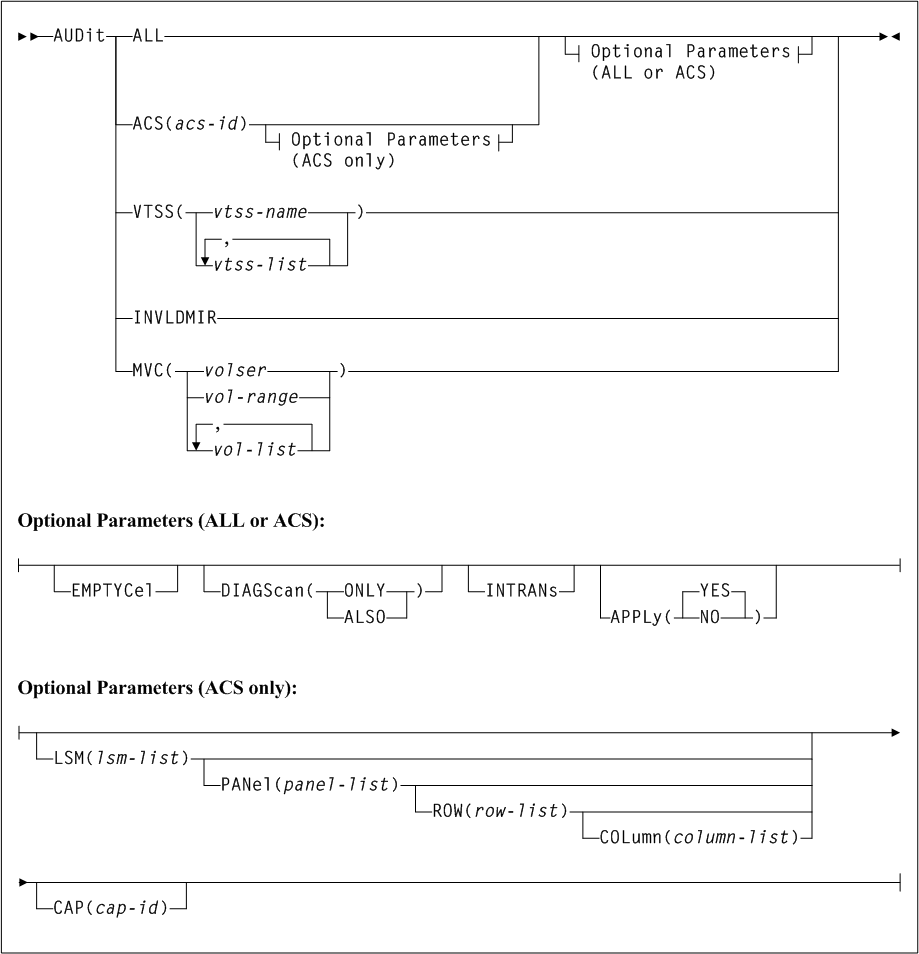
AUDit
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
Yes, when
MVCorVTSSis specified
Subsystem Requirements:
-
Active HSC/VTCS (
AUDit MVC,VTSS, orINVLDMIR) -
Active HSC at
FULLservice level (all others)
Description
The AUDit command performs a volume inventory audit for the following:
-
ACS or LSM
-
One or more specified LSMs within an ACS
-
One or more panels within an LSM
-
One or more rows within a panel
-
One or more columns (cells) within a row
-
One or more VTSSs
-
One or more MVCs
Optional parameters enable you to do the following:
-
Update the library control data set to reflect cartridges observed.
-
Produce a discrepancy list and do not update the control data set.
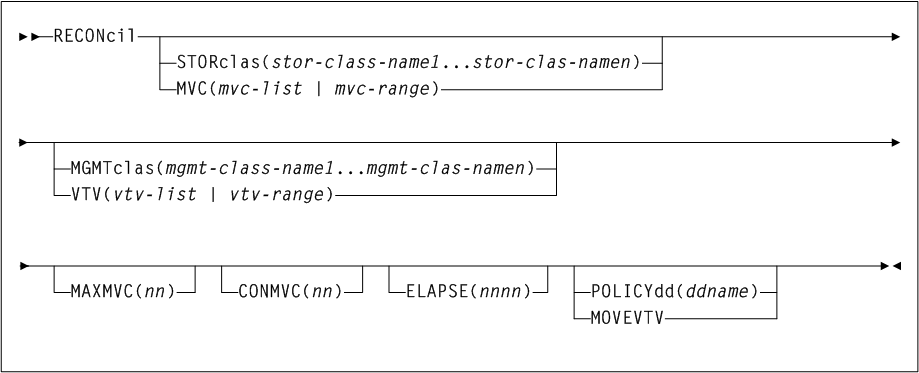
Parameters (Real Volume Audit)
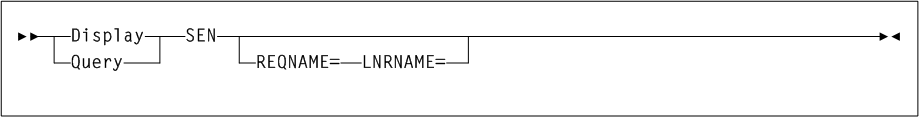
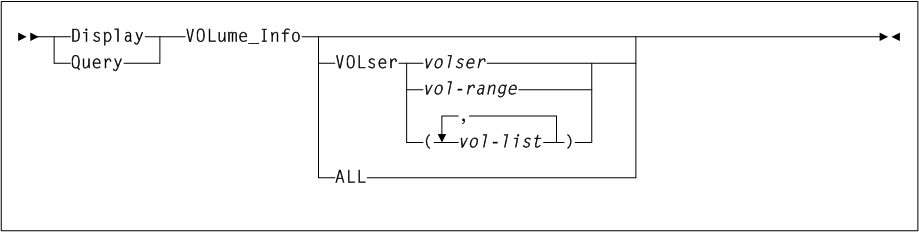
As shown in Figure 3-4, the AUDit command includes the following parameters:
- ALL
-
optionally, specifies that the total library is to be audited.
- ACS(acs-id)
-
optionally, specifies that only a particular ACS in the library is to be audited.
acs-idindicates a one or two digit hexadecimal ACS identifier.Note:
If theACSparameter is specified with noLSMparameters, the audit is performed on all LSMs in the ACS at the same time (multitasking). To audit only certain LSMs within an ACS, you must code theLSMparameter with the LSM or list of LSMs.
Optional Parameters (ALL or ACS)
The following parameters may be specified with either ALL or ACS:
- EMPTYCel
-
optionally, specifies that only empty cells are to be audited. This parameter cannot be used in combination with
AUDItparameterDIAGScan(ONLY).The main benefit provided by auditing only empty cells is reducing the time required to run an audit.
Note:
Oracle does not recommend running an empty cell audit on an SL8500 library because the time to run the audit is not substantially reduced.Typically, users may specify this parameter when:
-
they have entered an LSM and placed new cartridges in empty cells, or
-
they need to correct cartridge location information for library volumes that have been manually moved to empty cells.
In either case, if
APPLy(YES)is specified, the CDS is updated to reflect that these cells are no longer empty.Caution:
In either case, ifAPPLy(YES)is specified, the CDS is updated to reflect that these cells are no longer empty. -
- DIAGScan
-
optionally, specifies that diagnostic cells are to be scanned. The HSC scans these cells one at a time and displays the contents of each cell in the
AUDItutility report.DIAGScanis mutually exclusive withROWandCOLumn. It can be used in combination with all otherAUDItparameters.- ONLY
-
specifies that only diagnostic cells should be scanned. This parameter cannot be specified in combination with the
EMPTYCelparameter. - ALSO
-
specifies that diagnostic cells should also be scanned along with the normal
AUDItutility operations.
Note:
Cartridge movement between diagnostic cells and regular storage or CAP cells is not supported by the LMU, so diagnostic cell contents can only be reported. - INTRANs
-
optionally, specifies that in-transit cartridges in an LSM are to be processed. All in-transit cartridges, except those identified in the note below, are read and ejected as part of an
AUDItutility operation.INTRANsis mutually exclusive withAPPLY(NO).-
Only the first two cells (columns 0 and 1) in a 9310 playground are accessible to an in-transit audit. Cartridges in other cell positions in a 9310 playground (columns 2 through 5) cannot be ejected by an in-transit operation.
-
9740 diagnostic cells cannot be scanned by an audit.
-
- APPly
-
optionally, specifies whether the control data set is updated.
- YES
-
specifies that the Audit operation ejects cartridges with duplicate volume serial numbers, unreadable or illegal external media labels, and/or new cartridges unreadable external labels, and performs corrective actions to the control data set to reflect the physical contents of storage cells.
YESis the default. - NO
-
specifies that a discrepancy listing is produced, and the control data set is not updated.
Optional Parameters (ACS Only)
The following parameters may only be specified with ACS:
- LSM(lsm-list)
-
optionally, specifies that only certain LSMs within the specified ACS are to be audited.
lsm-listis a single LSM number or a list of LSM numbers. An LSM number is a hexadecimal value (00-17). An LSM range is not allowed. If a list is specified, the elements must be separated by blanks or commas, and the entire list enclosed in parentheses. - PANel(panel-list)
-
optionally, specifies that only certain panels within an LSM are to be audited. If this parameter is specified, the
LSMparameter may contain only one LSM number.panel-listis a single panel or a list of panels. Panel ranges are not allowed. If a list is specified, the elements must be separated by blanks or commas, and the entire list enclosed in parentheses. Apanellistelement is a one or two digit decimal number, specific to the LSM type. See "Panels" for a list of valid values.The SL3000 library has static panels numbers starting with the left-most back panel (panel 0) and ending with the right-most front panel (panel 23) on a fully-configured library. The panel numbering starts with the BDM, the only required module (panels 12 and 13), and works outward to the left and to the right.
Panels 0 (CAP panel) and 1 (drive panel) are allowable entries for an SL8500 audit, however, in this case the HSC displays a condition code 0 because it does not find any storage cells on these panels.
- ROW(row-list)
-
optionally, specifies that only certain rows within the specified LSM panel are to be audited. If this parameter is specified, the
LSMandPANelparameters may contain only one element.row-listis a single row or a list of rows. Ranges are not allowed. If a list is specified, the elements must be separated by blanks or commas, and the entire list enclosed in parentheses. Arowlistelement is a one or two digit decimal number, and is specific to the LSM type. See "Rows" for a list of valid values. - COLumn(column-list)
-
optionally, specifies that only certain columns (cells) within an LSM panel row are to be audited. If this parameter is specified, the
LSM,PANel, andROWparameters may contain only one element.column-listis a single column, or a list of columns. Ranges are not allowed. If a list is specified, the elements must be separated by blanks or commas, and the entire list enclosed in parentheses. Acolumnlistelement is a one or two digit decimal number and is specific to the LSM type. See "Columns" for a list of valid values.-
A list of rows cannot be specified if a list of columns is specified.
-
A list of columns cannot be specified if a list of rows is specified.
-
All SL3000 columns are numbered 0-5 (left to right).
-
- CAP(cap-id)
-
optionally, specifies a particular Cartridge Access Port to be used for any required cartridge ejections during the Audit operation.
cap-ididentifies one or more CAPs. The format isAA:LL:CC, whereAA:LLindicates the LSM id, andCCindicates the CAP. See "CAP Numbers" for a list of valid values.If a
CAPis not specified, a CAP in the identified ACS is selected based on theCAPPrefoperator command. See "CAPPref" for more information.MultiACS audits cannot specify the
CAPparameter. A CAP is chosen for each ACS based upon CAP preference values.
Parameters (Virtual Volume Audit)
As shown in Figure 3-4, the AUDit command includes the following parameters for a virtual volume audit:
- VTSS(vtss-name or vtss-list)
-
optionally, specifies an audit of one or more VTSSs.
vtss-nameorvtss-listindicates the names of one or more VTSSs. - INVLDMIR
-
optionally, specifies an audit of MVCs with invalid MIRs.
- MVC(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
optionally, specifies an audit of one or more MVCs.
volser,vol-rangeorvol-listindicates the volser, volser range, or volser list of MVC(s) to be processed.
Parameters (Virtual Volume Audit)
As shown in Figure 3-4, the AUDit command includes the following parameters for a virtual volume audit:
- VTSS(vtss-name or vtss-list)
-
optionally, specifies an audit of one or more VTSSs.
vtss-nameorvtss-listindicate the names of one or more VTSSs to be processed. - INVLDMIR
-
optionally, specifies an audit of MVCs with invalid MIRs.
- MVC(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
optionally, specifies an audit of one or more MVCs.
volser,vol-rangeorvol-listindicates the volser, volser range, or volser list of MVC(s) to be processed.
Audit Report
An audit report lists the VTVs and MVCs that are different from those listed in the CDS, as shown in Example 3-3. In this example, the report shows all MVCs or VTVs as new entries in the CDS, which is typical of the output of a VTCS audit run after you lost all copies of the CDS, then ran recovery procedures.
AUDIT REPORT FOR MVC EVT500
X28955 VTV ADDED AS PRIMARY COPY (BLOCK:00000000)
X20000 VTV ADDED AS PRIMARY COPY (BLOCK:0940044D)
======== AUDIT OF MVC EVT500 COMPLETED SUCCESSFULLY ========
AUDIT REPORT FOR MVC EVT501
X28956 VTV ADDED AS PRIMARY COPY (BLOCK:00000000)
X20007 VTV ADDED AS PRIMARY COPY (BLOCK:0940044D)
X20010 VTV ADDED AS SECONDARY COPY (BLOCK:11400899)
X20069 VTV NOT CURRENT (BLOCK:1A400CE5)
X20067 VTV NOT CURRENT (BLOCK:334016AB)
======== AUDIT OF MVC EVT501 COMPLETED SUCCESSFULLY ========
AUDIT REPORT FOR VTSS HBVTSS17
X20000 VTV VALID
X20002 VTV VALID
X20005 VTV VALID
X20006 VTV VALID
X20007 VTV VALID
X30052 VTV VALID
X30053 VTV VALID
X30054 VTV VALID
======== AUDIT OF VTSS HBVTSS17 COMPLETED SUCCESSFULLY ========
AUDIT REPORT FOR VTSS HBVTSS16
X20183 VTV VALID
X20185 VTV VALID
X20188 VTV VALID
X20190 VTV VALID
X20191 VTV VALID
X20194 VTV VALID
X41091 VTV VALID
X41093 VTV VALID
======== AUDIT OF VTSS HBVTSS16 COMPLETED WITH 1 WARNING ========
AUDIT EXCEPTION REPORT
VTSS HBVTSS16: 1 WARNINGS REPORTED
SLS1315I SWS500.V5.CDS WAS SELECTED AS THE PRIMARY CONTROL DATA SET
Note:
An audit also generates the following:-
MVC summary and detail reports
-
Display VTSSsummary and detail output -
For every VTV resident on the VTSS, the VTV volser, size in MB, and Management Class
AUDit Report Messages
For every VTV found on an MVC or VTSS, the audit report lists one of following:
VVVVVV VTV possibly corrupt (Block:BBBBBB)
Explanation: During the audit, an I/O error occurred for VTV VVVVVV at block BBBBBB on the MVC being audited.
VVVVVV VTV not found [ , no MVC copies left ]
Explanation: The audit did not find VTV VVVVVV on the MVC or VTSS being audited. If no MVC copies left appears, no MVCs contain copies of t he VTV.
VVVVVV VTV not found on CDS (Block:BBBBBB)
Explanation: The audit did not find VTV VVVVVV on the MVC or VTSS being audited. If no MVC copies left appears, no MVCs contain copies of t he VTV.
VVVVVV VTV not current (Block:BBBBBB)
Explanation: The audit did not find VTV VVVVVV on the MVC or VTSS being audited. If no MVC copies left appears, no MVCs contain copies of t he VTV.
VVVVVV VTV not current (Block:BBBBBB)
Explanation: The audit did not find VTV VVVVVV on the MVC or VTSS being audited. If no MVC copies left appears, no MVCs contain copies of t he VTV.
VVVVVV VTV not current (Block:BBBBBB)
Explanation: The audit did not find VTV VVVVVV on the MVC or VTSS being audited. If no MVC copies left appears, no MVCs contain copies of t he VTV.
VVVVVV VTV Added as secondary copy (Block:BBBBBB)
Explanation: The audit found the second most current copy of VTV VVVVVV at block BBBBBB of the MVC being audited; the audit added this location to the CDS as the secondary MVC copy of the VTV.
VVVVVV Duplicate copy ignored (Block:BBBBBB)
Explanation: The audit found a duplicate copy of VTV VVVVVV at block BBBBBB and ignored this copy.
VVVVVV Link to old version on MVC MMMMMM removed
Explanation: The audit found a newer version of the VTV and removed the link to the old version from the CDS.
VVVVVV Old VTV version deleted from VTSS SSSSSSSS
Explanation: The audit found an old version of the VTV and deleted it from the VTSS.
VVVVVV Old version of VTV retained [ VTSS SSSSSSSS ]
Explanation: The audit found an old version of the VTV, which is the only copy, and retained this version. If VTSS SSSSSSSS appears, the audit found the VTV on a different VTSS than the one that was audited.
VVVVVV Version older than MVC copies [ VTSS SSSSSSSS ]
Explanation: The audit found a version of the VTV that is older than copies on the MVC. If VTSS SSSSSSSS appears, the audit found the VTV on a different VTSS than the one that was audited.
VVVVVV Newer version of VTV found [ on VTSS SSSSSSSS ]
Explanation: The audit found a newer version of the VTV and updated the CDS with this location. If on VTSS SSSSSSSS appears, the audit found the VTV on a different VTSS than the one that was audited.
VVVVVV VTV discovered [ VTSS SSSSSSSS ]
Explanation: The audit found a current version of the VTV on a VTSS whose location was unexpected and updated the CDS with this location. If on VTSS SSSSSSSS appears, the audit found the VTV on a different VTSS than the one that was audited.
VVVVVV VTV valid [ VTSS SSSSSSSS ]
Explanation: The audit found a valid version of the VTV and updated the CDS with this location. If VTSS SSSSSSSS appears, the audit found the VTV on a different VTSS than the one that was audited.
*** VVVVVV no access to VTSS SSSSSSSS ***
Explanation: The audit found a valid version of the VTV which is on a VTSS that the host cannot access.
MVC MMMMMM STATUS CHANGED FROM EXPORT TO CONSOLIDATE VOLUME
Explanation: The audit discovered current VTVs on an export MVC that was created by export by VTV or Management Class. The audit changed the MVC status from export to consolidate and updated the CDS to add the MVC and its VTVs.
EXPORT MVC MMMMMM IS NOW MADE EMPTY IN THE CDS
Explanation: The audit discovered no current VTVs on an export MVC that was created by export by VTV or Management Class. The audit marked the MVC as empty.
WARNING MVC MMMMMM IS AN OUTPUT MVC FROM AN EXPORT OPERATION - FORCING READONLY
Explanation: The audit forced read-only status on export MVC MMMMMM.
Audit terminated. Unable to determine the position of the end of VTV VVVVVV on MVC MMMMMM
Explanation: VTCS issued an Inventory MVC ECAM request to determine the position and volser of a VTV on the MVC being audited. VTSS indicated, in the ECAM response, that it was unable to determine the position of the end of the VTV. Because VTCS needs that information to determine the position of the next VTV on the MVC (assuming end of tape has not been reached), VTCS had to terminate the audit with RC=8. The MVC is left in Audit status. To resolve the condition, drain the MVC. If you cannot drain the MVC, contact Oracle StorageTek Software Support.
BACKup
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Note:
Backup to tape is not supported.Description
The BACKup command produces a backup of the library control data set (CDS).
The utility automatically selects the primary CDS copy based on the specified CDS DD statements or the CDS order used by the active HSC on the system.
If you want to back up a single, specific copy of the CDS, you can specify a single DD statement, SLSCNTL, to point to the file you want to back up. In general, however, you should only back up the primary CDS; the HSC RESTORE utility automatically creates the correct number of CDS copies when it executes.
Note:
-
Refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Legacy Interfaces Reference for information about using
BACKupwhen copies of the CDS are in different locations. -
See "PITCOPY" for information about the
PITCOPYcommand as an alternative to backup.
Parameters
None. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Legacy Interfaces Reference for information about using BACKup when copies of the CDS are in different locations.
Additional JCL Requirements
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statements apply to the BACKup JCL:
- SLSBKUP
-
specifies the created backup data set. The
LRECLandBLKSIZEof this data set default to 4096.
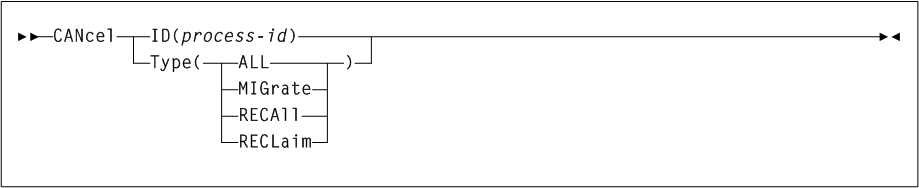
CANcel
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-6, the CANcel command includes the following parameters:
- ID(process-id)
-
specifies a process to cancel.
process-idindicates the process ID. - Type
-
optionally, specifies the type of process to cancel.
- ALL
-
Cancel all processes.
- MIGrate
-
Cancel all migration processes.
- RECAll
-
Cancel all recall processes.
- RECLaim
-
Cancel all reclaim processes.
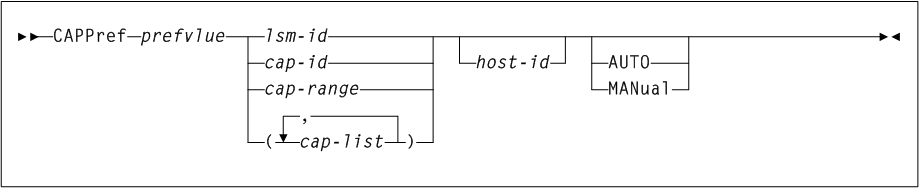
CAPPref
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIB -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The CAPPref command assigns a preference value to one or more designated CAPs, and places a CAP into automatic or manual mode.
Several HSC commands and utilities require the use of a CAP and give you the option to either specify the CAP to use, or allow the HSC to automatically select a CAP. When you allow the HSC to make the selection, the CAP is chosen based on availability and the CAP preference value.
Assigning CAP preference values establishes an ordered list of CAPs from which the HSC selects an available CAP with the highest nonzero preference value. A CAP's preference value is zero until it is changed by a CAPPref command. Zero preference CAPs are never automatically selected by the HSC; however, they can be explicitly requested by the user.
Note:
-
A CAP preference value is only in effect on the host that executes the command.
-
CAP mode (automatic or manual) is in effect on all hosts system-wide for each CAP; it cannot be set discretely for each host.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-7, the CAPPref command includes the following parameters:
- prefvlue
-
specifies a preference value which is assigned to all listed CAPs. Preference values are decimal in the range from 0-9.
A CAP with a preference value of 9 has the highest priority and is always selected first when it is available. If two or more available CAPs in an ACS have the highest preference value, the one with the lowest CAPid is selected.
The preference value for a PCAP must be zero. A PCAP is only used when explicitly requested by the user; the HSC does not automatically select a PCAP.
To use the CAPPref command to place a PCAP into
AUTOorMANualmode, specify a prefvlue of 0. - lsm-id
-
identifies an LSM. The format of an
lsm-idisAA:LL, whereAAindicates the ACSid (decimal 00-99) andLLindicates the LSM number (decimal 00-99).Note:
If you enter this parameter when there is more than one CAP in the specified LSM, an error message is generated. - cap-id, cap-range, or cap-list
-
identifies one or more CAPs. The format of a
capidisAA:LL:CC, whereAA:LLindicates the LSMid, andCCindicates the CAP. See "CAPid" for a list of valid values.Note:
-
If SL3000 library CAPs are not present, the HSC reports them as ”not installed.” This keeps CAP addresses from changing as new CAPs are added.
-
SL3000 and SL8500 libraries do not contain a PCAP.
A
caprangeidentifies an inclusive range of multicell CAPs; PCAPs are excluded from the range. The beginning and ending values in a range must be valid CAPids and neither CAPid can specify a PCAP. The rules for specifying ranges apply.PCAPs must be explicitly specified in the
CAPPrefcommand.Example 1:
00:00:00-00:03:00In this example, all CAPs in LSMs 00:00, 00:01, 00:02, and 00:03, except PCAPs, are included in this range.
Example 2:
00:00:00-00:03:01In this example, CAPid 00:00:00 is either a standard CAP or a magazinestyle CAP. CAPid 00:03:01 is a magazinestyle CAP. All CAPs in LSMs 00:01 and 00:02, except PCAPs, are included in this range.
Each
caplistelement can be either a single CAPid or a CAPid range. The elements in a list must be separated by a comma or a blank, and the entire list must be enclosed in parentheses. -
- host-id
-
optionally, specifies that the
CAPPRefcommand is to be performed only if thehostidparameter matches the identifier of the issuing host (the SMF system identifier for both JES2 and JES3).-
If
CAPPrefis issued fromPARMLIBand ahost-idis specified, the command is executed only by the host with the matching ID. -
If
CAPPrefis issued fromPARMLIBand ahost-idis not specified, the command is executed by each host that accessesPARMLIB.
Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Managing HSC and VTCS for more information about
PARMLIB. -
- AUTO
-
optionally, indicates that the specified CAPs are to be placed in automatic mode (referred to as automode). Automode CAPs remain unlocked when not in use.
AUTOis the initial setting for a PCAP.When a CAP is in automode, you can initiate an enter operation without issuing an
ENtercommand. You do this by opening the CAP door, placing one or more cartridges inside, and closing the CAP. The CAP is locked while the enter is being processed; then it is unlocked again.Automode CAPs can be used for eject processing by either:
-
specifying the
CAPidon anEJectcommand orEJECtutility, or -
assigning a preference value and allowing the HSC to automatically select the CAP
A CAP in automode is locked whenever it is selected for an eject operation, to prevent an enter operation on this CAP until the eject completes.
Note:
HSC termination will be slower with CAPs in automode; especially in a multiplehost environment. -
- MANual
-
optionally, indicates that the specified CAP is to be locked when not in use.
MANualis the initial setting for all multicartridge CAPs.AUTOorMANualsettings are sent hosttohost using LMU broadcast and the status is preserved in the control data set. For this reason, it is recommended that you not make frequent changes to the CAP mode.A
prefvlueof 0 must be specified when using theCAPPrefcommand to set a PCAP toAUTOorMANualmode.
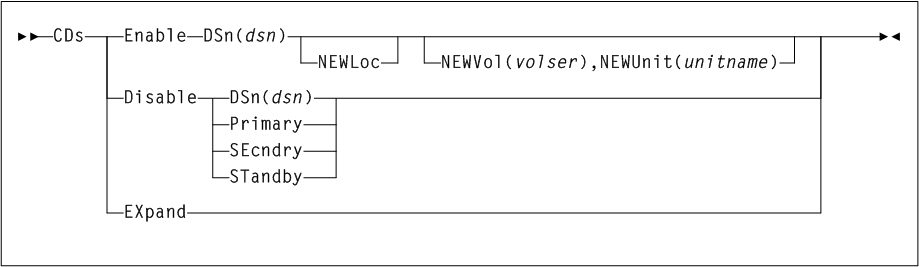
CDs
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIB -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Description
The CDs command enables, disables, relocates, or expands a control data set on an active HSC (or, in a multiple-host environment, on all active hosts) without requiring you to stop or substantially disrupt normal tape processes.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-8, the CDs command includes the following parameters:
- Enable
-
allocates and activates any preexisting, renamed, or new CDS specified by the
DSnparameter. TheCDs Enablecommand can allocate and activate a CDS residing in a new location, either with a preexisting or a new data set name, when theNEWLocparameter is specified. MVS catalog services are used to resolve the volume and unit definitions, if theNEWVolorNEWUnitparameters are not specified.The specified control data set must be named in the
CDSDEFcontrol statement inPARMLIB.- DSn(dsn)
-
specifies the control data set name to allocate for all hosts.
dsnindicates the data set name. This parameter is required. - NEWLoc
-
optionally, indicates that a relocation activity has occurred for the CDS named by the
DSnparameter. MVS uses the catalog facility to determine the volume location of the relocated CDS. - NEWVol(volser)
-
optionally, specifies the volume for a relocated CDS copy. In MVS if the new CDS copy is not cataloged, this parameter is required. If
NEWVolis specified, butNEWUnitis not,NEWUnitdefaults toSYSALLDA.volserindicates the volume.NEWVolis required if the user is executing the command in the HSC VM environment. - NEWUnit(unit-name)
-
optionally, specifies the unit name for a relocated CDS copy. This parameter defaults to
SYSALLDAif it is omitted andNEWVolis specified.unitnameindicates the unit name.NEWUnitis required if the user is executing the command in the HSC VM environment.
- Disable
-
unallocates (makes inactive) the specified CDS. The
CDs Disablecommand does not disable the last active copy of the control data set.- DSN(dsn)
-
optionally, specifies the control data set name to unallocate for all hosts.
dsnindicates the data set name. - Primary
-
optionally, indicates that the current primary control data set is to be disabled.
- SEcndry
-
optionally, indicates that the current secondary control data set is to be disabled.
- STandby
-
optionally, indicates that the current standby control data set is to be disabled.
- EXpand
-
expands all enabled CDSs to the maximum number of 4096 blocks that can fit in the physical space allocated for the CDS. The maximum number of 4096 blocks is determined by the smallest CDS copy.
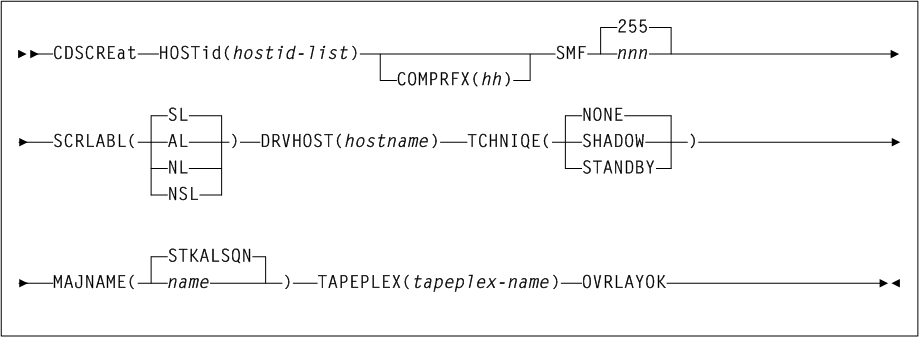
CDSCREat
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
None.
Description
The CDSCREat utility uses a small set of parameters to define the CDS for a tapeless configuration. A tapeless configuration may include VLE hardware but may not include any defined ACSs or real tape drives.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-9, the CDSCREat command includes the following parameters:
- HOSTid(hostid-list)
-
specifies the list of SMF host IDs on which this system can be executed. This parameter is required.
hostid-listindicates one or more host ids. You can specify a maximum of 16 host IDs. - COMPRFX(hh)
-
optionally, specifies the two-character hexadecimal representation of the command prefix to be used to enter commands to the subsystem. If this parameter is omitted or is set to a null value (40), then you must use the MVS
MODIFYcommand to direct requests to the subsystem, for example,F HSC0,D CDS. See Table 3-14 under theSET COMPRFXcommand for valid values.hhindicates the two-character hexadecimal value. - SMF(nnn)
-
optionally, specifies the SMF ID of statistics data that will be written to the
SMFdata set.nnnindicates the SMF ID. The value must be between 128 and 255.If this parameter is omitted, the value is set to 255.
- SCRLABL
-
optionally, specifies the label type used as the scratch default. Specify one of the following:
-
SLindicates standardlabeled tape. This is the default if the parameter is omitted. -
ALindicates ANSIlabeled tape. -
NLindicates nonlabeled tape. -
NSLindicates nonstandard labeled tape.
-
- DRVHOST(hostname)
-
optionally, specifies the host ID that will be used as the "master" value for drive addresses. If drive addresses are different for different hosts, a
DRVHOSTshould be set to allow SMC to map client drive addresses to fixed server drive addresses.host-nameindicates the "master" host id. - TCHNIQE
-
optionally, specifies the recovery technique (number of CDS copies) that will be created and used by the system.
-
NONEspecifies one CDS copy. This is the default if the parameter is omitted. -
SHADOWspecifies two CDS copies. -
STANDBYspecifies three CDS copies.
If this parameter is omitted, the default value is
NONE. TheCDSCREATutility validates that the specified (or implied) technique matches the number ofCDS DDstatements specified. -
- MAJNAME(name)
-
optionally, specifies an
ENQ/DEQ/RESERVE QNAME.nameindicates the a 1-8 characterQNAME.If this parameter is omitted, the default value is
STKALSQN. - TAPEPLEX(tapeplex-name)
-
optionally, specifies a TapePlex name for the HSC/VTCS system.
tapeplex-nameis a 1-8 character TapePlex name. This must match the SMCTAPEPlexname.If this parameter is omitted, it is set automatically when SMC initially communicates with HSC/VTCS.
- OVRLAYOK
-
optionally, specifies that the input CDS file(s) may be existing CDS data sets, and that they may be overlaid by the create process. If this parameter is omitted, and any CDS file is an existing CDS file, the
CDSCREATprocess fails.
Additional JCL Requirements
Execution of this utility requires specification of a DD statement for each CDS copy indicated by the TCHNIQE parameter (or exactly one DD statement if the TCHNIQE parameter is omitted).
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statements apply to the CDSCREat JCL:
- SLSCNTL
-
specifies the primary CDS.
- SLSCNTL2
-
optionally, specifies the secondary CDS.
If a secondary CDS exists, include this statement so that if a switch occurs and the secondary CDS becomes active, the CDSs can be reordered to maintain database integrity.
- SLSSTBY
-
optionally, specifies the standby CDS.
CDSDAta
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The CDSDAta command produces XML output data for library configuration and volume and pool definitions from VOLPARM control statements.
Note:
No text output is produced by this command, so theSLSXML DD statement must be included in the SLUADMIN execution to create output from this command. See "Output Data Set Definition (DD) Statements" for more information.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-10, the CDSDAta command includes the following parameters:
- TYPE
-
specifies the type of CDS data for which output is produced. The
TYPEKeyword is positional and therefore optional. One of the listed types must be specified.- VOLPOOL
-
produces XML data for
VOLPARM VOLUMEpool definitions. - MVCPOOL
-
produces XML data for
VOLPARM MVCpool definitions. - SCRPOOL
-
produces XML data for
VOLPARM SCRATCHpool definitions. - CDS
-
produces XML CDS data.
- CAP
-
produces XML CAP data.
- LSM
-
produces XML LSM data.
- DRV
-
produces XML drive data.
- TYPE
-
specifies the type of CDS data for which output is produced. The
TYPEKeyword is positional and therefore optional. One of the listed types must be specified.-
VOLPOOLproduces XML data forVOLPARM VOLUMEpool definitions. -
MVCPOOLproduces XML data forVOLPARM MVCpool definitions. -
SCRPOOLproduces XML data forVOLPARM SCRATCHpool definitions. -
CDSproduces XML CDS data. -
CAPproduces XML CAP data. -
LSMproduces XML LSM data. -
DRVproduces XML drive data.
-
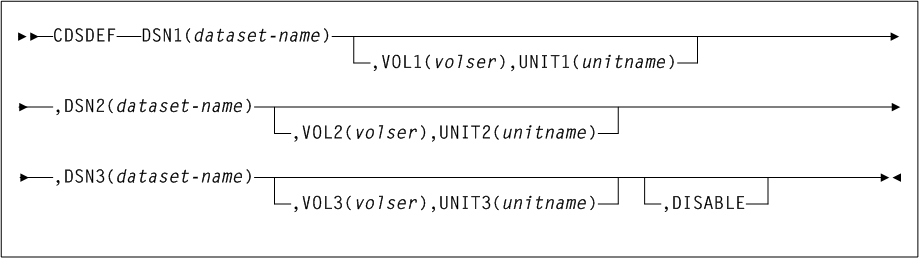
CDSDEF
Interfaces:
-
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
None.
Description
The CDSDEF command specifies control data set names, locations, and number of control data sets that you want running. This information is used by HSC during initialization.
CDSDEF is a required command.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-11, the CDSDEF command includes the following parameters:
- DSN1(dataset-name)
-
specifies the primary CDS.
dataset-nameindicates the name of an HSC control data set.At least one
DSNparameter must be specified, as many as three can be specified. If two data sets are specified, then the volume inventory information on both copies is kept current, and these two data sets are referred to as the primary and the secondary CDS.If all three are specified, then two copies are kept current and the third data set is a standby CDS which is enabled as the default condition. This standby CDS can be disabled with the
DISABLEparameter. In the case where a standby copy of the CDS is being used, you do not need to specify which two of the three CDSs are the primary and secondary copies. The HSC determines, based on last use, which two are the correct copies to use during the initialization of the Control Data Set Services.- ,VOL1(volser)
-
optionally, specifies a volume serial number of the DASD volume where the specified CDS resides. If the data set is not cataloged, this must be specified.
If omitted, volume and unit information is determined from the MVS catalog, and the
VOL1parameter is ignored. - ,UNIT1(unit-name)
-
optionally, specifies the unit parameter in the
SVC99dynamic allocation parameter list. If omitted,SYSALLDAis used.unit-namecan be an IBM-defined generic (for example,3390), a system-built esoteric (for example,SYSALLDA), a user-defined esoteric, or a specific device number. It is recommended that a general value ofSYSALLDAbe specified (or defaulted) to allow maximum flexibility and to reduce the need forCDSDEFupdates to keep them consistent with the active CDS.
- DSN2(dataset-name)
-
optionally, specifies a secondary CDS.
dataset-nameindicates the name of an HSC control data set.- ,VOL2(volser)
-
optionally, specifies a volume serial number of the DASD volume where the secondary CDS resides. If the data set is not cataloged, this must be specified.
- ,UNIT2(unit-name)
-
optionally, specifies the unit parameter in the SVC99 dynamic allocation parameter list. If omitted,
SYSALLDAis used.unit-namecan be an IBM-defined generic (for example,3390), a system-built esoteric (for example,SYSALLDA), a user-defined esoteric, or a specific device number. It is recommended that a general value ofSYSALLDAbe specified (or defaulted) to allow maximum flexibility and to reduce the need forCDSDEFupdates to keep them consistent with the active CDS.
- DSN3(dataset-name)
-
optionally, specifies a standby CDS.
dataset-nameindicates the name of an HSC control data set.- ,VOL3(volser)
-
optionally, specifies a volume serial number of the DASD volume where the standby CDS resides. If the data set is not cataloged, this must be specified.
- ,UNIT3(unit-name)
-
optionally, specifies the unit parameter in the SVC99 dynamic allocation parameter list. If omitted,
SYSALLDAis used.unit-namecan be an IBM-defined generic (for example,3390), a system-built esoteric (for example,SYSALLDA), a user-defined esoteric, or a specific device number. It is recommended that a general value ofSYSALLDAbe specified (or defaulted) to allow maximum flexibility and to reduce the need forCDSDEFupdates to keep them consistent with the active CDS. - ,DISABLE
-
optionally, disables the standby CDS. If this parameter is not specified, the default is to enable the standby CDS at HSC initialization.
If
DISABLEis specified, initialization verifies the standby CDS by allocating, opening, and reading the data set. The standby CDS is then closed and deallocated. This process enables manual control over the use of the standby CDS during a control data set switch situation.If the standby CDS is enabled, the HSC automatically uses it for switching. If it is disabled, it is not used. There is no enable parameter for
CDSDEF, as the enable condition is the default.
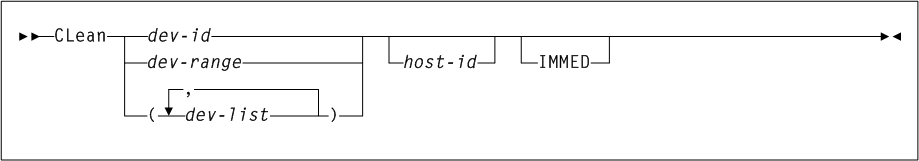
CLean
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIB -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The CLean command schedules a cleaning cartridge to be mounted on a library-controlled transport. The specified transport is flagged by the control data set and a cleaning cartridge is mounted prior to the next volume mount.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-12, the CLean command includes the following parameters:
- dev-id, dev-range, or dev-list
-
specifies a device address, range of device addresses, or list of addresses for which cleaning is to be scheduled. Each
devlistelement can be either a single device address or a range. The elements in a list must be separated by a comma or a blank, and the entire list must be enclosed in parentheses.- host-id
-
optionally, indicates that cleaning is to be performed for the device address of the specified host (the SMF system identifier for both JES2 and JES3).
- IMMED
-
optionally, specifies that an immediate clean of the device is to be preformed if the drive is idle. This occurs regardless of the
MNTD Autoclnsetting. If the device is not idle then the device is scheduled to be cleaned after the dismount of the volume that is currently mounted.
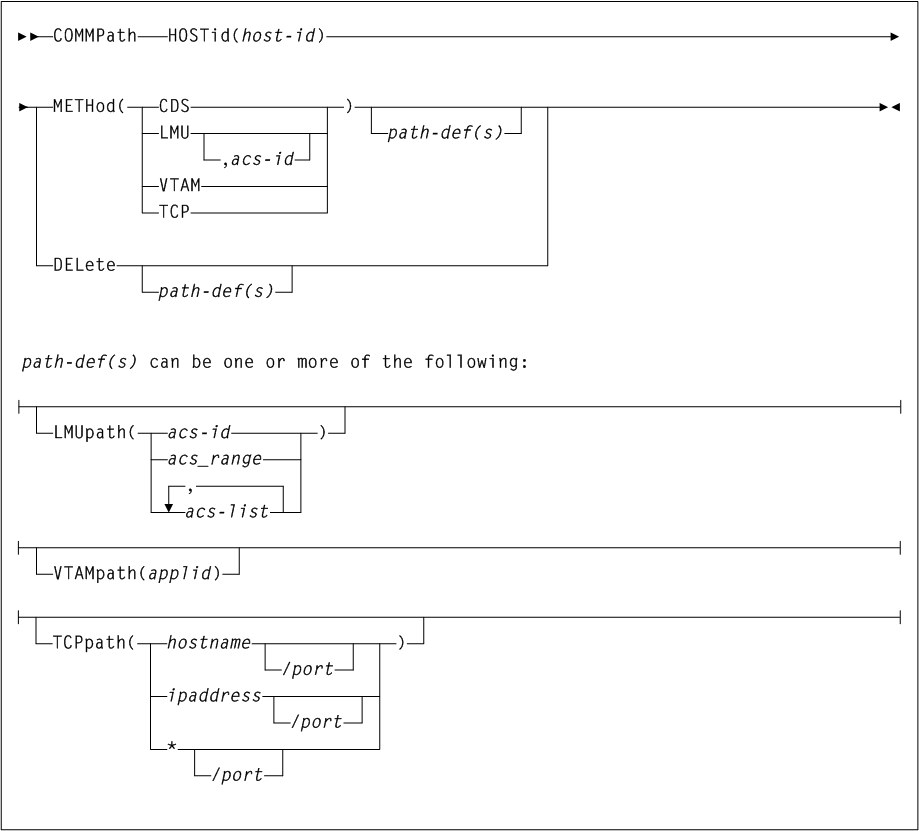
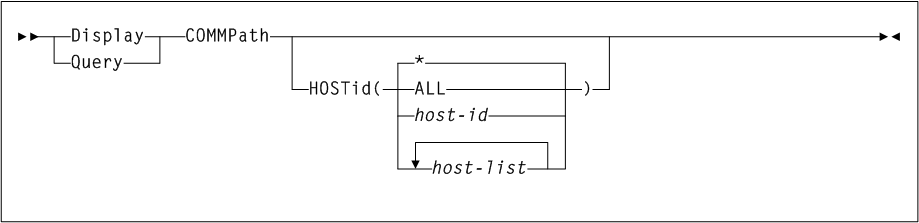
COMMPath
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Description
The COMMPath command is used in a multiple-host environment to do the following:
-
Set up a tiered communication service between HSC hosts which can be modified at any time without bringing down the HSC.
-
Define the hierarchy of methods available to each host for communication with other HSC hosts in the TapePlex.
-
Establish the current method of communication for an HSC host (or switch from one communication method to another).
In a single host environment, the COMMPath command has no effect.
It is recommended that the COMMPath command which defines the host-to-host communications hierarchy be defined in PARMLIB at startup. After startup, issue the COMMPath command from the console to switch or delete communication paths.
The hierarchy of available HSC host-to-host communication methods listed in order, according to burden on HSC performance, are:
-
TCP (least burden)
-
VTAM
-
LMU
-
CDS (greatest burden)
TCP and VTAM host-to-host communications are strongly recommended. LMU host-to-host communications method places a greater burden on HSC performance because it competes with library hardware communications. CDS host-to-host communications places the greatest burden on HSC performance because it requires access to the shared CDS.
The COMMPath command updates an in-memory table of definitions for the HSC host that executes the command. This table must contain a list of paths for this host and separate lists for each additional HSC host defined. Therefore, on each HSC host, you must issue the COMMPath command once to define the path itself, once to define the path(s) for a second host, and so on. For example, in a system with hosts A, B, and C:
COMMPATH commands in host A startup PARMLIB:
COMMPATH HOST(A) VTAMPATH(APPLID1) LMU(00) METHOD(VTAM)
COMMPATH HOST(B) VTAMPATH(ALLLID2) LMU(00) METHOD(VTAM)
COMMPATH HOST(C) VTAMPATH(APPLID3) LMU(00) METHOD(VTAM)
COMMPATH commands in host B startup PARMLIB:
COMMPATH HOST(A) VTAMPATH(APPLID1) LMU(00) METHOD(VTAM)
COMMPATH HOST(B) VTAMPATH(ALLLID2) LMU(00) METHOD(VTAM)
COMMPATH HOST(C) VTAMPATH(APPLID3) LMU(00) METHOD(VTAM)
COMMPATH commands in host C startup PARMLIB:
COMMPATH HOST(A) VTAMPATH(APPLID1) LMU(00) METHOD(VTAM)
COMMPATH HOST(B) VTAMPATH(ALLLID2) LMU(00) METHOD(VTAM)
COMMPATH HOST(C) VTAMPATH(APPLID3) LMU(00) METHOD(VTAM)
It is recommended that path methods mirror each other. However, in the above example, host C could set its method to LMU while host A and B continue to communicate using VTAM.
If an error occurs during a host-to-host communication, the HSC performs an automatic downward switch to the next lower defined communication method. After this switch is performed, an upward switch can only be performed using the COMMPath command.
If a COMMPath command is not defined for each host in a multiple-host environment, then the missing host's communication method defaults to CDS, which may impose a performance burden on all HSC hosts sharing the CDS. However, if the missing host is infrequently active (for example, a test system) then the additional performance burden would be minimal.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-13, the COMMPath command includes the following parameters:
- HOSTid(host-id)
-
specifies the host for which the command sets or modifies the parameters. This parameter is required for all
COMMpathcommands.host-idindicates the host identifier (the SMF system identifier for both JES2 and JES3). - METHod
-
optionally, specifies the current method of communications to be used for the specified host. This parameter enables you to switch to a higher, lower, or equivalent (for
LMUpathonly) level method of communications.- CDS
-
indicates that communication is to be through the control data set.
CDSis the initial setting for HSC hosttohost communications. - LMU
-
indicates that communication is to be through an LMU.
acs-idindicates theLMUpathdefinition that is to be the active (or current)LMUpath. If you do not supply anacsid, the firstLMUpathspecified in the list ofLMUpathdefinitions is made active.If
LMUis specified, theLMUpathparameter must have been specified in a previous command, or it must be included in the same command.If the LMU method is specified in
PARMLIB, the switch from CDS to LMU is delayed until the HSC initializes to the full service level.If the HSC service level drops to base, LMU communications are switched to CDS. When the full service level is restored, an upward switch to the LMU method requires you to issue another
COMMPathcommand. - VTAM
-
indicates that communication is to be through a VTAM network.
If
VTAMis specified, theVTAMpathparameter must have been specified in a previous command, or it must be included in the same command.A downward switch from the VTAM method is performed when the VTAM
APPLIDof the HSC is inactivated, or VTAM is shut down. - TCP
-
indicates that communications is to be through a TCP/IP network.
A downward switch from the TCP method is performed when a TCP/IP error occurs, or TCP/IP is shut down.
- LMUpath(acs-id, acs-range, or acs-list)
-
specifies one or more LMU paths that can be used for hosttohost communications. An LMU is eligible to be used for hosttohost communications if it is connected to other HSCs sharing a library.
acsidoracsrangeoracslistspecifies one or more specific LMUs. Eachacslistelement can be either a single ACSid or an ACSid range. The elements in a list must be separated by a comma or a blank, and the entire list must be enclosed in parentheses.If more than one eligible LMU is specified, the HSC begins searching for an available communications path beginning with the first
acsidin the list. The search continues until a path can be established or the end of the list is reached.The
LMUpathdefinitions are cumulative; that is, the definitions specified in a command are appended to the current list of definitions. You can insert an LMU path into the current list by specifying the LMU path that you wish to insert, followed by the LMU paths that are to come after it. If aCOMMPathcommand specifies an LMU path that is already defined in the list, the path is removed from its current position and appended to the end of the list as specified in the command.Note:
For a temporary LMU outage, it may be desirable to delete the LMU's path from the list. When the LMU becomes available again, it may be re-added. - VTAMpath(applid)
-
optionally, defines the VTAM application to be associated with an HSC host. The specified application name is used in the process of establishing a VTAM connection with other HSCs.
applidindicates the name defined by theVTAM APPLstatement for the HSC application. - TCPpath(hostname, ipaddress, or /port)
-
optionally, defines the host name and port number combination, or IP address (IPv4 or IPv6) and port number combination associated with an HSC host. The specified hostname is resolved into an IPv4 or IPv6 address. The combined IP address and port number combination is used to start a host-to-host
TCPPATHserver on the associated HSC host.hostnamemust be a resolvable host name.ipaddressmust be valid IPv4 or IPv6 format address. If you specify "*", the IP address of the current host (the issuer of the command) is used.portmust be a number between 1 and 65535 and be separated from the hostname, IP address, or "*" by a "/" character with no intervening blanks. If no "/" is found, then the default port number of 58080 is used.Specify the port number so that it does not conflict with TCP or UDP well known port numbers, or with other applications on this host. When a
TCPPATHserver is started on this host, it will listen on the specified port number for host-to-host communications from other HSC hosts.The following are examples of TCPpath definitions:
-
TCPPATH(10.135.73.101/50090) -
TCPPATH(PRODMVS/50090) -
TCPPATH(10.135.72.102) -
TCPPATH(*/50020) -
TCPPATH(*)
-
- DELete
-
optionally, specifies to delete the definitions specified by either or all of the
LMUpath,VTAMpath, orTCPpathparameters associated with the specified HSC host.-
If
LMUis not the current method, you can delete allLMUpathdefinitions by specifying theLMUpathkeyword without any values. -
If the current method is
LMU, theLMUpathcannot be deleted. -
If the current method is
VTAM, theVTAMpathdefinition cannot be deleted. -
If the current method is
TCP, theTCPpathdefinition cannot be deleted.
-
Note:
-
Specifying
COMMPATH HOSTID(id) METHOD(TCP)on the current host starts theTCPPATHserver for that host. -
Specifying
COMMPATH HOST(id) TCPPATH DELETEon the current host stops theTCPPATHserver for that host, as well as deletes theTCPPATHdefinition. -
One host cannot start or stop the
TCPPATHserver on another host.
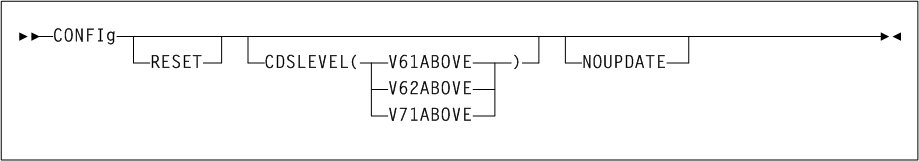
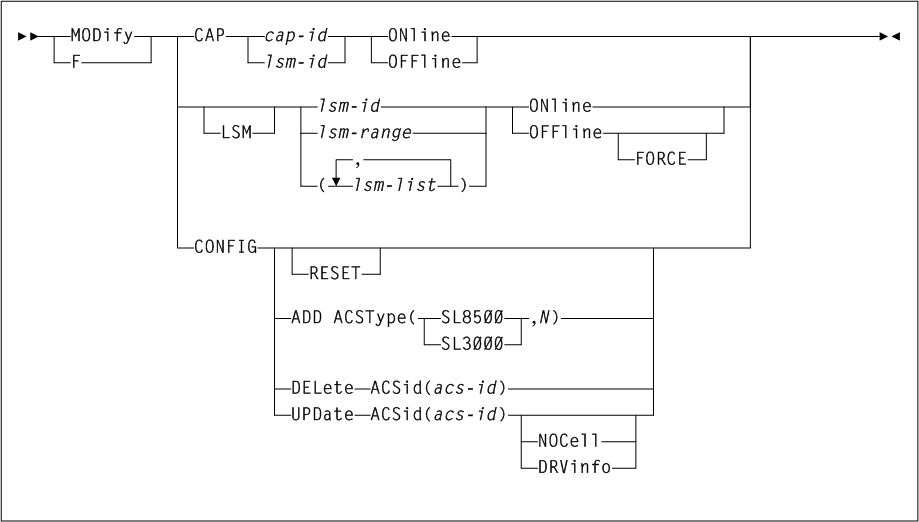
CONFIg
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required, and must be down on all hosts when running CONFIG RESET.
Description
The CONFIg command defines or modifies the VSM configuration stored in the HSC CDS. You create a single file that contains the CONFIg command and its input statements.
Note:
-
The
CONFIg GLOBALstatement specifies VTCS global values. This statement is required. See "CONFIg GLOBAL Statement". -
Dynamic reclaim requires an H level CDS.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-14, the CONFIg command includes the following parameters:
- RESET
-
optionally, resets the VSM configuration in the CDS.
Specify
RESETwhen:-
Changing the CDS to a lower level.
-
Adding
LOCKSTR=structure-name (throughCONFIg GLOBAL) to a CDS that did not previously useLOCKSTR=structure-name. -
Removing
LOCKSTR=structure-name (throughCONFIg GLOBAL) from a CDS. -
Removing 32 RTD support (i.e. move from a CDS that supported 32 RTDs to one that doesn't).
Do not specify
RESETwhen:-
Changing the CDS from F to G, G to H, or H to I.
-
Changing lock structure names (for example, going from
LOCKSTR=VTCSL1toLOCKSTR=VTCSL2). -
Changing VSM volumes (such as adding VTVs and MVCs). Note that VTV and MVC volumes cannot be removed by
RESETor any other VTCS utility. Removal of VTV and MVC volumes requires the definition of a new CDS and the use ofMERGEcds. -
Changing VSM policies (such as changing
AMTvalues).
Note:
-
HSC must be down on all hosts when you run
CONFIG RESET. The changes you made to RTD definitions take effect when you restart HSC. -
Although some changes can be done dynamically by running
CONFIGand not restarting HSC/VTCS, there may be additional parameter changes required to use any additional resources. -
If you run a
CONFIGwithRESET, then the status flags are reset and messageSLS6746Edisappears. If a VTSS was offline when you ran theCONFIG(withRESET), you must remember to audit the VTSS.
-
- CDSLEVEL
-
optionally, specifies one of the following CDS levels:
- V61ABOVE
-
creates an ”F” level CDS, which provides the following enhancements:
-
Full VSM4 Support
-
4 MVC copies
-
800Mb VTVs
-
Near Continuous Operations (NCO)
-
Bi-directional clustering
-
Improved CDS I/O performance - reduces I/O required to manage virtual scratch subpools
-
- V62ABOVE
-
creates a ”G” level CDS, which provides the following enhancements:
-
400Mb/800Mb/2Gb/4gb VTVs
-
Standard/Large VTV Pages
-
65000 VTVs per MVC
-
- V71ABOVE
-
creates an ”H” level CDS, which provides the following enhancements:
-
Dynamic reclaim
-
Autonomous device support
-
- NOUPDATE
-
optionally, specifies that the configuration is checked and any appropriate messages output, but no updates are made to the CDS.
CONFIg CLINK Statement
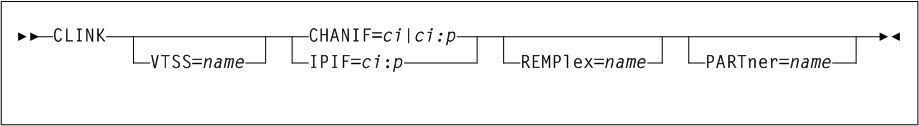
The CONFIg CLINK statement defines the channel interface between two VTSSs in a Cluster and enables you to define CLINKs on IP interfaces to support replication of VTVs over IP CLINKs.
The VTSSs can be in one of three modes:
-
Primary-Secondary, in which there are two VTSSs and you write
CLINKstatements for only the Primary. -
Peer-to-Peer, in which case there are two VTSSs and you write
CLINKstatements for both VTSSs to enable bi-directional VTV replication. -
Any-to-Any, in which there are more than two VTSSs in the cluster and the individual relationships are defined through
CLINKstatements.
In addition, CLINKs can be defined from the VTSS to perform electronic export to another TapePlex. These links need not be to the same VTSS within the remote TapePlex.
Each VTSS can either be connected to a maximum of three different TapePlexes, or two TapePlexes and a partner VTSS in a cluster.
An electronic export connection can always be to multiple VTSSs. A cluster connection can be to multiple VTSSs only if the CONFIg CLUSTER statement specifies more than two VTSS members.
Refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Disaster Recovery and Offsite Data Management Guide for examples.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-15, the CONFIg CLINK statement includes the following parameters:
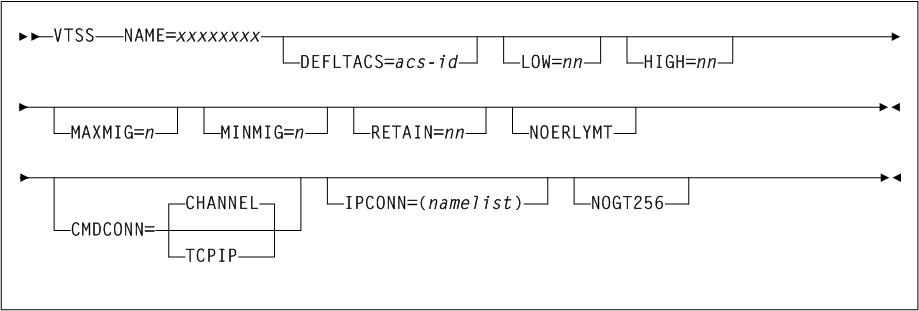
- VTSS=name
-
optionally, specifies the name of the VTCS that owns the CLINK. This is the VTSS from which the VTVs are replicated or exported.
If this parameter is omitted, by default, the CLINK is attached to the current VTSS being defined.
The VTSS name that you specify on a
CLINKstatement must be known to VTCS. That is, the VTSS name must be already defined in the CDS or it must be specified in aVTSSstatement that already exists in the current set ofCONFIGstatements. For example, the following is valid:VTSSNAME=VTSS1 LOW=70 HIGH=80 MAXMIG=3 RETAIN=5 CLINK VTSS=VTSS1 CHANIF=0AThe following is not valid unless
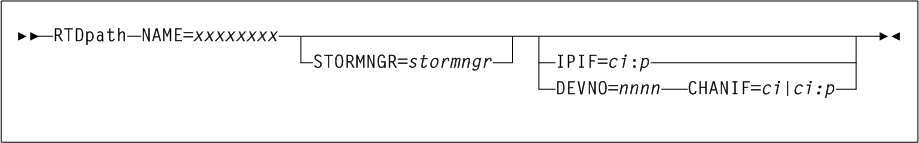
VTSS1is already defined in the CDS:CLINK VTSS=VTSS1 CHANIF=0A VTSSNAME=VTSS1 LOW=70 HIGH=80 MAXMIG=3 RETAIN=5 - CHANIF=ci or ci:p
-
specifies the channel interface on the VTSS that communicates with the RTD where:
-
cindicates the VTSS Storage Cluster number (0 or 1). -
iindicates the interface number (A, C, E, G, I, K, M, or O) -
pindicates the device number on the interface (0, 1, 2, or 3).
For a VSM 5, this value must match the actual FICON interface values. For a VSM 6, this must be unique for each VTSS, and does not correspond to an actual value on the VSM 6 FICON ports.
Regardless of whether the Maximum 32 RTDs feature is enabled, if you do not have greater than 16 RTDs attached to a VTSS, you can use the ”old” addressing scheme (
CHANIF=ci).If, however, the Maximum 32 RTDs feature is enabled and you have greater than 16 RTDs attached to a VTSS, you must use the ”new” addressing scheme (
CHANIF=ci:p).Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring HSC and VTCS for more information.
-
- IPIF=ci:p
-
optionally, enables Ethernet connection of two Native IP (IFF3 card) ports, where the
ci:pvalues are shown in parentheses before each Target IP Address on the IFF IP Configuration Status screen for each IFF ethernet port. Valid values forc:ipare:-
c indicates the VTSS Storage Cluster number (0 or 1).
-
i indicates the interface number (A or I)
-
p indicates the device number on the interface (0, 1, 2, or 3).
For VSM5s, this value must match the value specified on the VSM5 IFF Configuration Status Screen. For VSM 6s, this must be unique for each VTSS; and does not correspond to an actual value on the VSM 6 TCP/IP ports.
Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring HSC and VTCS for more information.
Note:
TheCLINKstatement must contain either theCHANIForIPIFparameter, but not both. -
- REMPlex=name
-
optionally, specifies the name of the TapePlex at the receiving end of the CLINK that receives the copies of the VTVs. During validation of the link, this name is compared with the
THISPLEXdefinition in the remote system configuration.The
REMPlexparameter indicates that the CLINK is to be used for electronic export. Absence of this parameter indicates that the CLINK is to be used for a cluster connection. - PARTner=name
-
optionally, specifies the name of the VTSS at the receiving end of the CLINK that receives copies of the VTVs.
This parameter is required for CLINKs used for electronic export, or where the cluster consists of more than two VTSSs.
During validation of the link, this name is compared with the VTSS name at the other end of the CLINK.
CONFIg CLUSTER Statement
The CONFIg CLUSTER statement defines the VTSSs in a Cluster.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-16, the CONFIg CLUSTER statement includes the following parameters:
- NAME=nnnnnnnn
-
specifies the 1 to 8 character identifier of the Cluster.
This parameter is required. There is no default value.
- VTSSs(vtss-list)
-
Specifies the names of the VTSSs in a cluster. At least two VTSSs must be specified. If more than two VTSSs are specified, then down level hosts will not function.
The relationship between each of the VTSSs is defined by the
CONFIG CLINKstatement. See "CONFIg CLINK Statement" for more information.This parameter is required. There is no default value.
VTSS names that you specify on a
CLUSTERstatement must be known to VTCS. That is, the VTSS names must be already defined in the CDS or must be specified in VTSS statements that already exist in the current set ofCONFIgstatements. For example, the following is valid:VTSSNAME=VTSS1 LOW=70 HIGH=80 MAXMIG=3 RETAIN=5 VTSSNAME=VTSS2 LOW=70 HIGH=80 MAXMIG=3 RETAIN=5 CLUSTER NAME=CLUSTER1 VTSSs=(VTSS1,VTSS2)
The following is not valid unless
VTSS1andVTSS2are already defined in the CDS:CLUSTER NAME=CLUSTER1 VTSSs=(VTSS1,VTSS2) VTSSNAME=VTSS1 LOW=70 HIGH=80 MAXMIG=3 RETAIN=5 VTSSNAME=VTSS2 LOW=70 HIGH=80 MAXMIG=3 RETAIN=5
The
DEComputility outputsCLUSTERstatements with blanks instead of commas as separators, which is also valid input toCONFIg. For example,DECompoutputs the following, which is valid input toCONFIg:CLUSTER NAME=CLUSTER1 VTSSs=(VTSS1 VTSS2)
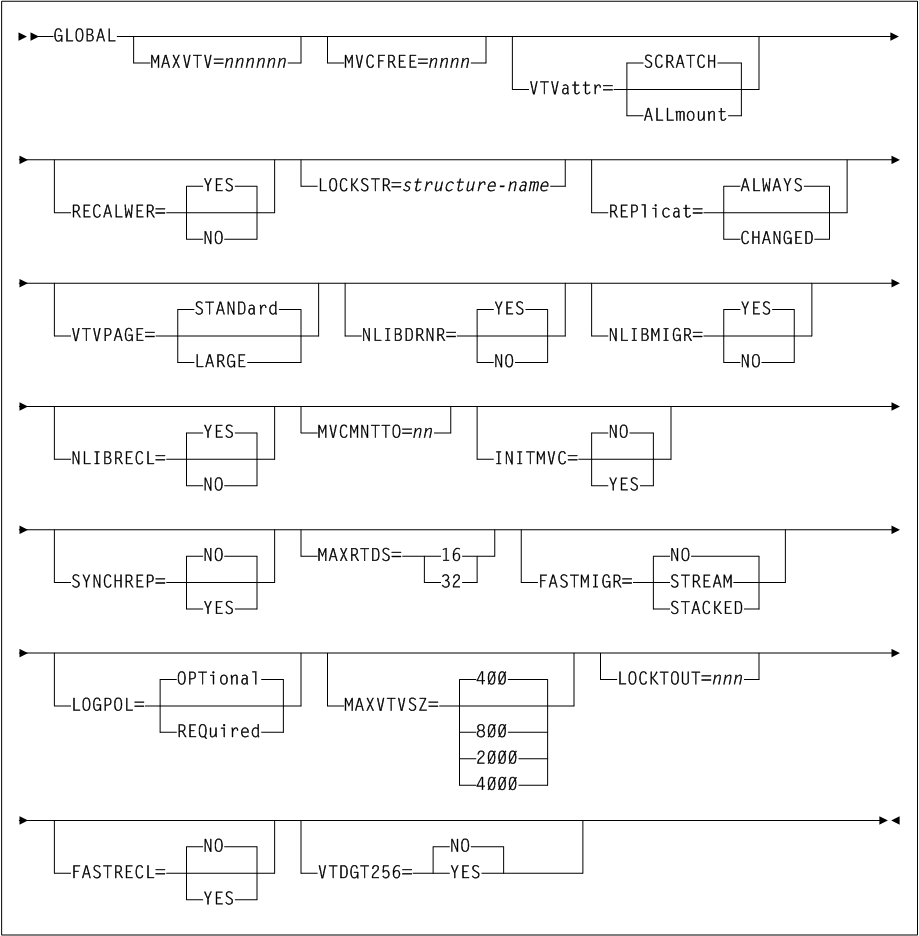
CONFIg GLOBAL Statement
The CONFIg GLOBAL statement specifies VTCS global values. This statement is required.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-17, the CONFIg GLOBAL statement includes the following parameters:
- MAXVTV=nnn
-
optionally, specifies the maximum number of VTVs that can be migrated to a single MVC. The default is 32000 for a D, E, or F level CDS and 65000 for a G level CDS. Valid values are:
-
4 to 32000 for a D, E or F level CDS
-
4 to 65000 for a G level CDS
For more information about CDS levels, see "CONFIg".
-
- MVCFREE=nnn
-
optionally, specifies the minimum number of free MVCs in the MVC pool. A free MVC has 100% usable space and does not contain any migrated VTVs. Valid values are 0 to 255. The default is 40.
If free MVCs is equal or less than this value, VTCS issues message
SLS6616Iand starts an automatic space reclamation.Note:
If you setMVCFREE=0, VTCS actually uses the default value (40). - VTVattr
-
optionally, specifies when VTCS assigns a Management Class to a VTV.
- SCRATCH
-
Assign a Management Class only when VTCS does a scratch mount of the VTV (the default).
- ALLmount
-
Assign a Management Class whenever VTCS mounts the VTV.
Caution:
If you specify that VTCS assigns a Management Class whenever VTCS mounts a VTV, these attributes can change, which can cause undesirable or unpredictable results.For example, if an application writes data set
PROD.DATAtoVTV100with a Management Class ofPROD, then writes data setTEST.DATAtoVTV100with a Management Class ofTEST, then the VTV (and both data sets) has a Management Class ofTEST. Similarly, it is possible to writeTAPEREQstatements or SMS routines that assign different Management Classes to the same data set (for example, based on job name), which can also cause a VTV's Management Class to change. - RECALWER
-
optionally, specifies whether VTCS recalls VTVs with read data checks (applies to recall and drain operations).
- YES
-
Recall VTVs with read data checks (the default).
- NO
-
Do not recall VTVs with read data checks.
- LOCKSTR=structure-name
-
optionally, specifies the Coupling Facility Structure that holds VTCS Lock Data.
structure-namemust be 16 characters or less and conform to IBM's standard for naming Coupling Facility Structures. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Installing ELS for more information.Caution:
CONFIG RESETis required to addLOCKSTR=structure-nameto a CDS that did not previously useLOCKSTR=structure-nameand to removeLOCKSTR=structure-namefrom a CDS.CONFIG RESETis not required to change lock structure names (for example, going fromLOCKSTR=VTCSL1toLOCKSTR=VTCSL2). - REPlicat
-
optionally, specifies when VSM replicates the VTV.
- ALWAYS
-
The replicate request is added to the VTCS replication queue every time the VTV is dismounted, regardless of whether the VTV was changed while it was mounted (the default).
- CHANGED
-
The replicate request is added to the VTCS replication queue if either of the following have occurred:
-
The VTV was changed while it was mounted.
-
The VTV was only read while mounted but less than the expected number of MVC copies of the VTV exist.
Once the expected number of MVC copies exist, replication does not occur.
Regardless of the
CONFIG GLOBAL REPlicatsetting, replication also requires that:-
The VTV must be dismounted in a VTSS that supports replication and there cannot be an identical copy of the VTV in the other VTSS in the Cluster.
-
In addition to the
CONFIG GLOBAL REPlicatvalue, you must specifyREPlicat(YES)on a VTV's Management Class for replication to occur.
-
- VTVPAGE
-
optionally, specifies the page size used to store VTV data in the VTSS and on the MVCs. This setting only applies to 400 MB and 800 MB VTVs. If
VTVPAGEis not specified on either theMGMTclasstatement or theCONFIG GLOBALstatement, the default isSTANDard.- STANDARD
-
standard page size, which is compatible with all VSM3 or VSM4 models and microcode levels.
- LARGE
-
large page size, which can provide improved performance within the VTSS and for migrates and recalls. Large page size requires a G level CDS. For more information on CDS levels, see "CONFIg". For 2 GB VTVs and 4 GB VTVs (
MAXVtvsz2000 or 4000), aVTVPAGEsetting ofLARGEis always used.VTVPAGEdoes not apply to VSM2s.VTVPAGE(LARGE)requires VSM4 or VSM5 microcodeD02.02.00.00or VSM3 microcodeN01.00.77.00. No installed option is required.MGMTCLAS VTVPAGE, if specified, overrides theCONFIG GLOBAL VTVPAGEvalue. IfVTVPAGEis not specified on either theMGMTclasstatement or theCONFIGGLOBALstatement, the default isSTANDard.Consider the following:
-
The page size of a VTV can only be changed by a VTV scratch mount. Additional restrictions may also apply for scratch VTVs that were previously resident in a VTSS.
-
If you specify
LARGEand the CDS level or VTSS microcode does not supportLARGE, then VTCS issues warning messages andVTVPAGEdefaults toSTANDard. -
If you specify
STANDardfor 2 GB or 4 GB VTVs, then VTCS issues warning messages and defaults toLARGE. -
Creating VTVs with large pages makes these VTVs unreadable in configurations that do not support large VTV pages.
-
- NLIBDRNR
-
optionally, specifies how VTCS handles non-library resident MVCs for drain or reclaim processing.
- YES
-
VTCS requests the mount of the non-library MVC. This is the default.
- NO
-
VTCS suppresses the mount and purges the request.
For drain, non-library resident MVCs can be selected.
For reclaim, only library resident MVCs can be selected for processing, never non-library ones. However, between the time a library resident MVC is selected and the time it is actually processed, it may have become non-resident by being ejected.
- NLIBMIGR
-
optionally, specifies whether non-library resident MVCs will be selected for Migration processing.
- YES
-
Allow non-library resident MVCs to be selected (default).
- NO
-
Do not allow non-library resident MVCs to be selected.
- NLIBRECL
-
optionally, specifies whether non-library resident MVCs will be selected for
Recallprocessing.- YES
-
Allow non-library resident MVCs to be selected (default).
- NO
-
Do not allow non-library resident MVCs to be selected.
- MVCMNTTO=nn
-
optionally, specifies the value in minutes when a mount of an MVC will timeout. Valid values are 5 to 30 minutes. The default is 15.
- INITMVC
-
optionally, specifies whether un-initialized MVCs are to be initialized when they are first mounted.
- NO
-
Un-initialized MVCs should not be initialized. This is the default.
- YES
-
Un-initialized MVCs should be initialized.
- SYNCHREP
-
optionally, specifies whether VTV synchronous replication feature is enabled.
- NO
-
Synchronous replication is not enabled (the default).
- YES
-
Synchronous replication is enabled.
Note:
SYNCHREP=YESmerely enables synchronous replication. To actually implement synchronous replication, you must create a Management Class that specifiesREPLicat=YES_SYNCFor more information, see "MGMTclas Control Statement".
- MAXRTDS
-
optionally, specifies the maximum number of RTDs supported.
- 16
-
up to 16 RTDs supported.
- 32
-
up to 32 RTDs supported.
- FASTMIGR
-
optionally, specifies whether the stacked or streamed migrates feature is enabled for all VTSSs that support this feature.
- STREAM
-
Specifies to use the streaming method for migrations. VTCS monitors responses from the RTD and uses them to decide as to when a VTV has become migrated. Full advantage is made of the buffer within the RTD to improve the throughput when performing migration.
This option also implies the use of the
STACKEDfeature. - STACKED
-
Specifies to use the stacked method for migrations. VTCS maintains a small queue of requests to the VTSS. Advantage is made of the various buffers in the VTSS and RTD to improve the throughput when performing a migration. For backward compatibility, the value
YESis the equivalent ofSTACKED. - NO
-
Disable stacked migrates (the default).
FASTMIGR=STREAMorSTACKEDhas the following prerequisites:-
FASTMIGR=STACKED: VSM4/VSM5 microcodeD02.05.00.00or higher. If this level of microcode is not installed on all VTSSs in the configuration, Stacked Migration will be limited to the VTSSs that have it installed. -
FASTMIGR=STREAM: VSM4/VSM5 microcodeD02.15.xx.00or higher. If this level of microcode is not installed on all VTSSs in the configuration, Streamed Migration will be limited to the VTSSs that have it installed. -
ELS 7.0 or higher with PTFs.
-
CDS level G or higher.
-
FICON ports for FICON RTDs and CLINKs.
For the Stacked Migration feature to be enabled, all hosts must be running the prerequisites, otherwise:
-
If a host is active and does not support or tolerate stacked migrates, then the
CONFIgutility returns an error. -
If a host is started and does not support or tolerate this feature, then the host shuts down.
- LOGPOL
-
optionally, specifies whether VTCS CDS logging is optional or required.
- OPTional
-
Logging is optional. This is the default. This mode is required for configurations that include 7.1 or 7.2 and lower level hosts.
- REQuired
-
Logging is enabled for all events on all hosts that share the CDS. This requires all hosts to be at level 7.0 or higher. The following events are logged:
-
new version of VTV
-
imported VTV
-
first use or re-use of an MVC
-
imported MVC
-
add VTV to MVC
-
VTV on an imported MVC
-
unlink VTV from MVC
-
reclaim VTV from MVC
-
reset MVC EOT backwards
-
electronic export of VTV
-
- MAXVTVSZ
-
optionally, specifies a default maximum compressed VTV size (MB) that may be used during the creation of VTVs. Valid values for this parameter depend on both the CDS level and the microcode levels of the applicable VTSSs.
- 400
-
400 MB. This is the default.
- 800
-
800 MB. The CDS must be at E level or above.
- 2000
-
2 GB. The CDS must be at G level or above.
- 4000
-
4 GB. The CDS must be at G level or above.
Considerations:
-
The size of a VTV changes only after it goes through a scratch cycle. Therefore, if you change the Management Class and
DISP=MOD, then it will still retain the original size. -
If you specify a VTV size that is not supported by the configuration, VTCS issues warning messages and
MAXVtvszdefaults to the largest VTV size supported by the configuration. -
MAXVtvszdoes not apply to VSM2s. -
MAXVTVSZ(2000)orMAXVTVSZ(4000)requires VSM4 or VSM5 microcodeD02.02.00.00or VSM3 microcodeN01.00.77.00. No installed option is required.
The
CONFIg GLOBALandMGMTCLAS MAXVTVSZparameters interact as follows:-
If
MAXVTVSZis specified onMGMTCLAS, this value overrides theCONFIg GLOBAL MAXVTVSZvalue. -
If
MAXVTVSZis not specified onMGMTCLAS, theCONFIg GLOBAL MAXVTVSZvalue, if specified, is used. Otherwise,MAXVTVSZdefaults to 400 MB. -
If
MAXVTVSZis not specified onMGMTCLASor onCONFIg GLOBAL,MAXVTVSZdefaults to 400 MB.
- LOCKTOUT=nnn
-
optionally, specifies the minimum number of minutes that a resource is locked before message
SLS6946Eis issued.Valid values are 0, or any value between 5 and 240. If 0 is specified, message
SLS6946Ewill not be issued when a required resource is locked. If this parameter is not specified, the current default of 10 minutes is retained.Note:
LOCKTOUTis only supported at ’F' level CDS (V61ABOVE) and above. - FASTRECL
-
Optionally specifies whether VTCS performs Early Time to First Byte (ETTFB), also known as concurrent tape recall/mount, for all VTSSs that support the feature. This parameter applies to recalls from RTDs and recalls from VLE.
- NO
-
Disable the ETTFB feature. This is the default.
- YES
-
Enable the ETTFB feature. If you globally enable this feature, you can disable it for individual VTSSs through the
CONFIg VTSS NOERLYMTparameter. See "CONFIg VTSS Statement" for more information.
- VTDGT256
-
Optionally, specifies whether greater than 256 VTDs are to be used.
Note:
VTDGT256=YESis only valid with VSM model 7 and above. VSM 7 VTSS supports 512 VTDs with current maintenance.- NO
-
Specifies that only the first 256 VTDs will be used. The first 256 VTDs are on control unit
00-0Fof the VTSS with VDID address ofx0000-x0F0F.NOis the default. - YES
-
Specifies that all configured VTDs in the VTSS can be used. This is only valid if the VTSS supports greater than 256 devices. The feature is globally enabled and applies to all VSMs that support greater than 256 devices. The feature can be disabled for an individual VTSS through the
CONFIG VTSS NOGT256parameter. See "CONFIg VTSS Statement" for more information.
CONFIg HOST Statement
The CONFIg HOST statement is an optional statement that defines an MVS host and, optionally, the NOMIGRAT and/or NORECLAM parameters.
If specified, the HOST statement must follow the VTSS statement for the VTSS attached to that host.
You must either specify all host definitions or none; if you specify only some of the hosts attached to a VTSS, VTCS will issue an error.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-18, the CONFIg HOST statement includes the following parameters:
- NAME=xxxx
-
specifies the
LIBGENed hostname.xxxxindicates the host name. - NOMIGRAT
-
optionally, specifies that this host cannot do migrations, consolidations, or export by VTV or Management Class from the VTSS(s) that the host accesses.
NOMIGRATcontrols both automatic and demand migrations and consolidations. This parameter is optional.Specifying
NOMIGRATalso causesNORECLAMto be set.IMMEDmigKEEPandIMMEDmigDELETEare mutually exclusive withCONFIG HOSTNOMIGRAT. If you specify both, theIMMEDmigvalue overridesNOMIGRAT, and VTCS does not issue a message about this override. - NORECLAM
-
optionally, specifies that this host cannot initiate automatic or demand reclaim processing using the VTSS(s) that the host accesses. The host can still perform MVC drains using
MVCDRain). This parameter is optional. - CMDCONN
-
optionally, specifies one of the following VTSS access methods:
- CHANNEL
-
indicates ESCON or FICON channel access. This is the default.
- TCPIP
-
indicates TCP/IP access. TCPIP requires a valid
CONFIg VTSS IPCONN=(name-list)value.
CONFIg MVCVOL Statement
The CONFIg MVCVOL statement defines a range of MVCs available to VTCS.
Oracle recommends that you use SET VOLPARM to define VTV and MVC ranges in the VTCS CONFIg.
-
See "SET VOLPARM" for more information about the
SET VOLPARMstatement. -
Refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Legacy Interfaces Reference for information about the use of the
VTVVOLandMVCVOLstatements inCONFIgto define volumes.
CONFIg RECLAIM Statement
The CONFIg RECLAIM statement controls demand and automatic MVC and VMVC space reclamation.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-19, the CONFIg RECLAIM statement includes the following parameters:
- THRESHLD=nn
-
optionally, specifies the percentage of fragmented space (
nn) that makes an MVC eligible for demand or automatic reclamation. Valid values are 4 to 98. The default is 75. - VLTHRES=nn
-
optionally, specifies the percentage of fragmented space (
nn) that makes a Virtual MVC (VMVC) eligible for demand or automatic reclamation. Valid values are 4 to 98. The default is 35.Note:
Reclaim on a VMVC consists of simply deleting the expired VTV images from the VMVC. That is, no recall and re-migrate of the VTV is required. VMVC reclaim is therefore much faster than MVC reclaim, and you can setVLTHRESlower (more aggressive) thanTHRESHLD. - MAXMVC=nn
-
optionally, specifies the maximum number of MVCs that will be processed by a single space reclamation task.
nnindicates the maximum number of MVCs. Valid values are 1 to 98. The default is 40.For automatic space reclamation to start, the number of eligible MVCs (determined by the
THRESHLDparameter) must also exceed theMAXMVCvalue. - START=nn
-
optionally, specifies the level at which automatic space reclamation starts for each ACS (not globally for all ACSs). Specify a percentage value, which is equal to:
Reclaim Candidates/(Reclaim Candidates+Free MVCs)* 100where:
-
Reclaim Candidatesindicates the number of Reclaim Candidates determined by theCONFIG RECLAIM THRESHLDparameter. -
Reclaim Candidates+Free MVCsequals the number of Reclaim Candidates plus the number of free MVCs.Valid values are 1 to 98. The default is 35.
-
- CONMVC=nn
-
optionally, specifies the maximum number of MVCs that VTCS concurrently processes for both drain and reclaim.
Valid values are 1 to 99. The default is 1.
- INPLACE
-
optionally, enables or disables dynamic reclaim support within VTCS. There is no default, though the absence of
INPLACEindicates that dynamic reclaim support is not enabled.- YES
-
Enable dynamic reclaim by formatting and processing all eligible MVCs as partitioned on a global (all storage class) basis.
- NO
-
Disable dynamic reclaim. This option will likely be accompanied by
STORCLASlevel overrides.
The CDS must be at H level before
INPLACEis accepted, enabling dynamic reclaim support. IfINPLACEis specified and the CDS is not at H level, the configuration fails and error messages are displayed.Only T10000B media is supported for dynamic reclaim. Sport volumes are not supported in partitioned format.
- INPTHRSH=nn
-
optionally, specifies the percentage of fragmented space that makes an MVC in partitioned format eligible for dynamic reclaim processing.
nnis a percentage between 3 and 97. This value must be less than theTHRESHLDvalue. The default is half theTHRESHLDvalue (rounded up).INPTHRSHcannot be specified withoutINPLACE.If
INPTHRSHis specified,THRESHLDmust also be specified. BothINPTHRSHandTHRESHLDplay roles when dynamic reclaim processes MVCs in partitioned format. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring HSC and VTCS for more information. - PROTECT=nn
-
optionally, specifies the time, in hours, to prevent (or protect) an MVC from being reused after it is drained or reclaimed. Valid values are 1 to 99.
CONFIg RTDpath Statement
The VTCS CONFIg RTDpath statement defines the path to one of the following:
-
RTDs operating under a local TapePlex. Local RTD connections are defined using the
DEVNOandCHANIFparameters and noSTORMGNRparameter. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring HSC and VTCS for more information. -
A remote library. Remote library connections are defined via the
DEVNO,CHANIFandSTORMGNRparameters. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring HSC and VTCS for more information. -
A VLE connected to a VTSS, defined using only the
STORMNGRandIPIFparameters. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring the Host Software for VLE for more information.
Except in tapeless environments, CONFIg RTDpath is required and must follow the VTSS statement that defines the VTSS to which the devices are connected.
The maximum number of each device type you can connect are as follows:
-
For a VSM2 or VSM3, 8 RTDs.
-
For a VSM4, 16 RTDs.
-
For a VSM5 or VSM6, 32 RTDs.
-
For a VSM5 or VSM6, 4 VLE appliances.
Note:
You must specify theRESET parameter to change RTD definitions if VTCS is running with a CDS level lower than V61ABOVE. See "CONFIg" for more information. For an initial RTD definition, if the RTD name displayed at the VTSS LOP is anything other than all blanks, you must also specify RESET.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-20, the CONFIg RTDpath statement includes the following parameters:
- NAME=xxxxxxxx
-
specifies the 1 to 8 character identifier of the RTD or VLE appliance.
-
During VTCS CONFIg processing, RTDs with the same name may be defined for multiple VTSSs. RTD names must be unique across all VTSSs.
-
For RTDs, you set or change the RTD identifier only using the
RTD NAMEparameter. To do so, the RTD identifier must be all blanks as displayed at the VTSS LOP or DOP. -
For VLEs or remote libraries, use any meaningful 1 to 8 character identifier.
This parameter is required; there is no default value.
-
- STORMNGR=stormngr
-
specifies one of the following:
-
VLE subsystem name
-
remote library
stormngrindicates the Storage Manager name:-
For VLEs, this value must match the VLE Subsystem Name.
-
For remote libraries, this value must match a TapePlex name defined on the SMC
TAPEPLEX NAMEparameter.
For more information, refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring the Host Software for VLE.
-
- IPIF=ci:p
-
The IPIF value for each VTSS to VLE port connection in
ci:pformat where:-
cindicates the VTSS Storage Cluster number (0 or 1). -
iindicates the interface number (A or I) -
pindicates the device number on the interface (0, 1, 2, or 3).
For a VSM5, this value must match the values specified on the VSM5 IFF Configuration Status Screen. For a VSM 6, this must be unique for each VTSS and does not correspond to an actual value on the VSM 6 TCP/IP ports.
-
- DEVNO=nnnn
-
specifies the unit address of the RTD or remote library. This parameter is required with
CHANIF. There is no default value. - CHANIF=ci or ci:p
-
specifies the channel interface on the VTSS that communicates with the RTD where:
-
cindicates the VTSS Storage Cluster number (0 or 1). -
iindicates the interface number (A, C, E, G, I, K, M, or O) -
pindicates the device number on the interface (0, 1, 2, or 3).
For a VSM5, this
CHANIFvalue must match the actual FICON interface values. For a VSM 6, this must be unique for each VTSS and does not correspond to an actual value on the VSM 6 FICON ports. For remote library connections, this value must be unique for each library and must follow theci:prules for RTDs.Regardless of whether the Maximum 32 RTDs feature is enabled, if you do not have greater than 16 RTDs attached to a VTSS, you can use the ”old” addressing scheme (
CHANIF=ci).If, however, the Maximum 32 RTDs feature is enabled and you have greater than 16 RTDs attached to a VTSS, you must use the ”new” addressing scheme (
CHANIF=ci:p).Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring HSC and VTCS for more information.
Caution:
For RTDs, driving mount and dismount commands to the device is version dependant. If the remote HSC server is running V6.2, then it is dependant upon the local SMC trapping the MVS message and forwarding the mount/dismount across to the HSC server as if it was a job. If the remote HSC server is running V7 or above, then this is automatically detected and VTCS directs a mount/dismount request directly to the remote HSC server. It is important that the SMC parameters only direct commands to servers of one of these types. -
CONFIg STORMNGR Statement
The CONFIg STORMNGR statement defines a VLE to VTCS.
Note:
-
Do not specify this statement when down-level hosts are active. Once
CONFIg STORMNGRis specified, down-level hosts no longer function. -
This statement requires CDS level
V62ABOVEor higher. -
This statement is an alternative to the CONFIg TAPEPLEX statement. That is, you can either specify a list of VLEs on
CONFIg TAPEPLEXor each VLE individually viaCONFIg STORMNGR. If you codeCONFIg STORMNGRstatements, they must immediately follow theCONFIg TAPEPLEXstatement to which theCONFIg STORMNGRstatements apply. -
For VTCS 7.2, you can define additional emulated VLE RTDs with the
VLEDEVparameter. For more information, refer to Oracle's VLE publication Configuring the Host Software for VLE.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-21, the CONFIg STORMNGR statement includes the following parameters:
- STORMNGR
-
specifies Subsystem Name of the VLE attached to the preceding
TAPEPLEXstatement. - NAME=name
-
the Subsystem name of the VLE, which is set by the VLE installation scripts.
- VLEDEV(device-id-list)
-
optionally, specifies the logical device IDs of a VLE. This parameter requires
CONFIG CDSLEVEL=V71ABOVE(CDS Level H) and applies to VLE 1.2.device-id-listis a list or range of device IDs whose format is an 'S' prefix followed by three hexadecimal characters. These IDs are similar to MVS device addresses but do not overlap with the MVS name space. You can specify up to 96 device IDs per VLE, which defines each VLE with 96 emulated devices, which enables VTCS to schedule up to 96 processes on each VLE.
CONFIg TAPEPLEX Statement
The CONFIg TAPEPLEX statement defines values to VTCS for Cross-TapePlex Replication (CTR) or for replication to a VLE.
-
Do not specify this statement when down-level hosts are active. Once
CONFIg TAPEPLEXis specified, down-level hosts no longer function. -
This statement requires CDS level
V61ABOVEor higher. -
Refer to Oracle's ELS publications Managing HSC and VTCS and ELS Disaster Recovery and Offsite Data Management Guide for more information about Cross-TapePlex Replication.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-22, the CONFIg TAPEPLEX statement includes the following parameters:
- THISPLEX=name
-
specifies the TapePlex name for this configuration. This name is associated with any VTV copies that are exported to other TapePlexes via Cross-TapePlex Replication.
nameindicates the TapePlex name. This name must match the name specified on an SMCLIBraryorTAPEPlexcommand defined in the local SMC. The following rules apply:-
The value must be between 1 and 8 characters in length.
-
The first character must be either an alpha character or digit.
-
The last character must be either an alpha character or digit.
-
Any character between the first and last must be either an alpha character, digit, or hyphen.
-
- RECVPLEX(tapeplex-list)
-
optionally, specifies the list of TapePlexes from which VTV copies can be received (from Cross-TapePlex Replication). Attempts by hosts to send or scratch VTV copies from TapePlexes that are not included on the list are rejected.
tapeplex-listindicates the list of TapePlex names. The following rules apply:-
The value must be between 1 and 8 characters in length.
-
The first character must be either an alpha character or digit.
-
The last character must be either an alpha character or digit.
-
Any character between the first and last must be either an alpha character, digit, or hyphen.
Note:
SpecifyRECVPLEXon the receiving TapePlex. You can also specifyRECVPLEXon the sending TapePlex to allow this TapePlex to recall a VTV from the receiving TapePlex. -
- STORMNGR(stormngr-list)
-
optionally, specifies Subsystem Names of the VLEs attached to this TapePlex.
stormngr-listindicates the list of VLE subsystem names. For more information, refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring the Host Software for VLE.
CONFIg VTD Statement
The CONFIg VTD statement defines the MVS unit address range of the VTDs in a VTSS. This statement is required and must follow the VTSS statement where the VTDs reside.
Note:
VSM2s and VSM3s provide 64 VTDs per VTSS. VSM4s and later models provide 256 VTDs per VTSS.You can specify the VTD unit addresses to either apply to all hosts or to define which VTDs are available to specific hosts. See "Specifying VTD Unit Addresses" for more information.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-23, the CONFIg VTD statement includes the following parameters:
- LOW=xxxx
-
specifies a four character valid MVS unit address (
xxxx) as the start of a range of VTDs. - HIGH=xxxx
-
specifies a four character valid MVS unit address (
xxxx) as the end of a range of VTDs. - CUADDR=xx
-
optionally, specifies a control unit identifier (xx) that matches its value in the IOCP. Valid values are 0 through 15 for VSM4 and 0 through 3 for VSM2 or VSM3. This statement is required only if a partial VTD range is specified for a host and the host does not have a path to the VTDs.
- NOVERIFY
-
optionally, suppresses VTD verification.
Normally, VTCS attempts verification of all predicted VTD identifiers associated with Virtual Tape Drives. In order to do this, each MVS I/O address must be available to allow the associated Host to issue the ECAM-T request
Virtual_Device_Identify. ECAM is the method VTCS uses to communicate with a VTSS when bringing a VTSS online and scheduling replication and migrations.In specific cases where, for example, VTCS is providing support for a remote client host, the local host, acting as a server for the remote client, may not have paths to the MVS I/O address. In these cases, any attempt at verification of the predicted VTD identifier fails and results in error messages posted to the operator.
NOVERIFYsuppresses verification and prevents these failures.When
NOVERIFYis specified for a device or range of devices, the following occurs:-
The device is reported to SMC so that VTVs can be mounted from MVS.
-
VTCS does not use that device for ECAM I/O. At least one device must be left without
NOVERIFYso that it can be used for ECAM I/O.
-
Specifying VTD Unit Addresses
To specify VTD addresses, do one of the following:
-
Specify the VTD unit addresses on a
VTDstatement following aVTSSstatement and do not specify anyHOSTstatements following theVTSSstatement. All hosts physically connected to the VTSS have access to its VTDs by the default addresses specified on theVTDstatement. -
Do not specify the VTD unit addresses on the
VTDstatement following aVTSSstatement. Instead, place aVTDstatement after aHOSTstatement for only those hosts for which you want to define connections to the previously defined VTSS. You must specify a placeholder (HOST NAMEwith noVTDparameter) for any hosts that you do not want connected to this VTSS.
The VTVs created and MVCs initially written to from a VTSS are considered to be resources of that VTSS. Therefore, only hosts with access to a VTSS have access to its VTVs and MVCs. In this type of ”restricted” access configuration, each host should have a separate VTV scratch pool to ensure that each host has accurate scratch counts. Similarly, free MVCs and MVC reclaim counts are reported on each host for the MVCs associated with the VTSS to which the host is connected.
You can specify different address ranges for each host, although Oracle recommends that you specify the same address ranges for all hosts for consistency of operations. If you specify different address ranges for different hosts, use the HSC SET DRVHOST and SMC DRIVEMAP statements if you have a client/server configuration. You must include UNITATTR MODEL(IGNORE) commands for all overgenned devices (including VTDs) on all MVS hosts.
Caution:
In a multi-host, multi-VTSS configuration, you can use this VTD addressing method to deny access to VTSSs to which hosts are physically connected. You must, however, use this method to deny access from hosts that are not physically connected to a VTSS. If you do not deny access, VTCS on a host that does not have physical connections to a VTSS may wait, trying to communicate with the VTSS while VSM operations may be stalled on all other hosts.CONFIg VTSS Statement
The CONFIg VTSS statement defines a VTSS and sets its operating values. This statement is required.
When you define a new VTSS, place its definition after any existing VTSS definitions, which must remain in their original order.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-24, the CONFIg VTSS statement includes the following parameters:
Note:
If you physically remove a VTSS from your configuration, reconfigure the VTSS with a VTSS statement only (no parameters).- NAME=xxxxxxxx
-
specifies the VTSS name (
xxxxxxxx). This parameter is required; there is no default value. The VTSS name can consist of the characters "A-Z", "0-9", "@", "$", and "#".You specify the VTSS name only via the
NAMEparameter, which sets the VTSS name in both the VTSS microcode (as displayed in theSubsystem Namefield in the LOP or VOP) and in the configuration area of the HSC CDS. After VSM is put into operation, the VTSS name is also stored in each VTV record in the CDS. Each VTV record contains the VTSS name on which that VTV is resident. If the VTV is migrated, the VTV record contains the VTSS name from which the VTV was migrated.Once you set the VTSS name via the
NAMEparameter, you cannot change this identifier in the HSC CDS. That is, theCONFIgutility does not allow you to change theNAMEparameter after an initial setting and changing the VTSS name using theSubsystem Namefield of the LOP or VOP cannot change the VTSS name in the HSC CDS.Caution:
Do not attempt to rename a VTSS that contains data on VTVs, which includes VTSS-resident VTVs and migrated VTVs.For an initial setting only (not a change), you can set the VTSS name in the
NAMEparameter only if the VTSS name value in the VTSS microcode is one of the following:-
The factory setting (all blanks).
-
A value of 99999999 (eight 9s).
Therefore, for an initial setting only, if the name in the VTSS microcode is not all blanks or 99999999, your Oracle StorageTek hardware representative must use the VTSS LOP or VOP to set the VTSS name to 99999999. This enables you to set the VTSS name to the value you want via the
NAMEparameter. -
- DEFLTACS=acs-id
-
optionally, VTCS supports multi-VTSS confirmations, and supports connecting multiple ACSs to each VTSS. In configurations where a VTSS is connected to multiple ACSs, use the
DEFLTACSparameter to specify the default ACS (acs-id) from which MVCs will be selected for migration, consolidation, and reclaim processing. You can migrate up to 4 VTV copies to separate ACSs (perMGMTclasstatement) from theMGMTclas MIGpolparameter (and ignores theDEFLTACSparameter, as described below).If you do not specify
DEFLTACS, the default value isx'FF', which enables VTCS to select MVCs from any ACS.VTCS ignores the
DEFLTACSvalue if you specify theDEFLTACSparameter and do either of the following:-
Specify the
ACSlistparameter of theMGMTclasstatement. -
Use a Storage Class.
-
- LOW=nn
-
optionally, specifies the low automatic migration threshold (LAMT) for this VTSS.
nnindicates the threshold value.Valid values are 5 to 95 and must be less than the
HIGHdefault threshold. The default is 70. - HIGH=nn
-
optionally, specifies the high automatic migration threshold (HAMT) for this VTSS.
nnindicates the threshold value.Valid values are 6 to 95 and must be greater than the LOW default threshold. The default is 80.
- MAXMIG=n
-
optionally, specifies the maximum number of concurrent automatic migration, immediate migration, and migrate-to-threshold tasks for this VTSS.
nindicates the number of tasks. Valid values are 1 to the number of RTDs attached to the VTSS. The default is half the number of RTDs attached to the VTSS. - MINMIG=n
-
optionally, specifies the minimum number of concurrent automatic migration, immediate migration, and migrate-to-threshold tasks for this VTSS.
nindicates the number of tasks. Valid values are 1 to theMAXMIGsetting. The default is 1 task. - RETAIN=nn
-
optionally, specifies the number of minutes that VTCS retains an MVC on an RTD in idle mode after a migration or recall. Retaining the MVC can reduce MVC mounts.
nnindicates the number of minutes. Valid values are 1 to 60. The default is 15.An MVC on an idle RTD is not dismounted until the
RETAINtime has elapsed, unless the RTD in question is required, and no other 'like RTDs' (same ACS, LSM, and device type) are free.An exception to this behavior occurs when the last operation on the RTD was a job-initiated recall or an 'MVC is full' condition has occurred. In this case, the MVC is dismounted from the idle MVC when VTCS has determined that, although the RTD is not currently needed, there are no other 'like' RTDs free.
- NOERLYMT
-
optionally, disables Early Time to First Byte (ETTFB), also known as the concurrent tape recall/mount feature, for this VTSS. This parameter only applies if
CONFIg GLOBAL FASTRECL=YES. This parameter applies to recalls from RTDs and recalls from VLE. - CMDCONN
-
optionally, specifies the VTSS access method:
- CHANNEL
-
indicates ESCON or FICON channel access. This is the default.
- TCPIP
-
indicates TCP/IP access. This requires a valid
CONFIg VTSS IPCONN=(name-list)value.
- IPCONN=(name-list)
-
optionally, specifies a comma-separated list of one to four IP addresses, either explicitly as IP addresses or implicitly by names that resolve to IP addresses, used to define TCP/IP connections.
name-listindicates the list of IP addresses or names. Values entered in the list cannot be verified until a VTCS system is initialized to use them. They must meet the following requirements:-
Any IPv4 values must be specified in format
nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn, where each byte is one to four hexadecimal characters. There must be four bytes, numeric only except for the decimal points. -
Any IPv6 values must be specified in format
x.x.x.x.x.x.x.x, where each byte is 0-255. There must be four bytes: 0-9, A-F (or a-f). IPv6 abbreviations are not allowed. The full eight part address must be specified. -
If names are specified, they can be a maximum of 60 characters. A name can be any valid
DNSnamecontaining only the characters A-Z, a-z, 0-9, '-', or '.'.
-
- NOGT256
-
optionally, disables greater than 256 VTD support for this VTSS. This parameter only applies if
CONFIG GLOBAL VTDGT256=YESis specified.Note:
VTDGT256=YESis only valid with VSM model 7 and above. VSM 7 VTSS supports 512 VTDs with current maintenance.
CONFIg VTVVOL Statement
The CONFIg VTVVOL statement defines a range of VTVs.
Oracle recommends using SET VOLPARM to define VTV and MVC ranges in the VTCS CONFIg.
-
See "SET VOLPARM" for more information about the
SET VOLPARMstatement. -
Refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Legacy Interfaces Reference for information about the use of the
VTVVOLandMVCVOLstatements inCONFIgto define volumes.
CONSolid
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Description
The CONSolid command consolidates VTVs on MVCs.
Note:
VTVs cannot be consolidated onto vMVCs in a VLE.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-25, the CONSolid command includes the following parameters:
- VTV(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
optionally, specifies one or more VTVs to consolidate.
volser,vol-range, orvol-listindicates the volser, volser range, or volser list of VTVs. You can specify a maximum of 2,000 VTVs. - MGMTclas(mgmtclas-name or mgmtclas-list)
-
optionally, specifies the names of one or more Management Classes that determine the VTVs to consolidate.
mgmt-class-nameormgmt-class-listindicates the names of one or more Management Classes that you defined on theMGMTclascontrol statement; for more information, see "MGMTclas Control Statement". You can consolidate a maximum of 2,000 VTVs by specifying a Management Class. - RECALWER
-
optionally, specifies whether VTCS recalls VTVs with read data checks.
- NO
-
Do not recall VTVs with read data checks. This is the default.
- YES
-
Recall VTVs with read data checks.
CONSolid Report Messages
The consolidation report displays the following messages:
MIGRATE ONLY FROM VTSS vtssname
Explanation: The VTV is resident on VTSS vtssname.
REMIGRATE FROM MVC mvcname VIA VTSS vtssname
Explanation: VTCS is recalling a VTV from MVC mvcname to consolidate the VTV
VTV vtvname NOT SELECTED; VTV IS SCRATCH
Explanation: VTCS will not consolidate the specified VTV, which is either scratch or not initialized.
VTV vtvname NOT SELECTED; VTV ALREADY CONSOLIDATED
Explanation: The specified VTV is already consolidated.
VTV vtvname NOT SELECTED; VTV RECORD NOT FOUND
Explanation: VTCS will not consolidate the specified VTV, which has no record in the CDS.
VTV vtvname NOT SELECTED; VTV STILL MOUNTED ON DRIVE
Explanation: VTCS cannot consolidate the specified VTV, which is mounted or in recovery.
REDRIVING REQUEST BECAUSE OF ERROR
Explanation: VTCS is retrying an unsuccessful consolidation request.
CONSOLID CMD PROBLEM DECODING VCI REQUEST FROM HSC
Explanation: The consolidation failed.
VTV vtvnumber NOT SELECTED: LIMITED ACCESS TO VTSS
Explanation: The consolidation request failed because a host not enabled for consolidation (via the NOMIGRAT parameter) issued the request.
MIGRATE NO MVCS AVAILABLE
Explanation: Sufficient free MVCs are not available to complete the request.
DBSERVer
Interfaces:
-
Console or Utility only
-
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC required. VTCS must not be active.
Description
The DBSERVer command starts or stops a VSM console oVTCS CDS database server. The oVTCS CDS database server services CDS database I/O requests from an oVTCS client.
Note:
You can only start an oVTCS CDS database server in an HSC subsystem with no executing VTCS component.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-26, the DBSERVer command includes the following parameters:
- LIST
-
optionally, list the settings and status of the oVTCS CDS database server.
- RESET
-
optionally, force a reset of the oVTCS CDS database server which closes the accepted socket, clear any pending work, and listen again for the oVTCS client to re-connect.
- START
-
optionally, start the oVTCS CDS database server.
- PORT(nnnn)
-
optionally, specifies the socket listener port.
nnnnindicates the port. If you do not specify this parameter, the default is 8081. - TASKS(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum number of tasks for asynchronous CDS reads.
nnindicates the maximum number of tasks. Allowable values are 1-25. If you do not specify this parameter, the default is 5. - RTIMEOUT(nnnnn)
-
optionally, specifies the reserve timeout.
nnnnindicates the timeout in minutes. Allowable values are 1-99999. If you do not specify this parameter, the default is 99999 (69 days). - RTMSG(nnnnn)
-
optionally, specifies the time interval to display the SLS0789I "CDS reserved by client" message.
nnnnnindicates the time interval in minutes. Allowable values are 1-99999. If you do not specify this parameter, the default is 60 (1 hour). - MAXDATA(nnnn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum CDS block length for tracing.
nnnnindicates the block length. Allowable values are 0-4906. If you do not specify this parameter, the default is 64.
- STOP
-
optionally, stop the oVTCS CDS database server.
- FORCE
-
optionally, force termination even when the oVTCS CDS database server has not terminated successfully.
DEComp
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-27, the DEComp command includes the following parameters:
- FLATdd(ddname)
-
optionally, specifies the output destination dd name if a flat file is required.
ddnameindicates the dd name of the flat file included in the JCL. - LISTDELR
-
optionally, list volser ranges of ”logically deleted” MVCs and VTVs.
Note:
LISTDELRis only valid for a CDS at level G or above.
Output
The following examples show sample output for the DEComp command.
FLATDD Parameter Output
Example 3-4 shows an example of DEComp output with the FLATDD parameter.
Example 3-4 DEComp FLATDD output
CONFIG CDSLEVEL(V62ABOVE)
GLOBALMAXVTV=32000 MVCFREE=40 VTVattr=ALLmount RECALWER=YES
REPlicat=ALWAYS LOCKSTR=STK_VTCS_LOCKS
RECLAIMTHRESHLD=70 MAXMVC=40 START=35 CONMVC=1 VLTHRES=1 +
INPLACE=Yes INPTHRSH=15
VTVVOL LOW=905000 HIGH=999999 SCRATCH
VTVVOL LOW=C00000 HIGH=C25000 SCRATCH
VTVVOL LOW=RMM000 HIGH=RMM020 SCRATCH
MVCVOL LOW=N25980 HIGH=N25989
MVCVOL LOW=N35000 HIGH=N35999
VTSSNAME=VTSS1 LOW=70 HIGH=80 MAXMIG=3 RETAIN=5
RTDNAME=VTS18800 DEVNO=8800 CHANIF=0A
RTDNAME=VTS18801 DEVNO=8801 CHANIF=0I
RTDNAME=VTS18802 DEVNO=8802 CHANIF=1A
RTDNAME=VTS18803 DEVNO=8803 CHANIF=1I
VTD LOW=8900 HIGH=893F
VTSSNAME=VTSS2 LOW=70 HIGH=80 MAXMIG=3 RETAIN=5
RTDNAME=VTS28804 DEVNO=8804 CHANIF=0A
TDNAME=VTS28805 DEVNO=8805 CHANIF=0I
RTDNAME=VTS28806 DEVNO=8806 CHANIF=1A
RTDNAME=VTS28807 DEVNO=8807 CHANIF=1I
VTDLOW=9900 HIGH=993F
SLSPRINT Output
Example 3-5 shows an example of DEComp output to SLSPRINT.
Example 3-5 DEComp SLSPRINT output
DECOM
SLS1315I SSRDMP.P775644.TESTCDS WAS SELECTED AS THE PRIMARY CONTROL DATA SET
TIME 09:07:06 VTCS DECOMPILE
CONFIG CDSLEVEL(V62ABOVE)
GLOBAL MAXVTV=32000 MVCFREE=40 VTVattr=ALLmount RECALWER=YES
REPlicat=ALWAYS LOCKSTR=STK_VTCS_LOCKS
RECLAIM THRESHLD=70 MAXMVC=40 START=35 CONMVC=1 VLTHRES=1 +
INPLACE=Yes INPTHRSH=15
VTVVOL LOW=905000 HIGH=999999 SCRATCH
VTVVOL LOW=C00000 HIGH=C25000 SCRATCH
VTVVOL LOW=RMM000 HIGH=RMM020 SCRATCH
MVCVOL LOW=N25980 HIGH=N25989
MVCVOL LOW=N35000 HIGH=N35999
VTSSNAME=VTSS1 LOW=70 HIGH=80 MAXMIG=3 RETAIN=5
RTDNAME=VTS18800 DEVNO=8800 CHANIF=0A
RTDNAME=VTS18801 DEVNO=8801 CHANIF=0I
RTDNAME=VTS18802 DEVNO=8802 CHANIF=1A
RTDNAME=VTS18803 DEVNO=8803 CHANIF=1I
VTDLOW=8900 HIGH=893F
VTSSNAME=VTSS2 LOW=70 HIGH=80 MAXMIG=3 RETAIN=5
RTDNAME=VTS28804 DEVNO=8804 CHANIF=0A
RTDNAME=VTS28805 DEVNO=8805 CHANIF=0I
RTDNAME=VTS28806 DEVNO=8806 CHANIF=1A
RTDNAME=VTS28807 DEVNO=8807 CHANIF=1I
VTDLOW=9900 HIGH=993F
DELETSCR
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Description
The DELETSCR command deletes scratch VTVs from VTSSs and unlinks any migrated VTVs from MVCs.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-28, the DELETSCR command includes the following parameters:
- VTVid(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
optionally, specifies one or more VTVs to be deleted.
volser,vol-range, orvol-listindicates the volsers of one or more VTVs. - MGMTclas(mgmtclas-name)
-
optionally, specifies the Management Class(es) of the VTVs.
mgmt-class-nameindicates the Management Class name that you specified on theMGMTclascontrol statement. - SCRPool(scrpool)
-
optionally, specifies the scratch pool(s) to be deleted. If the pool contains VTVs and real volumes,
DELETSCRdeletes only VTVs.scrpoolis an existing HSC scratch pool. - VTSS(vtss-name)
-
optionally, causes scratch VTVs within the specified VTSS to be deleted.
vtss-nameindicates the VTSS name.Note:
VTVid,MGMTclas,SCRPool, andVTSSare mutually exclusive. If you do not specify one of these parameters, VTCS processes all scratch VTVs. - NOTREF(days)
-
specifies the number of days since a VTV was last referenced for it to be deleted by
DELETSCR.daysindicates the number of days (1-999). - MAXVTV(nnn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum number of VTVs that
DELETSCRdeletes. Note that this is a maximum, not a target.nnnindicates the maximum number of VTVs (0-999). If not specified,DELETSCRdeletes all scratch VTVs. If you specify 0,DELETSCRdoes not delete any VTVs, but the summary report shows how many VTVs would have been deleted...at the point at which you ranDELETSCR(that is, the report is just a snapshot). - DETail
-
optionally, produce a detailed report that also shows detail and summary of VTVs that fall within the
NOTREFperiod.
DELETSCR Report
Example 3-6 is an example of a DELETSCR report for the following batch invocation:
DELETSCR MGMTCLAS(MC1) NOTREF(60) MAXVTV(10) DET
SLUADMIN (7.2.0) StorageTek Enterprise Library Software Utility PAGE 0001 TIME 06:32:03 SCRATCH VTV DELETE DATE 2015-03-31 SLS6833I VTV VTV100 deleted from MVC M00001 SLS6835I VTV VTV101 excluded – referenced within 60 days SLS6833I VTV VTV102 deleted from MVC M00003 SLS6835I VTV VTV103 excluded – referenced within 60 days SLS6835I VTV VTV104 excluded – referenced within 60 days SLS6833I VTV VTV105 deleted from MVC M00007 SLS6833I VTV VTV106 deleted from MVC M00157 SLS6834I VTV VTV107 deleted SLS6833I VTV VTV108 deleted from MVC M00072 SLS6833I VTV VTV110 deleted from MVC M00757 SLS6833I VTV VTV111 deleted from MVC M00767 SLS6833I VTV VTV112 deleted from MVC M01057 SLS6834I VTV VTV113 deleted SUMMARY: 10 scratch VTVs deleted 1 VTV EXCLUDED - NOT SCRATCH VOLUME 0 VTVS EXCLUDED - NOT INITIALIZED 3 SCRATCH VTVS EXCLUDED - REFERENCED WITHIN 60 DAYS 6 scratch VTV delete candidates bypassed after MAXVTV limit 10 reached
A DELETSCR report shows the following:
-
A line for each deleted VTV
-
If
DETailis specified, a line for each VTV excluded (did not fall within theNOTREFperiod). -
A summary showing:
-
Total VTVs deleted.
-
Total VTVs excluded - not scratch.
-
Total VTVs excluded - not initialized.
-
Total VTVs excluded - not resident or migrated.
-
Total VTVs excluded - referenced within the
NOTREFperiod. -
Total VTVs excluded -
MAXVTVlimit has been reached. -
Total VTVs excluded - not in the specified Management Class.
-
DIRBLD
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The DIRBLD command rebuilds the database directory for all defined CDS copies.
The control data set contains a directory of pointers to various important locations and if damaged, can cause operational problems. Normally, HSC corrects such errors automatically. The DIRBLD utility repairs a corrupted CDS database directory. This utility can be run while the HSC is stopped or running to repair damage to the directory and maintain continuous operation. It must be run using all CDS copies as input.
Caution:
Contact Oracle StorageTek Support before running theDIRBLD utility to insure that the CDS is not further damaged by inappropriate use or inappropriate operational conditions.DISMount
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The DISMount command dismounts a cartridge or VTV.
Although the volume may be rewound and unloaded by the operating system, it may not be dismounted from the real drive or VTD. This command is provided for instances where hosts are not communicating with a specific ACS (disconnected mode).
Hosts that are still communicating (connected mode) may be able to semi-automate tape handling for hosts that cannot communicate with a specific ACS. When HSC or VTCS does not dismount a volume, you must ensure that the volume is unloaded before you issue the DISMount command.
Note:
The HSCDISMount command does not support VTDs that are not defined in the VTCS CONFIG. The SMC DISMOunt command must be used in place of the HSC DISMount command for any VTDs that are not specified in the VTCS CONFIG.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-30, the DISMount command includes the following parameters:
- volser
-
optionally, specifies which volume to dismount. The
volseroperand is optional. If it is not specified, the robot dismounts whatever volume is mounted on the device.If
volseris not specified, a comma must be entered immediately before the device address to indicate the missing operand. For example:DISMOUNT ,B00 - devaddr
-
specifies the device address of the transport from which the volume is to be dismounted.
- host-id
-
optionally, indicates that the
DISMountcommand is to be performed for the device address of the specified host (the SMF system identifier for both JES2 and JES3). - FORCE
-
optionally, specifies that the drive will be unloaded before the volume is dismounted. This parameter is not valid for virtual drives.
Display
The Display command displays status and current settings for various ELS components.
Issue this command with any of the options listed in the following table. Each option is described individually, and in more detail, on the pages to follow.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
status for one or more ACSs. |
|
|
active VTCS processes |
|
|
CDS and ACS status |
|
|
HSC allocation settings |
|
|
CAP settings and status |
|
|
status of all copies of the CDS, some operational settings (e.g., the cleaning cartridge prefix, SMF record type, etc.), and the status of all HSC-defined hosts |
|
|
cluster link status |
|
|
cluster status |
|
|
detailed information for an ELS command |
|
|
current settings for HSC hosttohost communications |
|
|
|
|
|
current and queued mount activity for each transport address |
|
|
status information for real and/or virtual drives |
|
|
hardware status |
|
|
replication link and |
|
|
information about the definition data set, containing |
|
|
VTCS lock status |
|
|
LSM status |
|
|
detailed information for an ELS message |
|
|
information about active |
|
|
migration status |
|
|
current settings for HSC mount options set by the |
|
|
list of monitoring consoles. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Legacy Interfaces Reference for more information about this option. |
|
|
information about a specific MVC |
|
|
information about active MVCPool statements. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Legacy Interfaces Reference for more information about this option. |
|
|
information about a specific MVC pool |
|
|
current settings for general HSC options set by the |
|
|
status of paths from VTSSs to either RTDs or Virtual Libraries. |
|
|
status of queued VTCS processes |
|
|
VTV replication status |
|
|
all pending LMU requests |
|
|
usage information for the one or more RTDs |
|
|
scratch counts by subpool name, ACS id, LSM id, media type, recording technique, or owning host name |
|
|
information about the definition data set, containing |
|
|
|
|
|
Server (HSC) status, including service level and features |
|
|
current service level of the HSC on the system from which you issue the command |
|
|
status of pending requests currently active on the host issuing the command |
|
|
information about a Storage Class |
|
|
status of an external storage manager and the paths defined to it from the VTSSs. |
|
|
task status |
|
|
scratch count and scratch threshold information by subpool name, ACS id, LSM id, media name, and recording technique name |
|
|
information about the definition data set, containing |
|
|
volume information |
|
|
status information for real and/or virtual volumes |
|
|
diagnostic information for virtual scratch counts |
|
|
VTD status |
|
|
VTSS status |
|
|
VTV status |
Display ACS
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The Display Acs command displays the status of one or more ACSs. Information may include the following:
-
partition ID
-
LMU and HSC compatibility levels
-
redundant electronics connections (summary of all Library Controllers)
-
available scratch volumes and free cells
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-31, the Display Acs command includes the following parameters:
- acsid, acsrange, or acslist
-
one or more ACSs for which the system is to display status. Each
acslistelement can be either a single ACSid or an ACSid range. The elements in a list must be separated by commas or blanks, and the entire list must be enclosed in parentheses.If you do not supply an
acsid, the status of all defined ACSs in the library is displayed.
Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display Acs command:
Example 3-7 Display ACS output
SLS0000I D ACS SLS1969I User exit 15 module SLSUX15 INACTIVE SLS1000I ACS 00 status: Connected Active Queue elements 1 Partition ID=005 Compatibility levels: HSC=23, LMU=23 Redundant Electronics is Configured Scratch Volumes available...... 0 Free Cells available........... 20 SLS1000I ACS 01 status: Disconnect ACS slots available for COMPLEX 7
Display ACTive
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-32, the Display ACTive command includes the following parameters:
- DETail
-
optionally, display detailed status.
- VTSS
-
optionally, display processes for the specified VTSS.
vtss-nameindicates the VTSS name.
Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display Active command (with no detail):
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display Active DETail command:
Example 3-9 Display Active DETail output
Function ID VTV MVC RTD VTSS Task Reason Reclaim@ 62180 - - - - RCM Child Finish .ReclmMVC 62251 - V10191 - - RCM Chile Finish . VtvMover 62254 - V10191 - - RCM Child Finish . Migrate 02003 - - - TVSM22N1 Drv MVC for command . Migrate 02090 - - - TVSM22N1 Drv MVC for command . Migrate 02148 - - - TVSM22N1 Drv MVC for command . Migrate 02163 - - - TVSM22N1 Drv MVC for command . Migrate 02184 - - - TVSM22N1 Drv MVC for command . Migrate 02229 - - - TVSM20N1 Drv MVC for command . Migrate 02242 - - - TVSM20N1 Drv MVC for command Display@ 02277 - - - - DSP
Note:
*ABORT appears in the display of reclaim requests if the request has cancelled or abended.Fields
The Function column shows the hierarchy of requests by indenting. The VTSS column shows either a VTSS name or a VTSS list. The Task column shows which task is currently servicing the request (same information as reported in Display Tasks).
Depending upon the parameters supplied, the output may contain only requests for a specific VTSS, be just the requests in a queued state, be just requests in an active state or be all requests. As can be seen above, the VTV and MVC columns are also used to expose additional information about the nature and status of the request.
- Function
-
The type of request. The hierarchy of the requests and their relationship is implied by the indentation of the values in this column. A period (.) before the Function indicates that the Function is a child.
Function can take on one of the following values:
- AllocSCR
-
Job allocation request for a scratch VTV.
- AllocVTV
-
Job allocation request for a specific VTV.
- Audit#
-
Audit utility request.
- Cancel@
-
Cancel command.
- Consold#
-
Consolidate or export utility task.
- Consolid
-
Recall VTVs for remigration to a consolidation MVC. This will appear as a child request to an
Int_consorConsold#request. - DELETSCR
-
Delete scratch utility.
- Dismount
-
Dismount a VTV from a VTD.
- Display@
-
DisplayorQuerycommand. - Drain
-
Recall VTVs from MVC for remigration during drain or reclaim processing. This is a child of a
VtvMoverrequest. - Drain@
-
Draincommand or utility. - DrainMVC
-
There is one
DrainMVCrequest per MVC being drained.DrainMVC, which is a child request of aDrain@ request, is responsible for managing the entire drain process for a single MVC. The VTV column is used to indicate the status of the processing against the MVC. - Getconfig
-
Get configuration information.
- Getmgpol
-
Obtain current management and storage class definitions.
- HSCChnge
-
Notification of parameter files being changed.
- Import#
-
Importing of VTV or MVC by a utility.
- Int_cons
-
PGMIinitiated consolidate request. - Inventry
-
INVENTRYutility. - MEDVERfy
-
Media Verify parent task
- Mig_set@
-
Set migration threshold command
- Mig_thr@
-
Migrate to threshold command.
- Migrate
-
General request to perform the migrations of VTVs to a MVC. This may appear as a child to a number of other request types.
- Migrate@
-
Migratecommand or utility. This includes migrates to threshold and auto migrates. The latter two are signified further details in the VTV and MVC columns as to the source of the command and the target threshold. - Mount
-
Mount a VTV upon a VTD. Depending upon
Move MVC, which is a child request of aMoveVTV#request, is responsible for managing the entire VTV movement process for a single MVC. Depending upon circumstances, this may be subsequently seen as a VTV transfer or recall request. The VTV column is used to indicate the status of the processing against the MVC. - Move MVC
-
There is one Move MVC request per MVC being processed by reconcile or archive.
Move MVC, which is a child request of aMoveVTV#request, is responsible for managing the entire VTV movement process for a single MVC. The VTV column is used to indicate the status of the processing against the MVC. - MoveVTV#
-
This is a request from the
ARCHIVEorRECONCILEutility commands to move copies of VTVs between MVCs. The value -TIME- in the VTV column indicates that theELAPSEDparameter was specified. - MVC_chek
-
Query MVC. Check status of MVC.
- MVC_eot
-
Reset the end of tape position of an MVC after completing a drain or reclaim. This is a child of either a
DrainMVC,ReclmMVCorMove MVCrequest. - MVC_inv
-
Audit of an MVC. This will appear as a child request to an
Audit#request. - MVC_upd
-
Reset or update MVC status.
- MvcMaint
-
MVCMAINTutility request. - MVCpool#
-
Obtain details and status of MVC pools for a utility.
- PGMI_req
-
A request received through the PGMI interface that has yet to be decoded.
- QRY/SET@
-
QueryorSetcommand. - Query@
-
QueryorDisplaycommand. - Recall
-
General request to perform the recall of VTVs from an MVC. This may include a Cross TapePlex Autorecall (CTA) request from the mounting system.
Recall may appear as a child to a number of other request types.
- Recall@
-
Recallcommand or utility. - Reclaim@
-
Auto reclaimrequest or aReclaimcommand or utility. The value -TIME- in the VTV column indicates that theELAPSEDparameter was specified. - ReclmMVC
-
There is one
ReclmMVCrequest per MVC being reclaimed.ReclmMVC, which is a child request of aReclaim@request, is responsible for managing the entire reclaim process for a single MVC. The VTV column is used to indicate the status of the processing against the MVC. - Reconcil
-
Perform a crosscheck between the contents of the two VTSSs in a cluster.
- Replicat
-
Perform the replication of VTVs between VTSSs in a cluster.
- Scratch
-
A Scratch a VTV request from HSC.
- Sel_scr
-
PGMI select scratch.
- Set@
-
Setcommand. - Trace@
-
Tracecommand - Transfer
-
Mount a VTV upon a VTD by transferring the VTV between two VTSSs.
- Unload
-
Unload MVC from RTD.
- Unscratch
-
An
Unscratch a VTVrequest from HSC. - Vary@
-
A
Varycommand. This command applies to resources such as CLINKs, VTSSs and ACSs. - Vary_dev
-
Perform Vary processing against an individual RTD or CLINK. This will appear as a child request to a
VARY@request. - VTSS_inv
-
Audit of a VTSS. This will appear as a child request to an
Audit#request. - VTSS_list
-
Obtain a list of VTV resident within a VTSS. This will appear as a child request to a
Reconcilor auto migration request. - VTV_chek
-
Query VTV.
- VTV_list
-
Obtain a list of VTV resident within a VTSS. This will appear as a child request to a
Reconcilor auto migration request. This Function can show an invalid VTV ID ofVTS0B,VTS0CorVTS0Dand maybe other similar ones. It also shows aVTSS IDand a task ofSS. Invalid VTV IDs may occur because VTCS sometimes uses the fields that hold VTV/MVC volsers for other internal purposes, and the display routines don't filter out those cases. - VTV_upd
-
Resynchronize VTV status in the VTSS with the CDS.
- VtvMaint
-
VTVMAINTutility request. - VTVMover
-
There is one
VTVMoverrequest per MVC being drained or reclaimed. This is a child of either aDrainMVC,ReclmMVCorMove MVCrequest. This request is responsible for the movement of VTVs from one MVC to another
- ID
-
The process ID, which is a unique number in the range 0-65536. When the process ID reaches 65536 it wraps back to zero.
- VTV
-
the volser of the VTV currently being used in the process. For some types of request, this will contain additional information as to the nature and status of the request.
- MVC
-
the volser of the MVC currently used in the process. For some types of request, this will contain additional information as to the nature and status of the request.
- VTSS
-
The VTSS or the VTSS list name associated with the request. The special value
!ALLVTSSindicates that any VTSS with suitable requirements will be used. - RTD
-
the unit address of the RTD currently being used in the process.
- TASK
-
The task that is processing the queue or the task to which the requests is queued (same information as reported in
Display Tasks). Task displays one of the following values:- Clk
-
CLINK processor task.
- CMD
-
Command processor task.
- Csh
-
Clink scheduler task.
- DRV
-
RTD scheduler task.
- DSP
-
Main dispatcher task.
- INV
-
Inventory manager or audit task.
- MSc
-
Migration scheduler task.
- MVC
-
MVC lock task.
- RCM
-
Drain/space reclaim manager task.
- RTD
-
RTD task.
- Scr
-
Scratch manager task.
- SS
-
VTSS task.
- TSK
-
Waiting for processing lock on other host.
- unk
-
Unknown task.
- VTD
-
Waiting for VTD.
- VTV
-
Waiting for VTV lock.
- REASON
-
Indicates why the request is queued (queued processes only):
- ACTIVE
-
The request is currently being processed.
- CANCELLED
-
The request is terminating after being cancelled.
- Child Finish
-
The request has child requests and is waiting for them to finish.
- Created
-
The request is being created.
- DBU DROP
-
The request is currently held because the DBU is high.
- DEVICE LOCK
-
The RTD or CLINK device that the request requires is currently locked. This generally indicates contention with another host.
- MVC dismount
-
The request is waiting for an MVC to dismount.
- MVC for Class
-
The
SCHLIMITstorage class limit has been reached in MVC selection. - MVC for Command
-
The
SCHLIMITcommand concurrency limit has been reached in MVC selection. - MVC for Funct
-
The
SCHLIMITfunction limit has been reached in MVC selection. - MVC LOCK
-
The request is waiting for a lock on an MVC to free.
- MVC MOUNT
-
The request is waiting for a MVC to be mounted.
- MVC SELECTION
-
The request is queued awaiting a MVC or migration slot becoming available.
- MVC/SCHLIMIT=0
-
MVC selection determined that
SCHLIMIT=0has been specified. - QUEUED
-
The request is sitting in the input queue of the task and is waiting for another request to complete or be rescheduled.
- RTD ALLOCATION
-
The request is queued awaiting an RTD to become idle or free.
- RTD LOCK
-
The request is waiting for a lock on an RTD to free.
- RTD ONLINE
-
The request requires an RTD to be brought online to continue.
- STEAL A RTD
-
The request is waiting to steal an RTD allocation from another request.
- TASK LOCK
-
The request is waiting for a general task lock to free. This generally indicates contention with another host.
- VTD LOCK
-
The request is waiting for a lock on a VTD to free.
- VTVLOCK
-
The request is waiting for a lock on a VTV to free.
- Wait child
-
The request has been purged, but is waiting for child requests to finish.
- WAIT RESOURCE
-
The request is held awaiting a (non-specific) resource becoming available.
- Wait lock
-
The request is waiting for a lock to free.
Display ALl
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Display Cap
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-34, the Display Cap command includes the following parameters:
Note:
If the CAP status indicatesRECOVERY, refer to Oracle's ELS publication Managing HSC and VTCS for information about how to clear this condition.- all CAPs
-
displays all CAP activity for all ACSs online to this host.
- acsid
-
optionally, displays all CAP activity for a specified ACS.
- lsmid
-
optionally, displays all CAP activity for a specified LSM.
- capid
-
optionally, displays all CAP activity for a specified CAP.
Note:
-
The
acs-id,lsm-id, andcap-idparameters are positional operands. If no positional operand is specified, the default operation is to display the status of all CAP activity for all ACSs. -
The
acs-id,lsm-id, andcap-idmay be expressed as a list.
Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display Cap command for Bulk CAPs with 36 slot capacity:
Example 3-10 Display Cap output
SLS0000I D CAP
SLS2008I CAP Status: 874
CAP ID Size Partid Hostid Priority Mode Status
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
00:00:00 36-CELL None None 00 Idle Manual
Online
00:00:01 36-CELL None None 00 Idle Manual
Online
00:01:00 36-CELL None None 00 Idle Manual
Online
00:01:01 36-CELL None None 00 Idle Manual
Online
00:02:00 36-CELL None None 00 Idle Manual
Online
00:02:01 36-CELL None None 00 Idle Manual
Online
00:03:00 36-CELL None None 00 Idle Manual
Online
00:03:01 36-CELL None None 00 Idle Manual
Online
The Display Cap command displays the following information:
-
CAPid
-
CAP size:
-
PCAP (priority CAP)
-
21cell or 14cell 9740 (standard CAP)
-
40cell (enhanced CAP)
-
20cell (9360 CAP)
-
30cell (9360 optional CAP)
-
26-cell (SL3000 CAP)
-
234-cell (SL3000 AEM CAP)
-
39-cell (SL8500 CAP)
-
36-cell (SL8500 Bulk CAP)
-
-
Partition ID
-
Host ID of the host owning the CAP
-
Priority: CAP preference value
-
CAP mode:
-
cleaning -
draining -
ejecting -
entering -
idle
-
-
CAP status:
-
active -
automatic mode -
manual mode -
offline -
online -
recovery needed
-
Display CDS
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Description
Display CDS displays the status of all copies of the CDS, primary and secondary log files, operational settings (for example, the cleaning cartridge prefix, SMF record type, etc.), and the status of all HSC-defined hosts.
Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display CDS command:
Example 3-11 Display CDS output
SLS0000I D CDS SLS1969I User exit 15 module SLSUX15 INACTIVE SLS2716I Database Information 951 PRIMARY = SEA710.SPRG1.DBASEPRM.LGEN8501 VOLSER = HSC20J ACTIVE SECONDARY = SEA710.SPRG1.DBASESEC.LGEN8501 VOLSER = HSC20G ACTIVE CDS LEVEL = 060100 VER = 16012446 CDS CREATE = 20141203 13:49:56 LAST CDS BACKUP = NONE LAST CDS RESTORE = NONE CDS BLOCK COUNT = 7,200 CDS FREE BLOCKS = 4,135 ENQNAME = STKSBADD SMFTYPE = 245 CLEAN PREFIX = CLN LABTYPE = (00) SL NO LOG FILE DSN(S) DEFINED VAULT RECORDS NOT FOUND IN THIS CDS CDKLOCK RECORDS NOT FOUND IN THIS CDS LAST NCO ON ECCY START = 12/03/14 13:50:55 END = 12/03/14 13:53:19 HOSTID---LEVEL---DESCRIPTION--------------------- ECCL -.-.- -INACTIVE- ECCY 7.1.0 ACTIVE PRIMARY SECONDARY EC20 -.-.- -INACTIVE- EC21 -.-.- -INACTIVE-
Display CLInk
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Description
The Display CLInk command displays Cluster link (CLINK) status. Optionally, you can display CLINK status at the VTSS level, or display only those CLINKs that are in use, or in an error state.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-36, the Display CLInk command includes the following parameters:
- FROMvtss(vtss-name)
-
optionally, specifies the name of the VTSS that you want to display CLINKs from.
- INuse
-
optionally, displays only CLINKs that are in use.
- ERror
-
optionally, displays only CLINKs that are in an error state.
Note:
INuse and ERror are mutually exclusive.Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display CLInk command with no parameters:
Example 3-12 Display CLink output (no parameters)
VTSS Clink Name Status Usage Host Partner VTD
HBVTSS16 07 1A:0 PLEXNAME Online Free REMOTEAA 7
06 1E:0 PLEXNAME Online Free REMOTEBB 6
HBVTSS18 07 1A:0 -Cluster Online Free HBVTSS19 AB07
06 1E:0 -Cluster Online Free HBVTSS19 AB06
*SLS5013I Command completed (0)
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display CLInk command with FROM(DVTSS18) specified, to display output for CLINKs owned by VTSS DVTSS18.
Example 3-13 Display CLInk output (FROMvtss specified)
VTSS Clink Name Status Usage Host Partner VTD
DVTSS18 08 C0I SECNDARY On-Sync Free DVTSS17 #008
09 C1I SECNDARY On-Sync Free DVTSS17 #009
Fields
Display CLink command output includes the following fields:
- VTSS
-
the Primary or Sending VTSS name.
- CLINK
-
a composite of the device Id that has been assigned to the CLINK within the VTSS and the back end channel interface to which it is connected.
- NAME
-
one of the following values:
- name
-
the name of the TapePlex to which the CLINK is connected. This also indicates that the CLINK will be used for electronic exporting of VTVs. The VTSS name in the Partner column indicates the VTSS that will receive VTV copies over this CLINK.
- -Cluster
-
indicates that the CLINK is used for replication of VTVs within the TapePlex and is part of a cluster. The VTSS name in the Partner column indicates the other VTSS that operates in the cluster.
- STATUS
-
one of the following link statuses:
- Maint
-
The link has failed or it has been varied into maintenance mode.
- Offline
-
The link is offline and unavailable to all hosts and VTSSs.
- Online
-
The link is available for replication.
- P_offlne
-
The link is pending offline.
- P_online
-
The link is pending online.
- On-Sync
-
Available for synchronous replication.
- On-Async
-
Available for asynchronous replication.
- Recovery
-
The link is being reset following an error or a vary online operation.
- Unusable
-
Not available for replication due to hardware errors or assigned-elsewhere conditions.
- UUI err
-
This is a CLINK defined for electronic export and it has been unable to contact the remote VTCS. There should be messages in the HSC
JOBLOGthat indicate the reason for the problem. This could include problems with the definitions, the local SMC, or the remote HTTP server on the remote VTCS.
- USAGE
-
one of the following link usages:
- Assigned
-
Link is assigned to the host in the HOST field but is not currently replicating. This usage occurs when VTCS is starting or terminating link use or is attempting error recovery on the link after a replication failure.
- Free
-
Link is idle (not doing replications).
- Replicating
-
Link is actively doing replications.
- HOST
-
the host that the link is assigned to.
- PARTNER
-
the secondary or receiving VTSS.
- VTD
-
the address of the VTD on the partner VTSS that forms the other end point to the connection. For a cluster link, the MVS address of the VTD is reported. For an electronic export link, this is not possible as there is no access to the other TapePlex configuration. In this case, only the ordinal number of the VTV is reported.
Display CLUster
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display CLUster command:
Example 3-14 Display CLUster output
NAME VTSS STATE DIRECTION VTSS STATE MODE CLUSTER1 HBVTSS16 ONLINE ------> HBVTSS17 ONLINE Sync-replicate CLUSTER2 HBVTSS18 ONLINE <------ HBVTSS19 QUIESCED DEGRADED CLUSTER3 HBVTSS20 ONLINE <------ HBVTSS21 ONLINE Async-replicate CLUSTER4 HBVTSS22 QUIESCED <-----> HBVTSS23 ONLINE DEGRADED
Fields
Display CLUster command output includes the following fields:
- NAME
-
the Cluster name.
- VTSS
-
one of the VTSS in a Cluster.
- DIRECTION
-
One of the following:
- ----> or <----
-
Indicates the direction of VTV replication in Uni-Directional Cluster. VTVs can only be replicated from the Sending to the Receiving VTSS.
- <---->
-
Indicates that the VTSSs are configured as a Bi-Directional (Peer-to-Peer) Cluster. VTVs can be replicated from either VTSS to the other.
- STATE
-
one of the following VTSS states:
- QUIESCING
-
Quiescing state.
- QUIESCED
-
Quiesced state.
- OFFLINE
-
Offline state.
- OFFLINE-P
-
Offline pending state.
- ONLINE
-
Online state.
- ONLINE-P
-
Online pending state.
- STARTED
-
The VTSS is initialized and in process of going to the requested state (online, offline, or quiesced).
- MODE
-
one of the following Cluster operating modes:
- Async-replicate
-
Both VTSSs in the Cluster are online to VTCS. Production workload can go to either VTSS, but in the case of a Uni-Directional (Primary/Secondary) Cluster, VTVs can only be replicated from the Sending VTSS. Synchronous replication is not enabled across the cluster.
- Sync-replicate
-
Both VTSSs in the Cluster are online to VTCS. Production workload can go to either VTSS, but in the case of a Uni-Directional (Primary/Secondary) Cluster, VTVs can only be replicated from the Sending VTSS. Synchronous replication is enabled across the cluster.
- Degraded
-
One of the two VTSSs in a Bi-Directional (Peer-to-Peer) Cluster is either offline or quiesced. Production workload can go the remaining online VTSS. VTVs requiring replication, however, are allocated to the remaining VTSS only if no other Full-Function clusters are available and suitable. In this case, replicate VTVs are migrated immediately with keep and queued for replication when the other VTSS comes online.
When the other VTSS comes online, VTCS reconciles the contents of both VTSSs.
- Degraded-2ndary
-
The Primary is online to VTCS and the Secondary is either offline or quiesced. Workload can run on the Primary. VTVs requiring replication, however, are allocated to the Primary only if no other Full Function Clusters are available. In this case, Replicate VTVs are migrated immediately with keep and are queued for replication, which occurs when the Secondary comes online.
- Degraded primary
-
The Secondary is online to VTCS and the Primary is either offline or quiesced. Workload can run on the Secondary. VTVs requiring replication, however, are allocated to the Secondary only if no other Full Function Clusters are available. When the Primary comes back Online, VTCS reconciles the contents of the Primary and Secondary.
- Non-operational
-
No workload is possible on this Cluster.
- CLINKs offline
-
All defined CLINKs are offline. No workload is possible on this Cluster.
- Only 2ndary
-
The Secondary is online to VTCS and the Primary has no CLINKs online. Workload can run on the Secondary. VTVs requiring replication, however, are allocated to the Secondary only if no other Full Function Clusters are available.
- Only primary
-
The Primary is online to VTCS and the Secondary has no CLINKs online. Workload can run on the Primary. VTVs requiring replication, however, are allocated to the Primary only if no other Full Function Clusters are available. In this case, Replicate VTVs are migrated immediately with keep and are queued for replication.
Display CMD
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Description
The Display CMD command displays syntax and usage information for a VTCS or HSC command.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-38, the Display CMD command includes the following parameters:
- CMD or COmmand
-
the command name. If a command-name is not specified, a list of all HSC/VTCS commands is produced.
- command-name
-
the command name. If a command-name is not specified, a list of all HSC/VTCS commands is produced.
For certain commands that accept multiple options, including Display, a two-part command may be entered. For example:
D CMD D VTV
This command displays help information only for the Display VTV command.
Display COMMPath
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Description
The Display COMMPath command displays current settings for HSC hosttohost communications.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-39, the Display COMMPath command includes the following parameters:
- HOSTID
-
optionally, indicates that you want to obtain information about specific hosts.
- ALL
-
displays the settings for all defined hosts. Depending on the number of hosts in your environment, the display can be extremely long.
- host-id or host-list
-
the host or hosts about which you want information. The HSC issues console messages that display the current settings for each specified host.
The elements in a
hostlistmust be separated by commas or blanks, and the entire list must be enclosed in parentheses. Ranges are not valid. - *
-
displays the settings for the host on which you enter the command. This is the default if
HOSTidis specified without a value.
Display CONFIG
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display CONFIG command:
Example 3-15 Display CONFIG output
SLS6603I Configuration information
MaxVTV MVCFree VTVAttr RECALWER REPlicat VTVPAGE SYNCHREP
4000 2 Scratch Yes Always Standard No
MAXRTDs FASTMIGR INITMVC MAXVTVSZ FASTRECL LOCKTOUT
32 Yes Yes 4000 Yes 10
NLIBDRNR NLIBMIGR NLIBRECL MVCMNTTO LOGPOL VTDGT256
No No No 15 Optional Yes
This tapeplex: LOCALPLX
CDS level support: V5/5.1 V6 V6.1 V6.2 V7 V7.1
* * *
Reclaim : Max MVC Start Conmvc Threshold: Tape VL
4 10 1 30 70
Reclaim: MaxMVC Start Conmvc Inplace Threshold: Tape VL Inpthrsh
4 10 1 No 45 30 15
Auto Migr Thr Migr Tasks Default VSM 2GB/ Page RTDs
VTSSNAME Low High Min Max ACS Model 4GB Size Yes
DVTSS16 65 70 2 3 FF 5 Yes Large
Devno RTD Type Inplace ACS Retain VTSSNAME RTD NAME CHANIF
2A00 36CTRACK No 00 10 DVTSS16 SS162A00 00 0A:1
2A01 36CTRACK No TMVSB 10 DVTSS16 SS162A01 01 0A:0
2A02 36CTRACK No 00 10 DVTSS16 SS162A02 02 0E:0
Fields
Display CONFIG command output includes the following fields:
- MaxVTV
-
the
CONFIg GLOBAL MAXVTVsetting. - MVCFree
-
the
CONFIg GLOBAL MVCFREEsetting. - VTVAttr
-
the
CONFIg GLOBAL VTVattrsetting (SCRATCHorALLmount). - RECALWER
-
the
CONFIg GLOBAL RECALWERsetting (YESorNO). - REPlicat
-
the
CONFIg GLOBAL REPlicatsetting (ALWAYSorCHANGED). - VTVPAGE
-
the
CONFIg GLOBAL VTVPAGEsetting The VTV page size (STANDARDorLARGE). - SYNCHREP
-
the
CONFIg GLOBAL SYNCHREPsetting (YESorNO). - MAXRTDS
-
the
CONFIg GLOBAL MAXRTDSsetting (16or32). - FASTMIGR
-
the
CONFIg GLOBAL FASTMIGRsetting (YESorNO). - INITMVC
-
the
CONFIg GLOBAL INITMVCsetting (YESorNO). - MAXVTVSZ
-
the
CONFIg GLOBAL MAXVTVSZsetting (400,800,2000,or 4000). - FASTRECL
-
the
CONFIG GLOBAL FASTRECLsetting (YESorNO). - LOCKTOUT
-
the
CONFIg GLOBAL LOCKTOUTsetting (0or5-240). - NLIBDRNR
-
the
CONFIg GLOBAL NLIBDRNRsetting (YESorNO). - NLIBMIGR
-
the
CONFIg GLOBAL NLIBMIGRsetting (YESorNO). - NLIBRECL
-
the
CONFIg GLOBAL NLIBRECLsetting (YESorNO). - MVCMNTTO
-
the
CONFIg GLOBAL MVCMNTTOsetting (5-30minutes). - LOGPOL
-
the
CONFIg GLOBAL LOGPOLsetting (OPTionalorREQuired). - VTDGT256
-
the
CONFIg GLOBAL VTDGT256setting (YESorNO). - CDSLEVEL SUPPORT
-
the VTCS level(s) that can access the active CDS.
- THRESHLD
-
the
RECLAIM THRESHLDsetting. - MAX MVC
-
the
RECLAIM MAXMVCsetting. - START
-
the
RECLAIM STARTsetting. - CONMVC
-
the
RECLAIM CONMVCsetting. - VTSSNAME
-
the VTSS identifiers (
VTSS NAMEsettings). - AUTO MIGR THR, LOW
-
The low automatic migration threshold setting (
LAMT) for the VTSS. - AUTO MIGR THR, HIGH
-
The high automatic migration threshold setting (
HAMT) for the VTSS. - MIGR TASKS, MIN
-
The minimum number of concurrent automatic migration tasks setting (
MINMIG) for the VTSS. - MIGR TASKS, MAX
-
The maximum number of concurrent automatic migration tasks setting (
MAXMIG) for the VTSS. - DEFAULT ACS
-
The default ACS setting (
DEFLTACS) for the VTSS. - VSM MODEL
-
2, 3, or 4.
- 2GB / 4GB
-
VTSS configured for 2 GB or 4 GB VTV sizes (
YorN). - PAGE SIZE
-
VTV page size (
STANDARDorLARGE). - RTDs
-
indicates whether the VTSS has RTDs.
- DEVNO
-
RTD MVS device numbers for the VTSS (
RTD DEVNOsettings), or device numbers for a VLE, as generated by VTCS.-
Single-node VLE device numbers start with a "V".
-
Multi-node VLE device numbers are prefixed with an "S".
-
- RTD TYPE
-
the RTD type. This can include the VLE device type.
- Inplace
-
the
StorclasINPLACEsetting. - ACS
-
-
For local tape drives, this column displays the ACS or LSM to which the drive is attached.
-
For remote RTDs, this column displays '
name:number' wherenameindicates the name of the TapePlex andnumberindicates the number of the ACS in decimal. -
For VLEs, this column displays the VLE name.
-
- RETAIN
-
the
VTSS RETAINsetting. - VTSSNAME
-
the VTSS identifiers (
VTSS NAMEsettings) of the VTSSs connected to the RTD. - RTD NAME
-
the RTD names for the VTSS (
RTD NAMEsettings). - CHANIF
-
the RTD channel interface (
RTD CHANIFsettings).
Display DRives
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The Display DRives command displays current and queued mount activity for each transport address.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-41, the Display DRives command includes the following parameters:
- Library
-
only librarycontrolled drives are processed. This is the default.
- ACS(acs-id)
-
only drives in a specified ACS are processed.
acsidindicates the ACS for which the system is to display drive information. - LSM(lsm-id)
-
only drives in a specified LSM are processed.
lsmidindicates the LSM for which the system is to display drive information. - ACtive
-
only active drives are processed. This is the default.
- Idle
-
only idle drives are processed (includes drives that may be offline).
- ALl
-
all drives are processed regardless of status.
- BYDrive
-
displays the drives by host device address. This is the default.
- BYLoc
-
displays the drives by library location.
- SHOWSlot
-
optionally, displays the drives by host device address, and displays the drive bay location (slot) for drives in SL3000 and SL8500 libraries.
- DETail
-
optionally, displays the drive media types and recording techniques.
- IDEntity
-
optionally, displays the serial number and world wide name of a transport associated with a drive.
The tape library must be at a sufficient compatibility level to provide this information.
-
The serial number requires LMU level 13.
-
The WWN requires LMU level 21.
-
DISPLAY ACSshows the LMU compatibility level. In addition, the transport must supply the LMU with the serial number.
Note:
IDEntityandDETailare mutually exclusive. -
- MEDia(media-type)
-
optionally, limits the display of drives only to those that support the specified type of media. The default is for all types of media.
media-typeindicates the media type.See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for a list of valid
media-typevalues.Note:
IfMEDiais not specified, the drive is selected without regard to media type. - RECtech(recording-technique)
-
optionally, limits the display of drives only to those that support the specified recording technique. The default is for all recording techniques.
RECtechrefers to the method used to record data tracks on the tape surface.If
RECtechis not specified, the drive is selected without regard to recording technique.recording-techniqueindicates the recording technique.See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for valid
recording-techniquevalues.Note:
RECtechandMODelare mutually exclusive. - MODel(model-type)
-
optionally, limits the display of drives by the model type of a transport. You can enter a list of models, separated by commas. A list specifies a generic pool.
model-typeindicates the model type.See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for a list of valid
model-typevalues.Note:
MODelandRECtechare mutually exclusive. - UNIT(unit-address)
-
optionally, limits the display of drives to a unit address or a range of unit addresses.
unit-addressorunit-address-rangeindicates a single unit address or a range of addresses.
Display DRIVE_INFO
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-42, the Display DRIVE_INFO command includes the following parameters:
- ACtive
-
optionally, specifies that only drives with a volume mounted, or in the process of mounting or dismounting, are displayed.
- DEVADDR(device-address)
-
optionally, specifies that only the device with the specified drive ID is displayed.
device-addressindicates a three or four digit device address. - DRVLOC(drive-location)
-
optionally, specifies that only the single drive with a matching drive location ID is displayed.
drive-locationindicates the drive location id:For a real drive, use format
R:AA:LL:PP:DDwhere:-
AAindicates the acs ID. -
LLindicates the LSM number. -
PPindicates the panel. -
DDindicates the drive number.
For a virtual drive, use format
V:vtssname:nnnnwherennnnindicates the VTSS drive identifier. -
- LIBLOC(drive-id)
-
optionally, specifies that only the real drive with the specified drive ID is displayed.
drive-idindicates the drive ID, in the formatAA:LL:PP:DDwhere:-
AAindicates the acs ID. -
LLindicates the LSM number. -
PPindicates the panel. -
DDindicates the drive number.
-
- LIBRARY
-
optionally, specifies that only library (non-virtual) drives are displayed.
- LSMloc(lsm-id)
-
optionally, specifies that only drives in the specified LSM is displayed.
lsm-idindicates the LSM ID, in the formatAA:LLwhere:-
AAindicates the acs ID. -
LLindicates the LSM number.
-
- MODel(model-type)
-
optionally, specifies that only drives with the specified model type are displayed.
model-typeindicates the model type.See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for a list of valid
model-typevalues. - RECtech(recording-technique)
-
optionally, specifies that only drives with the specified recording technique are displayed.
recording-techniqueindicates the recording technique.See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for a list of valid
recording-techniquevalues. - VIRTual
-
optionally, specifies that only virtual drives (not library drives) are displayed.
Display EXceptns
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-43, the Display EXceptns command includes the following parameters:
- EXceptns or X
-
displays hardware status.
Errors are reported in either LSM
AA:LLorAA:LL:CCformat whereAAindicates the hexadecimal value for the ACS (00-FF),LLis hexadecimal value for the LSM (00-17), andCCindicates the hexadecimal value for the CAP identifier (00 through 0B).
Output
Display EXceptns displays status for the following:
-
all LMUs
-
all LSMs
-
all CAPs
-
all robotic hands
-
all pass-thru ports (PTPs)
-
all stations
Errors are reported in AA:LL:CC format, where AA indicates the decimal value for the ACS (00-99), LL is decimal value for the LSM (00-99), and CC decimal value for the CAP identifier (00 through 11). The following error messages are possible:
Table 3-2 Display EXceptns Error Messages
| Message | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The CAP is not operational. |
|
|
The CAP door is open. |
|
|
The CAP door is unlocked. |
|
|
The CAP is reserved. |
|
|
The pass thru port is inoperative. |
|
|
The robot hand is inoperative. |
|
|
The robot hand is in need of maintenance. |
|
|
The LSM is in a not ready state. |
|
|
The LSM is in an offline state. |
|
|
The LSM is in an online pending state. |
|
|
The LSM is in maintenance mode. |
|
|
The LSM door is open. |
|
|
The LMU will not be able to respond correctly to some of the status queries until its microcode is updated. This condition will also cause SLS0662I LMU Response Error to be issued just before SLS4610I. |
|
|
A hardware connection to the LMU is not usable. This may be normal for your configuration if the connection has never been made and is not necessary. The station number is in hex, so Station 0A is the tenth station, and Station 10 is really the sixteenth. |
|
|
The station number is in hex, so Station 0A is the tenth station, and Station 10 is really the sixteenth. |
The following messages are summaries:
-
No CAP problems were detected -
No Pass Thru Port problems were detected -
No Robot Hand problems were detected -
No LSM problems were detected -
No Station problems were detected
Message summaries only reflect that the LMU did not detect hardware errors. Something could be wrong with the software configuration, or with something that the LMU could not detect.
HSC processing continues and no user response is required.
Display LMUPDEF
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Display LOCKs
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display LOCKs command:
Example 3-16 Display LOCKs output
SLOT OWNING TASK TASK VTD MVC VTV WAITING WAITING ID HOST NBR TYPE HOST TASK 002 EC21 006 RTD EVS101 EC10 007 003 EC20 010 RTD EVS145 X15328 004 EC20 010 A91E X153234 CFLOCK CFLOCK OWNING NUMBER TYPE HOST 3 HOST TO HOST (TO ECCL) EC21
Fields
Display LOCKs command output includes the following fields:
- SLOT ID
-
Slot ID of the lock within the lock buffer.
- OWNING HOST
-
the host that owns the lock.
- TASK NBR
-
the task number associated with the lock.
- TASK TYPE
-
the task type.
- VTD
-
the associated VTD address on the issuing host.
- MVC
-
the locked MVC.
- VTV
-
the locked VTV.
- WAITING HOST
-
the host waiting for the lock or ALL if multiple hosts are waiting.
- WAITING TASK
-
the task waiting for the lock or ALL if multiple tasks are waiting.
- CF LOCK NUMBER
-
the Coupling Facility lock number.
- CF LOCK TYPE
-
one of the following VTCS Coupling Facility lock types:
- Host Footprint
-
used to serialize access to the host footprint list.
- Host to Host
-
used to serialize access to a given host to host list.
- Lock Data
-
used to serialize access to the VTCS lock data.
- Formatting
-
used to serialize the initial formatting of the structure; also used when rebuilding data.
- System
-
lock is held, but is not a lock used by VTCS; assume it is used by MVS.
- OWNING HOST
-
the host that owns the lock.
Display Lsm
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-46, the Display Lsm command includes the following parameters:
- lsmid, lsmrange, or lsmlist
-
optionally, one or more LSMs for which the system is to display information. If you do not supply an
lsmid, a status summary is displayed for every LSM in the library.Each
lsmlistelement can be either a single LSM ID or a range of LSM IDs. The elements in a list must be separated by commas or blanks, and the entire list must be enclosed in parentheses.An
lsmidformat isAA:LL, whereAAindicates the ACSid (decimal 00-99) andLLindicates the LSM number (decimal 00-99). - DETail
-
optionally, specifies whether detail information is displayed for each LSM.
- Yes
-
All detailed information is displayed for each LSM.
- No
-
Only summary information is displayed for each LSM.
When
DETail(No)is specified, the currentReadyorNot readystatus is not determined; the LSM shows asReadyunless it is offline.
Note:
If theDETail parameter is not specified, then detailed information is displayed only if specific LSM IDs are entered.Output
The Display Lsm command displays status for the following:
-
LSMid
-
LSM type
-
Online/offline status
-
Ready/not ready status
-
Automatic/manual status
-
May include detail information:
-
Audits in progress (if any)
-
CAP status, priority and owning host if CAP is not drained.
-
Number of free cells and scratch volumes. (Note: The number of free cells in the LSM does not include free cells on frozen panels.)
-
Each frozen panel, showing the total number of cells and number of free cells on the panel.
-
Display Message
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-30, the Display Message command includes the following parameters:
- Msg or Message
-
display detailed HSC or VTCS message information.
- msgnum
-
the four–digit numerical portion of the message identifier. Leading zeros are not required.
- msgrange or msglist
-
a range or list of messages for which the system is to display status. Each
msglistelement can be either a singlemsgnumor amsg-range. The elements in a list must be separated by commas or blanks, and the entire list must be enclosed in parentheses.
Note:
msg-range and msg-list are only valid when the Display Message command is issued from a utility or programmatic interface.Display MGMTDEF
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Display MIGrate
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-49, the Display MIGrate command includes the following parameters:
- VTSS(vtss-name)
-
Optionally, display migration status for a specified VTSS.
vtss-nameindicates the VTSS name. - DETail
-
Optionally, display detailed migration status by Storage Class.
- AUTO(stor-clas-name)
-
Optionally, display the number of VTVs for the specified storage class, and their time remaining on the
AUTOqueue. The time remaining is referred to as the age.stor-clas-nameindicates the Storage Class name. - DELAY(stor-clas-name)
-
Optionally, display the number of VTVs for the specified storage class, and their time remaining on the
DELAYqueue. The time remaining is referred to as the age.stor-clas-nameindicates the Storage Class name. - VTSS(vtss-name)
-
Display migration status for a specified VTSS (
vtss-name). - LISTVTVS
-
List the specific VTVs on the
AUTOqueue.VTSSmust also be specified.
Output (Display Migrate)
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display MIGrate command:
Example 3-17 Display MIGrate output
/SLS0000I D MIG VTSS(HBVTSS16) VTSSNAME: HBVTSS16 Active migration tasks: 4 Immediate migrate: Max wait: 5 MINUTES Immediate delay queue: Active Auto migrate: Host: EC20 MIGRATION TARGET: 70%
Fields
Display MIGrate command output includes the following fields:
- VTSSNAME
-
the VTSS migrating the VTVs.
- ACTIVE MIGRATION TASKS
-
the total number of migration tasks (automatic, immediate, and migrate-to-threshold).
- IMMEDIATE MIGRATE
-
either Not active if there are no current or pending immediate migrations or the maximum time that any VTV has been waiting for immediate migration. This field only shows status for the LPAR on which the query was issued.
- IMMEDIATE DELAY QUEUE
-
indicates whether there are VTVs on the Immediate Migrate Queue.
- AUTO MIGRATE
-
either Not active or the name of the host and migration target (
LAMTor specified threshold for a migration-to-threshold) if auto migration is active on any host.
Output (Display Migrate DETail)
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display MIGrate DEtail command:
Example 3-18 Display MIGrate DETail output
/SLS0000I D MIG DET VTSSNAME: DVTSS16 Active migration tasks: 2 Immediate migrate: Max wait: 1 minutes Immediate delay queue: Not active Auto migrate: Not active Storage ACS Max/Onl ---SCH-- Req --Auto-- ---Immed--- Weight Class RTDs Lim Pref Act GB Delay GB /Skip S1 00 16 16 1 0 1 - 1 9 50/ 0 S2 00 16 16 1 0 1 - 1 9 50/ 0
Fields
Display MIGrate command output includes the following fields:
- STORAGE CLASS
-
the Storage Class associated with the migration.
If you do not explicitly assign a Storage Class, an MVC's default Storage Class is the name of the last VTSS that wrote to the MVC for reclamation or migration and this class has the VTCS default media selections. To change these defaults, create a Storage Class with the VTSS name and specify the desired media selection order.
- ACS
-
the ACS defined for the Storage Class. For migrations to VLEs, this is the VLE name. If this column indicates
**ANY**, then migrations to any location are allowed, subject to any other restrictions. - MAX/ONL RTDs
-
-
the maximum number of RTD tasks based on the Storage Class and RTD configuration definitions.
-
the maximum number of tasks for those RTDs that are actually online (
MAX TASKSminus the number of offline RTDS).
-
- SCH
-
SCHLIMITandSCHPREFvalues fromMIGRSELstatements that apply to the active migration for the storage class. - Req Act
-
the number of active migration tasks.
- ACTIVE TASKS
-
the number of migration tasks currently active for the Storage Class.
- AUTO
-
indicates whether the Storage Class contains automatic migration VTVs.
- IMMED
-
indicates whether the Storage Class contains immediate migration VTVs.
- WEIGHT (percent)
-
the priority of the Storage Class compared to other Storage Classes for the VTSS. Storage Classes with higher priorities are assigned a greater proportion of migration tasks.
Output (Display MIGrate AUTO)
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display MIGrate AUTO command:
Display MNTD
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Display MONitor
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-51, the Display MONitor command includes the following parameters:
- ,PGMI
-
optionally, displays the status of the monitoring of move requests received by the programmatic interface.
- ,L
-
optionally, displays the type of requests being monitored by the specified console. Console IDs and console names must be two to eight characters long.
- cc
-
the console ID.
- name
-
the console name.
If both
PGMIandLare omitted, the status of all monitoring is displayed.
Display MVC
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-52, the Display MVC command includes the following parameters:
- volser
-
the volser of the MVC.
Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display MVC command:
Example 3-21 Display MVC output
Volser: 702532 Media: T1B000T1 ACSid: 00 Size(Mb): 1000000 Migrated Count: 19 Vtv Count: 19 %Used: 7.41 %Fragmented: 0.00 %Available: 92.59 %Usable: 0.00 Times Mounted: 77 Last Mounted: 2010Mar15 10:40:54 Last Migration: 2010Jan14 14:41:04 Last Drain/Reclaim: 2010Feb23 13:55:26 Owner: ALP VTSS: HBVTSSY MVCPOOL: ALPMVC Security access: No profile Status: Initialized Format: Partitioned
Fields
Display MVC command output includes the following fields:
- VOLSER
-
the volser of the MVC.
- MEDIA
-
the volume media type or recording technique. Should the value ’Need PTF' appear, then this host lacks support for this media type. Another host does have support for this media type.
- ACSID
-
the ACS containing the MVC, or the VLE containing remote MVC volumes or VMVCs in VLEs. This will not appear if the MVC has been ejected from the library.
**MANY**indicates that an MVC with a specific volser has been discovered in more than one location. MVCs in this state are marked unusable. - SIZE (MB)
-
the size of the MVC in megabytes.
- MIGRATED COUNT
-
the number of VTVs migrated.
- VTV COUNT
-
the number of active VTVs on the MVC.
- %USED
-
the percentage of the MVC used by valid VTVs.
- %FRAGMENTED
-
the percentage of the MVC that has invalid VTV space that is not available for use until it is reclaimed or the MVC is drained.
- %AVAILABLE
-
the percentage of the MVC that is physically available for use.
- %USABLE
-
the percentage of space on the MVC that can be used by VTCS. This may be zero even if there is still space physically available. For instance, if the VTV per MVC limit is reached then the
%Usablewill be reported as0%. Similarly, if an error has been reported against an MVC then VTCS will not use this MVC for output and the%Usablewill be reported as%0. - TIMES MOUNTED
-
the number of times the MVC has been mounted for writing or reading since it was added to the MVC inventory
- LAST MOUNTED
-
the date and time at which the MVC was mounted or attempted to be mounted upon a RTD.
- LAST MIGRATED
-
the date and time at which the last VTV migration was performed to the MVC.
- LAST VERIFIED
-
the date and time at which the last VTV media verify was performed to the MVC.
This date reflects the last time that VTCS knew the MVC contents were valid where the date is the most recent of the following:
-
The date/time the MVC was verified with
MEDVERfy. -
The date/time the MVC was migrated to from an empty state.
-
- LAST DRAIN/RECLAIM
-
the date and time at which the MVC was last processed by Drain or reclaim processing and had it's end-of-tape pointer reset.
- OWNER
-
the Storage Class that owns the MVC. An MVC only becomes a member of a storage class when it contains migrated VTVs.
- VTSS
-
the last VTSS that performed a migration to the MVC.
CONSOLIDATEappears in this field for consolidated VTVs. - MVCPOOL
-
either an MVC Pool Name (including
DEFAULTPOOL) orNOif the MVC is not defined on anMVCPoolstatement. - SECURITY ACCESS
-
VTCS permissions for the MVCs defined in an
MVCPOOLstatement (UPDATE,NO UPDATE, orNO PROFILE). - STATUS
-
one of the following statuses:
- INITIALIZED
-
The MVC has been initialized.
- BEING AUDITED
-
The MVC is either currently being audited or has been the subject of a failed audit. While in this state the MVC will not be used for migration and can be used for recalls. Due to the inherent state, recalls may fail because the CDS not yet up-to-date with the MVC contents. To clear this condition, rerun the
AUDITutility against this MVC. - LOGICALLY EJECTED
-
The MVC has either been the subject of an
MVCDRain Ejector the MVC was rejected for update by aRACROUTEcall. The MVC will not be used again for migration. To clear this condition, useMVCDRainagainst the MVC without theEjectoption. - NOT-INITIALIZED
-
The MVC has been defined via the
CONFIgutility, but has not ever been the subject of a successful VTV migration. - MOUNTED
-
The MVC is mounted on an RTD.
- IN ERROR
-
This is a generic error that indicates the MVC, drive, or combination of the two has specifically reported a problem whilst accessing the MVC. VTCS attempts to de-preference the usage of MVCs with this state. VTCS considers this to be the most serious affliction on a MVC when considering copies to be used for recalls.
In general, to clear this state:
-
If the MVC caused the problem, use a
DRAIN(EJECT)command to remove the MVC from service. -
If the RTD caused the problem, use the
MVCMAINTutility to reset the MVC state.
Note:
One or more of the following messages is issued forIN ERRORstatus:SLS6686,SLS6687,SLS6688,SLS6690. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Messages and Codes for recovery procedures for these messages. -
- MARKED FULL
-
The MVC is considered as being full and is not a candidate for further migrations. Due to the general behavior of tape media this can occur before the MVC has reached its nominal capacity.
- DRAINING
-
The MVC is either currently the subject of drain or reclaim processing. Should the processing fail, the MVC maybe left in this state as a safeguard. To clear this condition, perform an
MVCDRainagainst the MVC. - LOST - FAILED TO MOUNT
-
VTCS attempted to mount an MVC and the mount did not complete within a 15-minute time-out period. VTCS has had no specific error report although there could be combination of hardware problems, HSC problems, or by the MVC being removed from the ACS. VTCS attempts to de-preference the usage of MVCs with this state.
Determine the cause of the error and fix it. You can also use the VTCS
MVCMAINTutility to setLOST(OFF)for the following events:-
LOST(ON)was set due to LSM failures or drive errors that have been resolved -
LOST(ON)was set because the MVC was outside the ACS and has been reentered.
This condition is automatically cleared by VTCS if it subsequently requests a mount of the MVC and this is successful.
-
- DATA CHECK
-
A data check condition has been reported against this MVC. VTCS attempts to de-preference the usage of MVCs with this state. To get into this state, a data transfer must have failed upon two different RTDs.
To clear this state:
-
If all VTVs on the MVC are duplexed, use
MVCDRainon the MVC without theEjectoption. This recovers all VTVs and removes the MVC from service. -
If all VTVs on the MVC are not duplexed, VTCS
AUDITthe MVC. The audit will probably fail. After the audit, do anMVCDRAIN(no eject). This recalls the VTVs before the data-check area in ascending block-id order and the VTVs after the data-check area in a descending block-id order. Processing the VTVs in this sequence ensures that VTCS recovers as many VTVs as possible from the media. You then need to recreate the data for any VTVs still on the MVC.
Note that although this indicates that a specific failure has occurred when performing data transfers, this may not be a fault in the media. It could be that a RTD is writing data to the media out of specification. Patterns of failures are therefore important. As an example, lots of
DATA CHECKconditions suddenly occurring lots of drives and volumes. -
- READ ONLY
-
The MVC has been marked read-only because of one of the following conditions:
-
The MVC being the target of an export or consolidation process. The read-only state protects the MVC from further updates.
-
The MVC media is set to file protect. Correct the error and use the
MVCMAINTutility to setREADONLY(OFF). -
The MVC does not have the appropriate SAF rules set to enable VTCS to update the MVC. Correct the error and use the
MVCMAINTutility to setREADONLY(OFF). Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Installing ELS for information about defining a security subsystem user ID for HSC, SMC, and VTCS.
-
- RETIRED
-
The MVC is retired and is considered by VTCS as having reached the end of its useful life. VTCS will recall from, but not migrate to, the MVC. Replace the MVC as soon as possible. Once this has been done, use the
MVCMAINTutility to setRETIRED(OFF). - WARRANTY HAS EXPIRED
-
The MVC's warranty has expired. VTCS continues to use the MVC. You should start making plans to replace the MVC when it reaches Retired state.
- INVALID MIR
-
VTCS has received status from an RTD to indicate the MIR (media information record) for a 9x40 media is invalid. An invalid MIR does not prevent access to data but may cause significant performance problems while accessing records on the tape. The MVC is not capable of high-speed searches on areas of the tape that do not have a valid MIR entry.
VTCS attempts to de-preference MVCs with this condition. For recalls, if the VTV resides on multiple MVCs, VTCS selects MVCs with valid MIRs ahead of MVCs with invalid MIRs. VTCS avoids using MVCs with invalid MIRs for migration, unless the migration is at the beginning of the tape. Migrating from the beginning of tape will correct the MIR. VTCS detects the invalid MIR condition at either mount time or dismount time. If detected at mount time and the operation can be completed with another MVC, VTCS dismounts the first MVC and selects the alternate MVC.
VTCS has only a limited ability to switch to an alternate MVC. That is, it is mainly used for migrate and virtual mount. For MVCs with invalid MIRs, determine the cause of the error, which may be caused by media or drive problems, and fix the error. To recover an MVC with an invalid MIR, read the MVC to the end of the tape, via a VTCS audit. If the media is the problem, run an
MVCDRAIN EJECTto recall the VTVs and cause the MVC to be removed from the MVC pool. - MIGRATES NOT SUPPORTED
-
This host lacks support for performing migrations to this MVC. This is set by another host that does support migration.
- RECALLS NOT SUPPORTED
-
This host lacks support for performing recalls from this MVC. This is set by another host that does support recalls.
- RECLAIM NOT SUPPORTED
-
This host lacks support for considering this MVC for reclaim processing. This is set by another host that does support reclaim processing. This does not inhibit the MVC being processed through the
MVCDRaincommand. - DEDUP requested on last mount
-
DEDUP(YES)was requested on the last mount.
- FORMAT
-
the VTV format, standard or partitioned.
Display MVCPool
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
Display MVCPool displays information about a specific MVC pool.
Note:
-
When this command is issued, MVC location information is refreshed to ensure an accurate, up to date result.
-
MVCs in the following states are excluded from the MVC pool totals: EJECT, READONLY, DATACHECK, and Logically Deleted.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-53, the Display MVCPool command includes the following parameters:
- NAME(pool-name)
-
display information for the specified named MVC pool.
pool-nameindicates the MVC pool name as defined using theMVCPoolcontrol statement. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Legacy Interfaces Reference for more information.Alternatively, you can specify
ALLto display information for all named MVC pools (including the default poolDEFAULTPOOL). - STORCLAS(stor-clas-name)
-
display information about MVCs by Storage Class.
stor-clas-nameindicates the name of a specific Storage Class for which you want MVC usage displayed.This may be for current valid Storage Classes that you defined on the
STORclascontrol statement, or for Storage Classes which used to exist to which media is still assigned. See "STORclas Control Statement" for more information.To display all Storage Classes, specify
ALLor omit theSTORCLASparameter. - SPACE
-
optionally, display information about MVCs using the
SPACEoutput format. TheSPACEparameter is ignored when theD MVCPOOLis from a utility. - COUNTS
-
optionally, display information about MVCs using the
COUNTSoutput format. TheCOUNTSparameter is ignored when theD MVCPOOLis from a utility.
Note:
TheDisplay MVCPool command from a utility will produce the combined SPACE or COUNTS output.Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display MVCPool command with pool name POOL1 specified:
Example 3-22 Console Display MVCPool output (NAME POOL1)
MVCPOOL (POOL1) INFORMATION INITMVC MVCFREE THRESHOLD INPTHRSH MAXMVC START RECLAIM NO 2 30 43 4 10 DEMand ACS/ Media FREE-MVCS RECLAIM-MVCS USED-MVCS Location VOLS GB VOLS GB VOLS GB 00 ECART 120 96 2 0.5 90 45 TMVSB STK1R 30 600 1 3.5 25 350 00 TOTAL 150 696 3 4.0 115 395
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display MVCPool command with no pool name specified:
Example 3-23 Console Display MVCPool output (no NAME specified)
MVCPOOL INFORMATION MVCPOOL (POOL1) INFORMATION INITMVC MVCFREE THRESHOLD INPTHRSH MAXMVC START RECLAIM NO 2 30 43 4 10 DEMand ACS/ Media FREE-MVCS RECLAIM-MVCS USED-MVCS Location VOLS GB VOLS GB VOLS GB 00 ECART 310 248 4 1.2 100 65 00 ZCART 120 192 1 0.5 250 400 00 TOTAL 430 440 5 1.7 350 465 01 ECART 90 144 15 6.2 322 485 01 ZCART 35 700 3 11.3 43 675 01 TOTAL 125 844 18 17.5 365 1160 NON-LIB STK2P 22 1100 0 0 12 1565 NON-LIB TOTAL 22 1100 0 0 12 1565
The following figure shows an example of the output produced by the Display MVCPool SPACE console command with no pool name specified:
Example 3-24 Console Display MVCPool SPACE output (no NAME specified)
ACS/ Media Available Used Fragmented Unavailable Location Gb Gb Gb Gb 00 T1C000T2 1,081,197 1,050,309 646,823 35,551 00 ***Total 1,081,197 1,050,309 646,823 35,551 01 T1C000T2 1,167,239 1,046,045 604,593 581 01 ***Total 1,167,239 1,046,045 604,593 581
The following figure shows an example of the output produced by the Display MVCPool COUNTS console command with no pool name specified:
Example 3-25 Console Display MVCPool COUNTS output (no NAME specified)
ACS/ Media Total MVC Free MVC Location Count Count 00 T1C000T2 621 106 00 ***Total 621 106 01 T1C000T2 618 126 01 ***Total 618 126
Example 3-26 Utility Display MVCPool output (no NAME specified)
ACS/ Media Total MVC Free MVC Available Used Fragmented Unavailable Location Count Count GB GB GB GB 00 T1C000T2 621 106 1,081,197 1,050,309 646,823 35.551 00 ***Total 621 106 1,081,197 1,050,309 646,823 25,551 01 T1C000T2 618 126 1,167,239 1,046,045 604,593 581 01 ***Total 618 126 1,167,239 1,046,045 604,593 581
Fields
Display MVCPool command output includes the following fields:
- INITMVC
-
specifies whether un-initialized MVCs are to be initialized when they are first mounted.
- MVCFREE
-
the minimum number of free MVCs.
- THRESHOLD
-
the fragmented space threshold (as a percentage) that determines when an MVC is eligible for demand or automatic reclamation.
- INPTHRSH
-
the fragmented space threshold (as a percentage) that determines when an MVC in partitioned format is eligible for dynamic reclaim processing.
- MAXMVC
-
MVC limit for a single reclaim.
- START
-
specifies a percentage value that represents the ratio of reclaim candidates to total MVCs, which triggers automatic space reclamation.
- RECLAIM
-
specifies the space reclamation setting for the MVC pool.
- ACS
-
-
For local tape drives, this column displays the ACS or LSM to which the drive is attached.
-
For remote RTDs, this column displays
name:numberwherenameindicates the name of the TapePlex andnumberindicates the number of the ACS in decimal. -
For VLEs, this column displays the VLE name.
-
NLIB indicates MVCs that are now outside the library.
-
**MANY**indicates that an MVC with a specific volser has been discovered in more than one location. MVCs in this state are marked unusable. -
ACSs with no attached RTDs are flagged.
-
- MEDIA
-
the MVC media type.
- FREE-MVCS
-
MVCs that have 100% usable space and do not contain any migrated VTVs.The storage shown is the total free space based on media type capacity.
- RECLAIM-MVCS
-
MVCs eligible for space reclamation by this host. The storage shown is the total wasted space, including those MVCs not yet eligible for space reclaim.
- USED-MVCS
-
initialized MVCs that are partially or completely full.
- Total MVC
-
a count of the number of MVCs in the MVC pool.
- Free MVC
-
a count of the number of FREE MVCs in the MVC pool. Free MVCs have 100% usable space.
- Available
-
the size (Gb) of available MVC size in the MVC pool. This is the space that is available for migration.
- Used
-
the size (Gb) of space used in the MVC pool.
- Fragmented
-
the size (Gb) of wasted space in the MVC pool.
- Unavailable
-
the size (Gb) of unavailable size in the MVC pool. This space is not available for migration. MVCs with the following states are included in this total:
-
DATACHECK -
FULL -
BROKE -
READONLY -
RETIRED -
Warranty Expired
-
Display OPTion
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Display PATH
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Description
The Display PATH command displays the status of paths from VTSSs to either RTDs or virtual libraries.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-55, the Display PATH command includes the following parameters:
- PATH
-
optionally, restricts the display to the specified paths.
rtdnameorrtdname-listindicates the names assigned to the paths for accessing RTDs for Virtual Libraries from a VTSS. - VTSS
-
optionally, restricts the display to the paths from an individual VTSS.
vtss-nameindicates the name of the VTSS to which the paths are configured. - CLINK
-
optionally, include paths allocated for CLINKs in the display output. Paths for both cluster replication and electronic export are displayed.
Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display PATH command:
Example 3-27 Display PATH output
VTSSNAME Type RTD NAME CHANIF Device Target State
HBVTSS18 RTD SS182A01 01 C0E 2A01 Online
RTD SS182A06 00 C0I 2A06 Online
CLINK HBVTSS19 06 C1A CLUSTER1 On-Async
VLIB SS18IP0 04 I0A:0 V000 WILDCAT1 Online
VLIB SS18IP2 04 I1A:0 WILDCAT2 Online
EEXP HBVTSS16 05 I0I:0 PRIMARY On-Sync
HBVTSS19 RTD SS192A02 01 C0E 2A02 Online
RTD SS192A07 00 C0I 2A07 Online
VLIB SS19IP0 04 I0A:0 V010 WILDCAT1 Online
VLIB SS19IP2 04 I1A:0 WILDCAT2 Online
EEXP HBVTSS16 05 I0I:0 PRIMARY On-Sync
Fields
Display PATH command output includes the following fields:
- VTSSNAME
-
the name of the VTSS to which the path is attached.
- Type
-
The type of the path. This can be one of the following:
-
RTD– A direct connection to a RTD -
VLIB– A data path connection to a Virtual Library -
CLINK- A CLINK used for cluster replications within the tapeplex -
EEXP– A CLINK used for electronic export to another tapeplex
-
- RTDNAME
-
The name allocated to the path. For paths defined via the
RTDPATHstatement in the configuration, this is the name assigned through theRTDNAMEparameter. For aCLINKorEEXPtype path, this column will contain the target VTSS name. - CHANIF
-
the logical device ID assigned to the path and the
CHANIForIPIFvalue that was specified for the path. - Target
-
the destination subsystem for the path. For a
VLIBtype path, this contains theSTORMNGRname assigned to the Virtual Library. For aCLINKtype path, this contains the name of the cluster. For theEEXPtype paths, this contains the tapeplex name to which the path is connected. - Device
-
the destination device for the path. For an
RTDtype path, this contains the MVS address of the tape device. If this is aVLIBpath that is working in compatibility mode, this will contain the logical device address assigned to the path. - State
-
The current state of this path. This can be one of the following:
- Online
-
the path is online and available for use.
- On-Async
-
the path is online and available for use for asynchronous replication of VTVs.
- On-Sync
-
the path is online and available for use for synchronous replication of VTVs.
- Offline
-
the path or the device to which it connects has been varied offline.
- Maint
-
the path or the device to which it connects has been varied into an offline maintenance mode. This could be as a result of repeated failures.
Display Queue
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-56, the Display Queue command includes the following parameters:
- DETail
-
optionally, display detailed status.
- VTSS(vtss-name)
-
optionally, display processes for the specified VTSS.
vtss-nameindicates the VTSS name.
Display REPlicat
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display REPlicat command:
Example 3-29 Display REPlicat output
VTSS Name Host Qdepth
HBVTSSY PLEX1819 EC20 0
EC21 0
ECCL 0
ECCY 0
HBVTSS18 -Cluster EC20 0
EC21 0
ECCL 0
ECCY 0
*SLS5013I Command completed (0)
Fields
Display REPlicat command output includes the following fields:
- VTSS
-
the Primary or sending VTSS name.
- NAME
-
one of the following values:
- name
-
the name of the TapePlex to which CLINKs are connected from the VTSS.
- -Cluster
-
indicates that the VTSS is a member of a cluster and has CLINKs defined for replication to other VTSSs in the cluster.
- HOST
-
the host attached to the Primary VTSS.
- Qdepth
-
the total number of VTVs waiting to be replicated.
Display Requests
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Display RTD
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-59, the Display RTD command includes the following parameters:
- rtd–id, rtd-range, or rtd-list
-
optionally, the unit addresses of one or more RTDs.
- QUeued
-
optionally, display information about requests queued for the RTD.
Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display RTD command:
Example 3-30 Display RTD output
RTD MOUNT ALLOC HOST VTSS Status Top ID Top Host B200 - - - DHSS16 Offline 01265 ECC20 B201 - - - DHSS16 Offline 02368 ECC20 B202 - - - DHSS16 Online/free B201 - - - DHSS16 Online/free 0B79 - - - DHSS16 Online/free 0B7A DMV051* DMV051 EC20 DHSS18 Recall VTV 1600 MVS1 :Migrate 1601 MVS1 :Migrate
Fields
Display RTD command output includes the following fields:
- RTD
-
the unit address of the RTD.
- MOUNT
-
the volser of the MVC currently mounted (an
*indicates an in-process mount.) - ALLOC
-
the volser of the MVC allocated for mounting on the RTD.
- HOST
-
the host that currently owns the RTD.
- VTSS
-
one of the following:
-
The VTSS that is currently connected to the RTD.
-
The VTSS that has paths to the Storage Manager containing the vRTD.
-
-indicates that there are multiple VTSSs with paths to the Storage Manager containing the vRTD.
-
- Status
-
One of the following RTD statuses:
- AUDIT MVC
-
An MVC is being audited.
- BUSY
-
The RTD is busy (non-specific task).
- FAIL/OFFLINE
-
The RTD has been placed offline due to a failure.
- IDLE
-
An MVC is allocated to the RTD but the MVC is not being used.
- INITIALIZE
-
The host is verifying RTD status and availability.
- MAINTENANCE
-
The RTD is in maintenance mode.
- MIGRATE VTV
-
The RTD is migrating a VTV.
- OFFLINE
-
The RTD is offline and unavailable to all hosts and VTSSs.
- ONLINE/FREE
-
The RTD is online and available.
- PATH MAINT
-
One or more paths to the RTD have been varied into maintenance mode.
- PATH OFFLINE
-
The RTD status is unknown because the VTSS cannot contact the RTD or if the paths were not correctly configured.
- PATH SUSPEND
-
An RTD is globally online but the path from the VTSS is suspended due to the RTD being paired with a CLINK.
- PATHS OFFLNE
-
There are no online paths to the Storage Manager containing the vRTD and all paths to the Storage Manager containing the vRTD from at least one online VTSS are offline.
- RECALL VTV
-
The RTD is recalling a VTV.
- RECOVER RTD
-
The RTD is being reset after a problem, a vary, or an initialization.
- RECOVERY
-
The RTD is being reset following an error or a vary online mode.
- SUSPEND
-
The RTD operations are suspended. This occurs under the following conditions:
-
when two RTDs are connected to two separate ports on the same VSM4 ICE3 card CIP or VSM5, FICON and FIP.
-
when one or more RTDs and a CLINK are configured on the same port. The RTDs remain in
SUSPENDmode while the CLINK is online.
Note:
An RTD can only be online if the CLINK is offline. -
- UNKNOWN
-
There are no online paths to the Storage Manager containing the vRTD and none of the following statuses apply:
-
Paths Offlne -
VTSS Offline -
VTSSs Offlne
-
- UNLOAD MVC
-
A forced unload of the RTD is occurring.
- VTSS Offline
-
One of the following:
-
The VTSS to which the RTD is connected is offline.
-
There are no online paths to the Storage Manager containing the vRTD,
Paths offlnedoes not apply, and there is one offline VTSS with paths to the Storage Manager containing the vRTD.
-
- VTSSs Offlne
-
One of the following:
-
The RTD is connected to multiple VTSSs, all of which are offline.
-
There are no online paths to the Storage Manager containing the vRTD,
Paths offlnedoes not apply and there are multiple offline VTSSs with paths to the Storage Manager containing the vRTD.
-
- VTV TRANSFER
-
The RTD is migrating a VTV before recalling it on another VTSS.
- TOP ID
-
the process Id of the request that is top of the queue for next using this RTD from this host. The TOP ID column only applies for requests from the host upon which the command has been executed. This host may not have the top claim upon the RTD.
- TOP Host
-
the host which has the request that is at the top of the queue to use this RTD. The TOP HOST columns indicates which host has the top claim upon the RTD.
Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display RTD command with the QUed parameter:
Example 3-31 Display RTD output (Display RTD Queued)
ID Function Weight VTSS MVC list /
Storage Class
01360 <X00029> 432* HBVTSS18 021748 022524
01425 Recall 2 !ALLVTSS 021754
01423 Recall 2 !ALLVTSS 021675
01368 Recall 2 !ALLVTSS 022551
01381 Migrate 2 HBVTSS19 - *HBVTSS19
Fields
Display RTD command output includes the following fields:
- ID
-
the process ID, which is a unique number in the range 0 - 65536. When the process ID reaches 65536, it wraps back to zero.
- FUNCTION
-
the type of request that is queuing for an RTD. If it is a VTV volser inside angle brackets (<>), then this is an auto recall request for a virtual mount.
- WEIGHT
-
the weighting factor that VTCS has currently assigned to the request. The requests will be considered and queued (reported) according to this factor. An asterisks (*) next to the value indicates that the request has been waiting sufficiently long to warrant the stealing of another MVC's allocation.
- VTSS
-
the VTSS or the VTSS list name to be used for selecting RTDs. The special value
!ALLVTSSindicates that any VTSS with access to a suitable drive is eligible. - MVC LIST
-
the list of MVC for which we are attempting to select a RTD. For an auto recall request, this list may run to four MVCs. Conversely, for a migration request that is yet to select an MVC, this will be empty.
- STORAGE CLASS
-
the storage class for which the migration is destined. An asterisks (*) next to the value indicates that this storage class is in an error state.
Display SCRAtch
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Description
The Display SCRatch command displays scratch counts by subpool name, ACS id, LSM id, media type, recording technique, or owning host name.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-60, the Display SCRATch command includes the following parameters:
- acs-id
-
optionally, the ACS for which the system is to display scratch count information. If you specify
acs-idwithout an LSM number, selected scratch counts for the entire ACS are displayed. - lsm-id
-
optionally, the LSM for which the system is to display scratch count information.
- VSM
-
optionally, restricts the
Display SCRatchdisplay to subpools with virtual volumes. VSM is not allowed ifacs-idorlsm-idare also specified.
Note:
Ifacs-id or lsm-id is specified, it must be the first parameter after the SCRatch keyword. The VSM keyword is not positional.- SUBpool(subpool-name)
-
optionally, restricts the scratch count display to the named subpool only. If
SUBpoolis specified, then LSM and ACS totals will reflect only the named subpool.SUBpoolis not allowed ifHOSTidis also specified.subpool- nameindicates the name of the subpool. Specify up to 13 characters. - HOSTid(name)
-
optionally, restricts the scratch count display to subpools that are accessible from the named
HOSTid. IfHOSTidis specified, then LSM and ACS totals will reflect only subpools that can be accessed from the namedHOSTid.HOSTidis not allowed ifSUBpoolis also specified.nameindicates the SMFID or the SMC SERVER ALIASHOST ID of the host. Specify up to 8 characters. - MEDia(media-type)
-
optionally, restricts the scratch count display to the volumes compatible with the specified media name. If
MEDiais specified, then LSM and ACS totals will reflect only the compatible media types.media-typeindicates the media type.See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for a list of valid
media-typevalues. - RECtech(recording-technique)
-
optionally, restricts the scratch count display to volumes compatible with the specified recording technique. If
RECtechis specified, then LSM and ACS totals will reflect only the compatible recording techniques.recording-techniqueindicates the recording technique.See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for valid recording-technique values.
- DETail
-
optionally, lists scratch counts by all media and recording techniques. If specified, then an additional level of media and recording technique detail is displayed for every subpool.
DETailis not allowed if eitherMEDiaorRECtechare also specified. - REFresh
-
optionally, updates VSM scratch counts prior to the display occurring.
Note:
TheREFreshparameter causes additional I/Os to the CDS and must be used sparingly. - ALL
-
optionally, lists scratch counts for subpools that have both a 0 scratch count and 0 threshold value. Normally, the
Display SCRatchcommand will only list subpools that have either a non-zero scratch count or non-zero threshold value. Specification ofALLoverrides this filter and results in the display of all defined scratch pools.
Output
The following are examples of the output produced by the Display SCRatch command.
The following example shows counts for all LSMs in all ACSs:
Example 3-32 Display SCRatch output (all)
DISPLAY SCRATCH SLS2638I Scratch Summary ACS/LSM Subpool Name Label Media Rectech Count ========================================================== VSM SPV001 SL VIRTUAL VIRTUAL 930 VSM SPV002 SL VIRTUAL VIRTUAL 1036 VSM SPM001 SL VIRTUAL VIRTUAL 25 VSM Total VIRTUAL VIRTUAL 1991 ---------------------------------------------------------- LSM 00:00 SP001 SL All 13 LSM 00:00 SP002 SL All 31 LSM 00:00 SPM001 SL All 235 LSM 00:00 Non-Subpool All 11 LSM 00:00 Total All 290 LSM 00:01 SP001 SL All 9 LSM 00:01 Non-Subpool All 6 LSM 00:01 Total All 15 ACS 00 SP001 SL All 22 ACS 00 SP002 SL All 31 ACS 00 SPM001 SL All 235 ACS 00 Non-Subpool All 17 ACS 00 Total All 305 ==========================================================
The following example shows Display SCRAtch counts for a single subpool:
Example 3-33 Display SCRatch output (subpool)
DISPLAY SCRATCH SUBPOOL(SPM001) SLS2638I Scratch Summary ACS/LSM Subpool Name Label Media Rectech Count ========================================================== VSM SPM001 SL VIRTUAL VIRTUAL 25 ---------------------------------------------------------- LSM 00:00 SPM001 SL All 235 ACS 00 SPM001 SL All 235 ==========================================================
The following example shows Display SCRAtch counts for a single ACS:
Example 3-34 Display SCRatch output (ACS)
DISPLAY SCRATCH ACS 00 SLS2638I Scratch Summary ACS/LSM Subpool Name Label Media Rectech Count ========================================================== LSM 00:00 SP001 SL All 13 LSM 00:00 SP002 SL All 31 LSM 00:00 SPM001 SL All 235 LSM 00:00 Non-Subpool All 11 LSM 00:00 Total All 290 LSM 00:01 SP001 SL All 9 LSM 00:01 Non-Subpool All 6 LSM 00:01 Total All 15 ACS 00 SP001 SL All 22 ACS 00 SP002 SL All 31 ACS 00 SPM001 SL All 235 ACS 00 Non-Subpool All 17 ACS 00 Total All 305 ==========================================================
The following example shows Display SCRAtch count detail for a single LSM:
Example 3-35 Display SCRatch output (LSM)
DISPLAY SCRATCH LSM 01:00 DETAIL SLS2638I Scratch Summary ACS/LSM Subpool Name Label Media Rectech Count ========================================================== LSM 01:00 SP002 SL ECART 36TRACK 1 LSM 01:00 SP002 SL STANDARD 18TRACK 5 LSM 01:00 SP002 SL STANDARD 36TRACK 5 LSM 01:00 Non-Subpool All 8 LSM 01:00 Total All 19 ==========================================================
Display SEN
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Description
The Display SEN command displays SEN LISTEN requests and their status. This display can display a specific request, using the requestor and listener names, a list of related requests using only the requestor name, or all SEN requests.
Displayed information includes the following:
-
Requestor name and listener name if any.
-
EOT/EOMsettings -
Disable/enable status.
-
The token associated with the request.
-
The event list of the request.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-61, the Display SEN command includes the following parameters:
- REQNAME=
-
optionally, specifies the name of the requestor identified on the SEN request.
- LNRNAME=
-
specifies the name of the listener routine identified on the SEN request.
Supported VTCS SEN Events
The following table lists supported VTCS SEN events.
| Event Name | Numeric Equate |
|---|---|
|
|
01 |
|
|
02 |
|
|
03 |
|
|
04 |
|
|
05 |
|
|
06 |
|
|
07 |
|
|
08 |
|
|
09 |
|
|
10 |
|
|
11 |
|
|
12 |
|
|
13 |
|
|
14 |
|
|
15 |
|
|
16 |
|
|
17 |
Display SERVER
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Display SRVlev
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Display Status
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Description
The Display Status command displays the status of pending requests currently active on the host issuing the command.
Output
The Display Status command displays the following information to help you resolve problems during regular execution and termination of the HSC:
-
requests:
Dismount,Eject,Enter,Modify,Mount,Move,Vary,View -
information about the request, including:
-
the requester (such as Operator, PGMI, Clean, job name of utility)
-
physical element (such as CAPid, Drive, LSM, Station)
-
associated element for the request (such as CAPid belonging to an audit)
-
ready status of each queue, and whether a given queue is being purged or terminated
-
whether a switch is in progress for an ACS
-
Note:
-
Use the
Display DRivescommand for information about current and pending mount activity, and theDisplay Requestscommand for information about queued LSM requests. -
When an audit is running that is a full panel or more in scope, the current cell location points to the first cell in the panel being audited.
Display STORCLas
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-65, the Display STORCLas command includes the following parameters:
- stor-clas-name
-
the Storage Class name, which can be any Storage Class, not just those defined via the
MGMTDEFcommand. Thus,stor-clas-namecan take the value of avtss-nameor!ERROR, in order to allow details of migrations to these Storage Classes to be displayed. - DETail
-
optionally, the output lists VTVs currently queued for automatic migration or immediate migration with this Storage Class.
- MAXvtv(nnnn)
-
optionally, indicates the maximum number of VTVs to be listed in a single automatic migration or immediate migration list (for a VTSS).
nnnnindicates a maximum number of VTVs, from 0-9999. If not specified, a default value of 100 is used.MAXvtv(nnnn)impliesDETail.
Caution:
When you specifyMAXvtv(nnnn), high values can cause temporary system degradation due to the number of WTO (write to operator) messages issued.Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display STORCLas command:
Example 3-37 Display STORCLas output
Summary of storage class XCA8: MVCs must be in ACS 00 and MVCPool DEFAULTPOOL RTDs can be any device type MVCPool DEFAULTPOOL contains no free MVCs There is 1 VTV awaiting auto-migration from VTSS CLIVSS16 V00002 with MGMTCLAS XCA8 VTSS CLIVSS16 has no suitable RTDs online in ACS 00 VTSS CLIVSS17 has no suitable RTDs online in ACS 00
As shown in Example 3-37, Display STORCLas output displays the following:
-
The characteristics of the Storage Class (ACS, MVC Pool, and Media).
-
VTVs waiting migration to the Storage Class from any VTSS.
-
Requirements of the MVCs to be used for migration.
-
The device type(s) of the RTDs needed to write to the migration MVCs.
-
Any errors with regard to satisfying the migration requirements.
Display STORMNgr
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Description
The Display STORMNgr command displays the status of an external storage manager and the paths defined to it from the VTSSs.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-66, the Display STORMNgr command includes the following parameters:
- name
-
the storage manager name.
Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display STORMNgr command:
Example 3-38 Display STORMNgr output
Name Type Version Status VLELIB0 VLE 1.1 Online Features: Unknown Device Name VTSS CHANIF V000 SS16IP0 DVTSS16 08 I0A:0 V002 SS16IP1 DVTSS16 09 I0I:0 V001 SS16IP2 DVTSS16 0A I1A:0 V003 SS16IP3 DVTSS16 0B I1I:0 V010 SS17IP0 DVTSS17 08 I0A:0 V012 SS17IP1 DVTSS17 09 I0I:0 V011 SS17IP2 DVTSS17 0A I1A:0 V013 SS17IP3 DVTSS17 0B I1I:0
Fields
Display STORMNgr command output includes the following fields:
- Name
-
the name of the external storage manager
- Type
-
the type of Storage Manager:
-
HSC – An HSC in another TapePlex
-
VLE – A VLE
-
- Version
-
the software version currently executing on the Storage Manager
- Status
-
the current status of the Storage Manager
- Features
-
a list of significant features installed or supported by the Storage Manager
- Device
-
the destination device for the path. This column is blank in the connection to the Storage Manager is for autonomous device data transfers.
- Name
-
the name allocated to the path within the Storage Manager. This column is blank if the Storage Manager is just for servicing mounts and dismounts to the device. If this is for a CLINK, then this column displays the target VTSS name.
- VTSS
-
the name of a VTSS which has this connection to this Storage Manager. This column is blank if the device is driven directly by the Storage Manager.
- CHANIF
-
the logical device Id assigned to the path and the
CHANIForIPIFvalue that was specified for the path. This column is blank if the path to the Storage Manager is not directly from a VTSS.
Display TASKs
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display TASKs command:
Example 3-39 Display TASKs output
TASK TASK SLOT ID VTSS RTD CURRENT LOCKS WAITQ PENDQ NBR TYPE 003 PROCESS HELD COUN COUNT 000 DSP 019 518 T 001 SS 034 HBVTSS16 SS16B200 T 002 RTD 035 HBVTSS16 SS16B201 R 003 RTD 036 HBVTSS16 SS160B79 R 004 RTD 044 HBVTSS16 SS160B7A R 1 005 RTD 045 HBVTSS16 SS160B7C R
Fields
Display TASKs command output includes the following fields:
- TASK NBR
-
the task number for each task on the current host.
- SLOT ID
-
the LOCK identifier within the lock buffer.
- TASK TYPE
-
the task type:
-
INV- Inventory Manager -
CMD- Command Task -
Ctc- Cross TapePlex Communication Manager -
DSP- Dispatcher Task -
SS- VTSS Task -
RTD- RTD Task -
DRV- RTD Scheduler -
SCR- Scratch Manager -
RCM- Reclaim Manager -
MSC- Migration Scheduler -
CSH- Clink Scheduler -
CLK- CLINK Task -
UNK- Unknown
-
- VTSS
-
the VTSS name.
- RTD
-
the RTD name for RTD tasks.
- CURRENT PROCESS
-
the current process ID.
- LOCKS HELD
-
type of lock held:
-
T- Task lock -
M- MVC Lock -
V- VTV Lock -
D- VTD Lock -
R- RTD Lock
-
- WAITQ COUNT
-
the count of requests waiting for locks.
- PENDQ COUNT
-
the count of pending requests.
Display THReshld
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Description
Display THReshld displays scratch count and scratch threshold information by subpool name, ACS id, LSM id, media, and recording technique.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-68, the Display THReshld command includes the following parameters:
- THReshld
-
display scratch count and threshold information which can include scratch counts and scratch thresholds by subpool name, ACS id, LSM id, media, and recording technique.
- acs-id
-
optionally, the ACS for which the system is to display scratch count and scratch threshold information. If you specify
acs-idwithout an LSM number, selected scratch counts for the entire ACS are displayed. - lsm-id
-
optionally, the LSM for which the system is to display scratch count and scratch threshold information.
- VSM
-
optionally, restricts the
Display THReshlddisplay to subpools with virtual volumes. VSM is not allowed ifacs-idorlsm-idare also specified.Note:
optionally, restricts theDisplay THReshlddisplay to subpools with virtual volumes. VSM is not allowed ifacs-idorlsm-idare also specified. - SUBpool(subpool-name)
-
optionally, restricts the scratch count and scratch threshold display to the named subpool only. If
SUBpoolis specified, then LSM and ACS totals will reflect only the named subpool.SUBpoolis not allowed ifHOSTidis also specified.subpool-nameindicates the subpool name. Specify up to 13 characters. - HOSTid(name)
-
optionally, restricts the scratch count and scratch threshold display to subpools that are accessible from the named
HOSTid. IfHOSTidis specified, then LSM and ACS totals will reflect only subpools that can be accessed from the namedHOSTid.HOSTidis not allowed ifSUBpoolis also specified.nameindicates the SMFID or the SMC SERVER ALIASHOST ID of the host. Specify up to 8 characters. - MEDia(media-type)
-
optionally, restricts the scratch count and scratch threshold display to the volumes compatible with the specified media name. If
MEDiais specified, then LSM and ACS totals will reflect only the compatible media types.media-typeindicates the name of the desired media to display. See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for valid media name values.MEDiais not valid with theVSMparameter. - RECtech(recording-technique)
-
optionally, restricts the scratch count and scratch threshold display to volumes compatible with the specified recording technique. If
RECtechis specified, then LSM and ACS totals reflect only the compatible recording techniques.recording-techniqueindicates the name of the desired recording technique to display. See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for valid media name values.RECtechis not valid with the VSM parameter. - DETail
-
optionally, lists scratch counts and scratch threshold information by all media and recording techniques. If specified, then an additional level of media and recording technique detail is displayed for every subpool.
DETailis not allowed ifVSM,MEDiaorRECtechare also specified. - ALL
-
optionally, lists scratch counts for subpools that have both a 0 scratch count and 0 threshold value. Normally, the
Display THResholdcommand will only list subpools that have either a non-zero scratch count or non-zero threshold value. Specification ofALLoverrides this filter and results in the display of all defined scratch pools.
Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display THReshld command:
Example 3-40 Display THReshld command output
DISPLAY THRESHOLD SLS2649I Threshold Value Summary ACS/LSM Subpool Name Label Media Rectech Count Thresh =================================================================== VSM SPV001 SL VIRTUAL VIRTUAL 930 0 VSM SPV002 SL VIRTUAL VIRTUAL 1036 0 VSM SPM001 SL VIRTUAL VIRTUAL 25 0 VSM Total VIRTUAL VIRTUAL 1991 0 ------------------------------------------------------------------- LSM 00:00 SP001 SL All 13 0 LSM 00:00 SP002 SL All 31 0 LSM 00:00 SPM001 SL All 235 0 LSM 00:00 Total All 290 0 LSM 00:01 SP001 SL All 9 0 LSM 00:01 Total All 15 0 ACS 00 SP001 SL All 22 0 ACS 00 SP002 SL All 31 0 ACS 00 SPM001 SL All 235 0 ACS 00 Total All 305 0 ================================================================
Display Volser
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-69, the Display Volser command includes the following parameters:
- Volser or Volume
-
displays volume locations for the specified volumes. The information displayed includes:
-
status of volume (selected or unselected) and its location
-
the source, destination, and home location (in the case of an errant volume)
volser,volrange, orvollistindicates one or more VOLSERs for which the system is to display status. Eachvollistelement can be either a single VOLSER or a VOLSER range. You can display a range of up to 100 volumes.List elements must be separated by commas or blanks, and the entire list must be enclosed in parentheses.
-
- DETail
-
optionally, displays all available information about the specified volume(s).
Output
The Display Volser command displays the following information:
-
home cell location
-
whether the volume is a scratch cartridge
-
whether the volume is selected
-
owning host (displayed if the volume is selected)
-
drive address or drive ID (displayed if the volume is mounted)
-
whether an external label is present
-
whether the media label is readable by the robotic vision system (displayed if the external label exists)
-
when the volume was last inserted into the library
-
when the volume was last selected
-
select count
-
media type for the volume
-
recording technique for the volume
-
whether or not the media label was readable (
N/Aappears if the value was not read from the LMU) -
how the media type has been determined for the volume. The values that appear in this field include:
- YES
-
The media label and the
VOLPARMdefined for the volume agree. - NO
-
The media label and the
VOLPARMdefined for the volume do not agree. - VOLATTR Only
-
A
VOLPARMhas been defined, but the LMU has not determined the media type. - Label Only
-
The LMU has determined the media type, but a
VOLPARMhas not been defined. - Undefined
-
A
VOLPARMhas not been defined, and the LMU has not determined the media type.
-
whether or not the volumes are unusable (i.e., spent cleaning cartridges)
-
volume density for
STK1andSTK2media volumes. -
Media Warranty Life (MWL) percentage, stored on the cartridge MIR and collected during dismount processing. MWL percentage indicates how much of the media life has been used.
Note:
To collect and report media warranty life, tape libraries and transports must meet the following requirements:-
SL8500 or SL3000 libraries
-
LMU compatibility level 21 or higher
-
T9x40: all media and models at firmware level 1.42 or higher (except 9840B)
-
T10000: all models and media at firmware level 1.38 or higher
Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Managing HSC and VTCS for more information about media warranty life.
Display VOLume_Info
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-70, the Display VOLume_Info command includes the following parameters:
- VOLser
-
displays volume information for the specified volumes. The information displayed includes the following:
-
status of volume (selected or unselected) and its location
-
the source, destination, and home location (in the case of an errant volume)
volser,volrange, orvollistindicates one or more VOLSERs for which the system is to display status. Eachvollistelement can be either a single VOLSER or a VOLSER range. You can display a range of up to 100 volumes.List elements must be separated by commas or blanks, and the entire list must be enclosed in parentheses.
-
- ALL
-
Only real (non-virtual) volumes are listed. Volumes are listed in random order.
Display VSCRatch
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Description
The Display VSCRatch command displays diagnostic information for virtual scratch counts.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-71, the Display VSCRatch command includes the following parameters:
- subpool-name
-
optionally, a subpool name. Specify up to 13 characters.
If a subpool name is specified, the virtual scratch count display is restricted to the named subpool only.
Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display VSCRatch command:
Example 3-41 Display VSCRatch output
Scratch Label <--- Sizes available ---->
Subpool-Name Count Type 0.4GB 0.8GB 2GB 4GB
M0 972 SL Yes Yes Yes Yes
M1 994 SL Yes Yes Yes Yes
M2 1,000 SL Yes Yes Yes Yes
Fields
Display VSCRatch command output includes the following fields:
- Subpool-Name
-
the name of the scratch subpool. VTCS does not display scratch counts for non-subpool VTVs. If there are no VTV subpools defined, VTCS defines the Virtual Tapes pool for all VTVs.
- Scratch Count
-
the number of scratch counts.
- Label Type
-
one of the following scratch label types:
-
SLindicates standardlabeled tape. -
ALindicates ANSIlabeled tape. -
NLindicates nonlabeled tape. -
NSLindicates nonstandard labeled tape.
-
- Sizes available
-
valid VTV sizes (0.4 GB, 0.8 GB, 2 GB, or 4 GB).
Display VTD
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-68, the Display THReshld command includes the following parameters:
- VTSS(vtss-name)
-
Optionally, display status for the VTDs connected to the specified VTSS.
vtss-nameindicates the VTSS name. - ACtive
-
Display status for VTDs that have a VTV mounted. This can include both known and unknown VTDs.
- ALl
-
Display status for all VTDs.
- KNown
-
Display status for all VTDs that have a known MVS address on this system.
- UNknown
-
Display status for all VTDs that do not have a known MVS address on this system.
Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display VTD command:
Example 3-42 Display VTD output
Drive Location VTV Status Usage Client address A800 HBVTSS16 X00778 Available ECAM only A801 HBVTSS16 Available ECAM only A802 HBVTSS16 Available ECAM only A803 HBVTSS16 Available EC21:B412
Fields
Display VTD command output includes the following fields:
- Drive
-
The MVS device address of the VTD. If the device address is prefixed by a # sign then this is the address within the VTSS, the MVS address is unknown to this VTCS.
- Location
-
the VTSS that contains the VTD.
- VTV
-
the VTV volser if applicable.
- Status
-
one of the following VTD statuses:
- Available
-
The VTD is available for work.
- Dismounting
-
The VTV volser shown in the VTV column is was mounted on the VTD and the VTD has been unloaded. VTCS either has not received the dismount request or is currently in the progress of synchronizing the VTV and CDS information.
- Imported
-
The VTV volser shown in the VTV column has been electronically imported via the VTD. It is awaiting the confirmation request from the host that performed the export.
- Importing
-
The VTV volser shown in the VTV column is being electronically imported via the VTD.
- Mounted
-
The VTV volser shown in the VTV column is mounted on the VTD.
- Mounting
-
The VTV volser shown in the VTV column is in the process of being mounted on the VTD. Typically, this indicates that an auto recall is in progress.
- Mount (other)
-
The VTV volser shown in the VTV column is mounted on the VTD. The mount was not performed by the host on which the command was executed.
- Not Available
-
The VTD is not available for work.
- Redrive Later
-
A previous attempt to mount the VTV volser shown in the VTV column upon the VTD failed. It will be interpreted again within the next few minutes.
- Replicating
-
The VTV volser shown in the VTV column is in the process of being replicated.
- Undefined
-
The VTV volser shown in the VTV column is undefined.
- Unknown
-
The VTV volser shown in the VTV column is unknown.
- Usage
-
one of the following:
- Configuring
-
Configuration of the VTD is in progress.
- ECAM init error
-
Unable to initialise VTD through ECAM-t with VTSS.
- ECAM I/O error
-
ECAM-t I/O has failed on this VTD.
- ECAM only
-
The VTD is one of the VTDs connected to another VTSS for the process of replicating VTVs. In Example 3-42,
X00778is the VTV being replicated. - Not accessed
-
The VTD is not found in the VTSS configuration.
- Not verified
-
The VTD is defined with
NOVERIFYin the configuration.
- Client address
-
the address of the drive as reported by the client that last performed a mount on the VTD.
Display VTSS
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-73, the Display VTSS command includes the following parameters:
- vtss-name
-
optionally, indicates the VTSS for which to display status.
- DETail
-
optionally, display detailed VTSS status information including supported features.
- DIAG
-
optionally, display more detailed diagnostic information about the TCP/IP connections and control parameters in effect.
Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display VTSS command:
Example 3-43 Display VTSS output
VTSSNAME CAPACITY(GB) DBU HI LOW VTV MX MN Def AUTOMIG STATE RTDs
AMT AMT COUNT MT MT ACS
HBVTSS16 56.209 9 35 30 204 6 1 -- On-P Yes
HBVTSS17 56.209 7 35 30 218 4 3 02 On-P Yes
HBVTSS18 N/A N/A 35 30 N/A 3 1 01 Off Yes
HBVTSS19 93.184 5 35 30 110 3 1 01 On Yes
Fields
Display VTSS command output includes the following fields:
- VTSSNAME
-
the name of the VTSS.
- CPCTY(GB)
-
the total physical capacity in gigabytes of the specified VTSS.
- DBU
-
the percentage of disk buffer used of the total buffer capacity.
- HI AMT
-
the high AMT.
- LOW AMT
-
the low AMT.
- VTV COUNT
-
the number of VTVs resident on the VTSS.
- MX MT
-
the current
MAXMIGvalue. - MN MT
-
the current
MINMIGvalue. - DEF ACS
-
the default ACS.
- AUTOMIG
-
indicates which host is performing the auto migration and the threshold to which the VTSS is migrating.
- STATE
-
one of the following global VTSS states for all hosts:
- QUIESCING
-
Quiescing state.
- QUIESCED
-
Quiesced state.
- OFFLINE
-
Offline state.
- OFFLINE-P
-
Offline pending state.
- ONLINE
-
Online state.
- ONLINE-P
-
Online pending state.
- STARTED
-
The VTSS is initialized and in process of going to the requested state (online, offline, or quiesced).
- RTDs
-
indicates whether the VTSS has RTDs.
Display VTSS DETail Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display VTSS DETail command:
Example 3-44 Display VTSS Detail output
Vtss Host Nomigrat Noreclam State
HBVTSS16 EC104 Y Y Online
HBVTSS16 EC21 N Y Online
HBVTSS17 EC21 N Y Quiesced
HBVTSS17 EC10 Y Y Offline
VTSS TYPE SUPPORTED FEATURES
HBVTSS16 VSM5 2/4GB VTVS
LARGE PAGE VTVS
NOWAIT ON RTD MOUNT
BUDDY QUEUING
SYNC REPLICATE
LAST USE HINT
MGMT CLASS ON MVCS
CONNECT to 32 RTDS
STACKED MIGRATES
Fields
Display VTSS DETail command output includes the following fields:
- VTSSNAME
-
the VTSSs that the hosts in the HOST field can access.
- HOST
-
the hosts that have access to the VTSSs in the VTSSNAME field.
- NOMIGRAT
-
whether
NOMIGRATis set on for this host. - NORECLAM
-
whether
NORECLAMis set on for this host. - STATE
-
one of the following VTSS states for this host:
- QUIESCING
-
Quiescing state.
- QUIESCED
-
Quiesced state.
- OFFLINE
-
Offline state.
- OFFLINE-P
-
Offline pending state.
- ONLINE
-
Online state.
- ONLINE-P
-
Online pending state.
- STARTED
-
The VTSS is initialized and in process of going to the requested state (online, offline, or quiesced).
- ACCESS
-
The connection method employed for the host, either TCPIP or CHANNEL ECAM-T protocol.
- TYPE
-
VTSS model (
VSM2,VSM3,VSM4,VSM5, orunknown). - SUPPORTED FEATURES
-
One or more of the following:
- 400MB | 800MB | 2/4GB VTVS
-
Default VTV size.
- LARGE PAGE | STANDARD PAGE VTVS
-
Default VTV page size.
- NOWAIT ON RTD MOUNT
-
VTSS supports polling for RTD mount completion. It does not lock the Nearlink interface while waiting for the mount.
- BUDDY QUEUING
-
VTSS supports queueing of requests to more than one RTD on a Nearlink interface.
- REPLICATION
-
Asynchronous replication enabled.
- SYNC REPLICATE
-
Synchronous replication enabled.
- LAST USE HINT
-
VTSS supports cache management hints indicating when a VTV will be accessed in the near future.
- MGMT CLASS ON MVC
-
Audit MVC is able to return management class for VTVs.
- CONNECT TO 16 | 32 RTDS
-
Maximum number of RTDs per VTSS enabled.
- STACKED MIGRATES
-
Stacked migrates enabled.
- PARTITIONED RTDs
-
Partitioned RTDS enabled.
- T10KC Partition RTDs
-
T10KC partitioned RTDs enabled.
- Write New VOL1 Label
-
VTSS supports MVC labeling.
- CONCURRENT PORT I/O
-
VTSS supports multiple I/Os on a single physical nearlink interface.
- MANY-TO-MANY CONNECT
-
VTSS supports target VTD selection for a CLINK.
- IP REPLICATION
-
VTSS supports IP CLINKs and therefore a VLE connection.
- CONCURRENT TAPE RECALL/MOUNT
-
VTV mounts on VTDs can occur before the recall has completed.
- CONCURRENT TAPE RECALL/MOUNT *DISABLED
-
The Concurrent Tape Recall/mount feature is installed on the VTSS but has been disabled by either
CONFIG GLOBAL FASTRECL=NOorCONFIG VTSS NOERLYMT. - UNKNOWN VTSS FEATURE
-
VTSS feature found not supported by VTCS software level.
- Enhanced replication Release 1
-
VTSS supports enhanced synchronous replication.
- Supports VVV VTDs
-
VVVindicates the number of VTDs currently supported by the VSM 6 (or later). - NONE
-
No VTSS features defined.
Note:
-
If ETTB (Early Time to First Byte) is enabled, the following is displayed:
VTV mounts on VTDs can occur before the recall has completed. -
If ETTFB is disabled, the following is displayed:
The concurrent tape recall/mount feature is installed on the VTSS but has been disabled by either CONFIG GLOBAL FASTRECL=NO or CONFIG VTSS NOERLYMT.
Display VTV
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-74, the Display VTV command includes the following parameters:
- vtv-id
-
the ID of the VTV.
Output
The following is an example of the output produced by the Display VTV command:
Example 3-45 Display VTV output
Volser: X00000 VTSS HBVTSS19 Mounted A800 Uncompressed Size (Mb) 99.01 Compressed Size (Mb) 97.88 Maximum VTV size (Mb) 800 Page Size Standard Creation Date 2008Feb21 09:32:22 Last Mounted 2008Feb21 09:32:23 Last Recalled 2008Apr05 08:15:47 First Migrated 2008Apr25 08:58:28 Last Used Date 2008Apr25 08:58:28 MVC(s) 021681 021645 Block-id(s) 1A400D24 25401185 Management Class M13 SB Migrate Pending SA Status Initialized
Fields
Display VTV command output includes the following fields:
- VOLSER
-
the volser of the VTV specified in the query.
- VTSS
-
the VTSS where the VTV last or currently resides.
- MOUNTED
-
The MVS device address of the VTD. If the device address is prefixed by a # sign then this is the address within the VTSS, the MVS address is unknown to this VTCS.
- UNCOMPRESSED SIZE(MB)
-
the uncompressed size of the VTV (MB). This is the size of the VTV as perceived by the application programs.
- COMPRESSED SIZE (MB)
-
the compressed size of the VTV (MB). This is the raw space that will be occupied upon the MVCs or within the VTSSs.
- MAXIMUM VTV SIZE (MB)
-
the maximum (compressed) size of the VTV (400, 800, 2000 or 4000).
- CREATION DATE
-
the date and time when the VTV contents was last changed by an application.
- LAST MOUNTED
-
the date and time when the VTV contents was last mount for access by an application.
- LAST RECALLED
-
the date and time when the VTV was last recalled back from a MVC into a VTSS.
- FIRST MIGRATED
-
the date and time when the first MVC copy of this version of VTV was created.
- LAST USED DATE
-
the date and time when the VTV was last touched by VTCS. This includes most functions that update the status of the VTV in some way.
- MVC(S)
-
the MVC(s) where the VTV resides. This entry only appears when the VTV is migrated.
- BLOCK-ID
-
the logical block ID of the beginning of the VTV upon corresponding MVC. This entry only appears when the VTV is migrated.
- Partition-Id(s)
-
the starting partition id on the corresponding MVC. This entry only appears when the VTV is migrated.
- MANAGEMENT CLASS
-
the VTV's Management Class.
- MIGRATE PENDING
-
the Storage classes to which migrations are outstanding.
- ARCHIVE PENDING
-
the Storage classes to which migrations are outstanding in order to satisfy archiving requirements.
- REPLICATION STARTED
-
If the VTV is being replicated between VTSSs in a cluster, the name of the target VTSS is displayed.
- REPLICATED
-
If the VTV has been replicated to another VTSS in the TapePlex, the VTSS name displayed indicates where the replica can be found.
- IMPORTING
-
If the VTV is being mounted via a VTD, the VTD unit address is displayed.
- ELECTRONIC IMPORTED
-
If the VTV has been imported from another TapePlex. This will report the TapePlex name that owns the VTV
- EXPORTED
-
If the VTV has been exported to another TapePlex. The line will also list the TapePlexes to which the VTV copies has been successfully exported. An asterisks (*) next to the name indicates an export that has been rejected by the target TapePlex.
- STATUS
-
one or more of the following statuses:
- CONSOLIDATED
-
VSM has consolidated the VTV.
- DUPLEXED
-
The DUPLEX attribute has been assigned to this VTV. When VSM migrates the VTV, a copy will be written to two MVCs.
- EXPORT-NOT POSSIBLE
-
Export of this VTV to a remote TapePlex was attempted and the request was rejected. Typically, this is due to a different copy of the VTV residing in the remote TapePlex.
- EXPORT-REJECTED
-
Electronic export to one or more TapePlexes was actively rejected. This could be due to the target TapePlex not allowing import of the VTV, or a clash with copy status.
- EXPORT-REQUIRED
-
This VTV should be electronically exported and is currently queued for processing.
- EXPORT-STARTED
-
Electronic export is active for this VTV, but not yet complete.
- INITIALIZED
-
VTCS has used the VTV at least once.
- MIGRATED
-
VSM has migrated the VTV.
- MIGRATE PENDING
-
VTV migration is pending. This status is displayed when a VTV is initially created, or when the VTV requires reconciling or archiving. In these latter cases, individual MVC copies may indicate
ReconcilorDeletion. - REPLICATION COMPLETE
-
A fully replicated copy of this VTV is now resident in the Secondary VTSS.
- REPLICATION REQUIRED
-
This VTV should be replicated and is currently queued for processing.
- REPLICATION STARTED
-
Replication is active for this VTV but not yet complete.
- RESIDENT
-
The VTV is resident on the VTSS.
- SCRATCH
-
The VTV is in scratch status.
- UNINITIALIZED
-
The VTV has been defined via the
CONFIgutility, but has not ever been used. - AVOID EARLY MOUNT
-
Concurrent recall/mount encountered an error with this VTV. No further concurrent recall/mount activity will be attempted for this VTV.
Note:
VTVs that have incurred an ETTFB recall error have an error flag set in their VTV record in the CDS. This error indicates to VTCS that no further ETTFB recalls will occur for this VTV. When the error flag is on, the following is displayed:concurrent recall/mount encountered an error with this VTV. No further concurrent recall/mount activity will be attempted for this VTV.
DRAin
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The DRAin command terminates an eject or enter operation on one or more CAPs, which frees the CAP resources for use by other processes.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-75, the DRAin command includes the following parameters:
- cap-id or cap-list
-
one or more CAPs to be drained. The CAPids specified on a
DRAincommand must match the CAPids specified on the associatedEJectorENtercommand.The format of a
capidisAA:LL:CC, whereAA:LLindicates the LSMid, andCCindicates the CAP. See "CAPid" for a list of valid values.Each
caplistelement can be either anlsmidor acapidthat describes a specific CAP. The elements in a list must be separated by a comma or a blank, and the entire list must be enclosed in parentheses. - ENter
-
specifies that an enter operation is to be terminated on the specified CAPs.
ENteris the default. - EJect
-
specifies that an eject operation is to be terminated on the specified CAPs.
DRCHKPT
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS at FULL service level
Description
The DRCHKPT command establishes the system recovery point (checkpoint) from which MVC content can be recovered from for a period of time.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-76, the DRCHKPT command includes the following parameters:
- SET
-
Sets a date/time stamp in the active CDS which establishes the recovery point. Beginning at this recovery point, MVC content is guaranteed for a period of time in the future (for example, until another
DRCHKPTutility is run). - CLEAR
-
Removes any recovery point set in the active CDS. Once removed, MVC content cannot be guaranteed.
DRMONitr
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS at FULL service level
Description
The DRMONitr utility stalls job stream processing to ensure that critical data reaches its target destination. Once all identified data is accounted for, the utility ends.
DRMONitr can monitor for MVC and remote TapePlex copies being complete. It can also monitor for cluster replication being complete, in support of tapeless environments.
DRMONitr reports any VTV exception conditions found during execution.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-77, the DRMONitr command includes the following parameters:
- MGMTclas(name)
-
optionally, specifies a list of Management Classes to be monitored for VTV migrate/copy completion.
nameindicates one or more Management Classes.Specified Management Classes must be defined to the active VTCS system and must specify immediate migrate. For tapeless environments, specified Management Classes must specify
REPLICAT. - VTVid(volser)
-
optionally, specifies a list and/or range of VTV volsers to be monitored for migrate/copy completion.
volserindicates one or more volume serial numbers.The VTV's Management Class must be defined to the active VTCS system and must specify immediate migrate, i.e. the Management Class must specify
IMMEDmig(KEEP),IMMEDmig(DELETE)orIMMDELAY(n).For tapeless environments, the VTV's Management Class must specify
REPLICAT. - DSN(name)
-
optionally, specifies a list of data sets to be monitored for migrate/copy completion.
The VTVs containing these data sets must have Management Classes defined to the active VTCS system and must specify immediate migrate. For tapeless environments, the VTV's Management Class must specify
REPLICAT. - STORclas(name)
-
optionally, specifies the Storage Class locations that the identified VTV data is to be delivered to.
nameindicates one ore more Storage Class locations.Specified Storage Classes must be defined to the active VTCS system. Although this parameter is optional, the
STORclasparameter should only be omitted in tapeless environments. - REPLICAT
-
optionally, specifies that VTV cluster replication is to be monitored for completion. Replication must be specified on the VTV's Management Class policy for the VTV to be selected for monitoring. If replications are monitored in a tape environment, their completion overrides any Storage Class requirement.
- MAXAGE(nnn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum VTV age (time since last update), in hours, when monitoring migrations by Management Class (a
MGMTclasvalue is required).nnnindicates the age in hours.Valid values are 1 to 999. There is no default.If the VTV's age (time since last update) is greater than
MAXAGE, the VTV is not monitored.DRMONitrreports the number of skipped VTVs due toMAXAGE, if specified.If you do not specify
MAXAGE, any active VTV belonging to the specified Management Classes, regardless of age, is monitored for migrate or copy completion. - TIMEOUT(nnn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum time, in minutes, for
DRMONitrto run.nnnindicates the maximum time. Valid values are zero to 999. If you do not specify aTIMEOUTvalue, there is no limit on the time the utility can run (stall).A
TIMEOUTvalue of zero does not stall theDRMONitrutility. This special case reports on incomplete copies of specified VTV data.If a non-zero
TIMEOUTvalue is exceeded,DRMONitrends with RC 8 and generates an error message. If theTIMEOUTvalue specified was zero, a return code of 4 is set if a VTV's copy is detected as incomplete, otherwise a return code 0 is set.
Note:
You must specify eitherSTORclas or REPLICAT or both to specify the destination criteria. Otherwise DRMONitr ends with RC 8 and generates an error message. Additionally, Oracle recommends that you do not specify (or monitor) Storage Classes in tapeless environments because migrations are not possible.DRTEST
The DRTEST command sets up the environment for DR testing and optionally, starts and stops the test.
Issue this command from the SLUADMIN utility to set up the DR testing environment. Once the environment is set, you can issue DRTEST from a utility or the console to start or stop testing.
Issue this command with any of the options listed in the following table. Each option is described individually, and in more detail, on the pages to follow.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
creates a DR test CDS, normally run at the DR test site |
|
|
updates the production CDS without creating a |
|
|
removes all DR test settings in the production CDS |
|
|
starts the DR test on the production site. |
|
|
stops the DR test on the production site |
Note:
-
You can use a combination of these options provided you have correct environment and JCL requirements. For example,
DRTEST STOPandDRTEST RESETcan be run in the same job, however,DRTEST STOPmust be run beforeDRTEST RESET. -
Refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Disaster Recovery and Offsite Data Management Guide for information about how to use the
DRTESTutility.
DRTEST CREATE
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The DRTEST CREATE command creates a DR test CDS, normally run at the DR test site.
Note:
TheNOUPDprd parameter is only valid if the DRTEST PRIMEprd command is executed prior to the DRTEST CREATE command. See "DRTEST PRIMEprd" for more information.Consider the following:
-
DR test cannot be active. This refers to the production CDS status.
-
Active HSC/VTCS is not required.
-
If HSC/VTCS is active,
SLSCNTL DDstatement(s) identifying the production CDS are optional, and if included, must match the active HSC/VTCS. -
If HSC/VTCS is not active,
SLSCNTL DDstatement(s) identifying the production CDS are required.
-
-
SLSNEW DDstatement(s) identifying theDRTESTCDS(s) are required.
Sample Control Cards:
DRTEST CREATE HOSTID(ZIPF,ZIPG) - DRVTSS(VTSSW) - DRACS(00)
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-78, the DRTEST CREATE command includes the following parameters:
- HOSTID(hostid1,hostid2,...hostidn)
-
Specifies the host IDs replicated in the test CDS in available host-id positions. The combination of existing production
HOSTIDs and those identified in this parameter for replication cannot exceed the 16 host limit. If an additionalhost-id(not used in production) needs to be added for DR test purposes alone, this additionalhost-idwill use 2 of the 16host-idsin the limit. - DRVTSS(vtss1,vtss2,...vtssn)
-
Optionally, specifies the VTSS names available to the DR test site. Unless you also specify the
SHAREorSPAREparameter, these VTSSs are offline to the production site and online to the DR test site when the DR test starts.- SPARE
-
Optionally, specifies that the DR test VTSS(s) are spares and that identically named VTSS(s) exist and are online at the production site when the
DRTESTutility is run and during the DR test. - SHARE
-
Optionally, specifies that the DR test VTSS(s) are shared with the production site. During the DR test, both the test and production site may create VTVs in the DR test VTSS (based on the
VOLPARMdefinitions). The DR test cannot modify VTVs that are not in a DR test subpool. The parametersDRACSandSTORMNGRcannot be specified ifSHAREis specified.
- STORMNGR(stormngr-list)
-
Optionally, specifies the subsystem names of the VLEs attached to the DR test site TapePlex.
stormngr-listindicates the list of subsystem names. For more information, refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring the Host Software for VLE. - DRACS(acsid1, acsid2,...acsid16)
-
Optionally, specifies one or more ACSs available to the DR test site. Multiple ACS IDs must be specified as a list, and not as a range of ACS IDs. The ACSs are online to the DR test site but can remain connected (and usually are) to the production site when the DR test starts.
-
If the
DRVTSS SHAREparameter is specified, theDRACSparameter is not allowed. -
If the
STORMNGRparameter is specified, theDRACSparameter is allowed but not required.
-
- NOUPDprd
-
Optionally, does not update the input production CDS(s).
If this parameter is specified, you can use a single CDS production copy as input and that copy can be either the actual primary production CDS, a backup copy, or a mirrored copy.
This parameter is only valid if the
PRIMEprdfunction has already been run on the production CDS. See "DRTEST PRIMEprd" for more information.
Additional JCL Requirements
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statements apply to the DRTEST CREATE JCL:
- SLSNEW1
-
specifies the new primary copy of the test HSC CDS.
- SLSNEW2
-
specifies the new secondary copy of the test HSC CDS.
- SLSNEW3
-
specifies the new standby copy of the test HSC CDS.
- SLSJRN00 – SLSJRNnn
-
DDNAMEs for the DR test journal files, which are only valid if the current CDS defines journaling. There are two files perHOSTID:SLSJRN00andSLSJRN01forhostid1,SLSJRN02andSLSJRN03forhostid2, etc. - SLSSTATN
-
DDNAMEfor LMU station address changes forHOSTIDs. This file is optional, and if not supplied the same station addresses are used in the DR test CDS for theHOSTIDs as in the existing CDS.Each entry follows the HSC
SET SLISTATNutility format. See "SET SLISTATN" for more information. The following figure shows an example of theSLSSTATNfile: - SLSVTSS
-
DDNAMEfor VSM changes on the DR test CDS. This file is optional and is only used if the DR test configuration includes VSM elements. Typically, this file is used to change RTD hardware connection definitions in the DR test CDS but may be used to modify any VSM definitions on the DR test CDS because the file invokes the VTCSCONFIg RESETutility.Caution:
Improper use ofCONFIg RESETagainst the DR test CDS may render the DR test environment inoperable!Each entry follows the format of the
VTSS,VTD,RTD, andHOSTstatements of the VTCSCONFIgutility. See "CONFIg" for more information. The following figure shows an example of theSLSVTSSfile:CONFIG RESET VTSSNAME=VTSS01 LOW=70 HIGH=80 MAXMIG=1 MINMIG=1 RETAIN=10 RTDNAME=VTS18800 DEVNO=8800 CHANIF=0A RTDNAME=VTS18801 DEVNO=8801 CHANIF=0I RTDNAME=VTS18802 DEVNO=8802 CHANIF=1A RTDNAME=VTS18803 DEVNO=8803 CHANIF=1I HOST NAME=MVS1 VTDLOW=8900 HIGH=893F VTSSNAME=VTSS02 LOW=70 HIGH=80 MAXMIG=8 MINMIG=8 RETAIN=10 RTDNAME=VTS28805 DEVNO=8805 CHANIF=0A RTDNAME=VTS28806 DEVNO=8806 CHANIF=0E RTDNAME=VTS28807 DEVNO=8807 CHANIF=0I RTDNAME=VTS28808 DEVNO=8808 CHANIF=0M RTDNAME=VTS28809 DEVNO=8809 CHANIF=1A RTDNAME=VTS2880A DEVNO=880A CHANIF=1E RTDNAME=VTS2880B DEVNO=880B CHANIF=1I RTDNAME=VTS2880C DEVNO=880C CHANIF=1M HOST NAME=MVS2 VTD LOW=9900 HIGH=993F
DRTEST PRIMEprd
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
DRTEST PRIMEprd updates the production CDS without creating a DRTEST CDS.
Considerations:
-
DR test cannot be active. This refers to the production CDS status.
-
Active HSC/VTCS is not required.
-
If HSC/VTCS is active,
SLSCNTL DDstatement(s) identifying the production CDS are optional, and if included, must match the active HSC/VTCS. -
If HSC/VTCS is not active,
SLSCNTL DDstatement(s) identifying the production CDS are required.
-
-
SLSNEW DDstatement(s) identifying the DRTEST CDS(s) are required.
Sample Control Cards:
DRTEST PRIME HOSTID(ZIPF,ZIPG) - DRVTSS(VTSSW) - DRACS(00)
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-79, the DRTEST PRIMEprd command includes the following parameters:
- HOSTID(hostid1,hostid2,...hostidn)
-
Specifies the
HOSTIDs replicated in the test CDS in availablehost-idpositions. The combination of existing productionHOSTIDs and those identified in this parameter for replication cannot exceed the 16 host limit. If an additionalhost-id(not used in production) needs to be added for DR test purposes alone, this additionalhost-idwill use 2 of the 16 host-ids in the limit. - DRVTSS(vtss1,vtss2,...vtssn)
-
Optionally, specifies the VTSS names available to the DR test site. Unless you also specify the
SHAREorSPAREparameter, these VTSSs are offline to the production site and online to the DR test site when the DR test starts.- SPARE
-
Optionally, specifies that the DR test VTSS(s) are spares and that identically named VTSS(s) exist and are online at the production site when the
DRTESTutility is run and during the DR test. - SHARE
-
Optionally, specifies that the DR test VTSS(s) are shared with the production site. During the DR test, both the test and production site may create VTVs in the DR test VTSS (based on the
VOLPARMdefinitions). The DR test cannot modify VTVs that are not in a DR test subpool. The parametersDRACSandSTORMNGRcannot be specified ifSHAREis specified.
- STORMNGR(stormngr-list)
-
Optionally, specifies the Subsystem Names of the VLEs attached to the DR test site TapePlex.
stormngr-listindicates the list of Subsystem names. For more information, refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring the Host Software for VLE. - DRACS(acsid1, acsid2,...acsid16)
-
Optionally, specifies one or more ACSs available to the DR test site. Multiple ACS IDs must be specified as a list, and not as a range of ACS IDs. The ACSs are online to the DR test site but can remain connected (and usually are) to the production site when the DR test starts.
-
If the
DRVTSS SHAREparameter is specified, theDRACSparameter is not allowed. -
If the
STORMNGRparameter is specified, theDRACSparameter is allowed but not required.
-
DRTEST RESET
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The DRTEST RESET command removes all DR test settings in the production CDS.
Considerations:
-
DR test cannot be active. This refers to the production CDS status.
-
Active HSC/VTCS is not required.
-
If HSC/VTCS is active,
SLSCNTL DDstatement(s) identifying the production CDS are optional, and if included, must match the active HSC/VTCS. -
If HSC/VTCS is not active,
SLSCNTL DDstatement(s) identifying the production CDS are required.
-
-
SLSNEW DDstatement(s) identifying the DRTEST CDS(s) are required.
Sample Control Cards:
DRTEST PRIME HOSTID(ZIPF,ZIPG) - DRVTSS(VTSSW) - DRACS(00)
DRTEST START
Interfaces:
-
console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The DRTEST START command starts the DR test on the production site.
Note:
DRTEST START cannot run successfully until the production CDS is primed using DRTEST PRIMEprd or DRTEST CREATE.Considerations:
-
DR test cannot be active. This refers to the production CDS status.
-
Active HSC/VTCS is required.
-
SLSCNTL DDstatement(s) identifying the production CDS are optional, and if included, must match the active HSC/VTCS. -
SLSNEW DDstatement(s) identifying the DRTEST CDS(s) are not required, and if included, are ignored.
Sample control cards:
DRTEST START
DRTEST STOP
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The DRTEST STOP command stops the DR test on the production site.
Considerations:
-
DR test cannot be active. This refers to the production CDS status.
-
Active HSC/VTCS is required.
-
SLSCNTL DDstatement(s) identifying the production CDS are optional, and if included, must match the active HSC/VTCS. -
SLSNEW DDstatement(s) identifying the DRTEST CDS(s) are not required, and if included, are ignored.
Sample control cards:
DRTEST START
Note:
DRTEST STOP and DRTEST RESET can be run in the same job, however, DRTEST STOP must be run before DRTEST RESET.EEXPORT
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The EEXPORT command is used to perform electronic export functions. Use this command to manually export VTVs or re-drive rejected exports.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-186, the EEXPORT command includes the following parameters:
- VTV(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
specifies one or more VTVs to electronically export.
volser,vol-range, orvol-listindicate the volsers of one or more VTVs. You can specify a maximum of 2,000 volsers. - MGMTclas(mgmtclas-name or mgmtclas-list)
-
specifies one or more names of Management Classes that determine the VTVs to electronically export.
mgmt-class-nameormgmt-class-listindicates the Management Class name. This name must be 1 to 8 alphanumeric characters beginning with an alpha character and must follow SMS naming conventions. - TOPlex(name)
-
specifies the name of the TapePlex to which copies of the VTV are sent via electronic export. There must be at least one CLINK within the configuration that provides a route to the TapePlex.
nameindicates the target TapePlex name. - TOVTSS(vtss-name)
-
optionally, specifies the VTSS name to be preferenced as the receiving VTSS within the target TapePlex specified by the
TOPlexparameter.vtss-nameindicates the VTSS name.Note:
This is a preference only. Validation of the value is not performed. - ULINKMVC(volser)
-
specifies whether MVC copies on the target TapePlex are to be deleted as part of the export process.
volserindicates a volser from the MVC copy to be deleted from the target VTVs. If not specified, then all MVC copies of the VTV are deleted.This parameter only applies when the VTV version sent matches the version in the target TapePlex. If the versions sent is more recent, then the behavior is implicit.
This parameter can be used if the only MVC copies of a VTV in the target TapePlex become damaged. A replacement copy of the VTV can be supplied to the TapePlex via the
EEXPORTcommand. The damaged MVC copies are replaced by additional migrations from the VTV copy sent. - FORCE
-
specifies whether VTCS exports the VTV to locations with disregard for other criteria.
- YES
-
Export VTVs to the TapePlex specified in the
TOPlexparameter, regardless of whether the VTVs have been previously exported to the TapePlex, or the management class points to a storage class that specifies the target TapePlex. - NO
-
Export VTVs to the TapePlex specified in the
TOPlexparameter, but ignore any VTVs already marked as exported, and exclude any VTVs for which the management class does not point to a storage class that specifies the TapePlex in theTOPlexparameter. This is the default.
- REJECTED
-
specifies whether VTCS only selects VTVs recorded in the CDS as being rejected by the target TapePlex.
REJECTEDandFORCEare mutually exclusive.- NO
-
Ignore any VTVs already marked as exported, and exclude any VTVs for which the management class does not point to a storage class that specifies the TapePlex in the
TOPlexparameter. This is the default. - YES
-
Only select VTVs previously rejected by the target TapePlex.
- RECALWER
-
specifies whether VTCS recalls VTVs with read data checks.
- NO
-
Do not recall VTVs with read data checks. This is the default.
- YES
-
Recall VTVs with read data checks.
- NOWAIT
-
specifies that the utility does not wait for the operation to complete and returns after the request is submitted.
EJect
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The EJect command moves volumes to a Cartridge Access Port (CAP) for removal.
You can designate a single CAP or a list of specific CAPs. Specifying one or more CAPs limits cartridge ejection to those CAPs.
Ejections in a multiple ACS configuration may specify CAPs in each ACS if volumes reside in each ACS. If a list of CAPs is not provided, HSC selects the highest priority CAP available for each ACS (see "CAPPref").
You may elect to submit multiple EJect requests, each of which may specify a particular CAP. If you elect to specify a CAP in a multi-ACS configuration, then the list of volumes must reside within the CAP ACS.
Multiple CAPs within one ACS can be allocated to the EJECt utility. Specifying multiple CAPs in a single EJect utility typically improves performance by reducing pass-thrus.
If two CAPs are specified in the same LSM, cartridges in that LSM are ejected in sequential order. This is helpful for vaulting.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-84, the EJect command includes the following parameters:
- TEXT(text)
-
optionally, specifies the address of a 44-byte string issued whenever the operator is requested to open the CAP for an
EJectrequest. This text is displayed via messageSLS1251E.textindicates the text string. - PMSG(nn)
-
optionally, specifies a user defined message to be displayed in the SLConsole CAP status screen for a CAP when the door is unlocked for cartridge removal.
nnis a two character numeric value from 00 to 99. Specify one of the following values:-
00- No message is displayed. -
01- DisplayRemove cartridgesmessage. -
02- DisplayLib not availablemessage. -
03- DisplayLoad cartridgesmessage. -
04-99- Display customized user messages.
-
Option 1 Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-84, the EJect command includes the following parameters:
- volser, vol-range, or vol-list
-
one or more VOLSERs to be ejected. This can be a single VOLSER, a range of VOLSERs or a list of VOLSERs and/or VOLSER ranges in any combination.
If a list is specified, the elements must be delimited by commas or blanks, and the entire list enclosed in parentheses. A range of VOLSERs consists of a starting VOLSER and an ending VOLSER separated by a dash.
- acs-id, lsm-id, cap-id, or cap-list
-
the ACS, LSM, or CAP for the cartridges to be ejected.
acs-ididentifies the ACS containing the cartridges to eject. The HSC selects a non-zero preference CAP to use in the specified ACS.lsm-ididentifies the LSM containing the cartridges to eject. If the LSM has more than one CAP, an available CAP with the highest nonzero preference is selected.cap-ididentifies a specific CAP to use regardless of the assigned preference value.cap-idis of the formAA:LL:CC, whereAA:LLindicates the LSMid, andCCindicates the CAP number. The CAP numbers are dependent on the LSM type.cap-listrequires explicitly specified CAPids separated by commas. A CAPid range is not allowed. CAPids must be separated by blanks or commas, and the entire list must be enclosed in parentheses. If no CAP is specified, one is chosen in each ACS.Note:
If neitheracs-id,lsm-id,cap-id, orcap-listis specified, HSC selects a non-zero preference CAP in each ACS that contains volumes to be ejected. - SEQ
-
optionally, specifies whether or not CAP eject processing fills the CAP cells in the same order specified by the
volser,volser-range, orvol-list.If
SEQis not specified, but two CAPs are requested in the same LSM, and the LSM is not an SL8500, cartridges in the ACS are ejected in sequential order.For best performance,
SEQ(NO)is recommended.- NO
-
specifies to eject the requested volumes in the order of home cell location.
EJectprocessing fills the CAP or magazine (for the SL8500) according to the distance of the home cell to the CAP or magazine; that is, volumes closest to the CAP or magazine are ejected first. - YES
-
specifies to eject cartridges to the CAP in the order the volumes are listed in the associated
vol-list. The first cartridge requested appears in the topmost CAP cell, the second cartridge requested appears in the next CAP cell, etc. until the CAP is full or all cartridges have been moved to the CAP.
- WAITcap
-
optionally, specifies whether or not a list of ejecting volumes waits for an available CAP if one is not available.
- YES
-
specifies that the eject process waits indefinitely for a CAP to become available. YES is the default.
- NO
-
specifies that the eject process does not wait for a CAP if it is not available.
Option 2 Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-84, the Display EJect command includes the following parameters:
- SCRTCH
-
indicates that scratch volumes are to be ejected.
Note:
If neitheracs-id,lsm-id,cap-id, orcap-listis specified, HSC selects a non-zero preference CAP in each ACS that contains volumes to be ejected. HSC selects a non-zero preference CAP in ACS 00. - acs-id, lsm-id, cap-id, or cap-list
-
the ACS, LSM, or CAP for the cartridges to be eject.
acs-ididentifies the ACS containing the cartridges to eject. The HSC selects a non-zero preference CAP to use in the specified ACS.lsm-ididentifies the LSM containing the cartridges to eject. If the LSM has more than one CAP, an available CAP with the highest nonzero preference is selected.cap-ididentifies a specific CAP to use regardless of the assigned preference value.cap-idis of the formAA:LL:CC, whereAA:LLindicates the LSMid, andCCindicates the CAP number. The CAP numbers are dependent on the LSM type.cap-listrequires explicitly specified CAPids separated by commas. A CAPid range is not allowed. CAPids must be separated by blanks or commas, and the entire list must be enclosed in parentheses. If no CAP is specified, one is chosen in each ACS. - SUBpool(subpool-name)
-
optionally, specifies the subpool from which scratch volumes are to be ejected. If
MEDiaorRECtechare specified, cartridges are ejected for that media type or recording technique within the same subpool.subpool-nameindicates the name for the subpool. - VOLCNT(count)
-
optionally, specifies that a designated number of scratch volumes are to be ejected.
countindicates the number of scratch volumes to be ejected. - MEDia(media-type)
-
optionally, specifies that scratch cartridges of the desired media are to be ejected.
media-typeindicates the media type. See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for a list of valid media-type values.Note the following:
If
MEDiais not specified, the next scratch cartridge is selected without regard to media type ifRECtechdoes not exist. If bothMEDiaandRECtechare supplied, they must be compatible.If
SUBpoolis not specified, then the next scratch cartridge is selected without regard to whether it belongs to a subpool, is defined to the default subpool usingVOLPARMS, or belongs to no scratch subpool whatsoever. - RECtech(recording-technique)
-
optionally, specifies scratch cartridges of the desired recording technique are to be ejected.
RECtechindicates the method used to record data tracks on the tape surface.recording-techniqueindicates the recording technique. See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for valid recording-technique values.Note:
IfRECtechis not specified, the next scratch cartridge is selected depending on the media type (if supplied). If neither is supplied, the next scratch cartridge is selected without taking media type and recording technique into consideration. If bothRECtechandMEDiaare supplied, they must be compatible. - WAITcap
-
optionally, specifies whether or not a list of ejecting volumes waits for an available CAP if one is not available.
- YES
-
specifies that the eject process waits indefinitely for a CAP to become available. YES is the default.
- NO
-
specifies that the eject process does not wait for a CAP if it is not available.
ENter
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The ENter command makes a CAP in Automatic mode available for entering cartridges into an LSM.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-85, the ENter command includes the following parameters:
- acs-id
-
specifies the ACS where cartridges are to be entered. The HSC selects a nonzero preference manual mode CAP within the ACS to use.
- lsm-id
-
identifies one of the following:
-
an LSM with a single CAP
-
an LSM that contains multiple CAPs. The HSC selects an available manual mode CAP with the highest nonzero preference. CAPid 00 is selected if it is available, in manual mode, and has a preference value equal to or higher than other available manual mode CAPs in the LSM.
-
- cap-id
-
specifies a specific manual mode CAP to use regardless of availability or CAP preference. The format of a
capidisAA:LL:CC, whereAA:LLindicates the LSMid, andCCindicates the CAP. See "CAPid" for a list of valid values. - TLSM(lsm-id)
-
specifies the LSM to receive the entered cartridges.
lsm-idindicates the following:-
an LSM with a single CAP
-
an LSM that contains multiple CAPs. The HSC selects an available manual mode CAP with the highest nonzero preference. CAPid 00 is selected if it is available, in manual mode, and has a preference value equal to or higher than other available manual mode CAPs in the LSM.
The format of an LSMid is
AA:LL, whereAAindicates the ACSid (decimal 00-99) andLLindicates the LSM number (decimal 00-99). -
- SCRatch
-
optionally enables you to put the volumes you enter into scratch status. If you do not specify that the volumes are to be given scratch status, the system enters them as nonscratch volumes.
EXECParm
Interfaces:
-
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
None.
Description
The EXECParm command provides an alternative method for specifying GTF event and format IDs normally specified in the subsystem startup procedure. It also provides you with the option of displaying the command prefix preceding WTO or WTOR messages.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-86, the EXECParm command includes the following parameters:
- MSGPRFX
-
optionally, specifies control of whether the command prefix is to precede WTO or WTOR messages to the operator.
- Yes
-
indicates that the command prefix is to display preceding WTO or WTOR messages to the operator.
- No
-
indicates that the command prefix is not to display preceding WTO or WTOR messages to the operator.
- Eid(gtfeid)
-
optionally,
gtfeidspecifies a GTF event ID.PARM='Eid(userspecifiedeventid)'parameter is valid for use in the HSC initialization procedure as an alternative method of specifying the GTF event ID. - Fid(gtffid)
-
optionally,
gtffidspecifies a GTF format ID.PARM='Fid(userspecifiedformatid)'parameter is valid for use in the HSC initialization procedure as an alternative method of specifying the GTF format ID. - HOSTID(host-id)
-
optionally,
hostidspecifies the system ID associated with the request to process the EXECParm control statement.Note:
If thehost-idspecified does not match the host executing the command, the command is ignored and no message is issued.
EXPORT
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
-
Active HSC/VTCS at
FULLservice level required when specifying theVTVorMGMTCLASparameter. -
Active HSC/VTCS not required when specifying the
MVCorSTORclasparameter.
Note:
The CDS used by the utility must not be accessed by any other currently active HSC/VTCS host(s). Otherwise, error messageSLS6716E is issued and the utility fails.Description
The EXPORT command consolidates VTVs (if required) and creates a manifest file that lists VTVs and MVCs available for export from a VSM system.
Note:
-
EXPORT VTVandEXPORT MGMTclascannot consolidate VTVs on vMVCs in a VLE. -
EXPORT MVC and EXPORT STORclascan create a manifest for VTVs that have been migrated to vMVCs in a VLE.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-68, the EXPORT command includes the following parameters:
- VTV(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
specifies one or more VTVs to consolidate for export.
When an export by VTV is performed, the CDS does not maintain the MVC information in the VTV record. The MVC is marked as
(E)xport.volser,vol-range, orvol-listindicates the volsers of one or more VTVs. You can specify an unlimited number of VTVs.Note:
EXPORT VTVcannot consolidate VTVs on vMVCs in a VLE. - MGMTclas(mgmtclas-name or mgmtclas-list)
-
specifies one or more Management Classes that determine one or more VTVs to consolidate for export.
When an export by
MGMTclasis performed, the CDS does not maintain the MVC information in the VTV record. The MVC is marked as(E)xport.mgmt-class-nameormgmt-class-listindicate the names of one or more Management Classes you defined on theMGMTclascontrol statement. See "MGMTclas Control Statement" for more information.Note:
EXPORT MGMTclascannot consolidate VTVs on VMVCs in a VLE. - MVC(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
specifies one or more MVCs for export.
When an Export by MVC is performed, the CDS maintains the MVC information in the VTV record of the CDS. The MVC will is marked as
(R)ead-Only.volser,vol-range, orvol-listindicates the volsers of one or more MVCs. - STORclas(stor-clas-name or stor-clas-list)
-
specifies one or more Storage Classes that determine one or more MVCs for export.
When an Export by
STORclasis performed, the CDS maintains the MVC information in the VTV record of the CDS. The MVC will is marked as(R)ead-Only.stor-clas-nameorstor-clas-listindicate the names of one or more Storage Classes that you defined on theSTORclascontrol statement. See "STORclas Control Statement" for more information.Note:
EXPORT STORclascan create a manifest for VTVs that have been migrated to vMVCs in a VLE. - MANIFEST(ddname)
-
optionally, specifies the output destination
dd-nameof the manifest file. The default isMANIFEST. - RECALWER
-
optionally, specifies whether VTCS recalls VTVs with read data checks.
- Yes
-
Recall VTVs with read data checks (the default).
- No
-
Do not recall VTVs with read data checks.
Additional JCL Requirements
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statements apply to the EXPORT JCL:
- manifest file DD
-
DD statement for the manifest file (optional).
FMTLOG
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The FMTLOG command is part of the HSC/VTCS transaction logging service.
This command pre-formats a log file to be used by the logging service. It pre-formats data blocks and writes certain control information in the first record of the file. You can format a maximum of two log files with a single FMTLOG utility command.
Note:
You must pre-format a log file before activating it with theSET LOGFILE utility command. See "SET LOGFILE" for more information. You must execute the OFFload LOGfile before executing SET LOGFILE to specify a different log file data set name. See "OFFload" for more information.Additional JCL Requirements
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statements apply to the FORMAT LOGFILE JCL:
- SLSLOG1
-
specifies the log file to be formatted.
- SLSLOG2
-
specifies the second log file to be formatted.
IMPORT
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS not required
Description
The IMPORT command imports VTVs and MVCs listed on a manifest file into a VSM system.
Note:
Ensure that the ”to” CDS has the same features (enabled by CDS level) as the ”from” CDS. For example, if the ”from” CDS has large VTV page sizes enabled and 2/4 Gb VTVs have been created, then the ”to CDS” must have the same capabilities, otherwise the import fails.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-89, the IMPORT command includes the following parameters:
- VTV(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
specifies one or more VTVs to import.
volser,vol-range, orvol-listindicate the volsers of one or more VTVs. - MVC(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
specifies one or more MVCs to import.
volser,vol-range, orvol-listindicate the volsers of one or more MVCs. - REPLACE
-
specifies whether VTCS replaces the VTV record in the target CDS. There is no default. You must specify a value.
- NONE
-
Do not replace the VTV record. VTCS only creates new records for VTVs that are not duplicates and replaces records for VTVs not initialized in the target CDS.
- UPDATED
-
Replace the VTV record if it is a more recent version of the VTV, or if the CDS has no migrated or resident versions of the VTV. If it is an older or the same version, do not replace the VTV record.
- ALL
-
Replace any duplicate VTV records in the target CDS.
Considerations:
-
Ensure that you actually want to replace duplicate VTV records in the target CDS before you specify the
ALLparameter. You may want to do a ”validate” run withNOUPDATEto see which VTV records will be replaced. -
If a VTV record is replaced, all existing VTSS and MVC copies of the VTV are invalidated.
-
You cannot import an MVC if the target CDS records show that the MVC contains VTVs, even if you specify
REPLACE(ALL). In this situation, you must first drain (withEJect) the MVC on the target system and eject it from the ACS. You can then import the MVC that you exported from the source system.
- MANIFEST(dd-name)
-
optionally, specifies the input dd name of the manifest file.
dd-nameindicates the dd name of the manifest file. The default isMANIFEST. - NOUPDATE
-
optionally, specifies that VSM does not update the CDS, validates the import operation, and writes information messages to the job log.
- IMMDRAIN
-
optionally, specifies whether VSM will immediately drain imported MVCs.
- NO
-
Do not drain MVCs (the default).
- YES
-
Drain MVCs.
- INACTCDS
-
optionally, specifies that the import uses a different CDS from the CDS currently active on the HSC system where you are running the import job. Use the
SLSCNTLdefinition statement in theSLUADMINJCL to specify the alternate CDS.If HSC is down on the system where you are running the import job, the CDS on that system is assumed to be inactive, so you do not need to specify
INACTCDS.If you specify the
INACTCDSparameter, the CDS specified in theSLSCNTLdefinition statement in theSLUADMINJCL must be different from the CDS being used by HSC/VTCS (if active). - OWNRPLEX(name)
-
specifies ownership of a VTV being imported.
nameindicates the name of the TapePlex that owns the original copy of the VTV. This name must match one of the known TapePlex names in the configuration.If this name matches that indicated for the
THISPLEXparameter on theCONFIgTAPEPlexstatement, the electronic imported status is removed. - SETOWNER
-
specifies that ownership information is to be imported.
By default, any ownership information within the manifest is ignored. The
SERTOWNERparameter specifies that the TapePlex ownership and export fields are imported. VTVs appear as if electronically imported onDisplaycommands and reports.
Additional JCL Requirements
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statements apply to the IMPORT JCL:
- manifest file DD
-
DD statement for the manifest file.
INITialize
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
HSC at FULL service level
Description
The INITialize command enables you to batch enter cartridges into the library through the CAP, and invokes a user-specified program to write a magnetic label on each tape.
The robot accepts cartridges placed into the CAP and reads the Tri-Optic labels, and the HSC passes the VOLSERs to the user-specified program. The magnetically labeled cartridges can be ejected from the library or placed into cell locations. If the cartridges are stored in the library, the control data set is updated with the VOLSER and location information. The control data set can mark each cartridge as either scratch or nonscratch.
INITialize reads the external Tri-Optic labels and records them in a data set defined through the CNTLDD parameter. CNTLDD is a control statement parameter that describes the DDname to be used for TMSTPNIT control statements.
The INITialize utility does not initialize cartridges on its own; it invokes TMS, TLMS, or any other initialization utility, which performs the initialization. CNTLDD specifies, through the HSC to the TMS utility, the DD to be used for the input parameters the TMS utility requires.
Caution:
This utility must be executed on an MVS system running SMC and using a local HSC server.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-68, the INITialize command includes the following parameters:
- CAP(cap-id)
-
optionally, specifies a particular CAP to be used for the operation.
If CAP is not specified, the utility chooses a CAP in the ACS implied by the device allocated to satisfy the
SLSTAPE DDstatement.capidindicates the CAP. The format of acapidisAA:LL:CC, whereAA:LLindicates the LSMid, andCCindicates the CAP. See "CAPid" for a list of valid values. - PROGram(prog-name or IEHINITT)
-
optionally, specifies a program to be invoked to actually write the label (if not specified,
IEHINITTis assumed).prog-nameindicates the program that is to perform the initialization. - VERIFY(parameter-name)
-
optionally, specifies a parameter to be passed to the tape initialization program identified by the
PROGramparameter.VERIFYis valid only when thePROGramparameter specifiesTMSTPNIT.parameternameindicates the parameter passed to theTMSTPNITprogram. For example, if the following parameter is entered:VERIFY(ROBOT)TMSTPNIT suppresses the TMS CAL0TN01 message for NL (nonlabeled) tapes. Refer to the appropriate CA1 publication for valid parameter values.
- CNTLDD(dd-name or SYSIN)
-
optionally, specifies the DD statement to which initialization control statements are written, and from which the label program reads its control statements.
Note:
This is not your control data set.dd-nameindicates the name of the DD statement. Theddnameoption may only be specified when using CA1 (TMS) prior to version 5.1. The default value (SYSIN) MUST be used with CA1 (TMS) version 5.1 or later. - OPTION
-
optionally, specifies optional handling to be performed following the completion of label processing. If not specified, the default is retention of the new cartridges in the library with a nonscratch status.
- EJEct
-
specifies that the labeled volumes are to be ejected from the library after the labeling process is complete.
- SCRatch
-
specifies that the labeled volumes entering the library are to be added to the scratch list. If the volume is to be treated as scratch, the installation must inform the tape management system of the volume's scratch status.
Additional JCL Requirements
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statements apply to the INITialize JCL:
- SLSINIT
-
substitution control card format for the invoked initialization program.
- SLSTAPE
-
library transport on which the cartridge is mounted for labeling. To prevent a nonlibrary transport from being allocated, specify one of the following:
-
an esoteric containing only library transports
-
a specific library transport address
-
a
TAPEREQstatement to direct the allocation to a library transport -
a user exit (refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Legacy Interfaces Reference)
-
- CNTLDD or SYSIN
-
contains volume serial labeling information and is passed as input to the initialization program (
IEHINITTor the program specified by thePROGkeyword parameter).If
CNTLDDis specified in the utility control statement, then the DD name identifies the data set containing the labeling information. - SYSPRINT
-
output messages from
IEHINITT.contains volume serial labeling information and is passed as input to the initialization program (
IEHINITTor the program specified by thePROGkeyword parameter).If
CNTLDDis specified in the utility control statement, then the DD name identifies the data set containing the labeling information.
INVENTRY
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Description
The INVENTRY command lists all VTVs on specified MVCs.
Additionally, you can use this command to do the following:
-
Request that the contents of the specified MVCs are cross-checked with the information recorded in the CDS.
-
Terminate processing based on the end-of-tape position recorded in the CDS for the MVC, rather than at the MVC's physical end-of-tape.
-
Terminate processing for an MVC the first time a VTV is discovered that is incompatible with the information in the CDS.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-91, the INVENTRY command includes the following parameters:
- MVCid(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
specifies the MVC(s) to be inventoried.
volser,vol-range, orvol-listindicates the volsers of one or more MVCs. You can also specify one or more ranges. - CDScheck
-
optionally, specifies whether the contents of each inventoried MVC is checked against the information recorded in the CDS.
- None
-
Each VTV found on an inventoried MVC is listed via message
SLS6933I. The CDS is not checked.Noneindicates the default. - Mvc
-
Each VTV found on an inventoried MVC is listed via message
SLS6933I. The details of the VTV are obtained from the CDS. The MVC and CDS copies of the VTV are compared and listed as a comment onSLS6933I. If the CDS shows a resident or MVC copy of the VTV that differs from the copy listed inSLS6933I, its details are listed via messageSLS6934I. - Full
-
Each VTV found on an inventoried MVC is listed via message
SLS6933I.The details of the VTV are obtained from the CDS. The MVC and CDS copies of the VTV are compared and listed as a comment on
SLS6933I. If the CDS shows a resident or MVC copy of the VTV that differs from the copy listed inSLS6933I, its details are listed via messageSLS6934I. For each inventoried MVC, the CDS is checked to determine which CTCs are shown to have a copy on the MVC. Any MVCs that were not found on the MVC are listed in messageSLS6935E.
- STOPleot
-
optionally, specifies whether processing is to terminate when the logical end-of-tape position is reached. The logical end-of-tape position is the end-of-tape position recorded in the CDS for this MVC.
- NO
-
All VTVs are to be processed on each inventoried MVC. This is the default.
- YES
-
VTVs are processed on each inventoried MVC until one of the following occurs:
-
The MVC's physical end-of-tape is reached.
-
The first VTV is found on the MVC that is beyond the logical end-of-tape position, if this is earlier than the physical end-of-tape position. This setting is invalid with
CDScheck(None).
-
- TERMerr
-
optionally, specifies whether the inventory of an MVC is to terminate when it encounters the first inconsistency between the contents of the MVC and the VTVs that the CDS indicates are on the MVC. Such inconsistencies are listed via message
SLS6935E,SLS6936E, orSLS6938E.- NO
-
The inventory of an MVC is not to terminate when it encounters the first inconsistency between the contents of the MVC and the VTVs that the CDS indicates are on the MVC. This is the default.
- YES
-
The inventory of an MVC is to terminate when it encounters the first inconsistency between the contents of the MVC and the VTVs that the CDS indicates are on the MVC. This setting is invalid with
CDScheck(None).
Return Codes
The INVENTRY command includes the following return codes:
-
0indicates that all requested updates completed successfully. -
4indicates that one or more errors were found. Errors are listed via messageSLS6935E,SLS6396E,SLS6938E,SLS6939E,SLS6940EorSLS6941E. -
8indicates that one or more errors were found that are not specific toINVENTRYprocessing. For example,ECAMerrors.
Inventory Report
The following figure shows an example of an INVENTRY report produced by the following command:
INVENTRY MVC(021549)
In this example, the customer wishes to list all VTVs on MVC 021549 without cross-checking the VTVs found with the information recorded in the CDS.
In the sample output, each VTV found on the inventoried MVC is listed in message SLS6933I.
Inventry report for MVC 021549 SLS6933I MVC 021549 block 00000000: VTV Y00486 Created 2007Jul17 06:33:22 Migrated 2007Jul17 SLS6933I MVC 021549 block 05402F10: VTV Y00487 Created 2007Jul17 06:34:09 Migrated 2007Jul17 SLS6933I MVC 021549 block 0A405E1F: VTV Y00489 Created 2007Jul17 06:34:56 Migrated 2007Jul17 SLS6933I MVC 021549 block 0F408D2E: VTV Y00493 Created 2007Jul17 06:36:34 Migrated 2007Jul17 SLS6933I MVC 021549 block 10409E3C: VTV Y00492 Created 2007Jul17 06:35:46 Migrated 2007Jul17
LIBGen
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The LIBGen command decompiles the hardware configuration, VOLPARM, VAULT and LOGFILE information from the Control Data Set and creates a set of LIBGEN macros that reflects that information. The LIBGen decompile utility can be used to generate an initial set of LIBGEN macros that can be modified when you are adding new hardware to your installation that requires the creation of a new CDS.
Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring HSC and VTCS for detailed information about when to use this utility and how it functions.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-92, the LIBGen command includes the following parameters:
- TAPELESS
-
Optionally, provides a method to generate
CDSCREatsyntax from a CDS that currently contains library definitions, or to createLIBGENmacro syntax from a CDS currently defined as tapeless.- NO
-
Create
CDSCREatsyntax from a CDS that currently contains library definitions. - YES
-
Create
LIBGENmacro syntax from a CDS currently defined as tapeless.
If the
TAPEPLESSparameter is omitted, the default is based on the input CDS; that is, a tapeless CDS generatesCDSCREatsyntax and a CDS with library definitions generatesLIBGENmacro syntax. WhenTAPELESS(NO)is specified for a tapeless CDS, ACSs and LSMs must be defined prior to using theLIBGENmacros to define a new CDS.
Additional JCL Requirements
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statements apply to the LIBGen JCL:
- SLSLIBGN
-
output data set to accommodate the
LIBGENcreated by the utility.The data set has these characteristics:
LRECL=80, fixedblocked format (multiple of 80). The data set can be assigned to print or to output to a DASD. It may be assigned toDUMMYif only theSLSPRINToutput is desired. - SLSPARM
-
Output
VOLPARMcard images from CDS.SLSPARMis required whenVOLPARMrecords exist in the CDS. If theSLSPARM DDis not coded in the JCL, messageSLS0212Iis issued and the utility ends with a return code 4. - SLSSET
-
Output
CDSCREAT,SET VOLPARM,SET VAULTorSET VAULTVOL, and/orSET LOGFILEcontrol statements from the CDS. If theLIBGENutility attempts to output one of the above types of control statements and theSLSSET DDstatement is missing, a messageSLS0212Iis issued. If the statement to be produced isCDSCREAT, the utility terminates with a return code of 8; otherwise, processing continues and a return code of 4 is generated.
Output
LIBGen command output includes the following:
-
a valid
LIBGENfile matching the existing control data set. The output file has the following characteristics:-
All station and drive addresses are 4character addresses.
-
In cases where multiple parameters point to the same label statement, the utility duplicates the statement with a unique label and points each parameter to a different, although identical statement.
-
Labels generated in the output
LIBGENare listed in Table 3-6, below. -
If an
EJectpassword exists, it is not displayed. Instead, the following line is displayed:EJCTPAS=????????
-
-
messages associated with error conditions resulting from an unsuccessful execution of the utility.
Table 3-6 LIBGen Output Labels
| Device | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
ACS |
|
|
|
LSM |
|
|
|
STATION |
|
|
|
PANEL |
|
|
|
DRIVE |
|
|
LMUPDEF
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIB -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Description
The LMUPDEF command specifies the definition data set that contains network LMU attachment (LMUPATH) statements.
If a definition file is changed by a LMUPDEF operator command, and if the change is to be permanent, you must update PARMLIB before restarting the HSC.
If the definition file is to be modified for a given shift or application, remember that the new definition remains in effect until another definition is loaded or the HSC is recycled. The definition file then reverts to the PARMLIB specification. Thus, LMUPDEF can be used to temporarily change a definition file.
Note:
-
Definition commands issued on one host are in effect only on that host. If different hosts use the same definition data set, the
LMUPATHparameter statements are shared by those hosts. -
If you issue multiple
LMUPDEFcommands or statements, the last one processed is currently active. You can determine whichLMUPDEFstatement is active by entering theDisplay LMUPDEFcommand.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-93, the LMUPDEF command includes the following parameters:
- DATASET(dataset-name) or DSN(dataset-name)
-
specifies the name of the data set containing the
LMUPATHstatements to be processed and, optionally, anOPTION TITLEstatement.dataset-nameindicates the name of the data set containing theLMUPATHaddress parameters. If the data set name includes a member name,dataset.namemust be enclosed in quotes. For example:
DATASET(’YOUR.DSN(MEMBER)')
Note:
-
The definition data set may contain
VOLATTR,UNITATTR,TAPEREQ,LMUPATH, andOPTION TITLEstatements, but onlyLMUPATHandOPTION TITLEstatements are processed. -
If any other statement is encountered, an error message is issued and the statement is ignored.
-
See "OPTION TITLE Control Statement" for more information about the
OPTION TITLEcontrol statement.
- VOLume(volser)
-
optionally, specifies the serial number of the DASD volume on which the data set resides. This parameter is optional. Specify the
VOLumeparameter if the data set is not cataloged, or if a data set on a volume other than the volume indicated by the catalog is to be used.volserindicates the volume serial number for the definition data set. - UNIT(unit-name)
-
optionally, specifies the unit where the definition data set is located.
unit-nameindicates the unit name. If the definition data set is not cataloged and this parameter is omitted, a unit name ofSYSALLDAis the default. - HOSTID(host-id)
-
optionally, limits the execution of this control statement to the specified hosts. If one of the specified
host-ids matches the host executing this control statement, the control statement is executed for that host. Otherwise, it is ignored. If this parameter is omitted, the control statement is executed on all hosts.This parameter is valid only for use in
PARMLIB, so that multiple systems can share aPARMLIBmember containingTAPEREQ,VOLATTR,UNITATTR, orLMUPATHstatements for different releases of HSC. If entered from the console, messageSLS0018Iis issued.)hostidindicates the name of one or more hosts from which to execute this control statement. Multiple hosts must be separated by commas.
LMUPATH Control Statement
The LMUPATH control statement defines network LMU/Library Controller (LC) attachments. It is loaded by the LMUPDEF command.
Note:
If you are using the SL3000 or SL8500 partitioning feature, thePARTID parameter connects to a specific partition defined by the SL3000 or SL8500 library for the HSC host group. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring HSC and VTCS for information about how to use the partitioning feature.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-94, the LMUPATH control statement includes the following parameters:
- ACS(aa)
-
specifies the ACS name.
aaindicates the decimal ACSid value (00 through 99) to identify the LMU(s) used to communicate with a HSC. - LMUADDR
-
identifies an LMU/Library Controller (LC) by host name or IP address, for each ACS. To designate a single LMU/LC environment, specify one IP address or host name. To specify a dual LMU/LC environment or a dual IP connection to an SL8500, enter an additional IP address and/or host name.
The HSC automatically detects the type of connection, dual LMU for a 9330 or dual IP for an SL8500 library.
Users can intermix host name and IP addresses in one
LMUPATHcontrol statement. Each parameter entered must represent a different IP address.- lmu-hostname
-
a host name for the TCP/IP connection. The host name can be up to 24 characters long. The first character must be alphabetic.
- nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn
-
an IP address for the LMU/LC. A maximum of 40 IP addresses can be specified.
- PARTID(00n)
-
defines a partition ID for each ACS.
00nindicates a partition ID from 001 to 999.-
All three characters must be entered for the partition ID.
-
For this release, only IDs 001 through 008 are supported.
Note:
A partitioned SL3000 or SL8500 cannot use the multiple TCP/IP connection feature since partitioning applies only to a single SL3000 or SL8500 box. -
- PING(tt)
-
specifies the number of minutes in between requests sent from the HSC to the LMU. These requests are to keep the connection active, which prevents a firewall from closing the connection due to inactivity.
ttindicates the time in minutes from 00-99. The default is 5 minutes if this parameter is not defined, and entering 00 turns off this feature.
LOGUTIL
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The LOGUTIL command initiates the CDS recovery process for VTCS. It is used in the following scenarios:
-
The CDS has become unusable or corrupt and MVCs used since the date of the CDS backup need to be identified for
MVCAUDITpurposes. -
A VTSS has suffered a catastrophic data loss.
LOGUTIL calls the module that analyzes the input log files, and calls a recovery module to perform the appropriate recovery actions. Additionally:
-
The
LOGUTIL FOR_LOSTMVCstatement recovers VTVs that resided on a lost or damaged MVC. -
The
LOGUTIL GENAUDITstatement initiates a re-synchronization of the CDS to VSM viaMVCAUDITstatements. -
The
LOGUTIL_LOCATE_VTVstatement recovers older versions of VTVs. -
The
LOGUTIL UNDELETEstatement recovers deleted VTVs.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-95, the LOGUTIL command includes the following parameters:
- LOGDD(ddname)
-
specifies the DD name of the input log data sets.
ddnameindicates the DD name. - FROMDATE(yyyy-mm-dd)
-
optionally, specifies a starting date for logged events.
yyyy-mm-ddindicates the starting date.Note:
ForFROMDATEandFROMTIME, specify local dates/times as seen from the MVS system on whichLOGUTILruns.- FROMTIME(hh:mm:ss)
-
optionally, specifies a starting time for logged events.
hh:mm:ssindicates the starting time. The default is00:00:00.
- TODATE(yyyy-mm-dd)
-
optionally, specifies an ending date and time for logged events.
yyyy-mm-ddindicates the ending date.Note:
ForTODATEandTOTIME, specify local dates or times as seen from the MVS system on whichLOGUTILruns.- TOTIME(hh:mm:ss)
-
optionally, specifies an ending time for logged events.
hh:mm:ssindicates the ending time. The default is00:00:01.
- COMMANDS(ddname)
-
optionally, specifies the DD name of a data set that contains recovery commands.
ddnameindicates the DD name.
LOGUTIL FOR_LOSTMVC Statement
The LOGUTIL FOR_LOSTMVC statement recovers VTVs that resided on lost or damaged MVCs.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-96, the LOGUTIL FOR_LOSTMVC statement includes the following parameters:
- MVC(volser, volser-range, or volser-list)
-
specifies the MVC(s) to be recovered. You can specify a maximum of 1000 MVCs.
volser,volser-range, orvolser-listindicates the volser, volser range, or volser list to be processed. - VTV(volser, volser-range, or volser-list)
-
optionally, specifies specific VTV(s) to be recovered. You can specify a maximum of 300,000 MVCs.
Specified VTVs must reside on one or more of the recovery MVCs to be processed. When this parameter is coded, only VTVs specified are recovered (if they exist on the recovery MVCs).
volser,volser-range, orvolser-listindicates the volser, volser range, or volser list to be processed.This parameter behaves as a filter. If VTVs are specified that are not on the specified MVCs, they will not be recovered and will not be listed in the report output.
- SCRATCH
-
optionally, specifies to specify scratch VTVs. By default, scratch VTVs are not processed as part of the recovery.
- COMMANDS(ddname)
-
optionally, specifies the DD name of a data set that includes the recovery commands created when the
COMMANDSparameter is specified on theLOGUTILcommand.ddnameindicates the DD name.
LOGUTIL GENAUDIT Statement
The LOGUTIL GENAUDIT statement initiates a re-synchronization of the CDS to VSM through MVCAUDIT statements that are generated when the COMMANDS parameter is specified with the LOGUTIL command. The LOGUTIL GENAUDIT statement identifies MVCs for input to MVCAUDIT.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-97, the LOGUTIL GENAUDIT statement includes the following parameters:
- COMMANDS(ddname)
-
optionally, specifies the DD name of a data set that includes the recovery commands created when the
COMMANDSparameter is specified on theLOGUTILcommand.ddnameindicates the DD name.
The GENAUDIT COMMANDS parameter works with the LOGUTIL COMMANDS parameter as follows:
-
If you specify
LOGUTIL COMMANDS, theGENAUDITstatement outputs recovery commands to the specified data set even if you did not specifyGENAUDIT COMMANDS. -
If you specify
COMMANDSon bothLOGUTILandGENAUDIT, recovery commands are only output to theGENAUDIT COMMANDSdata set.
LOGUTIL LOCATE_VTV Statement
The LOGUTIL LOCATE_VTV statement recovers a non-current version of a VTV.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-98, the LOGUTIL LOCATE_VTV control statement includes the following parameters:
- VTV(volser, volser-range, or volser-list)
-
specifies specific VTV(s) to be recovered. You can specify a maximum of 1000 VTVs.
volser,volser-range, orvolser-listindicates the volser, volser range, or volser list to be processed. - COMMANDS(ddname)
-
optionally, specifies the DD name of a data set that includes the recovery commands created when the
COMMANDSparameter is specified on theLOGUTILcommand.ddnameindicates the DD name.The
LOCATE_VTV COMMANDSparameter works with theLOGUTIL COMMANDSparameter as follows:-
If you specify
LOGUTIL COMMANDS, theLOCATE_VTVstatement outputs recovery commands to the specified data set even if you did not specifyLOCATE_VTV COMMANDS. -
If you specify
COMMANDSon bothLOGUTILandLOCATE_VTV, recovery commands are only output to theLOCATE_VTV COMMANDSdata set.
-
- VERSION(-nn)
-
optionally, specifies the version of the VTV to recover.
-nnindicates the version. Valid values are -1 to -99. The default isVERSION(-1), which is one version older than the current version.Note:
VERSIONis mutually exclusive theDATEandTIMEparameters. - DATE(yyyy-mm-dd)
-
optionally, specifies the date of the VTV version to recover. If you specify
DATE, you must also specifyTIME.yyyy-mm-ddindicates the date, by year, month and day. - TIME(hh:mm:ss)
-
optionally, specifies the time of the VTV version to recover. If you specify
TIMEyou must also specifyDATE.hh:mm:ssindicates the time, in hours minutes and seconds.
LOGUTIL UNDELETE Statement
The LOGUTIL UNDELETE statement recovers deleted VTVs.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-99, the LOGUTIL UNDELETE control statement includes the following parameters:
- VTV(volser, volser-range, or volser-list)
-
specifies the VTV(s) to be recovered. You can specify a maximum of 1000 VTVs.
volser,volser-range, orvolser-listindicates the volser, volser range, or volser list to be processed. - COMMANDS(ddname)
-
optionally, specifies the DD name of a data set that includes the recovery commands created when the
COMMANDSparameter is specified on theLOGUTILcommand.ddnameindicates the DD name.The
UNDELETE COMMANDSparameter works with theLOGUTIL COMMANDSparameter as follows:-
If you specify
LOGUTIL COMMANDS, theUNDELETEstatement outputs recovery commands to the specified data set even if you did not specifyUNDELETE COMMANDS. -
If you specify
COMMANDSon bothLOGUTILandUNDELETE, recovery commands are only output to theUNDELETE COMMANDSdata set.
-
MEDVERfy
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Description
The MEDVERfy utility performs a Media Verification (MV) by verifying that VTV data can be read on MVCs or VMVCs (ELS 7.1 and VLE 1.2 and above only). For VLE, MEDVERfy ensures that deduplicated VMVCs can be ”rehydrated” (reconstituted).
The utility reports on MVCs that pass or fail verification and also produces XML output.
Parameters
The following three, mutually exclusive, keyword parameters identify the MVCs to be verified:
- MVCPOOL(name)
-
optionally, specifies an
MVCPOOLcontaining MVCs requiring data verification. An undefinedMVCPOOLvalue aborts the utility with RC 8.nameindicates the MVC pool name. - STORclas(name)
-
optionally, specifies a storage class for MVCs requiring data verification. Based on time of last verify and/or any frequency specified on the command, the utility selects the best MVC candidates for verification processing.
An undefined
STORclasvalue aborts the utility with RC 8.nameindicates the storage class name. - MVC(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
optionally, specifies a list or range of MVCs to be verified. For individual MVCs whose volser falls outside those defined in the CDS, the utility aborts with RC 8.
volser,vol-range, orvol-listindicates a volser, volser range, or volser list.Note:
Based on time of last verify and/or any frequency specified on the command, the utility selects the best MVC candidates, within the specified selection criteria, for verification processing. - MAXMVC(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum number of MVCs that will be processed by a single media verification task.
nnindicates the number of MVCs. Valid values are 1–99. If not specified, the default is 99. - CONMVC(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum number of MVCs that VTCS concurrently processes for media verification.
nnindicates the number of MVCs. Valid values are 1–99. If not specified, the default is 1. - FREQency(nnnn)
-
optionally, establishes the verification scheduling interval, in days, that MVCs are to be verified. To be selected for verification, the number of days since the MVC's last verify date must be greater than the number of days specified.
nnnnindicates the interval, in days. Valid values are 1-9999. There is no default. If not specified, the MVC's last verify date, alone, is used for selecting MVCs to verify. - TIMEOUT(nnnn)
-
optionally, specifies the allowable time, in minutes, for the media verification utility to run.
nnnnindicates the allowable time, in minutes. Valid values are 1-9999. There is no default. IfTIMEOUTis not specified, then there is no limit on utility run time.
Note:
Similar toRECLAIM processing, if any MVCs are being processed when the TIMEOUT value is reached, MEDVERfy completes processing on those MVCs, and then stops.MEDVERfy Reports
The following figure shows an example of a Media Verify report that indicates successful verification for MVC DMV100:
Example 3-49 MEDVERfy report (1 of 2)
Media Verify - -----------Media Verify request 6----------- Media Verify - 1 MVC(s) selected for processing MVC DMV100 - verifying media MVC DMV100 - verify complete No exceptions to report SLS0155I Condition code for utility function is 0
The report also lists MVCs not selected for MV processing under certain conditions. For example, in the following report, MVC DMV800 is skipped because it was mounted during verification selection:
Example 3-50 MEDVERfy report (2 of 2)
MEDVER MVC(DMV100,DMV800) CONMVC(1) TIMEOUT(180) MVC DMV800 skipped, is mounted Media Verify - -----------Media Verify request 21----------- Media Verify - 1 MVC(s) selected for processing MVC DMV100 - verifying media MVC DMV100 - verify complete No exceptions to report No exceptions to report SLS0155I Condition code for utility function is 0
MERGEcds
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE service level only
Description
Use the MERGEcds command to do the following:
-
Add or Change a configuration to reflect new ACSs or LSMs.
-
Consolidate multiple CDSs into one CDS.
-
Divide one CDS into multiple CDSs.
MERGEcdscopies volume information from each old CDS into the new CDS. -
Merge multiple ACSs into one ACS.
-
Divide one ACS into multiple ACSs.
-
Modify an ACSid and/or LSMid in order to renumber ACSs and LSMs.
-
Modify VTSS names.
-
Remove virtual or vault data from the CDS.
-
Change the number of slots reserved for vaulted volumes.
Note:
Before usingMERGEcds, refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring HSC and VTCS for detailed procedures used to run the utility.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-101, the MERGEcds command includes the following parameters:
- VALIDate
-
optionally, specifies to only validate that the configurations to be reconfigured or merged are compatible, but not perform the operation.
MERGEcds VALIDatereports any duplicate, in-transit, and errant volumes. - ALL
-
optionally, specifies to copy volume information for all ACSs and VTSSs from the "from" CDS to the "to" CDS. You can also specify the
ALLparameter to convert a CDS to extended format.-
For a CDS merge, the ACS ID and LSM IDs, and VTSS names must match.
-
If you are using VTCS, MVCs that are in the source (input) CDS but are not configured in the target (output) CDS, must be empty. An MVC is considered empty if it contains no current VTVs and, if previously used, has been drained.
Note:
ALLandSLSMERGE DDare mutually exclusive. If you do not specifyALL,MERGEcdsreads the parameters specified on theSLSMERGEcontrol statement. These parameters specify the ACSs, LSMs, VTSSs, and Vaults whose volume information you want to merge or reconfigure. See "SLSMERGE Control Statement" for more information. -
- DELVirt
-
optionally, specifies that VTV and MVC volume information is not copied to the ”to” CDS if both of the following are true:
-
The VTVs and MVCs defined in the "from" CDS are either uninitialized or empty.
An empty VTV is not VTSS resident and has no current MVC copies. An empty MVC contains no current VTVs and does not have an assigned
STORCLAS. An MVC is empty when%USEDis0%and%AVAILis100%on an MVC Report orQ MVCdisplay.Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Managing HSC and VTCS for instructions for removing MVCs from the pool.
-
The uninitialized or empty VTVs and MVCs in the "from" CDS are not defined in the "to" CDS. That is, no duplicate volsers exist.
DELVirthas no effect unlessALLVIRTis specified on theSLSMERGEcontrol statement. -
- NOMSG
-
optionally, suppresses message
SLS4245I, which displays the volser of an MVC or VTV that was not copied to the ”to” CDS.NOMSGhas no effect unlessDELVirtis specified on theMERGECDScontrol statement andALLVIRTis specified on theSLSMERGEcontrol statement.
Additional JCL Requirements
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statements apply to the MERGEcds JCL:
- SLSFCNTL
-
specifies the current primary copy of the ”from” HSC CDS.
- SLSFCTL2
-
specifies the secondary copy of the CDS, if one is defined.
- SLSFSTBY
-
optionally, specifies the standby copy of the CDS, if one is defined.
Note:
If more than one of these statements are present, HSC determines the primary CDS from the Database Heartbeat (DHB) record of the ”from” CDS. The ”from” CDS is not modified. If a single CDS (SLSFCNTL) is specified, ensure that it is the primary CDS. No DHB validation occurs.SLSMERGE Control Statement
The SLSMERGE control statement specifies the "from" and "to" ACSs, LSMs, or Vaults to use for a merge, and enables you to rename a VTSS in the Resident VTSS field.
Note:
-
The
SLSMERGEcontrol statement is optional and is mutually exclusive with theMERGEcds ALLparameter. -
If you use
SLSMERGEcontrol statements, you must includeMERGEstatements that account for all data in the ”from” CDS.For example, if your ”from” CDS contains real, virtual, and vault data, you must supply a control card for each of these types to specify whether they are to be copied to the ”to” CDS. If you do not want a particular type of data to be copied to the ”to” CDS, issue the appropriate
NOparameter (NOREAL,NOVIRT, orNOVALT) to exclude it.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-102, the SLSMERGE control statement includes the following parameters:
Caution:
The ”real” parameters (FACS, TACS, FLSM, TLSM) and ”vault” parameters (FVAULT, TVAULT) act as selection criteria, while the ”virtual” parameters (FVTSS, TVTSS) act only as rename criteria.Parameters (Real Volumes)
For REAL volumes, the following parameters apply:
- FACS(acs-id)
-
specifies the ”from” ACS.
- TACS(acs-id)
-
specifies the ”to” ACS.
- FLSM(lsm-id)
-
specifies the ”from” LSM.
- TLSM(lsm-id)
-
specifies the ”to” LSM.
- ALLREAL
-
Merge all real data only.
- NOREAL
-
Do not merge real data.
Parameters (CDS Containing Virtual Data)
If the CDS contains VIRTUAL data, the following parameters apply:
- FVTSS(vtss-name)
-
specifies the ”from” VTSS name.
- TVTSS(vtss-name)
-
specifies the ”to” VTSS name.
You cannot use
MERGEcdsto remove data for certain VTSSs from the CDS.FVTSSandTVTSSact only as rename criteria. When these parameters are specified,ALLVIRTis implied.For example:
MERGE FVTSS(VTSS18) TVTSS(VTSS17)In this example, all VTV records are copied to the new CDS, but the Resident VTSS field is changed from
VTSS18toVTSS17. All VTSSs not specified in these statements are automatically merged to the same-named VTSS in the new CDS. - ALLVIRT
-
Merge all virtual data only.
- NOVIRT
-
Do not merge virtual data.
MERGMFST
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The MERGMFST command merges multiple manifest files produced by EXPORT into a single file.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-103, the MERGMFST command includes the following parameters:
- MERGEIN(manifin)
-
specifies the DD statement for one or more input manifest files.
manifinindicates the DD name. - MERGEOUT(manifout)
-
specifies the DD statement for the merged manifest file.
manifoutindicates the DD name.
Additional JCL Requirements
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statements apply to the MERGMFST JCL:
- manifin DD
-
DD statement for the input manifest file(s).
- manifout DD
-
DD statement for the merged manifest file.
METAdata
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Description
The METAdata command displays XML tags associated with a function that produces XML output.
Note:
No text output is produced by theMETAdata command. If neither XML nor CSV output is requested, the command will not produce any output.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-104, the METAdata command includes the following parameters:
- command-name
-
The command for which metadata is to be produced.
When the command contains "two parts" such as
Display Volume, both portions should be entered. TheMETAdatacommand uses the same abbreviations for thecommand-nameas the command itself, for example:METAdata D V
Tags Produced
The METAdata command itself does not support metadata.
The following tags are produced by the METAdata command:
- <command_name>
-
The full name of the command.
- <security_level>
-
Required security level if command authorization is in effect. Values are
QUERY,SET, andADMIN. - <command_tags>
-
Header tag for all XML tags.
The following tags are produced by the METAdata command:
- <tag_data>
-
Header tag for each XML tag.
- <tag_name>
-
The XML tag name, for example, volser.
- <tag_type>
-
Values are header (header XML tag), data (XML data tag, normally associated with a value), and trailer (indicates the position of the trailer tag associated with a header tag).
- <occurrences>
-
The maximum number of expected occurrences, for tags that may occur multiple times. This may be either a numeric value or "unlimited."
The following tags are produced by the METAdata command:
- <data_type>
-
Indicates the type of data expected in the tag value. Produced only for data tags. Values include: char, numeric, flag, hex, date, time.
- <maximum_size>
-
Indicates the maximum output data size.
MGMTDEF
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Description
The MGMTDEF command loads the following control statements from a specified definition data set:
-
MGMTclas -
MIGRSEL -
MIGRVTV -
MVCATTR -
STORclas -
STORLST -
STORSEL -
VTSSLST -
VTSSSEL
Note:
When HSC/VTCS is active and theMGMTDEF command is issued to re-load MGMTclas control statements, the 'changed' control statements only affect newly created VTVs. Additional action is required to apply the changes to existing VTVs.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-105, the MGMTDEF command includes the following parameters:
- DATASET(dataset-name) or DSN(dataset-name)
-
specifies the definition data set that contains the
MGMTclasandSTORclasstatements to load.dataset-nameindicates the data set name. - VOLume(volser)
-
optionally, specifies the DASD volume where the definition data set resides. This parameter is optional, unless the data set is not cataloged, or the data set resides on a volume other than the volume indicated by the catalog.
volserindicates the DASD volser. - UNIT(unitname)
-
optionally, specifies the DASD device where the definition data set resides.
unitnameindicates the DASD unit name. If the definition data set is not cataloged and this parameter is omitted, the unit name defaults toSYSALLDA. - HOSTID(host-id)
-
optionally, specifies the host for execution of the
MGMTDEFcommand. This parameter is only valid whenMGMTDEFis specified as aPARMLIBcontrol statement.host-idindicates the name of one or more hosts from which to execute theMGMTDEFcommand. Multiple hosts must be separated by commas.
MGMTclas Control Statement
The MGMTclas control statement defines a VSM Management Class. It is loaded by the MGMTDEF command.
Note:
-
By default, advanced VSM management features are automatically enabled. The
FEATurescommand, included in previous ELS releases to enable these features, is no longer valid. -
ELS includes parameters designed to improve migration control. If you choose not to use these features, refer to Oracle's ELS publication Legacy Interfaces Reference for information about existing legacy
MGMTclasparameters. -
When HSC/VTCS is active and the
MGMTDEFcommand is issued to re-loadMGMTclascontrol statements, the 'changed' control statements only affect newly created VTVs. Additional action is required to apply the changes to existing VTVs.For example, If you change the
IMMDELAYvalue, you must recycle the HSC to apply the change to existing VTVs. If you change theMIGpolvalue from one storage class to two, you must recall the VTV to allow for creation of the second migrated copy.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-106, the MGMTclas command includes the following parameters:
- NAME(mgmt-class-name)
-
specifies the name of the Management Class.
mgmt-class-nameindicates the Management Class name. This name must be one to eight alphanumeric characters beginning with an alpha character and must follow SMS naming conventions. - ACSlist(acs-id or acs-id,acs-id)
-
optionally, specifies the ACSs from which RTDs and MVCs are selected. If not specified, the default is the ACS specified on the
CONFIG DEFLTACSparameter.See DUPlex, below, for information about using the
DUPlexandACSlistparameters.acs-idoracs-id,acs-idindicates either one or two ACS IDs. An ACSid is a two digit decimal ACS identifier from 00-99. - ARCHAge(nnn)
-
optionally, specifies the age (in days) of a VTV before it is archived as specified by
ARCHPol. If you specifyARCHAge, you must specifyARCHPol.This parameter is optional; there is no default value. Valid values are 1 to 999.
nnnindicates the VTV age in days. - ARCHPol(stor-class-name or stor-class-list)
-
optionally, specifies up to four Storage Classes that specify the ACS and media type of the archive MVCs. If you specify:
-
If you specify one Storage Class, VTCS archives one copy of a VTV.
-
If you specify multiple Storage Classes (with different
ACSvalues, differentMEDIAvalues, or both), VTCS archives multiple copies of the VTV to different MVCs in different ACSs. -
If you specify multiple Storage Classes with identical
ACSandMEDIAvalues, VTCS archives multiple copies of the VTV to the same ACS and media type but to different MVCs.
Note:
Multiple Storage Classes onARCHPolalso affects how VTV recall, MVC space reclamation, and VTV consolidation function.This parameter is optional; there is no default value. If you specify
ARCHPol, you must specifyARCHage.stor-clas-name1...stor-clas-namenindicates the names of one or more Storage Classes that you defined on theSTORclascontrol statement. Greater than two copies requires you to specifyCDSLEVEL(V6ABOVE)orCDSLEVEL(V6ABOVE)on theCONFIGstatement. -
- CONSRC(stor-class-name)
-
optionally, specifies the Storage Class that species a preference for the source MVC ACS and media for consolidation of VTVs that are migrated and copied to multiple MVC locations or media types. If the MVC in the specified Storage Class is unavailable, and the specified Storage Class is not the last (in order specified in the migration policy), VTCS uses the MVC associated with the last Storage Class. If the MVC in the specified Storage Class is unavailable and the specified Storage Class is the last (in order specified in the
MIGpolparameter), VTCS uses the MVC associated with the previous Storage Class (in order specified in theMIGpolparameter).stor-class-nameindicates the name of a Storage Class that you defined on theSTORclascontrol statement. - CONTGT(stor-class-name)
-
optionally, specifies the Storage Class that determines the output MVC ACS and media for VTV consolidation (executing
CONSolid,EXPORT VTVorEXPORT MGMTclas). Note that the media preferencing is in the opposite order of the list of media types specified on the Storage Class.This parameter is optional; there is no default value. If you do not specify a value for
CONTGT, VTCS selects the output MVC as follows:-
For single-ACS and dual-ACS configurations, the media selection order for VTV consolidation.
-
For multiple ACS systems, VTCS selects MVCs from the default ACS specified by the
CONFIG DEFLTACSparameter.
stor-class-nameindicates the name of a Storage Class that you defined on theSTORclascontrol statement. -
- DELSCR
-
optionally, specifies whether VSM deletes scratched VTVs.
- NO
-
Do not delete scratched VTVs (the default).
- YES
-
Delete scratched VTVs unless this would cause a processing delay due to unavailable resources.
- FORCE
-
Delete scratched VTVs and wait for access to any resources that are required. This may cause a processing delay.
Caution:
When you scratch a VTV withDELSCR YESattribute, VSM erases the VTV data at scratch synchronization time, which eliminates the ability ”unscratch” a VTV to recover data!Also note that when using HSC to perform scratch synchronization, it is possible that a volume that is scratch in the TMC at the beginning of scratch synchronization run and also scratch in the CDS from the previous scratch update run (and thus is in the list for HSC to scratch in the CDS) is accessed by a job during the scratch update run and written to and made non-scratch by the TMS in the TMC. In this case, it is still possible for HSC to scratch the volume because it was in the originally extracted list of volumes to be scratched. Therefore, Oracle strongly recommends that you do not run any jobs that use scratches during HSC scratch synchronization.
See "Scratch Conversion Utility (SLUCONDB)" for more information about HSC scratch synchronization with the Scratch Conversion Utility (
SLUCONDB).Refer to the LCM User's Guide for more information about LCM scratch synchronization with the
SYNCVTVfunction. - DISCARD(nnnn)
-
optionally, specifies the discard time in hours. This value represents the time after a VTV is dismounted that the VTV is kept in the buffer. After this time value expires, the VTV is preferred for deletion from the VTSS buffer if all required copies of the VTV exist on MVCs.
nnnnindicates the time in hours. Valid values are 0 to 9999. The default is 9999.When
IMMEDmigis specified,DISCARDis not used for immediate migration processing. It is only applicable forAUTOmigration requests. IfRESTIMEis also specified for a VTV, it overrides theDISCARDvalue. - DUPlex
-
optionally, specifies whether VSM will migrate two copies of the VTV to two MVCs.
DUPlexandMIGpolare mutually exclusive.- NO
-
Do not duplex the VTV (the default).
- YES
-
Duplex the VTV.
The following table describes possible scenarios using the
DUPlexandACSlistparameters:Table 3-7 MGMTclas ACSlist/DUPlex Scenarios
DUPlex Setting ACSlist Setting Action YEStwo ACSs
VSM migrates the VTVs to two MVCs, one in each ACS. (This scenario is the normal one for duplexing to two ACSs.)
YESone ACS
VSM migrates the VTVs to two MVCs in the ACS specified.
NOtwo ACSs
VSM ignores the
DUPlexpolicy and migrates the VTVs to two MVCs, one in each ACS.NOone ACS
VSM migrates the VTVs to one MVC in the ACS specified.
- MIGpol(s1 or s1,s2 or s1,s2,s3 or s1,s2,s3,s4)
-
optionally, specifies up to four Storage Classes that specify the ACS and media type of migration MVCs.
DUPlexandMIGpolare mutually exclusive.-
If you specify one Storage Class, VTCS migrates one copy of a VTV.
-
If you specify multiple Storage Classes (with different
ACSvalues, differentMEDIAvalues, or both), VTCS makes multiple copies the VTV to different MVCs in different ACSs. -
If you specify multiple Storage Classes with identical
ACSandMEDIAvalues, VTCS makes multiple copies of the VTV to the same ACS and media type but to different MVCs.
Note:
Multiple Storage Classes onMIGpolalso affects how VTV recall, MVC space reclamation, and VTV consolidation function.This parameter is optional; there is no default value.
s1ors1,s2ors1,s2,s3ors1,s2,s3,s4indicates the names of up to 4 Storage Classes that you defined on theSTORclascontrol statement. Greater than two copies requires you to specifyCDSLEVEL(V61ABOVE)or greater on theCONFIGstatement.Note:
TheCONFIG GLOBAL REPLicatparameter specifies when to replicate a VTV (always, or only when changed while mounted). -
- EEXpol(s1 or s1,s2)
-
optionally, specifies the storage classes for electronic export.
s1ors1,s2indicates a maximum of two Storage Classes that specify theTAPEPLEXparameter. If these storage classes do not specify theTAPEPLEXparameter, an error condition results.-
If there are two
TAPELEXstorage classes, then they must specify different destination TapePlex names. -
A warning will be generated if the two TapePlex storage classes are specified with the
SYNC=YESparameter. It is only possible to synchronously export to one other TapePlex. -
If there is a conflict, electronic export functionality takes precedence over replication with a cluster.
-
If either one of the storage classes referenced contains the
THISPLEXname, then the storage class is silently ignored. This enables common storage class definitions to be applied across TapePlexes.
-
- IMMDELAY(nnnn)
-
optionally, specifies the immediate migration delay time; the amount of time after VTV dismount that the migration should be queued for action.
This enables VTVs used in multi-step jobs to remain resident for a specified time before being processed for migration.
nnnnindicates the immediate migration delay time in minutes. Valid values are 0 to 9999 (the default).If
IMMDELAY=9999then immediate migration does not occur. Migration and deletion is handled through auto or command migration.When this value is specified,
MIGRSELandMIGRVTVhave no influence on migration control.RESTIMEandDISCARDparameter values represent buffer management priorities:-
If the
IMMDELAYvalue is less than theRESTIMEvalue, keep the VTD in the VTSS as a priority. -
If the
IMMDELAYvalue is greater than theRESTIMEvalue but less than theDISCARDvalue, manage the buffer according to LRU (default state). -
If the
IMMDELAYvalue is greater than theDISCARDvalue, remove the VTD from the VTSS as a priority.
The
IMMDELAYparameter is designed to replace theIMMEDmigparameter, described in Oracle's ELS publication ELS Legacy Interfaces Reference. These parameters are mutually exclusive. The following table describes equivalent values:Table 3-8 IMMDELAY and IMMEDmig Equivalent Values
IMMDELAY or DISCARD Values Equivalent IMMEDmig Value Action IMMDELAY(1-9998)NoneDelay migration for the specified number of minutes.
IMMDELAY(9999)IMMED(NONE)VSM does not immediately migrate the VTV, but migrates it according to standard VSM migration criteria.
MIGRSELandMIGRVTVhave no influence on migration control.IMMDELAY(0)DISCARD(9999)IMMED(KEEP)VSM immediately migrates a VTV and keeps a copy resident on the VTSS until the VTV becomes eligible for deletion.
IMMDELAY(0)DISCARD(0)IMMED(DELETE)VSM immediately migrates the VTV and then deletes it from the VTSS.
Note:
If you specifyREPlicat YESorYES_SYNC, VTCS defaults toIMMDELAY 0. If you specifyREPlicat YESorYES_SYNCin combination withIMMDELAY 9999, VTCS ignores theIMMDELAYparameter without issuing a message. For example:MGMT NAME(REPIMNO) REP(YES) IMMDELAY(9999)causes VTCS to use
IMMDELAY 0and perform immediate migration. To suppress immediate migration, add aMIGRVTV MGMTclas(x)IMMDELAY(9999)statement for the management class. See "MIGRVTV Control Statement" for more information. -
- MAXVtvsz
-
optionally, specifies the maximum size for VTVs in this Management Class. Valid values for this parameter depend on both the CDS level and the microcode levels of the applicable VTSSs.
- 400
-
400 MB. This is the default.
- 800
-
800 MB. The CDS must be at a E level or above.
- 2000
-
2 GB. The CDS must be at a G level or above.
- 4000
-
4 GB. The CDS must be at a G level or above.
Considerations:
-
The size of a VTV changes only after it goes through a scratch cycle. Therefore, if you change the Management Class and
DISP=MOD, then it will still retain the original size. -
If you specify a VTV size that is not supported by the configuration, VTCS issues warning messages and
MAXVtvszdefaults to the largest VTV size supported by the configuration. -
MAXVtvszdoes not apply to VSM2s. -
MAXVTVSZ(2000 | 4000)requires VSM4 or VSM5 microcode D02.02.00.00 or VSM3 microcode N01.00.77.00. No installed option is required.
- NOMIGRAT
-
optionally, specifies that VTVs in the Management Class are not candidates for migration, consolidation or export, but are candidates to reside on a tapeless VTSS.
VTSS selection is changed to prefer tapeless VTSSs for VTVs in Management Classes with
NOMIGRAT, and to disallow VTVs withoutNOMIGRATfrom VTSSs with no RTDs.NOMIGRATis mutually exclusive withACSLIST,IMMDELAY,DUPLEX,MIGPOL,ARCHAGE,ARCHPOL,RESTIME,CONSRCandCONTGT. - REPlicat
-
optionally, specifies whether VSM replicates the VTV.
Synchronous replication must be enabled through the
CONFIG GLOBAL SYNCHREPparameter. For more information, see "CONFIg GLOBAL Statement".If you specify
REPlicat YESorYES_SYNC, VTCS defaults toIMMDELAY 0. If you specifyREPlicat YESorYES_SYNCin combination withIMMDELAY 9999, VTCS ignores theIMMDELAYparameter without issuing a message. For example:MGMT NAME(REPIMNO) REP(YES) IMMDELAY(9999)causes VTCS to use
IMMDELAY 0and perform immediate migration.To suppress immediate migration, add a
MIGRVTV MGMTclas(x) IMMDELAY(9999)statement for the management class. See "MIGRVTV Control Statement" for more information.- NO
-
Do not replicate the VTV (the default).
- YES
-
Asynchronously replicate the VTV.
- YES_SYNC
-
Synchronously replicate the VTV.
- RESTIME(nnnn)
-
optionally, specifies how long VTCS attempts to keep a VTV as VTSS-resident before becoming a preferred automatic migration candidate.
This parameter is optional; there is no default value. Valid values are 1 to 9999. Value 9999 specifies that the VTVs in this Management Class are resident permanently unless VTSS space management requires VTCS to automigrate the VTV and then delete it from the VTSS.
nnnnindicates the residency time in hours.RESTIMEandIMMEDmig(DELETE)are mutually exclusive.RESTIMEtakes effect when a VTV is created, and does not apply to a recalled VTV. - VTVPAGE
-
optionally, specifies that the page size used to store VTV data in the VTSS and on the MVCs. This setting only applies to 400 MB and 800 MB VTVs. If
VTVPAGEis not specified on either theMGMTclasstatement or theCONFIG GLOBALstatement, the default isSTANDard.- STANDARD
-
standard page size, which is compatible with all VSM3 or VSM4 models and microcode levels.
- LARGE
-
large page size, which can provide improved performance within the VTSS and for migrates and recalls. Large page size requires a G level CDS. For more information on CDS levels, see "CONFIg". For 2 GB VTVs or 4 GB VTVs (
MAXVtvsz2000or4000), aVTVPAGEsetting ofLARGEis always used.
Considerations:
-
VTVPAGEdoes not apply to VSM2s.VTVPAGE(LARGE)requires VSM4 or VSM5 microcode D02.02.00.00 or VSM3 microcode N01.00.77.00. No installed option is required. -
MGMTCLAS VTVPAGE, if specified, overrides theCONFIg GLOBAL VTVPAGEvalue. IfVTVPAGEis not specified on either theMGMTclasstatement or theCONFIgGLOBALstatement, the default isSTANDard. -
The page size of a VTV can only be changed by a VTV scratch mount. Additional restrictions may also apply for scratch VTVs that were previously resident in a VTSS.
-
If you specify
LARGEand the CDS level and/or VTSS microcode do not supportLARGE, VTCS issues warning messages andVTVPAGEdefaults toSTANDard. -
If you specify
STANDardfor 2 GB or 4 GB VTVs VTCS issues warning messages and defaults toLARGE. -
Creating VTVs with large pages makes these VTVs unreadable in configurations that do not support large VTV pages.
-
The
VTVPAGEvalued specified for this Management Class overrides the global value specified on theCONFIgutility.
- WRITE
-
optionally, specifies the VTSS-resident VTV
VOLSAFEpolicy as follows:- MANY
-
specifies no
VOLSAFEwrite protection. This is the default. - ONCE
-
specifies partial (write once)
VOLSAFEprotection. After the VTV is non-scratch, it cannot be overwritten or appended while it is VTSS-resident. - APPEND
-
specifies full
VOLSAFEprotection. This is only supported for VSM6 systems.-
VTV data can be appended once non-scratch.
-
Data cannot be overwritten.
The
Display VTVcommand andVTVRPTreport will indicate that the VTV is write-append protected.VTVs with full
VOLSAFEprotection can only be scratched withRACF ALTERauthority. Use the following RACF commands to set RACF authority:RDEFINE TAPEVOL volser UACC(NONE) PERMIT volser CLASS(TAPEVOL) ID(userid) ACCESS(ALTER)
-
- EDLTeexp
-
optionally, specifies whether pending Electronic Export VTVs are candidates for early deletion. The VTVs will only be deleted if all CLINKs to the remote Tapeplex are not operational. The
EDLTeexpoption requires that theEEXPOLandMIGPOLpolicies be set for the management class.Note:
For the early delete VTVs to be electronically exported, you must run the VTCSRECONCILutility after the remote Tapeplex CLINKs are variedONLINE.
MIGRSEL Control Statement
The MIGRSEL control statement controls migration request settings for a Storage Class, VTSS, and/or host. It is loaded by the MGMTDEF command.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-107, the MIGRSEL control statement includes the following parameters:
- STORclas(stor-clas-name)
-
optionally, specifies a Storage Class to which the migration settings apply. If you do not specify a Storage Class, the statement applies to all Storage Classes.
stor-clas-nameindicates the Storage Class name you defined on aSTORclascontrol statement. - VTSS(vtssname)
-
optionally, specifies a VTSS to which the migration settings apply. If you do not specify a VTSS, the statement applies to all VTSSs.
vtssnameindicates the VTSS name. - HOST(host-id)
-
optionally, specifies one or more hosts to which the migration settings apply. Any hosts not specified on this parameter ignore the settings. If you do not specify one or more hosts, the settings apply to all hosts.
host-idindicates a host identifier (maximum 8 characters). - FUNCtion
-
optionally, specifies the type of migration to which the settings apply:
- IMMED
-
migrations resulting from either of the following:
-
MGMTclas IMMEDmig(KEEP) -
MGMTclas IMMEDmig(DELETE)
-
- AUTO
-
automatic migrate to threshold migration processing.
- RECLAIM
-
migrations resulting from
MVC DRAINorRECLAIMrequests. - DEMAND
-
migrations resulting from a
MIGRATEcommand or utility (demand migrations).
- IMMWAIT(nnn)
-
optionally, makes the
MIGRSELrule sensitive to the state of the current immediate migration work load. The specified value provides an immediate migration wait time or age, in minutes, that thisMIGRSELmigration rule will apply to. This value is compared against the amount of time VTVs have been waiting for immediate migration to a particular storage class. If the amount of time (minutes) that VTVs have been waiting is less than or equal to theIMMWAITvalue theMIGRSELrule will apply.nnnindicates the immediate migration wait time or age, in minutes. Valid values are 0 to 999. The default is 999.-
The default value of 999 makes the rule apply to all VTV wait times.
-
A value of zero is used for applying
MIGRSELrules if immediate migration is not active.
-
- SCHPREF(n)
-
optionally, preferences automatic and immediate migration per storage class.
MIGRSEL VTSSandHOSTallow you to specify the VTSS and host to which the preferencing applies.nindicates the preferencing value. Valid values are 0 to 9. The default is 0.-
Higher values can produce quicker migration times, but may not optimize MVC usage.
-
Lower values may produce slower migration times, but may optimize MVC usage.
The
MIGRSEL SCHPREFsetting may be affected by the number of RTDs available, theSCHLIMITsetting, and theGLOBAL MAXMIGparameter for the VTSS. -
- SCHLIMIT(nn)
-
optionally, de-preferences migration per Storage Class.
nnindicates the preferencing value. Valid values are 0 to 99. The default is 99, which indicates no limit, up to theVTSS MAXMIGvalue.Lower values de-preference migration, and you can specify automatic, immediate, demand, and reclaim migrates. Lower values can do the following:
-
Optimize MVC usage.
-
Preference migration to other Storage Classes.
-
Limit migration to keep RTDs available for auto recalls.
-
Reduce MVC swapping when workloads change.
For auto and immediate migration processing,
MIGRSEL SCHLIMITde-preferences migration for the VTSS to storage class relationship. This comparison is not global and only effects requests driven by the individual VTCS host.For demand migration requests,
MIGRSEL SCHLIMITwill cause the request to be held if the scheduling of it would cause the number of globally active migration requests on the VTSS that satisfy the sameFUNCTIONandSTORCLASselection criteria to be exceeded. The migration requests will be released and an MVC picked once the constraint subsides. -
MIGRVTV Control Statement
The MIGRVTV control statement controls individual VTV copies processed by immediate migration. It is loaded by the MGMTDEF command.
This statement defines how the behavior of an individual immediate migrate should be modified depending upon various environmental considerations. The MIGRVTV rules are searched for each immediate migrate instance of a VTV. The first match found for each instance is used to modify the immediate migrate.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-108, the MIGRVTV control statement includes the following parameters:
- MGMTclas(mgmt-clas-name)
-
optionally, specifies a Management Class to which the migration settings apply. If you do not specify a Management Class, the statement applies to all Management Classes.
mgmt-clas-nameindicates the name of a Management Class you defined on the MGMTclas control statement. - VTSS(vtssname)
-
optionally, specifies a VTSS to which the migration settings apply. If you do not specify a VTSS, the statement applies to all VTSSs.
vtssnameindicates the VTSS name. - STORclas(stor-clas-name)
-
optionally, specifies a Storage Class to which the migration settings apply. If you do not specify a Storage Class, the statement applies to all Storage Classes.
stor-clas-nameindicates the name of a Storage Class you defined on theSTORclascontrol statement. - INDEPEND
-
Affected VTVs are independent of any other VTV migrate instance. This is the default and applies to any migrates that do not match a
MIGRVTVrule or any rule without anINITIALorSUBSEQNTparameter. - INITIAL
-
Affected VTV migrates are scheduled and performed before any migrate instances that match to a rule with the
SUBSEQNTparameter. - SUBSEQNT(timeout)
-
Affected VTV migrates are scheduled and performed after any migrate instances that match to a rule with the
INITIALparameter.timeoutindicates the time in minutes after which the rule expires. This is in addition to anyIMMDELAYvalue applied to theINITIALmigrate instances. - IMMDELAY(time)
-
optionally, specifies the immediate migration delay time; the amount of time after VTV dismount that the migration should be queued for action. This enables VTVs used in multi-step jobs to remain resident for a specified time before being processed for migration.
This
IMMDELAYparameter may be used to override theIMMDELAYvalue in the management class definition for the VTV as a whole. If the delay exceeds theDISCARDvalue in the management class, then the migrate will cause an implicit deletion of the VTV copy from the source VTSS.If a delay time of 9999 is specified by this parameter or the
IMMDELAYparameter in the management class, then the specific migrate instance is deleted and must later be serviced using auto/command migration.nnnnindicates the immediate migration delay time in minutes. Valid values are 0 to 9999 (the default).Considerations:
-
If
IMMDELAY=9999then immediate migration does not occur. Migration and deletion is handled via auto/command migration.When this value is specified,
MIGRSELandMIGRVTVhave no influence on migration control. -
If
IMMDELAY=0then immediate migration is scheduled immediately. -
If
IMMDELAYis less than 9999 andDISCARDis greater thanIMMDELAYthen immediate migration occurs and deletion is deferred to auto/command migration. -
If
IMMDELAYis less than 9999 andDISCARDis less than or equal toIMMDELAYthen immediate migration and immediate deletion occur together. -
If auto migration encounters a VTV that has passed its
DISCARDtime, the VTV is moved to the front of the migration queue, and it will be processed first.
-
MVCATTR Control Statement
The MVCATTR control statement assigns a swap-to RTD device type to an MVC media name. When an error occurs while reading an MVC on an RTD, VTCS may swap the MVC to another RTD to retry the operation.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-109, the MVCATTR control statement includes the following parameters:
- MEDIA(media-name)
-
specifies the MVC media name to which the attribute is assigned. Only one
MVCATTRshould be coded for eachmedia-name.media-nameindicates the MVC media name. See Table 3-9. - SWAPTO(device-type)
-
defines the RTD device type the MVC is swapped to (if possible).
device-typeindicates the RTD device type. See Table 3-9.
Table 3-9 Valid MVC Media Names and Compatible SWAPTO RTD Device Types
| Valid MEDIA Names | Compatible SWAPTO Device Types |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
STORclas Control Statement
The STORclas control statement defines a VSM Storage Class. It is loaded by the MGMTDEF command.
This statement can specify whether a VTV copy is to be written to:
-
An MVC (with required attributes)
-
The name of a remote TapePlex to which a copy of the VTV is to be exported. It also specifies whether a storage class uses partitioned media.
-
The subsystem name of a VLE.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-110, the STORclas control statement includes the following parameters:
- NAME(stor-clas-name)
-
specifies the name of the Storage Class.
stor-clas-nameindicates the Storage Class name. This name must be 1 to 8 alphanumeric characters beginning with an alpha character and must follow SMS naming conventions. - ACS(acs-id)
-
optionally, specifies the ACSs from which RTDs and MVCs are selected.
acs-idindicates a two digit decimal ACS identifier from 00-99. - STORMNGR(name)
-
optionally, specifies one of the following:
-
VLE subsystem name
-
remote library
nameindicates the Storage Manager name:-
For VLEs, this value must match the VLE Subsystem Name.
-
For remote libraries, this value must match a TapePlex name defined on the SMC
TAPEPLEX NAMEparameter.
For more information, refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring the Host Software for VLE.
You can specify both
STORMNGRandACSparameters to restrict selection of MVCs to the library in the remote TapePlex with the designated ACS number.- VLEDELET
-
optionally, control when deletion of the VTV from the VLE occurs.
- DELAY
-
The deletion of the VTV from the VLE will be delayed until the vMVC is mounted for migration.
DELAYis the default. - RECLAIM
-
The deletion of the VTV from the VLE will be done when the
RECLAIMutility is run against the vMVC.
Caution:
The current CDS backup can no longer be used as a DR baseline for vMVC content if you use theDRCHKPTutility and/or theCONFIG RECLAIM PROTECTparameter to protect CDS backup content for vMVCs, and thenRECLAIMa vMVC for aSTORCLASthat specifiesVLEDELET(RECLAIM). -
- MEDIA(list)
-
optionally, specifies a preference list of MVC media types. This list supersedes the default media selection list. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring HSC and VTCS for more information.
listindicates the preference list of media types. - MVCPOOL(poolname)
-
optionally, specifies the Named MVC Pool from which volumes are selected. If you do not specify an MVC Pool name, the volumes are selected from the default pool (
DEFAULTPOOL).poolnameindicates the name of an MVC Pool that you defined on theMVCPoolcontrol statement. - MIGRATE
-
optionally, for Management Classes with
REPLICAT(YES)that reference this Storage Class, specifies the source VTSS (in a Cluster) for VTV migration. This parameter cannot be specified ifFROMLSTis specified.- RECEIVER
-
VTSS that receives the replicated VTV (the default), which is the Secondary VTSS in a Primary-Secondary Cluster.
- SENDER
-
VTSS that sends the replicated VTV, which is the Primary VTSS in a Primary-Secondary Cluster.
- EITHER
-
Either VTSS in a Peer-to-Peer Cluster. The source VTSS is randomly selected.
- TAPEPLEX(name)
-
optionally, specifies the name of the TapePlex to which a copy of the VTV is exported. At least one VTSS in the configuration must also specify this name in a CLINK definition.
nameindicates the TapePlex name. - SYNC
-
optionally, specifies whether the exporting of a VTV to TapePlex is performed synchronously.
- NO
-
export of VTV to TapePlex is performed asynchronously. This is the default.
- YES
-
export of VTV to TapePlex is performed synchronously.
If a VTV is specified with two storage classes that specify synchronous exporting, only the first one is honored while the second is exported asynchronously. Likewise, if synchronous replication is specified in the management class, then synchronous exporting is ignored.
- FROMLST(vtss-list-name)
-
optionally, when migrating or exporting to a Storage Class, provides VTCS with a list of VTSSs to source the VTV.
FROMLSTapplies to both Clustered VTSSs and to VLE to VLE connections. For more information, see "FROMLST Parameter Usage".vtss-list-nameindicates the name of a VTSS list (as specified in aMGMTDEF VTSSLSTcontrol statement). See "VTSSLST Control Statement" for more information. - INPLACE
-
optionally, specifies whether Dynamic Reclaim is enabled for this Storage Class. See "Dynamic Reclaim Usage" for more information.
- NO
-
Dynamic Reclaim is not enabled for this Storage Class.
- YES
-
Dynamic Reclaim is enabled for this Storage Class.
- DEDUP
-
optionally, specifies whether VTV data migrated to VMVCs in a VLE is deduplicated.
- NO
-
Do not deduplicate VTVs. This is the default.
- YES
-
Deduplicate VTVs when migrated to VMVCs.
The
DEDUPvalue is a Storage Class attribute that applies to all VMVC mount requests sent to a VLE.DEDUPapplies to all migrations that occur for the life of the mount. To change theDEDUPvalue, the VMVC is dismounted, theDEDUPvalue is changed, and the VMVC is remounted.
Dynamic Reclaim Usage
Dynamic Reclaim only applies to T10000B and above media (full and full encrypted only) that have been formatted by T10000 drives capable of creating partitions. It requires an H level CDS, VSM5 microcode D02.11.16.00 or later, and T1010000B firmware 1.41a.209 or later.
You can specify Dynamic Reclaim policies at the global, system wide level or on a Storage Class and MVC pool level. Use the VTCS CONFIg RECLAIM statement to set the global policies:
-
The
INPLACEparameter controls the usage of Dynamic Reclaim. Its setting can either be explicitly specified on theSTORCLASstatement or inherited from theRECLAIMstatement in the VTCS configuration. The default isINPLACE=NO. The setting that is derived for a Storage Class does not force usage of media formatted in either mode. It is acceptable to use this parameter with drives or media that do not support partitioning. Also, any media written in a different mode continues to be a migration target. This helps avoid the need to actively manage the transition when Dynamic Reclaim is enabled. Its effect is to cause new media allocated to the Storage Class to be formatted and written in either standard (INPLACE=NO) or partitioned (INPLACE=YES) mode. The switch can only occur when media is empty. -
If a hard switch-over between standard and dynamic reclaim is required, then a lengthy process involving parameter settings (for example,
MEDIAon theSTORCLASstatement) is required. MVCs must be removed from the MVC pool or set into a read-only state, usingMVCMAINT. Also, MVCs formatted in the wrong mode must be drained. -
The
INPTHRSHparameter specifies the fragmentation level that makes partitioned MVCs eligible for Dynamic Reclaim. When a partitioned MVC's fragmentation falls between theINPTHRSHandTHRESHvalues, it first becomes eligible for Dynamic Reclaim. If no space is freed on the initial reclaim attempt, the reclaim is retried when the fragmentation level has risen significantly. Should the fragmentation level reach the standardTHRESHOLD, then a fall-back method of moving VTVs is performed.
VTCS CONFIg RECLAIM statements provide the global defaults for the system. You can override these defaults at the Storage Class and MVCPool level:
-
The
STORCLAS INPLACEparameter specifies whether Dynamic Reclaim is enabled for a Storage Class. Initially, you may wish to specifyINPLACE(NO)in the VTCSCONFIg RECLAIMstatement andINPLACE(YES)for selected Storage Classes, in order to evaluate the effects of Dynamic Reclaim. Subsequently, if you wish to apply Dynamic Reclaim to all eligible media, you can specifyINPLACE(YES)on the VTCSCONFIG RECLAIMstatement. -
The
INPTHRSHparameter on thePOOLPARMstatement can be used to set a Dynamic Reclaim threshold specifically for this set of MVC media. This is useful when you wish to treat certain MVCs differently from the VTCSCONFIG RECLAIMdefaults.
Dynamic Reclaim can be disabled either globally at a system wide level or at the Storage Class level:
-
To disable Dynamic Reclaim globally, specify
INPLACE(NO)in the VTCSCONFIg RECLAIMstatement and ensure that any Storage Class definition does not override this setting. -
To disable Dynamic Reclaim for one or more Storage Classes, change
INPLACEtoNOin the Storage Class policy statements.
Note:
Any MVCs that are currently in use for migration will continue in partitioned format. If you wish to stop active MVCs from further migrates, then use theMVCMAINT utility to mark them as read-only. Once the partitioned volumes are empty, they are automatically re-used in non-partitioned mode. An MVC becomes empty either when all VTVs have expired or the MVC has been DRAINed.STORMNGR and ACS Parameter Interactions
The STORclas statement now enables you to specify both the ACS and STORMNGR parameters. The statement is generally neutral to whether the target is to a local HSC tape library, a VLE or a remote tape library. The interaction of these parameters is as follows:
-
If neither the
ACSorSTORMNGRparameters is specified, MVCs are selected from all available. -
If only the
ACSparameter is specified, the selection of MVCs is restricted to the library serviced by the local HSC with the designated ACS number. -
If only the
STORMNGRparameter is specified, then selection of MVCs is restricted to the specified VLE or remote library complex. For a remote library complex, this applies only to ACS 0. -
If both the
ACSandSTORMNGRparameters are specified, selection of MVCs is restricted to the library in the remote tapeplex with the designated ACS number.
The ACS and STORMNGR parameters allow the explicit specification of the location of the Storage Class. Whenever possible, use ACS and STORMNGR instead of implicit location selection by using the MVCPOOL and MEDIA parameters.
FROMLST Parameter Usage
If you do not specify FROMLST, the default behavior is as follows:
-
For Clustered VTSSs, if a copy resides on multiple VTSSs in the cluster, the VTV can be sourced from any available VTSS, which may not be optimal if the VTSS and the connected ACS are geographically distant from each other.
-
For VLE to VLE connections, if a VTV copy resides on both a VTSS and one VLE and you want to migrate it to a connected VLE, the default is to use the VLE to VLE connection. Similarly, this may not be optimal if the connected VLEs are geographically distant from each other.
Figure 3-111 shows a DR scenario with a local VLE (LOCVLE) and remote VLE (REMVLE) connected to VTSSA. You wish to migrate two VTV copies:
-
First, a local copy from
VTSSAtoLOCVLE. -
Second, a copy via VLE-to VLE copy from
LOCVLEtoREMVLE.
To make the VTV copies as desired, do the following:
-
Create a
VTSSLSTstatement to create a VTSS list that contains onlyVTSSA.VTSSLST NAME(VSM2VLE) VTSS(VTSSA) -
Create a
STORCLASstatement that sends a VTV copy toREMVLE.STORCLAS NAME(FORREMOT) STORMNGR(REMVLE) -
Create a
MIGRVTVstatement that delays the migration copy toREMVLE.MIGRVTV STOR(FORREMOT) IMMDELAY(360)The migration delay is 360 minutes to allow the migration to the local site occur first; then the migration to the remote site is by VLE-to-VLE copy. Note that 360 minutes is just an example value, you can specify values of up to 9998 (do not specify 9999, because then the VTV is only migrated via automigration).
-
Create a
STORCLASstatement that sends a VTV copy toLOCVLE.STORCLAS NAME(FORLOCAL) STORMNGR(LOCVLE) FROMLST(VSM2VLE)Note that the
FROMLSTparameter specifies that the local VTV copy is sourced fromVTSSA. -
Finally, create a
MGMTCLASstatement that specifies two VTV copies, one to the local site and one to the remote site:MGMTCLAS NAME(DRVLE) MIGPOL(FORLOCAL,FORREMOT)
STORLST Control Statement
The STORLST control statement specifies a list of Storage Classes and their corresponding preferencing. It is loaded by the MGMTDEF command.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-112, the STORLST control statement includes the following parameters:
- NAME(stor-list-name)
-
specifies the name of the Storage Class list.
stor-list-nameindicates the list name (a maximum of 8 alphanumeric characters). - STORclas(stor-clas-name)
-
specifies one to ten Storage Classes on the Storage Class list.
stor-clas-nameindicates the name of a Storage Class that you defined on theSTORclascontrol statement. - PRIority(order)
-
a list of priorities corresponding to the Storage Classes specified on the
STORclasparameter.orderindicates the specified priority. Valid values are 0 to 9 (highest priority), and the default is 5. You can assign the same priority to multiple Storage Classes. For example, if two Storage Classes both have a priority of 9, VTCS selects randomly from the two. A 0 (zero) priority specifies that VTCS selects the Storage Class only if all other Storage Classes are unavailable (for example, no free MVCs available for write).The Storage Class list is further qualified by the criteria specified by the
MGMTclasandVTSSparameters of theSTORSELstatement.
STORSEL Control Statement
The STORSEL control statement defines a Storage Class usage rule that applies to the Storage Class list and its preferencing specified on a referenced STORLST control statement. It is loaded by the MGMTDEF command.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-113, the STORSEL control statement includes the following parameters:
- FUNCtion(function)
-
optionally, specifies the VSM function to which the rule applies. Only one function can be specified per statement. If this parameter is omitted, it applies to all functions. If all functions do apply, then it makes economical sense to omit the
FUNCtionparameter, thus reducing the number of statements to 25% of what would otherwise need to be coded.functionindicates the function name, as described in the following table:Function Explanation SPECIFICApplies to automatic recall of a specific VTV for mounting. The list of Storage Classes is determined by the specified statement. This list influences the list of RTDs eligible to mount the MVC in the Storage Class to recall the VTV.
RECALLApplies to demand recall of a specific VTV for mounting. The list of Storage Classes is determined by the specified
STORLSTstatement. This list influences the list of MVC copies of a VTV to select the optimal MVC for recall of the VTV.EXPORTApplies to export. The list of Storage Classes is determined by the specified
STORLSTstatement. This list influences the list of MVC copies of a VTV to select the optimal MVC for export of the VTV.CONSOLIDApplies to consolidate. The list of Storage Classes is determined by the specified
STORLSTstatement. This list influences the list of MVC copies of a VTV to select the optimal MVC for consolidation of the VTV - HOST(host-id)
-
optionally, specifies one or more hosts to which the rule applies. If this parameter is used, any hosts not specified on this parameter ignore the rule. If the parameter is not used, the statement applies to all hosts.
host-idindicates a host identifier (maximum 8 characters). - MGMTclas(mgmt-class-name)
-
optionally, specifies a Management Class.
mgmt-class-nameindicates the name of a Management Class that you defined on theMGMTclascontrol statement. - VTSS(vtss-name)
-
optionally, specifies a VTSS.
vtss-nameindicates the VTSS name, as follows:-
For automatic recalls, the VTSS where the recall is performed.
-
For all other functions, the VTSS where the VTV previously resided. This may be determined from the
VTSSvalue shown in theDisplay VTVoutput.
-
- STORLST(stor-list-name)
-
specifies a list of Storage Classes and their corresponding preferencing.
stor-list-nameindicates the name of a Storage Class list that you defined on theSTORLSTcontrol statement.Note:
The Storage Class list specified on theSTORLSTparameter is further qualified by the criteria specified by theMGMTclasandVTSSparameters.
VTSSLST Control Statement
The VTSSLST control statement specifies a list of VTSSs and their corresponding preferencing. It is loaded by the MGMTDEF command.
VTCS first determines a system priority for each VTSS, based on various factors. For example, whether the VTSS can service the request, whether the required resources are online/available or whether the VTSS is in a compromised state (high DBU).
When more than one VTSS has the highest system priority, VTSSLST priorities can be used to influence which VTSS is used. However, VTSSLST is only considered when there is an obvious choice of VTSSs with equal abilities to service a request.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-114, the VTSSLST control statement includes the following parameters:
- NAME(vtss-list-name)
-
specifies the name of the VTSS list.
vtss-list-nameindicates the list name (a maximum of 8 alphanumeric characters). - VTSS(vtss-name)
-
specifies one to sixty four VTSSs on the VTSS list.
vtss-nameindicates a VTSS name. - PRIority(order)
-
optionally, lists priorities corresponding to the VTSS names specified on the
VTSSparameter.orderindicates the specified priority. Valid values are 0 to 9 (highest priority), and the default is 5. You can assign the same priority to multiple VTSSs.Within a set of VTSSs with the highest system priority:
-
If two or more VTSSs have the same highest
VTSSLSTpriority, VTCS selects randomly from the two (according to factors such as DBU and VSM model). -
A 0 (zero) priority specifies that VTCS selects the VTSS only if all other VTSSs are unavailable (for example, unavailable due to DBU > 95%, VTSS offline, all RTDs offline, or all VTDs are busy).
Specifying priority zero does not ensure that the VTSS will never be selected. To ensure that the VTSS is never selected, do not specify the VTSS in the
VTSS(..)list.
-
Note:
The VTSS list specified on theVTSSLST parameter is further qualified by:
-
The function specified on
VTSSSELstatement. -
The criteria specified by the
MGMTclas,VTSS,STORclas, andMVCpoolparameters of theVTSSSELstatement. -
Other factors such as RTD connectivity.
For example, in scratch allocation, the list of VTSSs is reduced to the VTSSs that can meet Management Class policies (such as
REPLICAT(YES)). If the list of VTSSs is reduced to zero, the request fails.
VTSSSEL Control Statement
The VTSSSEL control statement defines a VTSS usage rule that applies to the VTSS list and its preferencing specified on a referenced VTSSLST control statement. It is loaded by the MGMTDEF command.
Note:
VTSSSEL statements are honored only if the VTVs on the MVCs being processed are not resident in a VTSS. If the VTVs are resident, then VTCS ignores the VTSSSEL statement and migrates the VTV from the VTSS where it is resident.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-115, the VTSSSEL control statement includes the following parameters:
- FUNCtion(function)
-
optionally, specifies the VSM function to which the rule applies. Only one function can be specified per statement. If this parameter is omitted, it applies to all functions. If all functions do apply, then it makes economical sense to omit the
FUNCtionparameter, thus reducing the number of statements to 25% of what would otherwise need to be coded.functionindicates the function name, as described in the following table:Function Description SCRATCHApplies to non-specific (scratch) VTV allocation. The list of eligible VTDs is determined by the specified
VTSSLSTstatement. ThePREVVTSS, STORclasandMVCpoolparameters do not apply.SPECIFICApplies to specific VTV allocation. The list of eligible VTDs is determined by the specified
VTSSLSTstatement. TheSTORclasandMVCpoolparameters do not apply.RECALLApplies to demand recall. The list of eligible VTSSs for recall is determined by the specified
VTSSLSTstatement. The VTSS list also determines the search order for an RTD to service the MVCs selected for recall (derived from the VTVs selected). TheMGMTclasparameter does not apply.RECLAIMApplies to reclaim. The list of eligible VTSSs for reclaim is determined by the specified
VTSSLSTstatement. The VTSS list also determines the search order for an RTD to service the MVCs selected for reclaim. TheMGMTclasparameter does not apply.DRAINApplies to drain. The list of eligible VTSSs for drain is determined by the specified
VTSSLSTstatement. The VTSS list also determines the search order for an RTD to service the MVCs selected for drain. TheMGMTclasparameter does not apply.MOVEVTVSApplies when an
ARCHIVEorRECONCILcommand has theMOVEVTVparameter specified. The list of eligible VTSSs for moving the VTVs via is determined by the specifiedVTSSLSTstatement. The VTSS list also determines the search order for an RTD to service the MVCs selected for processing. TheMGMTclasparameter does not apply.AUDITApplies to MVC audit. The list of eligible VTSSs for audit is determined by the specified
VTSSLSTstatement. The VTSS list also determines the search order for an RTD to service the MVCs selected for audit. TheMGMTclasparameter does not apply.EXPORTApplies to export. The list of eligible VTSSs for export is determined by the specified
VTSSLSTstatement. VTSS list also determines the search order for an RTD to service the MVCs selected for export. TheMGMTclasparameter does not apply.CONSOLIDApplies to consolidate. The list of eligible VTSSs for consolidation is determined by the specified
VTSSLSTstatement. VTSS list also determines the search order for an RTD to service the MVCs selected for consolidation. TheMGMTclasparameter does not apply. - HOST(host-id)
-
optionally, specifies one or more hosts to which the rule applies. If this parameter is used, any hosts not specified on this parameter ignore the rule. If the parameter is not used, the statement applies to all hosts.
host-idindicates a host identifier (maximum 8 characters).Note:
The VTSS list specified on theVTSSLSTparameter is further qualified by the criteria specified by theMGMTclas,VTSS,STORclas, andMVCpoolparameters. - MGMTclas(mgmt-class-name)
-
optionally, specifies a Management Class.
mgmt-class-nameindicates the name of a Management Class that you defined on theMGMTclascontrol statement. - PREVvtss(vtss-name)
-
optionally, specifies a VTSS where a VTV:
-
Is resident
-
Was migrated from
vtss-nameindicates the VTSS name. -
- STORclas(stor-clas-name)
-
optionally, specifies a Storage Class and applies only when MVCs are used to select VTSSs.
stor-clas-nameindicates the name of a Storage Class that you defined on theSTORclascontrol statement. - MVCpool(poolname)
-
optionally, specifies a Named MVC Pool and applies only when MVCs are used to select VTSSs.
poolnameindicates the name of an MVC Pool that you defined on theMVCPoolcontrol statement. - VTSSLST(vtss-list-name)
-
optionally, specifies a list of VTSSs and their corresponding preferencing.
vtss-list-nameindicates the name of a VTSS list that you defined on theVTSSLSTcontrol statement.
MIGrate
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Parameters (Format 1)
As shown in Figure 3-116, the MIGrate command (format 1) includes the following parameters:
- VTVid(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
specifies the VTVs to migrate.
volser,vol-range, orvol-listindicates the volsers of one or more VTVs. You can also specify one or more ranges. - DSN(name)
-
specifies data sets used to select VTVs to migrate.
nameindicates the data set name. Table 3-12 describes the valid wild cards for data set names. You cannot address a member of a GDG using a wildcard.Wildcard Description *
A qualifier or one or more characters within a qualifier. An asterisk can precede or follow a set of characters.
**
zero or more qualifiers. A double asterisk cannot precede or follow any characters; it must be preceded or followed by either a period or a blank.
% or ?
Exactly one alphanumeric or national character.
%% or ??
One to eight percent signs or question marks can be specified in each qualifier.
Note:
Wildcard are only supported on MVS systems runningDFSMS/MVS 1.4or greater. At systems below this level the catalog search does not support wildcard. - MGMTclas(mgmt-class-name)
-
specifies one or more Management Classes that determine one or more VTVs to migrate.
MGMTclas,VTVid, andDSNare mutually exclusive.mgmt-class-nameindicates the names of one or more Management Classes that you defined on theMGMTclascontrol statement. For more information, see "MGMTclas Control Statement". - DELETE
-
optionally, specifies whether VSM deletes VTVs from the VTSS after migrating the VTVs.
- NO
-
Do not delete VTVs from the VTSS after migrating the VTVs.
- YES
-
Delete VTVs from the VTSS after migrating the VTVs (the default).
- NOWAIT
-
specifies that the utility does not wait for the operation to complete and returns after the request is submitted.
Parameters (Format 2)
As shown in Figure 3-117, the MIGrate command (format 2) includes the following parameters:
- VTSS(name)
-
specifies one or more VTSSs to migrate to the specified threshold.
nameindicates the names of one or more VTSSs. - THRESHLD(value)
-
specifies that VTCS runs the VTSS space management/VTV migration cycle until VTSS space reaches the specified threshold. Valid values are 0 to 95%.
valueindicates the threshold to migrate to (percent of VTSS space).
MNTD
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-118, the MNTD command includes the following parameters:
- AUTocln
-
controls automated transport cleaning.
- OFf
-
disables the automated cleaning function.
OFfis the initial value for the HSC. - ON
-
enables the following HSC cleaning functions:
-
the automated cleaning function, which detects when a transport requires cleaning and schedules the mount of a cleaning cartridge. For an LMU at level 22 or above, the cleaning occurs after the next dismount. For all other levels, the cleaning occurs prior to the next volume mount.
-
the
CLeancommand which is used to schedule the mount of a cleaning cartridge for a specified transport. See "CLean" for more information.
-
- Dismount
-
specifies whether volumes are to be deleted automatically from the control data set when a dismount is requested in a manual mode LSM for a volume that was mounted by the robot before the LSM was modified offline.
- Auto
-
indicates that volumes are to be automatically deleted from the control data set when a manual dismount is requested for a volume that was mounted by the robot.
Autois the initial value for the HSC. - Manual
-
directs the HSC to issue a message prompting the operator to decide whether the volume is to be deleted from the control data set when a manual dismount is requested for a volume that was mounted by the robot.
Setting
DismounttoManualis useful when an LSM is modified offline for only a short time. In this case, the operator can choose to not respond to the dismount message and leave the volume mounted on the transport. When the LSM is modified online the HSC redrives the outstanding dismount request, causing the robot to dismount the volume and place it in a storage cell.
- Ejctauto
-
controls automatic ejection of cleaning cartridges that have exceeded their maximum use.
In a multihost environment, the
EJctautosetting for a given ACS should be the same on all hosts.EJctautostatus is not shared among the HSCs on different hosts.- ON
-
directs the HSC to automatically eject cleaning cartridges that have exceeded the number of times they can be used (as specified by the
MNTDMAXcleanorVOLATTRMAXcleanparameters).ONis the initial value for the HSC. - MSg
-
directs the HSC to prompt the operator to either eject an over uselimit cartridge from the ACS or to keep a cleaning cartridge in the ACS.
- OFf
-
directs the HSC to keep an over uselimit cleaning cartridge in the ACS. A message is issued displaying the cleaning cartridge's volser and describing this action.
- ACS(acs-id)
-
optionally, specifies that the
EJctautosettings apply only to the specified ACS. If this parameter is omitted,EJctautosettings affect all ACSs.acs-idindicates a decimal value from 00 to 99 that identifies the ACS. A single digitacs-idcan be entered.
- Float
-
specifies whether the HSC is to select a new home cell location when it dismounts a volume that required a passthru when it was mounted.
In multihost environments, the
Floatsetting for a specific ACS should be the same on all hosts.Floatstatus is not shared among the HSCs on different hosts.- ON
-
directs the HSC to select a new home cell location for the volume in the LSM where the dismount occurs (provided a cell is available). If no cells are available in the new LSM, a location is chosen in the nearest LSM with free cells or the volume can be forced to its original home cell. Setting Float to
ONreduces the number of pass-thru operations.ONis the initial value for the HSC. - OFf
-
directs the HSC to return the volume to its original home cell location when it is dismounted.
Note:
TheMNTDFloatOFfcommand is useful for remote ACS/CDS link down situations to avoid control data set integrity issues by making sure cartridges are returned to their original home cell locations. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Legacy Interfaces Reference for information about remote libraries. - ACS(acs-id)
-
optionally, specifies that the Float setting applies only to this ACS. If the ACS parameter is omitted, the Float setting affects all ACSs.
acs-idindicates a decimal value from 00 to 99 that identifies the ACS. A single digitacs-idcan be entered.
- MAXclean(count)
-
specifies the maximum number of times a cleaning cartridge is to be used.
-
The
EJctautosetting in effect for the ACS controls how cleaning cartridges are handled when they exceed their maximum use. -
In a multihost environment, the
MAXcleansetting should be the same on all hosts. TheMAXcleanvalue is not shared among the HSCs on different hosts. -
Follow the cartridge vendor's recommendations for the number of times a cleaning cartridge should be used.
countindicates a decimal value, in the range from 1 through 32767. The initial value for the HSC is 100.The
countvalue applies to each cleaning cartridge in the library. When a cleaning cartridge is used count number of times, it is not selected if there are cleaning cartridges compatible with the transports in the ACS that have been used less than count number of times. Over uselimit cleaning cartridges may be automatically ejected, depending on theMNTDEJctautosetting. -
- MMount
-
specifies whether or not a mount message is issued during manual mode. This enables the operator to retain a manually mounted volume in the control data set.
- Delete
-
generates a manual mode mount message which prompts the operator to respond
Dto delete the volume from the control data set, orIto ignore the mount request.Deleteis the initial value of the HSC. - Reply
-
generates a manual mode mount message which prompts the operator to reply
MtoDOMthe message and retain the volume in the control data set, orIto ignore the mount request.
Note:
WhenMNTD MMount(Reply)is specified, the HSC action for a manual mode dismount is determined by theMNTD Dismountsetting. - PASSTHRU(count)
-
specifies the maximum number of passthrus that can occur to allow cartridge archival if
SCRDISM(ARCHIVE)is specified.countindicates the maximum number of passthrus allowed for archival of cartridges. Allowable values are decimal in the range from 1 through 99. The initial value of the HSC is 1. - Scratch
-
determines how a scratch volume is selected to satisfy a scratch mount request for a manual mode LSM.
- Manual
-
specifies that the operator must select a scratch volume when a scratch mount is requested for a manual mode LSM.
Manualis the initial value for the HSC. - Auto
-
directs the HSC to select a scratch volume when a scratch mount is requested for a manual mode LSM. If
Scratchis set toAuto, the HSC manual mount message indicates the cartridgeVOLSERand cell location as if it were a request for a specific volume.
- SCRDISM
-
specifies whether or not scratch volumes mounted in a 9310 or 9360 LSM are to be automatically archived to a larger or slower LSM upon dismount.
Note:
9740 LSMs cannot attach to any other type of LSM. Thus,SCRDISMdoes not affect mounts in ACSs containing 9740s.- CURRENT
-
indicates that scratch volumes mounted in a 9310 or 9360 LSM are to be dismounted according to the
MNTDFloat parameter setting.CURRENTis the initial value for the HSC. - ARCHIVE
-
indicates that scratch volumes mounted in a 9310 or 9360 LSM are to be archived into a larger or slower storage device. Archival occurs only if the number of passthrus does not exceed
PASSTHRU. Archival of a cartridge can occur:-
from a 9360 to either a 9310 or a 4410
-
from a 9310 to a 4410.
SCRDISM(ARCHIVE)overrides theMNTD Floatparameter setting.The
ARCHIVEparameter does not affect dismounts in ACSs containing 9740 LSMs. -
- HOSTID(host-id)
-
optionally, identifies the host associated with the
MNTDcommand. This enables you to restrict certain startup options to a specific host.If this parameter is not specified, the command is executed by each host that accesses
PARMLIB.hostidindicates the host ID (the SMF system identifier for both JES2 and JES3).Note:
If thehostiddoes not match the host executing the command, a message is issued and the command is not processed.
MODify
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The MODify command performs the following functions:
-
modifies a CAP or an LSM online or offline to all hosts, independent of the issuing host
-
starts dynamic hardware reconfiguration for a SL3000 or a SL8500 library
-
adds, deletes, or updates an SL3000 or SL8500 ACS definition in the CDS that was preallocated using the
SLILIBRY FUTRACSparameter
Dynamic hardware reconfiguration for the SL3000 and SL8500 libraries represents the portion of Near Continuous Operation (NCO) that enables you to dynamically add or delete drives and expansion panels.
Enter the MODify CONFIG command to activate dynamic hardware reconfiguration.
Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring HSC and VTCS for more information about Near Continuous Operation and dynamic hardware reconfiguration.
Caution:
Before you enterMODify CONFIG, perform a backup of the CDS.It is possible to remove LSMs from the SL8500 configuration without performing a LIBGEN, MERGEcds, and recycle of the HSC. However, this operation requires assistance from Oracle StorageTek Support.
The MODify command differs from the Vary command in the following ways:
-
The
MODifycommand places a specified CAP or LSM online/offline globally to all hosts.-
A CAP that is modified offline cannot be used for eject/enter processing.
-
An LSM that is modified offline must be operated in manual mode.
-
A manual mode LSM is still available for diagnostic requests from a host.
-
-
The
Varycommand places a host station online/offline to an LMU.-
A host that has all of its LMU stations varied offline is disconnected from all LSMs attached to the LMU.
-
An LSM can still be used to semi-automate cartridge handling for a disconnected host by issuing HSC commands from a connected host.
-
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-119, the MODify command includes the following parameters:
- CAP
-
specifies that a CAP is to be modified online/offline to all hosts.
- cap-id
-
a specific CAP to be modified online/offline. The format of a
capidisAA:LL:CC, whereAA:LLindicates the LSMid, andCCindicates the CAP. See "CAPid" for a list of valid values. - lsm-id
-
a standard CAP to be modified online/offline. The format of an
lsm-idisAA:LL, whereAAindicates the ACSid (decimal 00-99) andLLindicates the LSM number (decimal 00-99). - ONline
-
specifies that the CAP is to be modified online to all hosts. When a CAP is modified online, the HSC attempts to restore the CAP mode (automatic or manual) that was in effect when the CAP was modified offline.
- OFFline
-
specifies that the CAP is to be modified offline to all hosts. Modifying a CAP offline places it in an unavailable state, preventing it from being allocated. The CAP mode (automatic or manual) is retained in the control data set.
-
Be sure to specify the
CAPparameter to modify a CAP offline. If the LSM is online, and you specify anlsmidto modify the CAP offline but do not specify the CAP parameter, the LSM will be modified offline. -
Use this command only in an emergency. Make sure the CAP is not being used by another active process. Issuing the
MODifycommand on an active CAP may cause the process using the CAP to receive errors.
-
- LSM
-
optionally, indicates that one or more LSMs are to be modified online/offline to all hosts.
- lsmid, lsmrange, or lsmlist
-
one or more LSMs to be modified online/offline to all hosts. Each
lsmlistelement may be either a singlelsm-idor anlsm-range. The elements in a list must be separated by commas or blanks, and the entire list must be enclosed in parentheses.The format of an
lsm-idisAA:LL, whereAAindicates the ACSid (decimal 00-99) andLLindicates the LSM number (decimal 00-99). - ONline
-
specifies that the LSMs are to be modified online to all hosts. Modifying an LSM online places it in automatic mode. When an LSM is modified online, CAPs that were in auto mode before the LSM was modified offline are again placed in auto mode (unlocked state).
- OFFline
-
specifies that the LSMs are to be modified offline to all hosts. Modifying an LSM offline places it in manual mode. CAPs in a manual mode LSM cannot be used, but the auto/manual state of each CAP is retained.
- FORCE
-
specifies that the LSM(s) is to be modified offline immediately. FORCE is only used with the
OFFlineparameter to modify an LSM offline.
- CONFIG
-
optionally, initiates the Near Continuous Operation (NCO) for hardware reconfiguration process for SL3000 and SL8500 libraries. This is a system wide change which propagates to all hosts connected to the CDS.
Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring HSC and VTCS for more information about Near Continuous Operation and dynamic hardware reconfiguration. Before you enter
MODify CONFIG, perform a backup of the CDS.- no parms
-
optionally, initiates the Near Continuous Operation (NCO) for hardware reconfiguration process for SL3000 and SL8500 libraries. This is a system wide change which propagates to all hosts connected to the CDS.
-
Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring HSC and VTCS for more information about Near Continuous Operation and dynamic hardware reconfiguration.
-
Before you enter
MODify CONFIG, perform a backup of the CDS.
-
- RESET
-
resets internal flags for any host that may be failing as a hardware configuration is being performed. The
RESETalso terminates any active dynamic hardware reconfiguration in the HSC complex during the hardware and software comparison phase. When the failing host comes back up, the new hardware configuration is automatically recognized and implemented.A reset is intended only to reset a failing host and does not initiate the actual dynamic hardware reconfiguration operation. The
MODify CONFIGcommand, without theRESETparameter, must be run separately to invoke dynamic hardware reconfiguration. - ADD
-
initiates an NCO configuration change to add one or more ACSs to the HSC configuration. The ACS added takes on the library characteristics of the library type specified by the
ACSTypeparameter. The number of ACSs that can be added is limited by the number specified on theSLILIBRY FUTRACSparameter.- ACSType
-
specifies the library type to use for the configuration change. Options are
SL3000orSL8500.Additionally, you can specify
N(separated by a comma) to indicate the number of ACSs to add, from 1 to 9. If this keyword is not specified, 1 is the default.
- DELete ACSid(acs-id)
-
initiates an NCO configuration change to delete the disconnected ACS specified in the
ACSid(acs-id)parameter.After the ACSid is deleted, the ACS cannot be re-added if the ACS was defined by a
SLIACSstatement. If the ACS was added by a priorMODify CONFIG ADDcommand, the ACS can be re-added.-
If the ACSid is the not highest numbered ACS, the ACS is placed in "unallocated" status.
-
If the ACSid is the highest numbered ACS, the ACS is entirely deleted and can be re-added as a different ACSType.
-
If the ACSid is not the highest numbered ACS, the ACS becomes a place holder with a status of unallocated and can be re-added only as the same ACSType.
-
- UPDate ACSid(acs-id)
-
initiates an NCO configuration change to update the ACS configuration specified in the
ACSid(acs-id)parameter. This is a system wide change, and other hosts connected to the CDS are notified of the change.The
ADDandDELeteparameters are only valid if theFUTRACSparameter was specified in theSLILIBRYmacro during theLIBGENprocess.- NOCell
-
Used in conjunction with
ACSacs-idto bypass cell discovery within the ACS. This option is used only for drive and/or CAP changes and will reduce the reconfiguration time. - DRVinfo
-
Used in conjunction with
ACSacs-idto update drive information (for example, serial number, worldwide name) for all drives of an ACS. This option is used only when replacing defective drives with drives of the same type.Note:
When this command option is invoked, it executes immediately and does not disrupt library activity.
Mount
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The Mount command mounts a scratch or specific volume on a transport, or mounts a VTV on a VTD and optionally assigns a Management Class to that VTV.
Do not use this command to manage a mount that appears to have been missed by a batch job. Instead, use the SMC RESYNCHronize command to automate pending mounts. See "RESYNChronize" for more information.
Note:
The HSCMount command does not support VTDs that are not defined in the VTCS CONFIG. The SMC Mount command must be used in place of the HSC Mount command for any VTDs that are not specified in the VTCS CONFIG.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-118, the Mount command includes the following parameters:
To Mount a Specific Volume on a Transport
- volser
-
specifies the volume to be mounted.
- devaddr
-
specifies the device address of the transport on which to mount the volume.
- host-id
-
optionally, indicates that the volume is to be mounted on the device address defined to the specified host (the SMF system identifier for both JES2 and JES3).
Note:
Thehost-idspecified is only used for device address resolution. Thehost-idfor subpool validation is obtained from the command origin. - Readonly
-
indicates that the volume is to be mounted for readonly access.
If you do not supply a
hostidand do specifyReadonly, a comma must be entered immediately beforeReadonlyto indicate the missing operand. For example:MOUNT 123456 0B0,,READONLY - ForceRT
-
optionally, enables a volume to be mounted on a device with a different recording technique. The media type for the volume must be compatible with the device. Caution should be used because it is possible to mount a volume written at a high density on a drive that is not capable of reading the high density.
To Mount a Scratch Volume on a Transport
- SCRTCH
-
specifies a scratch volume is to be mounted.
- PRIVAT
-
specifies a scratch volume is to be mounted.
- devaddr
-
specifies the device address of the transport on which to mount the volume.
- host-id
-
optionally, indicates that the volume is to be mounted on the device address defined to the specified host (the SMF system identifier for both JES2 and JES3).
Note:
Thehost-idspecified is only used for device address resolution, Thehost-idfor subpool validation is obtained from the command origin. - SUBpool(subpool-name)
-
optionally, indicates the scratch volume is to be taken from a scratch subpool. If this parameter is not specified, then the behavior is dependent upon how scratch pools were defined:
-
If
VOLPARMspecified, then the volume will be selected from theDEFAULTPOOLwhich contains all scractch tapes in the ACS that were specified inVOLPARMbut were not assigned to a named subpool. -
If
VOLPARMnot specified (that is,VOLATTR, orUX03scratch pool definitions), then the volume will be selected fromsubpool-0which contains all scratch tapes in the ACS including both non-subpool and subpool volumes.
-
- MEDia(media-type)
-
optionally, specifies the type of media for the scratch volume. The specified media must be compatible with the requested
devaddr.media-typeindicates the media type.See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for a list of valid
media-typevalues.Note:
IfMEDiais not specified, the next scratch cartridge is selected without regard to media type.
To Mount a VTV on a VTD and Optionally, Assign a Management Class
- volser
-
specifies a specific VTV volser. volser indicates the volser of a specific VTV.
- SCRTCH
-
specifies the scratch VTV attribute (
SCRTCH). - devaddr
-
specifies the MVS device address of the VTD to use to mount the VTV.
- MGMTclas(mgmt-class-name)
-
optionally, specifies a Management Class you defined on the
MGMTclascontrol statement.mgmt-class-nameindicates the Management Class name.
MOVe
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The MOVe command moves volumes to specified locations within the same LSM or to any other LSM within an ACS.
Note:
-
Movement of volumes to all LSMs is done on a first-come first-served basis. As volumes are moved, should an LSM become fully populated before the move request is satisfied for that LSM, the move request continues with the movement of volumes designated for the next LSM specified in the request. An LSM is fully populated when all available cells contain tape cartridges. This process continues until the entire move request is completed or all destination LSMs are full.
-
Moves are performed one at a time to allow for other LSM activity.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-121, the MOVe command includes the following parameters:
- Flsm(lsm-id)
-
specifies the ’’From'' LSMid in the format
AA:LLthat the cartridges are to be moved from. If you specify theFlsmparameter, you may not specify theVolumeparameter.lsmidindicates the LSM identifier name. An LSMid (lsm-id) is made up of the ACSid (decimal 00-99) and the LSM number (decimal 00-99) separated by a colon (:). - Panel(panel-list)
-
specifies a panel number to be moved from. This parameter has a corequisite of the
Flsmparameter and is required.An entire panel can be emptied if the
RowandColumnparameters are not specified.panellistindicates a one or two digit panel number. Ranges are not valid. This parameter cannot contain a list if a list is specified for theRoworColumnparameter.Panels specified by
panellistare excluded as destination panels if cartridges are being moved within the same LSM.A
panellistelement is a one or two digit decimal number, specific to the LSM type. See "Panels" for a list of valid values.- Row(row-list)
-
specifies a list of rows to be moved from. This parameter has a corequisite of the
Panelparameter.rowlistindicates a one or two digit row number or list of row numbers. The maximum list allowed is four rows. However, this parameter cannot contain a list if a list was specified for theColumnparameter. Ranges are not valid.A
rowlistelement is a one or two digit decimal number, specific to the LSM type. See "Rows" for a list of valid values. - Column(column-list)
-
specifies a list of columns to be moved from. This parameter has a corequisite of the
Rowparameter and is optional. If this parameter is not specified, all columns will be moved for the rows specified.columnlistindicates a one or two digit column number or list of column numbers. This parameter cannot contain a list if a list was specified for theRowparameter. Ranges are not valid.A
columnlistelement is a one or two digit decimal number, specific to the LSM type. See "Columns" for a list of valid values.
- Volume(vol-list)
-
optionally, specifies volumes to be moved.
vollistindicates a list of volumes (a maximum of 300 can be specified) or a range of volumes. If you specify theVolumeparameter, you may not specify theFlsmparameter. - TLsm(lsm-list)
-
specifies the target LSM(s). This is a required parameter. The LSMs are specified as
AA:LL, whereAAindicates the ACSid andLLindicates the LSMid. The ACSid:-
must be identical to the
Flsmparameter ’’aa'' (ACSid), or -
must be the same ACS in which the volume resides if the
Volumeparameter is specified.
lsmlistindicates a list of LSMs (a maximum of 24 can be specified). Ranges are invalid. An LSMid (lsm-id) is made up of the ACSid (decimal 00-99) and the LSM number (decimal 00-99) separated by a colon (:).- TPanel(panel)
-
optionally, specifies the panel in the
TLsmto move the cartridge(s) to.panelindicates a one or two digit panel number. This parameter cannot contain a list or range. See "Panels" for a list of valid values.
-
MVCDRain
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Description
The MVCDRain command recalls all current and scratched VTVs from an MVC and, optionally, ”virtually” ejects the MVC, making it unavailable for VSM use without physically ejecting it from the library. You can use this command to override the CONFIG RECLAIM CONMVC setting.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-122, the MVCDRain command includes the following parameters:
- MVCid(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
drain one or more MVCs by volser.
volser,vol-range, orvol-listindicates the volsers of one or more MVCs up to a maximum of 50.- Eject
-
optionally, specifies that VTCS ”virtually” ejects the MVC (the MVC will not be used for output).
For virtual MVCs (VMVCs):
-
MVCDRAINwith theEJECTparameter physically deletes the VTVs.The current CDS backup can no longer be used as a DR baseline for VMVC content if you use the
DRCHKPTutility or theCONFIG RECLAIMPROTECTparameter to protect CDS backup content for VMVCs, and then issue theMVCDRAIN EJECTcommand. -
MVCDRAINwithout theEJECTparameter does not delete the VTVs, but updates the CDS record to show no VTVs on the VMVC.
-
- CONMVC(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum number of MVCs that VTCS concurrently processes for both drain and reclaim.
nnindicates the number of MVCs. Valid values are 1 to 99. If not specified, the default is theCONMVCvalue specified on theCONFIG RECLAIMstatement.
- MVCPOOL(poolname)
-
drain the MVCs in the specified Named MVC Pool.
pool-nameindicates the name of an MVC Pool that you defined on theMVCPoolcontrol statement. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Legacy Interfaces Reference for more information. - STORCLAS(storclas-name)
-
drain the MVCs in the specified Storage Class.
stor-class-nameindicates the name of a Storage Class that you defined on theSTORclascontrol statement; for more information, see "STORclas Control Statement". - RECALWER
-
optionally, specifies whether VTCS recalls VTVs with read data checks.
- NO
-
Do not recall VTVs with read data checks. This is the default.
- YES
-
Recall VTVs with read data checks.
- NOWAIT
-
optionally, specifies that the utility does not wait for the operation to complete and returns after the request is submitted.
- WARRANTY
-
optionally, selects MVCs with expired warranties (denoted by a
Win the Status T column on anMVCReport). - RETIRED
-
optionally, selects MVCs that are retired (denoted by a
Tin the Status T column on anMVCReport). - ERROR
-
optionally, selects MVCs that are in error (denoted by a
Bin the Status B column on anMVCReport). - DATACHK
-
optionally, selects MVCs that have a data check (denoted by a
Din the Status D column on anMVCReport).
MVCMAINT
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
-
Active HSC/VTCS required if
RENVTSSis specified -
Can run in batch-only mode when there are no hosts active (on any LPAR) using the CDS that is to be updated
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-123, the MVCMAINT command includes the following parameters:
- MANIFEST(ddname)
-
specifies the input ddname of the manifest file. Note that you can specify a merged manifest file or multiple manifest files.
ddnameindicates the DD name of the manifest file. The default isMANIFEST.When specified, VTCS reads the
MANIFESTfile to discover which MVCs are to be updated (all MVCs in the manifest file). VTCS then updates the MVCs in the CDS with the actions specified by the remaining parameters (LOST,READONLY, etc) - MVC(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
optionally, specifies the MVCs whose read/write attribute is changed.
volser,vol-range, orvol-listindicates the volsers of one or more MVCs. You can specify a maximum of 50 MVCs. - READONLY
-
optionally, sets the read/write status of the MVC.
- ON
-
MVC is readonly.
- OFF
-
MVCs is writable.
- LOST
-
optionally, sets the ”lost” status of the MVC.
- ON
-
MVC is lost.
- OFF
-
MVCs is not lost.
- ERROR
-
optionally, sets the error status of the MVC.
- ON
-
MVC is in error.
- OFF
-
MVCs is not in error.
- EJECT
-
optionally, sets the ”logical eject” status of the MVC.
- ON
-
MVC is ”logically ejected”.
- OFF
-
MVC is not ”logically ejected”.
- RETIRED
-
optionally, sets the ”retired” status of the MVC.
- ON
-
MVC is retired.
- OFF
-
MVC is not retired but is still in ”expired warranty” state (still selectable for output).
- WARRANTY
-
optionally, sets the ”expired warranty” status of the MVC.
- ON
-
MVC's warranty has expired.
- OFF
-
MVC's warranty has not expired.
Note:
WARRANTYandRETIREDare mutually exclusive. - INVLDMIR
-
optionally, sets the invalid MIR status of the MVC.
- ON
-
MIR is invalid.
- OFF
-
MIR is not invalid.
- REPLACED
-
optionally, updates various MVC fields in the MVC record after an MVC is physically replaced.
- NONE
-
The MVC record is not updated.
- MEDIA
-
The following MVC fields are updated:
-
MVC media type is cleared
-
Count of times mounted is set to zero
-
Warranty Expired Flag is turned off
-
Invalid MIR Flag is turned off
-
Retired Flag is turned off
-
Broke/Error Flag is turned off
-
Lost Flag is turned off
-
Data Check Flag is turned off
-
VTSS Last Written By is cleared
-
Date/Time MVC was last written to is cleared
-
Storage Class is cleared
-
Date/Time of Last Drain/Reclaim is cleared
-
Date/Time of Migrate from Empty State is cleared
-
Date/Time the MVC was last mounted is cleared
Note:
This parameter requires the MVC to be empty (contain zero) and unmounted.REPLACEDis mutually exclusive with theLOST,ERROR,EJECT,RETIRED,WARRANTY, andINVLDMIRparameters. -
- RENVTSS(vtss-name)
-
optionally, sets the name of the owning VTSS to
vtss-name.vtss-nameindicates the new VTSS name. This must be the name of an existing VTSS in your configuration.Note:
To useRENVTSS, the host on whichMVCMAINTis run must have access to the owning VTSS.
Additional JCL Requirements
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statements apply to the MVCMAINT JCL:
- manifest file DD
-
DD statement for the manifest file.
Note:
-
MVCMAINTJCL may specify the CDS to be updated if the CDS is in use by HSC/VTCS on the LPAR whereMVCMAINTis run. If specified, the CDS data sets specified inMVCMAINTJCL must match the CDS data sets used by HSC/VTCS. -
MVCMAINTJCL must specify the CDS to be updated ifMVCMAINTis being executed in batch-only mode, i.e. when there are no hosts active (on any LPAR) using the CDS.
Return Codes
The MVCMAINT command includes the following return codes:
-
0indicates that all requested updates for the MVC completed successfully. -
4indicates that one requested update for the MVC failed and at lest one other requested update completed successfully. -
8indicates that all requested updates for the MVC failed.
Note:
The final return code for theMVCMAINT job is the largest return code generated by any single MVC updated. For example, if 5 MVCs generate a return code 0 and one MVC generates a return code 8, the final return code is 8.MVCMAINT Report
The following is an example of an MVCMAINT report produced by the following command:
MVCMAINT MVC(022577-022579) READONLY=OFF
MVC RC
022577 04
022578 04
022579 04
MVCMAINT EXCEPTION REPORT
*SLS6737I MVC 022578 ALREADY HAS READONLY(OFF); REQUEST IGNORED
*SLS6737I MVC 022579 ALREADY HAS READONLY(OFF); REQUEST IGNORED
SLS1315I SWS500.V5.CDS WAS SELECTED AS THE PRIMARY CONTROL DATA SET
MVC Number Size Mount <----Status---> <------Last Mounted----->
Volser VTVs %Used %Avail %Frag (GB) Count I B L D R U T M Date Time VTSS ACSID Owner/
Consolidate Time
022577 0 0.00 99.96 0.04 .4 1 I - - - - C - - 2012Feb04 09:14:23 00 S1
022578 0 0.00 99.96 0.04 .4 4 I - - - - U - - 2012Mar08 10:11:04 VTSS16 00 S1
022579 0 0.00 99.96 0.04 .4 4 I - - - - U - - 2012Mar08 10:11:04 00 S1
3 INITIALIZED MVCS PROCESSED
0 NON_INITIALIZED MVCS PROCESSED
0 NON-LIBRARY MVCS PROCESSED
As shown in Example 3-51, the MVCMAINT report shows:
-
Status of MVCs processed - volser and return code (
0- all updates completed,4- some updates completed,8- no updates completed). -
An exception report of the reason for all uncompleted updates.
-
An MVC summary report.
MVCPLRPT
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-124, the MVCPLRPT command includes the following parameters:
- MVCPOOL(poolname)
-
optionally, report on MVCs in the specified Named MVC Pool.
poolnameindicates the name of an MVC Pool that you defined on theMVCPoolcontrol statement. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Legacy Interfaces Reference for more information.To report on all Named MVC Pools (including
DEFAULTPOOL), specifyALLor omit theMVCPOOLparameter. - STORCLAS(storclas-name)
-
optionally, report on MVCs in the specified Storage Class.
stor-clas-nameindicates the name of a Storage Class that you defined on theSTORclascontrol statement. See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for more information. You can also specify Storage Classes which used to exist to which media is still assigned.To report on all Storage Classes, specify
ALLor omit theSTORCLASparameter value.The
STORCLASparameter enables you to filter the MVCs reported from theMVCPOOL, i.e. only those MVCs with a matching Storage Class are reported. If theSTORCLASparameter is specified then the summary counts section will contain Storage Class subtotals, either for every Storage Class encountered if the parameter valueALLor no value is specified, or for those media types where there are MVCs matching the specified value. - DETail
-
Report MVC detail lines (the default).
- SUMmary
-
Report summary counts only.
Named MVC Pool Report
The following is an example of a report for Named MVC Pool CUST1POOL.
Example 3-52 Named MVC Pool report
SLUADMIN (7.3.0) TAPEPLEX=PRIMARY StorageTek Enterprise Library Software Utility SSYS=SLS0 PAGE 00002
TIME 08:23:02 Details MVCPOOL CUST1POOL DATE 2016-05-10
MVC Avail Used Frag Unaval Size <----Status--->
Volser VTVs (GB) (GB) (GB) (GB) (GB) I B L D R U T M
711807 0 0 0 0 40 40 - - - - - J T - Not in summary
740260 1880 3,925 506 67 0 4,498 P - - - - U - -
740261 133 4,075 423 0 0 4,498 P - - - - U - -
740262 1507 3,901 536 61 0 4,498 P - - - - U - -
740263 201 3,927 571 0 0 4,498 P - - - - U - -
740264 1867 3,995 450 53 0 4,498 P - - - - U - -
741031 0 4,498 0 0 0 4,498 P - - - - U - -
741044 0 0 0 0 5,000 5,000 P - - - R U - - Not in summary
SLUADMIN (7.3.0) TAPEPLEX=PRIMARY StorageTek Enterprise Library Software Utility SSYS=SLS0 PAGE 00003
TIME 08:23:02 Details MVCPOOL CUST1POOL DATE 2016-05-10
INITMVC MVCFree Threshold INPTHRSH Max MVC Start RECLaim
Yes 1 95 90 10 95 AUTo
ACS/ Media Total MVC Free MVC Available Used Fragmented Unavailable
Location Count Count Gb Gb Gb Gb
00 T1C000T2 6 1 24.321 2,486 181 0
00 ***Total 6 1 24,321 2,486 181 0
Summary of MVCs by usage:
7 Total MVCs processed
0 Standard MVCs processed
7 Partitioned MVCs processed
0 Un-initialized MVCs processed
1 Free MVCs available
0 MVCs with status AUDIT
0 MVCs with status DRAIN
0 MVCs with status EXPORT
1 MVCs marked EJECTed
0 MVCs marked FULL
0 MVCs with maximum VTVs
1 MVCs marked Read-Only
0 MVCs with status Broken
0 MVCs with status Lost
0 MVCs with Expired Warranty
0 MVCs marked Retired
0 MVCs have Invalid MIRs
0 MVCs have Data-Checks
0 MVCs with status CONSOLIDATE
6 MVCs are USABLE
Fields
The following list describes the Named MVC Pool report fields. The Summary fields are either for a Storage Class or a Named MVC Pool, depending on which was specified on the report JCL. If a Storage Class specifies a Named MVC Pool, the report gives information for that subpool.
- MVC Volser
-
the MVC volser.
- Number of VTVS
-
the number of current VTVs on the MVC. If the MVC has been used for VTV export, this field reports
EXPVTV. - Available (GB)
-
the available space, specified in Gb, on the MVC.
- Used (GB)
-
the used space, specified in Gb, occupied by current VTVs on the MVC.
- Fragmented (GB)
-
the fragmented space, specified in Gb, occupied by non-current VTVs on the MVC. This space is not usable until it is reclaimed or the MVC is drained.
- Unavailable (GB)
-
the unavailable space, specified in Gb, on the MVC. MVC with the following states are unavailable:
-
FULL -
BROKE -
RETIRED -
DATACHECK -
READONLY -
Warranty Expired
-
- Size (GB)
-
the media size of the MVC specified in Gb. This will only be determined after VTCS has used an MVC. "UNKNOWN" appears in this field until VTCS migrates a VTV to the MVC.
MVCs in a VLE have a nominal capacity of 250Gb. When VTVs are migrated with deduplication to a vMVC, the VTVs are divided into VTV unique data and data shared with other VTVs, which can reside on different vMVCs. As a result:
The sum of the VTVs can exceed the 250Gb vMVC media size, because the VTVs reference shared data that exists on other vMVCs.
Conversely, the sum of the VTV sizes on a full vMVC can be less than the 250Gb media size because the vMVC contains shared data for VTVs that reside on other vMVCs. For example, in an extreme case, a vMVC can have zero VTV copies but have zero available or fragmented space (the vMVC is full of shared VTV data).
- STATUS
-
one or more of the following statuses:
- I
-
The MVC has been initialized. A partitioned MVC is indicated by a P.
- B
-
The MVC has an error that should be investigated. The error may not make the MVC unusable, but VTCS will not select the MVC for migration for 12 hours after it is marked
B. After the 12 hour period, the MVC will be least preferred for subsequent migrations, and recalls from the MVC may cause VTCS to drain it. This error condition may be accompanied by messagesSLS6686,SLS6687, SLS6688,SLS6690, and/orSLS6693.Any of the following conditions can cause this MVC error:
-
MVC corrupted by another job (other than VTCS/VTSS)
-
attempt to use a read-only MVC for migration
-
DDR swap failure
-
RTD failure
-
- L
-
The MVC was not mounted in response to the last mount request. The MVC can still be used for migration, but will not select the MVC for migration for 12 hours after it is marked
L. After the 12 hour period, the MVC will be least preferred. This condition will clear itself the next time that the MVC is mounted. - D
-
A data check was reported for this MVC. VSM will not use this MVC again for migration.
- R
-
the MVC has been marked read-only.
- U
-
one of the following usage statuses:
- U
-
the MVC is available for output (migration, reclamation, export, or consolidation).
- -
-
the MVC is not available for output (migration, reclamation, export, or consolidation).
- A
-
The MVC is either being audited or the audit failed. If the audit failed, VTCS will not use the MVC for migration. To clear this condition, rerun the
AUDITagainst this MVC. - C
-
The MVC is a consolidation MVC.
- E
-
The MVC is an export MVC.
- F
-
There is no space available on the MVC.
- J
-
Either you issued an
MVCDRain EJectfor the MVC or the MVC was ejected for update by aRACROUTEcall. The MVC will not be used again for migration or recall. To clear this condition, useMVCDRainagainst MVC without theEJectoption. - N
-
Either the MVC is being drained because of an automatic drain or demand reclaim or an explicit
MVCDRaincommand, or the previousDRAINrequest failed, in which case VTCS will not use the MVC for migration. To clear this condition, enterMVCDRainagainst MVC without theEJectoption. - X
-
The MVC has reached the maximum VTVs per MVC.
- T
-
One of the following statuses:
- T
-
The MVC is retired.
- W
-
The MVC's warranty has expired.
- M
-
The MVC has an invalid MIR.
- Not in summary
-
MVC with the following states are not included in the MVCPLRPT summary:
-
EJECTED -
READONLY -
DATACHECK -
Logically Deleted
-
Summary for Storage Class or Named MVC Pool
This section shows number of MVCs and total storage (Gb) by ACS and media type:
- Total MVC count
-
Total number of MVCs.
- Free MVC count
-
MVCs that have 100% usable space and do not contain any migrated VTVs. The storage shown is the total free space based on media type capacity.
- Available (GB)
-
Available space, specified in Gb, on the MVC.
- Used (GB)
-
Used space, specified in Gb, occupied by current VTVs on the MVC.
- Fragmented (GB)
-
Fragmented space, specified in Gb, occupied by non-current VTVs on the MVC. This space is not usable until it is reclaimed or the MVC is drained.
- Unavailable (GB)
-
Unavailable space, specified in Gb, on the MVC.
MVCRPt
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-118, the MVCRPt command includes the following parameters:
- MVCid(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
optionally, specifies the MVCs for the report. If you do not specify the MVCs, the report includes all MVCs in your VSM system.
volser,vol-range, orvol-listindicates the volsers of one or more MVCs. - STORclas(storclas-name)
-
optionally, specifies a storage class with the MVCs to be reported.
stor-clas-nameindicates a 1-8 character storage class name.Note:
STORclasis mutually exclusive withMVCid,ALL, andMANIFEST. - ALL
-
optionally, generate a report for all MVCs according to the selection criteria, even those that would otherwise be omitted.
- MANIFEST(ddname)
-
optionally, specifies the input DD name of the manifest file used to generate the report.
ddnameindicates the DD name of the manifest file. Note that you can specify a merged manifest file or multiple manifest files. - DETail
-
optionally, produce a detailed MVC report. See Example 3-54 for an example. If you do not specify this option, the default is to produce a summary MVC report. See Example 3-53 for an example.
- CHECK
-
optionally,
MVCRPtdoes limited MVC integrity checking, during which the CDS is reserved. Use only if directed by Oracle StorageTek Software Support. - WRITABLE
-
optionally,
MVCRPtignores read only MVCs on MVC detailed reports and when you specify theCHECKparameter.
MVC Reports
The following sections describe the MVC summary and detailed reports produced by the MVCRPt command.
MVC Summary Report
The following figure shows an example of an MVC summary report:
Example 3-53 MVCRPt MVC summary report
MVC Number Size Mount <----Status---> <------Last Mounted-------> Location Owner/Comment/
Volser VTVs %Used %Avail %Frag (GB) Count I B L D R U T M Date Time VTSS / ACS ID Consolidate Time
DMV600 40 11.11 70.60 18.29 930.0 257 P - - - - U - - 2009Sep30 13:42:27 DVTSS16 00 DMV600
DMV601 0 0.00 100.00 0.00 500.0 256 I - - - - U - - 2009Sep29 16:59:59 00
DMV602 0 0.00 100.00 0.00 500.0 256 I - - - - U - - 2009Sep29 16:59:59 00
DMV603 0 0.00 100.00 0.00 500.0 256 I - - - - U - - 2009Sep29 16:59:59 00
DMV604 0 0.00 100.00 0.00 500.0 256 I - - - - U - - 2009Sep29 16:59:59 00
DMV605 0 0.00 100.00 0.00 500.0 256 I - - - - U - - 2009Sep29 16:59:59 00
DMV606 0 0.00 100.00 0.00 500.0 256 I - - - - U - - 2009Sep29 16:59:59 00
DMV607 0 0.00 100.00 0.00 500.0 256 I - - - - U - - 2009Sep29 16:59:59 00
DMV608 0 0.00 100.00 0.00 500.0 256 I - - - - U - - 2009Sep29 16:59:59 00
DMV609 0 0.00 100.00 0.00 500.0 256 I - - - - U - - 2009Sep29 16:59:59 00
DMV610 0 0.00 100.00 0.00 500.0 256 I - - - - U - - 2009Sep29 16:59:59 00
DMV611 0 0.00 100.00 0.00 500.0 256 I - - - - U - - 2009Sep29 16:59:59 00
DMV612 0 0.00 100.00 0.00 500.0 256 I - - - - U - - 2009Sep29 16:59:59 00
DMV613 0 0.00 100.00 0.00 500.0 256 I - - - - U - - 2009Sep29 16:59:59 00
DMV614 0 0.00 100.00 0.00 500.0 256 I - - - - U - - 2009Sep29 16:59:59 00
DMV615 0 0.00 100.00 0.00 500.0 256 I - - - - U - - 2009Sep29 16:59:59 00
DMV616 0 0.00 100.00 0.00 500.0 256 I - - - - U - - 2009Sep29 16:59:59 00
DMV617 0 0.00 100.00 0.00 500.0 256 I - - - - U - - 2009Sep29 16:59:59 00
DMV618 0 0.00 100.00 0.00 500.0 256 I - - - - U - - 2009Sep29 16:59:59 00
DMV619 0 0.00 100.00 0.00 500.0 256 I - - - - U - - 2009Sep29 16:59:59 00
20 Initialized MVCs processed
19 Initialized MVCs are standard format
1 Initialized MVCs are partitioned
0 Non-Initialized MVCs processed
0 Non-Library MVCs processed
SLS0155I Condition code for utility function is 0
Fields
The MVCRPt MVC summary report includes the following fields:
- MVC Volser
-
the MVC volser.
- Number of VTVS
-
the number of current VTVs on the MVC. If the MVC has been used for VTV export, this field reports
EXPVTV. - %Used
-
the percentage of the MVC used by current VTVs.
- %Avail
-
the percentage of the MVC that is physically available for use.
- %Frag
-
the percentage of the MVC that contains non-current VTVs. This space is not usable until it is reclaimed or the MVC is drained.
- Size (GB)
-
the size of the MVC (GB). This will only be determined after VTCS has used an MVC.
N/Aappears in this field until VTCS migrates a VTV to the MVC.Note that MVCs in a VLE have a nominal capacity of 250 GB. When VTVs are migrated with deduplication to a VMVC, the VTVs are divided into VTV unique data and data shared with other VTVs, which can reside on different VMVCs. As a result:
The sum of the VTVs can exceed the 250 GB VMVC media size, because the VTVs reference shared data that exists on other VMVCs.
Conversely, the sum of the VTV sizes on a full VMVC can be less than the 250 GB media size because the VMVC contains shared data for VTVs that reside on other MVCs. For example, in an extreme case, a VMVC can have zero VTV copies but have zero available or fragmented space (the MVC is full of shared VTV data).
- Times Mounted
-
the number of times that the MVC has been mounted for writing or reading since it was added to the MVC inventory.
- STATUS
-
one or more of the following statuses:
- I
-
The MVC has been initialized. MVCs written in partitioned format are indicated by the letter 'P' under this column.
- B
-
This is a generic error that indicates the MVC, drive, or combination of the two has a problem. VTCS attempts to de-preference MVCs with this state. To clear this state:
If the MVC caused the problem, use a
DRAIN(EJECT)command to remove the MVC from service.If the RTD caused the problem, use the
MVCMAINTutility to reset the MVC state.Note also that one or more of the following messages is issued for
BROKENstatus:SLS6686,SLS6687,SLS6688,SLS6690. For detailed recovery procedures for these messages, refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Messages and Codes. - L
-
VTCS attempted to mount an MVC and the mount did not complete within a 15-minute time-out period. VTCS is attempting to recover from a situation that may be caused by hardware problems, HSC problems, or by the MVC being removed from the ACS. VTCS attempts to de-preference MVCs with this state.
If VTCS does perform a subsequent successful mount of an MVC with
LOST(ON)state, VTCS sets the state toLOST(OFF).Determine the cause of the error and fix it. You can also use the VTCS
MVCMAINTutility to setLOST(OFF)for the following events:LOST(ON)was set due to LSM failures or drive errors that have been resolvedLOST(ON)was set because the MVC was outside the ACS and has been reentered. - D
-
A data check condition has been reported against this MVC. VTCS attempts to de-preference MVCs with this state. To clear this state:
If all VTVs on the MVC are duplexed, use
MVCDRainon the MVC without the Eject option. This recovers all VTVs and removes the MVC from service.If all VTVs on the MVC are not duplexed, VTCS
AUDITthe MVC. The audit will probably fail. After the audit, do anMVCDRAIN(no eject). This recalls the VTVs before the data-check area in ascending block-id order and the VTVs after the data-check area in a descending block-id order. Processing the VTVs in this sequence ensures that VTCS recovers as many VTVs as possible from the media. You then need to recreate the data for any VTVs still on the MVC. - R
-
The MVC has been marked read-only because of one of the following conditions:
The MVC being the target of an export or consolidation process. The read-only state protects the MVC from further updates.
The MVC media is set to file protect. Correct the error and use the
MVCMAINTutility to setREADONLY(OFF).The MVC does not have the appropriate SAF rules set to enable VTCS to update the MVC. Correct the error and use the
MVCMAINTutility to setREADONLY(OFF). Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Installing ELS for information about defining a security subsystem user ID for HSC, SMC, and VTCS. - U
-
One of the following usage statuses:
- U
-
The MVC is available for output (migration, reclamation, export, or consolidation).
- -
-
The MVC is not available for output (migration, reclamation, export, or consolidation).
- A
-
The MVC is either being audited or the audit failed. If the audit failed, VTCS will not use the MVC for migration. To clear this condition, rerun the
AUDITagainst this MVC. - C
-
The MVC is a consolidation MVC.
- E
-
The MVC is an export MVC.
- F
-
There is no space available on the MVC.
- J
-
Either you issued
MVCDRainEJectfor the MVC or the MVC was ejected for update by aRACROUTEcall. The MVC will not be used again for migration or recall. To clear this condition, useMVCDRainagainst MVC without theEJectoption. - N
-
Either the MVC is being drained because of an automatic drain or demand reclaim, or an explicit
MVCDRaincommand, or the previousDRAINrequest failed, in which case VTCS will not use the MVC for migration. To clear this condition, enterMVCDRainagainst MVC without theEJectoption. - X
-
The MVC has reached the maximum VTVs per MVC.
- T
-
One of the following statuses:
- T
-
The MVC is retired. VTCS will recall from, but not migrate to, the MVC. Replace the MVC as soon as possible.
- W
-
The MVC's warranty has expired. VTCS continues to use the MVC. You should start making plans to replace the MVC when it reaches Retired state.
- M
-
VTCS has received status from an RTD to indicate the MIR (media information record) for a 9x40 media is invalid. An invalid MIR does not prevent access to data but may cause significant performance problems while accessing records on the tape. The MVC is not capable of high-speed searches on areas of the tape that do not have a valid MIR entry.
VTCS attempts to de-preference MVCs with this condition. For recalls, if the VTV resides on multiple MVCs, VTCS selects MVCs with valid MIRs ahead of MVCs with invalid MIRs. VTCS avoids using MVCs with invalid MIRs for migration, unless the migration is at the beginning of the tape. Migrating from the beginning of tape will correct the MIR.
VTCS detects the invalid MIR condition at either mount time or dismount time. If detected at mount time and the operation can be completed with another MVC, VTCS dismounts the first MVC and selects the alternate MVC. Note that VTCS has only a limited ability to switch to an alternate MVC. That is, it is mainly used for migrate and virtual mount.
For MVCs with invalid MIRs, determine the cause of the error, which may be caused by media or drive problems, and fix the error.
To recover an MVC with an invalid MIR, you simply need to read the MVC to the end of the tape, which can be done via a VTCS audit. If the media is the problem, run an
MVCDRAIN EJECTto recall the VTVs and cause the MVC to be removed from the MVC pool.
- Last Mounted
-
the date and time that the MVC was last mounted and the VTSS where the MVC was last used.
- Location/ACS ID
-
the ACS containing the MVC, or the VLE containing remote MVC volumes or VMVCs in VLEs.
**MANY**indicates that an MVC with a specific volser has been discovered in more than one location. MVCs in this state are marked unusable. - Owner/Consolidate Time
-
If the MVC is empty, this field is null. If the MVC is a consolidation MVC, this field displays the time of the consolidation. If the MVC is a migration MVC and contains current VTVs, this field displays the MVC's Storage Class. If no Storage Class was explicitly assigned via the
MGMTclasstatement, the default Storage Class is the name of the last VTSS that wrote to the MVC for reclamation or migration.If VTCS receives a request to migrate a VTV that is assigned to an invalid Management Class, VTCS will dynamically create the !
ERRORStorage Class and migrate the VTVs defined by the invalid Management Class to the !ERRORStorage Class. Use this Storage Class to identify and correct invalid Management Classes, drain the affected MVCs, and resubmit the request. - Initialized MVCs processed
-
the total number of initialized MVCs. Also includes a breakdown of the number of MVCs that are standard format or partitioned.
- Non-Initialized MVCs processed
-
the number of non-initialized MVCs.
- Non-library MVCs processed
-
the number of non-library MVCs processed.
MVC Detailed Report
The MVC detailed report provides all the fields from the MVC summary report and a separate section that lists additional fields. The following figure shows an example of these additional fields from an MVC detailed report.
Example 3-54 MVCRPt MVC detailed report (additional fields)
Vtv Size Block Management Migration Block Message Volser (MB) Id Class Date Count DX0000 1802.24 0000/00000000 MF 2010Aug16 29078 DX0001 282.62 0000/00007196 MF 2010Aug16 4567 DX0002 3850.24 0000/0000836D-0001 MF 2010Aug16 62109 DX0003 1802.24 0001/0001760A MF 2010Aug16 29077 DX0004 2764.80 0001/0001E79F-0002 MF 2010Aug16 44602 DX0005 778.24 0002/000295D9 MF 2010Aug16 12561 DX0006 1802.24 0002/0002C6EA MF 2010Aug16 29077 DX0007 180.22 0002/0003387F MF 2010Aug16 2915 DX0008 2826.24 0002/000343E2-0003 MF 2010Aug16 45593 DX0009 3850.24 0003/0003F5FB-0004 MF 2010Aug16 62109 DX0010 266.24 0004/0004E898 MF 2010Aug16 4303 DX0011 3440.64 0004/0004F967-0005 MF 2010Aug16 55503 DX0012 1290.24 0005/0005D236 MF 2010Aug16 20819 DX0013 282.62 0005/00062389 MF 2010Aug16 4567 DX0014 3850.24 0005/00063560-0006 MF 2010Aug16 62109 DX0015 1802.24 0006/000727FD MF 2010Aug16 29077 DX0016 282.62 0006/00079992 MF 2010Aug16 4567 DX0017 1802.24 0006/0007AB69 MF 2010Aug16 29077 DX0018 2826.24 0006/00081CFE-0007 MF 2010Aug16 45593 DX0019 778.24 0007/0008CF17 MF 2010Aug16 12561 DX0020 1802.24 0007/00090028-0008 MF 2010Aug16 29077 DX0021 2826.24 0008/000971BD MF 2010Aug16 45593 DX0022 3850.24 0008/000A23D6-0009 MF 2010Aug16 62109 DX0023 282.62 0009/000B1673 MF 2010Aug16 4567 DX0024 3850.24 0009/000B284A-000A MF 2010Aug16 62109 25 VTVs found for MVC:DMV600 Last migrate:2010Aug16 13:00:04 181 unused / 11 used partitions found for MVC:DMV600 Unused partitions : --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- --- 00B 00C 00D 00E 00F 010 011 012 013 014 015 016 017 018 019 01A 01B 01C 01D 01E 01F 020 021 022 023 024 025 026 027 028 029 02A 02B 02C 02D 02E 02F 030 031 032 033 034 035 036 037 038 039 03A 03B 03C 03D 03E 03F 040 041 042 043 044 045 046 047 048 049 04A 04B 04C 04D 04E 04F 050 051 052 053 054 055 056 057 058 059 05A 05B 05C 05D 05E 05F 060 061 062 063 064 065 066 067 068 069 06A 06B 06C 06D 06E 06F 070 071 072 073 074 075 076 077 078 079 07A 07B 07C 07D 07E 07F 080 081 082 083 084 085 086 087 088 089 08A 08B 08C 08D 08E 08F 090 091 092 093 094 095 096 097 098 099 09A 09B 09C 09D 09E 09F 0A0 0A1 0A2 0A3 0A4 0A5 0A6 0A7 0A8 0A9 0AA 0AB 0AC 0AD 0AE 0AF 0B0 0B1 0B2 0B3 0B4 0B5 0B6 0B7 0B8 0B9 0BA 0BB 0BC 0BD 0BE 0BF
Fields
The MVCRPt MVC detailed report includes the following additional fields:
- VTV Volser
-
the volsers of the VTVs on the MVC.
- Size (MB)
-
the uncompressed size of the VTV (MB).
- Block ID
-
the partition id and logical block ID of the beginning of the VTV on the MVC. If there are VTVs spanning partitions, the
spanned topartition is shown to the right of theblockidlocation. - Management Class
-
the VTV's Management Class.
- Migration Date
-
for migrates done by a 6.0 system or above only, the approximate date that the VTV copy was migrated. This date is approximate because it is recorded in the CDS as the number of days since VTV creation, and time zone adjustments can cause the value to slip a day.
- Block Count
-
the decimal number of blocks of data that the VTV occupies on the MVC.
- Message
-
reports the results of MVC integrity checking. Any message not listed below should be reported to Oracle, as it may indicate a serious problem with the CDS except messages that can appear if the MVC is being audited or has failed an audit while the MVC report is being run. An MVC report returns a minimum return code of 4 if any MVCs in audit state are encountered; the audit state also prevents some other errors from being reported.
nnnnempty space to previousExplanation: Informational message, indicating that there are
nnnn(decimal) blocks of free space before this VTV on the MVC.Migrated size was not as expectedExplanation: If output for VTV
von MVCm, it indicates that the (compressed) size of VTV v migrated to MVC m was different to the (compressed) size of VTVvrecorded in the CDS.This is normal if VTV
vhad previously been recalled with error. Otherwise this indicates a possible error which should be reported to Oracle StorageTek software support. - Used/Unused Partitions
-
Summary of used and unused partitions for the MVC.
OFFload
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The OFFload command offloads transaction records from active log file(s) used by the HSC Transaction Logging Service and saves them in a sequential data set so that space in the log files can be reused.
If logging is currently active, you must run the OFFload LOGFILE utility to change log file names.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-126, the OFFload command includes the following parameters:
- LOGFILE
-
This keyword is required. Generally, OFFload LOGFILE is issued without parameters. The utility selects the input log data set from the active log data sets as recorded in the CDS.
- LOGDSN(primary-log-file-dsn)
-
optionally, offloads the log file without using or updating the CDS. Use this parameter in any case where the CDS is restored, or is otherwise considered to be unreliable.
primary-log-file-dsnindicates the data set name for the primary log file.For example:
OFFLOAD LOGFILE LOGDSN(hsc.log1) - RESTART
-
optionally, restarts the offload, selecting the input log file from among the group of log data sets that were active when the failed offload started. It also uses the block number range used by the failed offload.
Use this parameter to recover the records from the log data set(s) that become inactive when a failed offload causes a log data set switch.
Additional JCL Requirements
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statements apply to the OFFload LOGFILE JCL:
- SLSOFFLD
-
specifies the output data set
It is recommended that no DCB be specified for this data set. If a DCB is specified, the
RECFMandLRECLare ignored.
OPTION TITLE Control Statement
The OPTION TITLE control statement specifies an identifying string for a definition data set. This identifying string can be any information that helps the user describe the contents of the definition data set. You can specify this statement in a definition data set along with the following:
-
LMUPDEF -
MGMTDEF -
TREQDEF(SMC)
You can also specify this control statement using the following legacy HSC commands, as described in the ELS Legacy Interfaces Reference:
-
MVCDEF -
SCRPDEF -
VOLDEF
The OPTION TITLE statement must be placed in a definition data set; it cannot be issued as an operator command. If more than one OPTion statement is specified in the definition data set, only the identifying string of the last OPTion statement encountered is retained.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-127, the OPTION TITLE control statement includes the following parameters:
- identifying-string
-
indicates an identifying string for the definition data set. The maximum length of the identifying string is fifty characters. If the identifying string includes one or more spaces, or any characters other than alphabetic, numeric, or national (for example, $, @, #), it must be enclosed in quotes.
- TRACE or TRACEF
-
optionally, used to control internal tracing of HSC table lookups. During problem resolution, Software Support may request that you specify one of these parameters.
OPTion
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-128, the OPTion command includes the following parameters:
- Dialog
-
enables HSC messages to be written to the operator console and/or the system log. These messages indicate that the HSC is waiting for an active task to complete before the HSC terminates. The initial
Dialogvalue is set by theEXECstatement during HSC startup.- Off
-
specifies that messages are not to be written.
Offis the default value for the HSC if theDialogparameter is not specified on theEXECstatement. - Both
-
specifies that messages are written to the system log and the operator console.
- Console
-
specifies that messages are written to the operator console only.
- Log
-
specifies that messages are written to the system log only.
- DISCmsg
-
specifies whether or not the
ACSacsidis disconnectedmessage (SLS1664A) is displayed for the specified ACS.This option is useful when an ACS has been added to the
LIBGENin advance to provide for future expansion. EnteringDISCmsgenables the user to turn off the display for those ACSs that will not be connected until later.- SHow
-
Displays the
ACSacsidis disconnectedmessage (SLS1664A) for an ACS. This is the initial value. - SUppress
-
Suppresses the
ACSacsidis disconnectedmessage (SLS1664A) for an ACS. - ACS(acs-id)
-
optionally, specifies the ACS for which the command applies. If ACS is not specified, the
DISCmsgsetting entered (Show or Suppress) applies to all ACSs.acsidindicates the decimal ACSid value (00-99). If ACS is not specified, all ACSs are affected.
- DUPOFL
-
optionally, enables the duplicate VOLSER process to continue when the VOLSER being entered into the CAP shows in the CDS that it exists in an ACS that is disconnected, or in an LSM that is offline.
- OFF
-
disables the duplicate VOLSER process. This is the default.
- ON
-
enables the duplicate VOLSER process.
- EJLimit(count)
-
indicates the maximum number of cartridges that can be specified on one
EJectcommand.countindicates the maximum number of cartridges. Allowable values are 1 through 9999. The HSC initial value is 300. - ENTdup
-
specifies whether the HSC prompts the operator when an enter operation finds a duplicate VOLSER in the control data set, but cannot locate the cartridge in the ACS.
When someone attempts to enter a cartridge with a VOLSER that duplicates an entry in the control data set, the HSC attempts to locate the original cartridge. The
ENTdupoption determines how the HSC responds when the cartridge is not in its home cell, is not selected, and is not errant.- Auto
-
instructs the HSC to delete the cartridge in the control data set and allow the enter to continue.
- Manual
-
instructs the HSC to issue a console message when a duplicate VOLSER is entered. The message prompts the operator to decide whether the HSC should delete the cartridge in the control data set and allow the enter to continue, or eject the duplicate cartridge.
Manualis the initial value for the HSC.
- Output
-
specifies whether the output messages are displayed on the console in uppercase or mixed case.
- Upper
-
specifies uppercase.
Upperis the initial value for the HSC. - Mixed
-
specifies mixed case.
- SEN
-
enables or disables the Significant Event Notification (SEN) facility. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Programming Reference for more information about the SEN.
- ON
-
enables the SEN facility.
- OFF
-
disables the SEN facility. In this mode, the SEN facility accepts registration requests. However, invocation of listener programs is not performed. This is the initial value for HSC.
- Viewtime(count)
-
specifies the length of time in seconds the system is to hold an LSM camera in one location when the
VIewcommand is issued. See "VIew" for more information.countindicates the number of seconds. Allowable values for count are decimal in the range from 5 through 120. The initial value for the HSC is 10 seconds.The
VIewcommand enables the user to override theOPTion Viewtimesetting for a single viewing operation.An SMF record (subtype 8) is written when the
VIewcommand is issued to document robot activity. - Warnmsg(minutes)
-
sets the number of minutes between scratch depletion messages.
minutesindicates the number of minutes. Allowable values for minutes are 1 through 65535. The initial value is 5 minutes. - HOSTID(host-id)
-
optionally, identifies the host associated with the
OPTioncommand. This enables you to restrict certain startup options to a specific host.If this parameter is not specified, the command options are applied to each host that accesses
PARMLIB.hostidindicates the host identifier (the SMF system identifier for both JES2 and JES3).Note:
If thehostiddoes not match the host executing the command, a message is issued and the command is not processed.
PITCOPY
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The PITCOPY command uses a utility snapshot feature to produce a point-in-time copy of the CDS. PITCOPY ensures CDS backup integrity by performing a CDS RESERVE to ensure that any ongoing updates are serialized. The PITCOPY function backs up only the primary CDS. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Managing HSC and VTCS for more information about how to use the PITCOPY utility.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-129, the PITCOPY command includes the following parameters:
- METHOD
-
specifies the snapshot copy utility to use for the
PITcopy.- ADRDSSU
-
DFSMSdss SnapShot/DFSMSdss FlashCopy (ADRDSSU)
- SIBBATCH
-
StorageTek SVAA SnapShot (SIBBATCH) utility
- FDRSNAP
-
specifies that messages are written to the operator console only.
Additional JCL Requirements
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statements apply to the PITCOPY JCL:
- SLSPARMP
-
specifies a parameter file containing control statements to back up the CDS data set defined as
SLSCNTL. Note that this may not be the primary CDS data set at the time the backup is taken. - SLSPARMS
-
specifies a parameter file containing control statements to back up the CDS data set defined as
SLSCNTL2. - SLSPARMB
-
specifies a parameter file containing control statements to back up the CDS data set defined as
SLSSTBY. - SYSIN
-
specifies a file to be output by the
PITCOPYfunction and used as input to the snapshot copy function. When thePITCOPYfunction determines the primary CDS, it copies the appropriateSLSPARMxfile intoSYSIN.
Note:
-
Other definition statements are required by the snapshot utility you are requesting.
-
If you use Oracle's StorageTek
SVAA SnapShotfunction, it is recommended that you use theSOURCEoption specifying the data set name, rather than theINDDNAMEoption specifying theDDNAME; or that you always include the DD statements for the CDS data sets. If the dynamic CDS allocation feature is used, the primary CDS is automatically allocated toSLSCNTL. Therefore, a control statement inSLSPARMS, for example, to back up theSLSCNTL2DD, would result in backing up a CDS copy that is not the primary.
RECall
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-130, the RECall command includes the following parameters:
- VTVid(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
specifies the VTVs to recall.
volser,vol-range, orvol-listindicates the volsers of one or more VTVs. You can also specify one or more ranges. - DSN(name)
-
specifies data sets used to select VTVs to recall.
nameindicates the data set name. Table 3-12 describes the valid wildcards for data set names. - MGMTCLAS(mgmt-class-name or mgmt-class-list)
-
specifies one or more Management Classes that determine one or more VTVs to recall.
mgmt-class-nameormgmt-class-listindicates the names of one or more Management Classes that you defined on theMGMTclascontrol statement. For more information, see "MGMTclas Control Statement".MGMTCLAS,VTVid, andDSNare mutually exclusive. - RECALWER
-
optionally, specifies whether VTCS recalls VTVs with read data checks.
- NO
-
Do not recall VTVs with read data checks. This is the default.
- YES
-
Recall VTVs with read data checks.
- VTSS(name)
-
specifies where the VTVs are recalled as follows:
-
If you do not specify a VTSS (the default), VTCS attempts to recall the VTVs to the VTSS of creation if it is accessible. Otherwise VTCS recalls the VTVs to the VTSS with the lowest DBU.
-
If you specify a single VTSS, VTCS attempts to recall the VTVs to the specified VTSS if it is accessible. Otherwise, VTCS recalls the VTVs to the VTSS with the lowest DBU.
-
If you specify a list of VTSSs, VTCS attempts to recall the VTVs to the VTSS of creation if it is on the list and accessible, otherwise VTCS recalls the VTVs to the VTSS with the lowest DBU on the list.
nameindicates the names of one or more VTSSs. -
- NOWAIT
-
optionally, specifies that the utility does not wait for the operation to complete and returns after the request is submitted.
RECLaim
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Description
The RECLaim command performs demand MVC space reclamation. This command can also override the CONFIG RECLaim settings for the THRESHLD, INPTHRSH, MAXMVC, and CONMVC parameters.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-131, the RECLaim command includes the following parameters:
- MVCPOOL(poolname)
-
reclaim the MVCs in the specified Named MVC Pool.
poolnameindicates the name of a Named MVC Pool that you defined on theMVCPoolcontrol statement. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Legacy Interfaces Reference for more information. - STORCLAS(stor-clas-name)
-
reclaim the MVCs in the specified Storage Class.
stor-clas-nameindicates the name of a Storage Class that you defined on theSTORclascontrol statement; for more information, see "STORclas Control Statement". - ACSid(acs-id)
-
reclaim the eligible MVCs in the specified ACS.
acs-idindicates a two digit decimal ACS identifier from 00-99. - MVC(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
reclaim the specified MVC(s).
volser,vol-range, orvol-listindicates the volsers of one or more MVCs. You can also specify individual MVCs and ranges in a list. For example:(MVC000-MVC005,MVC010,MVC015) - MAXMVC(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum number of MVCs that will be processed by a single space reclamation task.
nnindicates the maximum number of MVCs. Valid values are 1 to 98. There is no default; if not specified, theCONFIG RECLAIMvalue (or default) is used.For automatic space reclamation to start, the number of eligible MVCs (determined by the
THRESHparameter) must also exceed theMAXMVCvalue. - THRESH(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the percentage of fragmented space that makes an MVC eligible for demand or automatic reclamation.
nnindicates the percentage of fragmented space. Valid values are 4 to 98. If not specified, theCONFIG RECLAIMvalue (or default) is used. - INPTHRSH(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the percentage of fragmented space that makes an MVC in partitioned format eligible for dynamic reclaim processing. This value overrides the global
INPTHRSHvalue specified in theCONFIg RECLAIMstatement. If this parameter is not specified, the current active globalINPTHRSHvalue is used.nnindicates a percentage between 3 and 97. This value must be less than theTHRESHLDvalue.Note:
IfINPTHRSHis specified,THRESHLDmust also be specified. BothINPTHRSHandTHRESHLDplay roles when space reclamation processes MVCs in partitioned format. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring HSC and VTCS for more information. - MOVEDATA
-
optionally, specifies the extent of VTV data movement to occur as a result of an MVC being reclaimed by the
RECLaimcommand.- Standard
-
Move all VTV copies from the MVC being reclaimed to the currently applicable Storage Classes as specified in the
MGMTclasorSTORclasdefinitions.A new
STORclasdefinition may have been explicitly implemented byMGMTDEFchanges, or it could be as a result of anARCHIVEpolicy specifying a newSTORclastaking effect.This is the default.
- Minimum
-
For an ALP MVC being reclaimed
INPLACE, if the fragmentation percentage space in a partition exceeds theTHRESHvalue specified on theRECLaimcommand, move all VTV copies from the MVC being reclaimed to the currently applicable Storage Classes as specified in theMGMTclasorSTORclasdefinitions. This option supplies the Defrag function for an ALP MVC.If a VTV spans partitions, it may have a segment in a low-use partition. For a partition to be eligible for defrag, the total size of all VTVs that reside partially or completely within the partition is used to calculate the used space associated with the partition.
For defrag to occur, the total associated used space must be less than 100 minus the
THRESHvalue percentage of the partition size. This prevents theRECLaimfrom potentially recalling a large amount of data residing in multiple partitions to free up a small amount of space in a single partition.Do not move VTV copies from a VLE VMVC to a new Storage Class.
- None
-
Do not move VTV copies from any MVC. This turns off all data movement.
Empty partitions on an ALP MVC that is being reclaimed
INPLACEare freed. Additionally, free space on VLE VMVCs becomes available.
- CONMVC(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum number of MVCs that VTCS concurrently processes for both drain and reclaim.
nnindicates the number of MVCs. Valid values are 1 to 99. If not specified, the default is theCONMVCvalue specified on theCONFIG RECLAIMstatement. - ELAPSE(nnnn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum time for the reclaim in minutes. If the maximum time expires, VTCS issues message
SLS6682I. If there are no MVCs currently mounted, reclaim stops when theELAPSEvalue is reached. If any MVCs are currently mounted when theELAPSEvalue is reached, reclaim processes the mounted MVCs and then stops.nnnnindicates the reclaim time in minutes. Valid values are 1 to 1440. If not specified, there is no time limit on the reclaim process. - NOWAIT
-
optionally, specifies that the utility does not wait for the operation to complete and returns after the request is submitted.
RECONcil
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Description
The RECONcil command reconciles VTV media and location (moves VTVs from one Storage Class to another).
RECONcil performs a series of cross-checks between the MVCs, VTVs, STORCLAS and MGMTCLAS definitions.
RECONCIL has two phases:
-
In the first phase, VTCS selects MVC and Storage Classes to be checked. MVCs are checked to ensure they meet the Storage Class definitions and ACS definitions. If inconsistencies are found, then the VTVs on those MVCs are added to the list of VTVs to be recalled and re-migrated to give correct MVC, ACS and Storage Class copies for that VTV. The
RECONcilparametersSTORCLASandMVClimit the checking in this phase. -
In the second phase, VTCS selects the VTVs and Management Classes to establish the correct number and location of VTV copies. Any VTVs with inconsistencies are added to the list of VTVs to be recalled and re-migrated. The
RECONcilparametersMGMTCLASandVTVlimit the checking in this phase.
Parameters
The STORclas and MVC parameters limit the first phase of checking to the specified Storage Classes or MVCs. If STORclas or MVC are not specified, VTCS checks all MVCs by default.
As shown in Figure 3-132, the RECONcil command includes the following parameters:
- STORclas(stor-class-name1...stor-class-namen)
-
optionally, specifies one or more Storage Classes.
stor-class-name1...stor-class-namenindicates one or more Storage Classes. - MVC(mvc-list or mvc-range)
-
a list or range of MVCs. This parameter is mutually exclusive with
STORclas.mvc-listormvc-rangeindicate a list or range of MVCs. - MGMTclas(mgmt-class-name1...mgmt-class-namen)
-
optionally, specifies one or more Management Classes. This parameter is mutually exclusive with
VTVid.mgmt-class-name1...mgmt-class-namenindicates one or more Management Classes. - VTV(vtv-list or vtv-range)
-
optionally, specifies a list or range of VTVs. This parameter is mutually exclusive with
MGMTclas.vtv-listorvtv-rangeindicates a list or range of VTVs. - MAXMVC(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum number of MVCs that will be processed by a single reconciliation task.
nnindicates the number of MVCs. Valid values are 1 to 98. If not specified theCONFIG RECLAIMvalue (or default) is used. This parameter is ignored ifMOVEVTVis not specified. - CONMVC(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum number of MVCs that VTCS concurrently processes during subsequent recall and migrate operations.
nnindicates the number of MVCs. Valid values are 1 to 99. If not specified theCONFIG RECLAIMvalue (or default) is used. This parameter is ignored ifMOVEVTVis not specified. - ELAPSE(nnnn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum time for the reconciliation in minutes. If the maximum time expires, VTCS issues message
SLS6682I. If there are no MVCs currently mounted, reconciliation stops when theELAPSEvalue is reached. If any MVCs are currently mounted when theELAPSEvalue is reached, reconciliation processes the mounted MVCs and then stops.nnnnindicates the time in minutes. Valid values are 1 to 1440. If not specified, there is no time limit on the reconciliation process. This parameter is ignored ifMOVEVTVis not specified. - PLICYdd(ddname)
-
optionally, specifies the DD name of a file containing an alternate
MGMTclasstatement. This parameter is mutually exclusive withMOVEVTV.ddnameindicates the DD name. - MOVEVTV
-
optionally, move VTVs per the currently active Management Policies as specified by the
MGMTclasstatements that apply to the VTVs. If you do not specifyMOVEVTV, only a report is generated. (no VTVs are moved). This parameter is mutually exclusive withPOLICYdd.
RECONcil Reports
The following shows examples of RECONcil reports.
RECONcil Report (MOVEVTV Not Specified)
The following is an example of a RECONcil report:
Example 3-55 RECONcil report (MOVEVTV not specified)
VTV Size Comp <----Creation----> MGMT MVC1 MVC2 MVC3 MVC4 Tapeplex REASON
Volser (MB) % Date Time CLASS
DX1000 358.4 0 2009Jan18 16:00:00 M5 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1001 358.4 0 2009Jan18 15:59:58 M5 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1008 358.4 0 2009Jan18 15:59:43 M5 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1009 358.4 0 2009Jan18 15:59:41 M5 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1010 358.4 0 2009Jan18 15:59:40 M5 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1011 25.6 0 2009Jan18 15:59:38 M5 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1020 358.4 0 2009Jan18 15:59:19 M5 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1021 358.4 0 2009Jan18 15:59:18 M5 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1024 358.4 0 2009Jan18 15:59:12 M5 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1025 358.4 0 2009Jan18 15:59:10 M5 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1028 358.4 0 2009Jan18 15:59:04 M6 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1029 358.4 0 2009Jan18 15:59:01 M6 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1032 358.4 0 2009Jan18 15:58:56 M6 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1033 358.4 0 2009Jan18 15:58:54 M6 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1036 358.4 0 2009Jan18 15:58:48 M5 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1037 358.4 0 2009Jan18 15:58:46 M6 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1050 51.2 0 2009Jan18 15:58:20 M5 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1051 51.2 0 2009Jan18 15:58:17 M5 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1052 51.2 0 2009Jan18 15:58:15 M5 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1053 51.2 0 2009Jan18 15:58:14 M5 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1054 51.2 0 2009Jan18 15:58:12 M5 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1055 51.2 0 2009Jan18 15:58:10 M6 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1056 51.2 0 2009Jan18 15:58:08 M6 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1057 51.2 0 2009Jan18 15:58:06 M6 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1058 51.2 0 2009Jan18 15:58:04 M6 SECNDARY EEXPORT
DX1059 51.2 0 2009Jan18 15:58:02 M6 SECNDARY EEXPORT
Total VTVs = 26 Total Size = 5913MB
SLUADMIN (7.2.0) StorageTek Enterprise Library Software Utility PAGE 00003
TIME 08:06:35 Reconcile Tapeplex Report DATE 2015-01-19
Tapeplex Candidate VTVs Total VTV size (MB)
SECNDARY 26 5913.60
DX1000 DX1001 DX1008 DX1009 DX1010 DX1011 DX1020 DX1021 DX1024 DX1025 DX1028 DX1029 DX1032 DX1033
DX1036 DX1037 DX1050 DX1051 DX1052 DX1053 DX1054 DX1055 DX1056 DX1057 DX1058 DX1059
Total tapeplexes = 1 Total Size = 5913MB
SLS0155I Condition code for utility function is 0
Fields
The RECONcil report includes the following fields:
- VTV volser
-
the VTV volser.
- Size (MB)
-
The uncompressed size of the VTV (MB).
<MOUNT>indicates that the VTV was mounted when the report ran.<FENCED>indicates that the VTV's state is unknown. If<FENCED>appears, contact Oracle StorageTek Software Support. - Comp %
-
The VTV compression percentage achieved. This is the difference between the uncompressed and compressed VTV size expressed as a percentage of the uncompressed VTV size. For example if a 100 MB VTV compresses to 40 MB then the compression% will be given as 60%. A compression of 0% indicates that no compression was possible on the VTV.
- Creation Date and Time
-
The date and time that the VTV was created.
- MGMT Class
-
The name of the Management Class for the VTV specified.
- MVC1, MVC2, MVC3, MVC4
-
The MVC(s) affected as a result of the
Reconcil. - Tapeplex
-
The TapePlex name.
- Reason
-
The reason for the VTV selection: media type, media location, migration (space release), immediate migration, or Storage Class.
The RECONcil Tapeplex Report section displays the number of candidate VTVs and Total VTV size (MB) for each TapePlex.
MVC Report Fields
The following list describes the RECONcil MVC report fields. The data for each MVC is followed by one or more VTV volsers with copies on the MVC. This section of the report is followed by a total line showing the number of candidate MVCs and the size in MB to be recalled and remigrated:
- MVC Volser
-
The MVC volser.
- MVC Media Type
-
The MVC type.
- Media Size (MB)
-
The size of the MVC (MB). This will only be determined after VTCS has used an MVC.
UNKNOWNappears in this field until VTCS migrates a VTV to the MVC. - Storage Class/Consolidate time
-
The MVC's Storage Class or time the VTVs on it were consolidated.
- Candidate VTVs
-
The number of candidate VTVs on the MVC.
- Total VTV Size (MB)
-
The size of all candidate VTVs on the MVC in MBs.
- Location (ACS ID)
-
The ACS where the MVC resides. If blank, the MVC is not currently in an ACS.
RECONcil MOVEVTV Report
The following is an example of a RECONcil report produced by the RECONcil command issued with the MOVEVTV parameter:
Example 3-56 RECONcil MOVEVTV report
Move VTV - MVC 022705 ignored, MAXMVC reached Move VTV - VTV X04898 ignored, all MVC copies rejected Move VTV - 4 MVCs selected for processing Move VTV - 5 VTVs selected for processing Move VTV - 5 VTV copies to be processed Move VTV - 0 VTV copies not matched to request Move VTV - 1 VTV copies rejected by MAXMVC limit Move VTVs - MVC 023484 selected and contains 1 VTVs Move VTVs - MVC 022628 selected and contains 1 VTVs Move VTVs - MVC 022631 selected and contains 2 VTVs Move VTVs - MVC 022608 selected and contains 1 VTVs Recall from MVC 022628 to VTSS HBVTSS17 SLS6683I Bulk recall of 1 VTVs issued to MVC 022628 SLS6644I VTV X99909 recalled from MVC:022628 Block:25401431 SLS6637I Recall from MVC 022628 completed Recall from MVC 023484 to VTSS HBVTSS17 SLS6683I Bulk recall of 1 VTVs issued to MVC 023484 SLS6644I VTV X04897 recalled from MVC:023484 Block:02402581 SLS6637I Recall from MVC 023484 completed Recall from MVC 022608 to VTSS HBVTSS16 SLS6683I Bulk recall of 1 VTVs issued to MVC 022608 SLS6637I Recall from MVC 022608 completed Migrate to storage class HBVTSS16 from VTSS HBVTSS17 SLS6681I VTV X99909 migrated to MVC:022589 Block:01400025 StorCl:HBVTSS17 MgmtCl:SIMPLEX SLS6636I Demand migration to MVC 022589 completed Recall from MVC 022631 to VTSS HBVTSS16 SLS6683I Bulk recall of 2 VTVs issued to MVC 022631 SLS6644I VTV X99910 recalled from MVC:022631 Block:03400141 SLS6644I VTV X99908 recalled from MVC:022631 Block:05400281 SLS6637I Recall from MVC 022631 completed
RECOVer
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIB -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The RECOVer command recovers the resources owned by a host that becomes inoperable. Cross-host recovery frees library resources that are owned by the failing host, and transfers that ownership to the recovering host. These resources include CAPs, which can be activated by only one host at a time, and volumes, which are assigned to a particular host while moving or mounting.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-133, the RECOVer command includes the following parameters:
- host-id
-
identifies the host for which to perform recovery (the SMF system identifier for both JES2 and JES3).
- FORCE
-
optionally, indicates that recovery is to be performed for the specified host even if the HSC has not detected that the host is inactive. This enables the recovery of a host when the active flag for that host is still on.
Caution:
Use theFORCE operand with great caution. Make sure the specified host is inactive before specifying this operand. Forced recovery of an active host requires that the HSC on that host be recycled. All database activity is prohibited on the recovered host, which can cause unexpected abends when tape activity occurs, or when the HSC is recycled on that host.RELease
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The RELease command frees an allocated CAP, making it available for other processes, without requiring a recycle of all HSCs sharing the control data set.
A CAP can be left allocated to a host if the HSC on that host terminated without performing recovery while the CAP was active.
This command can be issued from any connected host. The operator is required to confirm the release operation by responding to a console message.
Caution:
Use this command as a last resort. Make sure the CAP is not being used by another active process. Issuing theRELease command on an active CAP may cause the process using the CAP to receive errors.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-134, the RELease command includes the following parameters:
- cap-id
-
identifies the CAP to be released. The format of a
capidisAA:LL:CC, whereAA:LLindicates the LSMid, andCCindicates the CAP. See "CAPid" for a list of valid values.Note:
The format of an LSMid isAA:LL, whereAAindicates the ACSid (decimal 00-99) andLLindicates the LSM number (decimal 00-99).
REPLaceall
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The REPLaceall command deletes the scratch list in the CDS and optionally replaces it with a new list.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-135, the REPLaceall command includes the following parameters:
- VOLser(vol-list)
-
optionally, specifies the list of volume serial numbers to be added, deleted, or replaced in the scratch list(s).
vollistindicates the volume serial numbers; this can be a single volume, a list of volume serial numbers, ranges of volume serial numbers, or combinations of lists with ranges delimited by commas. The entire list must be enclosed in parentheses.
RESTore
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
HSC must be down (inactive)
Description
The RESTore command restores, or re-creates the library Control Data Set (CDS) from a previous CDS backup copy. If multiple CDS DD statements are specified, then multiple CDS copies are created in the RESTore process.
Caution:
It is critical that you restore all data sets referenced by the HSC (primary, secondary, standby). Failing to restore all data sets can cause CDS mismatches. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Managing HSC and VTCS for detailed information about when to use this utility and how it functions.Additional JCL Requirements
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statements apply to the RESTore JCL:
- SLSCNTL
-
specifies the primary CDS.
- SLSCNTL2
-
optionally, specifies the secondary CDS.
If a secondary CDS exists, include this statement so that if a switch occurs and the secondary CDS becomes active, the CDSs can be reordered to maintain database integrity.
- SLSSTBY
-
optionally, specifies the standby CDS.If a standby CDS exists, include this statement so that if a switch occurs and the standby CDS becomes active, the CDSs can be reordered to maintain database integrity.
- SLSBKUP
-
the backup data set.
SCRAtch
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-137, the SCRAtch command includes the following parameters:
- VOLser(vol-list)
-
specifies the list of volume serial numbers to be added, deleted, or replaced in the scratch list(s).
vollistindicates the volume serial numbers; this can be a single volume, a list of volume serial numbers, ranges of volume serial numbers, or combinations of lists with ranges delimited by commas. You can specify a maximum of 100 volume serial numbers. The entire list must be enclosed in parentheses.
SCREdist
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The SCREdist command redistributes, or balances, the number of scratch volumes across the library.
SCREdist permits the redistribution of scratch volumes either:
-
among LSMs implied by the specification of an ACS, or
-
among the LSMs explicitly identified through an optional parameter.
SCREdist enables you to select one media type and recording technique. If specified, scratch volume redistribution will be based on the MEDia and RECtech settings.
If neither MEDia nor RECtech is specified, volumes are redistributed without regard to media type or recording technique.
When only the ACS parameter is specified, the redistribution method transfers cartridges from LSMs with a greater number of scratch volumes to LSMs with a lesser number of scratch volumes. The process is repeated until the number of scratch volumes in each LSM is within the defined scratch tolerance level.
Distribution in an ACS containing a mix of LSMs (4410s, 9310s, 9360s, 9740s) is performed based on a percentage of scratch cartridges in the ACS. That is, the utility causes each LSM to have the same percentage of scratch tapes within the ACS as the LSM has cells within the ACS. For example, in an ACS where a 9310 LSM contains 80 percent of the cells within the ACS, 80 percent of the scratch tapes will reside in the 9310.
Note:
The SL3000 and SL8500 are standalone libraries and cannot be combined with any other LSM type.After Scratch Redistribution is completed, only the specified LSMs contain scratch cartridges, if the LSM parameter was specified.
Concurrent redistributions among different ACSs are accomplished by multiple executions of this utility program.
Redistribution moves non-scratch cartridges to make space for scratch cartridges. The actual number of scratch cartridges moved may vary depending on the number of free cells and the number of scratch cartridges available.
Note:
Cartridges cannot be transferred to a frozen panel.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-138, the SCREdist command includes the following parameters:
- ACS(acs-id)
-
specifies one ACS in the library in which the scratch volumes are to be redistributed.
acsidindicates the ACS. The one or two digit decimal ACS identifier. - LSM(lsm-list)
-
optionally, specifies that only certain LSMs within an ACS are to contain scratch cartridges (if not specified, scratch volumes are redistributed across all LSMs in the ACS).
lsmlistindicates a single LSM or a list of LSMids. An LSMid (lsm-id) is made up of the ACSid (decimal 00-99) and the LSM number (decimal 00-99) separated by a colon (:). An LSM range is not allowed.The element(s) contained in an
lsmlistmust be enclosed in parentheses; multiple elements must be separated by blanks or commas. - SUBpool(subpool-name)
-
optionally, specifies the subpool name from which scratch volumes are to be redistributed.
subpoolnameindicates the subpool. - BALtol(tolerance-value)
-
optionally, specifies a balance tolerance value. Scratch volumes are distributed based on this specified value.
tolerancevalueindicates a percent value that identifies when cartridge redistribution ends. Valid values are 1 through 999, where the values indicate a percentage from .1 to 99.9 (i.e., 1 signifies .1 percent; 999 equals 99.9 percent). The initial value for the HSC is 1. Iftolerancevalueis not specified in this utility, HSC uses the initial value for scratch redistribution.The utility finishes redistributing scratch cartridges when the percentage of scratch tapes in all specified LSMs is within
tolerancevalue/ 2 percentage points of each LSM's percentage of cells in the ACS.For example, assume an ACS has one 4410 LSM with 5,000 cells, one 9360 (WolfCreek) LSM with 1,000 cells, and 600 total scratch tapes in the ACS. Scratch Redistribution attempts to put 500 scratches in the 4410 and 100 scratches in the 9360.
Entering
BALtol(100)specifies a setting of 10 percent, which means that the utility ends when all LSMs are within ±5 percent of the expected number of scratches for each LSM (500 for the 4410, 100 for the 9360).The expected number can be determined as follows:
expnumlsm=totscracsx(totcellslsm/totcellsacs)where:
-
expnumlsmindicates the expected number of scratches for each LSM. -
totscracsindicates the total number of scratches in the ACS. -
totcellslsmindicates the total number of cells in the LSM. -
totcellsacsindicates the total number of cells in the ACS.
In the previous example, the 4410 should have a range 470530 scratches and the 9360 a range of 70130. To determine the
BALtolrange:BALtol range =expnumlsm+(baltol/1000 xtotscracs) \ 2where:
-
BALtol rangeindicates the range of balance tolerance value. -
expnumlsmindicates the expected number of scratches for each LSM (see above). -
baltolindicates the usersupplied percent value (tolerance-value) that specifies when scratch cartridge redistribution ends. -
totscracsindicates the total number of scratches in the ACS.
-
- MEDia(media-type)
-
optionally, specifies the type of cartridge to redistribute across the ACS.
media-typeindicates the media typeSee Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for a list of valid
media-typevalues. - RECtech(recording-technique)
-
optionally, specifies the method used to record data tracks on the tape surface.
Note:
IfRECtechis not specified, the next scratch cartridge is selected depending on theMEDiatype that has been specified.recording-techniqueindicates the recording technique. See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for validrecording-techniquevalues.
SCRPT
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
-
Active HSC not required
-
SMC must be active and communicating with at least one VLE with the deduplication feature enabled to generate data in the report output. The output report must run from an authorized library.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-139, the SCRPT command includes the following parameters:
- STORclas(storage-class-name or storage-class-list)
-
specifies the names of one or more Storage Classes. If not specified, the report applies to all Storage Classes.
storage-class-nameorstorage-class-listindicate the Storage Class name or list of Storage Classes. Storage Class names must be 1 to 8 alphanumeric characters beginning with an alpha character and must follow SMS naming conventions.
SCRPT Report
The following is an example of the SCRPT report:
Storage STORMNGR Node Total Capacity Used Compressed Uncompressed Reduction
Class MVCs (GB) (GB) (GB) (GB) Ratio
PROD1 VLELIB1 0 4 1000 200 800 3200 16.0:1
1 3 750 200 400 1600 8.0:1
2 5 1250 200 400 1600 8.0:1
3 4 1000 0 0 0 1.0:1
VLELIB1 16 4000 600 1600 6400 10.7:1
Total= 16 4000 600 1600 6400 10.7:1
{All} VLELIB1 0 4 1000 200 800 3200 16.0:1
1 3 750 200 400 1600 8.0:1
2 5 1250 200 400 1600 8.0:1
3 4 1000 0 0 0 1.0:1
VLELIB1 16 4000 600 1600 6400 10.7:1
Total= 16 4000 600 1600 6400 10.7:1
Fields
The SCRPT report includes the following fields:
- Storage Class
-
The Storage Class.
- STORMNGR
-
The VLE subsystem name.
- NODE
-
The server node.
- Total MVCs
-
Total count of VMVCs in this grouping.
- Capacity (Gb)
-
Total capacity in Gbs of all VMVCs in this grouping.
- Used (Gb)
-
Total Gbs of used VMVC space in this grouping.
- Compressed (Gb)
-
Total Gbs of compressed data in this grouping, which is equal to the size of the data as the VTSS compresses it (at a 4:1 ratio) and writes it to a VTV.
- Uncompressed (Gb)
-
Total Gbs of uncompressed data in this grouping, which equals the original size of the data before the VTSS compresses it and writes it to a VTV.
- Reduction Ratio
-
The approximate reduction ratio for the data, which is Uncompressed Gb divided by Used Gb. The Reduction Ratio, therefore, includes both VTSS compression and VLE deduplication. A larger reduction ratio indicates more effective compression and deduplication. For example, the VTSS receives 16 Mb of data, compresses it to 4Mb, and writes the compressed data to a VTV. VLE subsequently deduplicates the VTV to 2Mb and writes it to a VMVC. Thus, the reduction ratio is 16Mb2Mb or 8.0:1.
Because the calculation is done using Mb, it is possible to see 0Gb in the Used or Uncompressed fields, yet see a reduction ratio other than 1.0:1.
SENter
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The SENter command schedules an enter on a CAP that is currently allocated to an eject operation. The SENter command must be issued from the host that has the CAP allocated for ejecting cartridges.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-140, the SENter command includes the following parameters:
- cap-id
-
capidindicates the CAP to use to enter the cartridge. One CAP must be specified and it must be allocated to the host issuing theSENtercommand.The format of a
capidisAA:LL:CC, whereAA:LLindicates the LSMid, andCCindicates the CAP. See "CAPid" for a list of valid values.
Note:
The format of an LSMid isAA:LL, where AA indicates the ACSid (decimal 00-99) and LL indicates the LSM number (decimal 00-99).SET
The SET command enables you to change selected library configuration settings without performing a library reconfiguration. It performs operations directly on the control data set and does not require the HSC to be active.
Issue this command with any of the options listed in the following table. Each option is described individually, and in more detail, on the pages to follow.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
cleaning cartridge prefix |
|
|
HSC/VTCS command prefix |
|
|
whether to allow all SMC client systems to use device addresses defined in the SMC |
|
|
eject password |
|
|
SL8500 Bulk CAP skip global setting |
|
|
whether to disallow (freeze) or allow (unfreeze) additional cartridges to be stored on a panel or LSM |
|
|
changes an old host id to a new host id |
|
|
specifies that the HSC active and release level indicators are to be cleared for the designated host |
|
|
defines primary and secondary log files to include logical transactions necessary to recover the CDS. |
|
|
specifies that the |
|
|
changes the following VTCS migration parameters:
|
|
|
specifies that a new host is to be added |
|
|
enables or disables the VTCS to |
|
|
specifies that the LMU station addresses are to be set |
|
|
specifies that the device numbers for the drives in a particular panel are being changed or added |
|
|
specifies that the LMU station addresses are to be set. |
|
|
specifies that the SMF record type used by the HSC is to be set |
|
|
specifies that the TapePlex is to be used |
|
|
specifies that the control data set recovery technique is to be set |
|
|
The |
|
|
The |
|
|
The |
|
|
The |
|
|
The |
SET CLNPRFX
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The SET CLNPRFX command sets a cleaning prefix.
Note:
HSC must be shut down on all systems before changing the cleaning prefix.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-141, the SET CLNPRFX command includes the following parameters:
- prefix
-
indicates a 3character prefix for the cleaning cartridges. Valid characters are AZ, 09, $, #, and @.
Note:
HSC must be shut down on all systems before changing the cleaning prefix.
SET CLNPRFX Procedure
To change a cleaning cartridge prefix:
-
Eject all cleaning cartridges from all ACSs. The HSC records information about cleaning cartridges in the CDS.
-
Terminate the HSC on all hosts.
-
Change the cleaning prefix using
SET CLNPRFX. -
Initialize the HSC on any desired hosts.
-
Enter new cleaning cartridges identified with the new prefix into all ACSs.
Note:
It is preferable to enter new cleaning cartridges because a cartridge's select count is set to zero when it is ejected and reentered. The select count tracks the number of times a cleaning cartridge has been used.SET COMPRFX
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-142, the SET COMPRFX command includes the following parameters:
- cmdhex
-
indicates the 2character hexadecimal code of the command prefix. Do not choose a value that conflicts with values assigned to other subsystems. The characters associated with each code are shown in Table 3-14.
The command prefix is not valid until the HSC or VTCS system is recycled.
Make sure that the prefix character used does not conflict with any of the following:
-
another subsystem's command prefix character (such as $ for JES2 or * for JES3, or ; the delimiter for TSO).
-
the command delimiter for MVS, specified as the value for the
CMDDELIMkeyword inSYS1.PARMLIB(CONSOLxx) and described in the IBM z/OS Installation and Tuning Guide. -
a JES line editing character as specified in the JES installation statements or default. For JES2 the initialization statement is
CONDEF. -
For JES3 the installation statement is
CONSTD. Descriptions of these statements and default values can be found in the appropriate IBM z/OS JES3 Installation and Tuning Guide.
If you are running the HSC on a VM host that shares the CDS with a HSC running on MVS, make sure that your command prefix character does not conflict with any of the VM facilities, such as the CP line editing symbol. The following table maps command prefix codes to characters:
-
Table 3-14 Mapping of Command Prefix Codes to Characters
| Hex | Character | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
null |
blank |
|
|
cent |
|
|
|
. |
period |
|
|
< |
less than |
|
|
( |
left parenthesis |
|
|
+ |
plus |
|
|
| |
vertical bar |
|
|
& |
ampersand |
|
|
! |
exclamation point |
|
|
$ |
dollar sign |
|
|
* |
asterisk |
|
|
) |
right parenthesis |
|
|
; |
semicolon |
|
|
not symbol |
|
|
|
- |
minus |
|
|
/ |
slash |
|
|
, |
comma |
|
|
% |
percent |
|
|
_ |
underscore |
|
|
> |
greater than |
|
|
? |
question mark |
|
|
: |
colon |
|
|
# |
crosshatch |
|
|
@ |
at sign |
|
|
= |
equals sign |
|
|
" |
double quote |
If you specify a null command prefix (hex 40), you must use the MVS MODIFY command to perform any HSC operator command.
For example: F SLS0 MOUNT EDU050,B30
where:
-
Fis an abbreviation for the MVSMODIFYcommand. -
SLS0is an HSC subsystem. -
MOUNTis an HSC operator command. -
EDU050is aVOLSER ID. -
B30is a designated tape drive.
SET DRVHOST
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The SET DRVHOST command directs SMC client systems to use drive addresses defined in the SMC DRIVemap command to influence allocation and request mounts and dismounts.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-143, the SET DRVHOST command includes the following parameters:
- OFF
-
indicates that each HSC reports device addresses to SMC clients based on drives defined for that host in the HSC
SLILIBRY LIBGENmacro. host-id-
a host name defined in the CDS.
SET EJCTPAS
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The SET EJCTPAS command sets a HSC eject password. This password is not valid until the HSC system is recycled.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-144, the SET EJCTPAS command includes the following parameters:
- newpswd
-
a 1 to 8character eject password.
The new password must be alphanumeric: AZ (capital letters only) and 09. If
newpswdis omitted, eject password checking is disabled.Note:
newpswdis not be displayed onSLSPRINT. - ,OLDPASS(oldpswd)
-
specifies that the old eject password is being specified. The old password must be specified to change or delete a password. To delete an old password, omit it from the syntax, that is,
OLDPASS(). If there is not currently an eject password, this parameter can be omitted.oldpswdindicates the 1to 8character old eject password.Note:
oldpswdis not displayed onSLSPRINT.
SET EJCTSKP
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The SET EJCTSKP command enables or disables the SL8500 Bulk CAP global setting that requests the EJECT process skip the last slot of the magazines on rails 1-3 and the first slot of rail 4. These empty cells provide the ability to more easily remove the magazine from the CAP.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-145, the SET EJCTSKP command includes the following parameters:
- OFf
-
Disables this setting for all Bulk CAPs.
- ON
-
Enables this setting for all Bulk CAPs.
Note:
Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring HSC and VTCS for information about how to change CAP types from SL8500 standard rotational CAPs to Bulk CAPs, or vice versa.SET FREEZE
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The SET FREEZE command specifies whether to disallow (freeze) or allow (unfreeze) additional cartridges to be stored on a panel or LSM.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-146, the SET FREEZE command includes the following parameters:
- ON
-
specifies to freeze a panel or LSM, which prevents additional cartridges from being moved to it. This restriction includes allocating new cartridge locations on a panel or LSM as a result of the following:
-
a
MOVecommand, utility, or PGMI request -
cartridge entry into the ACS
-
float, scratch dismount, or scratch redistribution processing.
If a cartridge on a frozen panel is selected (e.g., through a mount request), it may be returned to its home cell on the frozen panel after fulfilling the request.
Cartridges already located on a frozen panel or LSM must be deliberately moved off using the
MOVecommand, utility, or PGMI request, or cartridges can be ejected by running theEJECtcommand orEJECtutility. -
- OFF
-
specifies to unfreeze a panel or LSM, which enables additional cartridges to be moved to it.
- FORLSMID(lsm-id)
-
specifies that the operation is being restricted to a specific panel or LSM.
lsm-idindicates the LSMid (AA:LL) of the LSM being frozen or unfrozen. An LSMid (lsm-id) is made up of the ACSid (decimal 00-99) and the LSM number (decimal 00-99) separated by a colon (:). - FORPANEL(panel)
-
optionally, specifies that the operation is being restricted to a specific panel.
panelindicates the 2-digit ID of the panel to be frozen or unfrozen. The specified panel must be an existing drive panel in the LSM. See "Panels" for a list of valid values.
Note:
-
If frozen panels already exist in an LSM, and then you freeze the entire LSM, all panels will be unfrozen when you unfreeze the LSM.
If you want some panels to remain frozen after unfreezing the entire LSM, you can add
SET FREEZE ON FORLSMID FORPANELstatements to the sameSLUADMIN JOBSTEP. -
When an LSM is frozen, no new cell allocations occur. However, any cartridge from the frozen LSM that is currently mounted on a drive will return to its home cell.
-
Frozen or unfrozen panels and LSMs are recognized immediately by all active HSCs. It is not necessary to stop and reinitialize active HSCs to detect changes made by
SET FREEZE.On a frozen panel, if a panel type is changed by running the
MERGEcdsorReconfigurationutility, the new panel is not frozen. If the panel type did not change, the panel remains frozen after a merge or reconfiguration.
SET HOSTID
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The SET HOSTID command renames a host ID.
Note:
If other hosts are active at the time of the host name change, some messages on those active hosts may display the old host name. After the HSC is restarted on those hosts, the new host name appears in the messages.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-147, the SET HOSTID command includes the following parameters:
- HOSTID(newhost)
-
specifies that the old host ID is being changed to a new name.
newhostindicates a 18 character host ID, which represents the SMF system ID for both JES2 and JES3.newhostcannot already be defined in the CDS. - FORHOST(oldhost)
-
specifies the old host ID.
oldhostindicates a 1to 8character host ID. This host must not be marked active in the CDS. A HSC can be down but still marked active.SET HOSTIDwould fail to run. To be marked inactive, the HSC, in the host that is down, must be brought up and then shut down. Also, another host could perform crosshost recovery on the HSC that is down, but marked active. Either of these change the status in the CDS of the down HSC from active to inactive. See "SET HSCLEVel" for information about resetting operating flags.Note:
You must delimit theHOSTID(newhostoroldhost) with quotes when this ID is in lower case.
SET HSCLEVel
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The SET HSCLEVel command clears HSC active and release level indicators for a designated host.
Note:
If used,HSCLEVel should be performed only when the host designated in hostid is inactive.These indicators remain set after an abrupt termination of the HSC has occurred. For example, a cancellation of the HSC or a crash of the operating system.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-148, the SET HSCLEVel command includes the following parameters:
- OFF
-
specifies that the HSC active and HSC release level indicators for the designated host are to be cleared.
- FORHOST(host-id)
-
specifies that the active indicators are to be cleared for the designated host.
hostidindicates the 1 to 8character host ID of the host to which the operation is restricted.
Note:
Oracle recommends the following alternatives to executingSET HSCLEVel because they reset the HSC indicators and recover resources owned by the failing host:
-
Restart the HSC on the host.
-
Enter the
RECoverhostidFORCEoperator command.
SET LOGFILE
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The SET LOGFILE command is part of the HSC Transaction Logging Service, introduced in HSC 7.0.
This command defines primary and secondary log files used by the HSC transaction logging service to record VTCS logical transactions necessary to recover the CDS.
If it becomes necessary to restore a CDS, the information in these log files can be used to reduce the amount of time required to restore the VTCS data in the CDS back to the proper state.
Note:
-
Log files must be pre-formatted using the
FMTLOGutility. See "FMTLOG" for more information. -
If logging is not currently active, log file names specified in the
SET LOGFILEcommand are activated immediately. -
If logging is currently active, you must run the
OFFload LOGFILEutility using theOFFload LOGFILEcommand to change the log files. See "OFFload" for more information.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-149, the SET LOGFILE command includes the following parameters:
- primary-log-file-dsn
-
the data set name for the primary log file. This parameter is required.
- OFF
-
Specify
OFFin place of the primary-log-file-dsn to indicate that logging should be terminated. Logging will continue on the HSC subsystem until you runOFFload LOG, unless you also specify theIMMEDparameter.- IMMED
-
specifies that logging should be immediately stopped on all active HSC subsystems. When
IMMEDis specified, any previous log data cannot be offloaded.
- secondary-log-file-dsn
-
optionally, the data set name for the secondary log file. This parameter is required if a secondary log file was previously defined.
When changing only the secondary log file data set name, you must re-specify the existing primary log file data set name in the primary log file data set name position.
- OFF
-
Specify
OFFin place of thesecondary-log-file-dsnto change from duplex to simplex logging.
SET MAJNAME
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required. HSC must be shut down on all systems before changing the QNAME.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-150, the SET MAJNAME command includes the following parameters:
- qname
-
a 1 to 8character
QNAME. TheQNAMEis blank padded on the right. The name should conform to the requirements for aQNAME. If any hosts are MVS hosts, to prevent conflicts with the operating system, theQNAMEshould not start withSYSAthroughSYSZ. Since the HSC is authorized, theSYSAthroughSYSZnames would be allowed, but deadlock may result.
Note:
HSC must be shut down on all systems before changing theQNAME.SET MIGOPT
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Description
The SET MIGOPT command changes the following migration parameters:
-
Maximum and minimum concurrent automatic migration, immediate migration, and migrate-to-threshold tasks.
-
High and low AMTs.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-151, the SET MIGOPT command includes the following parameters:
- VTSS(vtssname)
-
optionally, specifies the VTSS whose migration parameters you want to change. If you do not specify a VTSS, the changes affect all VTSSs.
vtssnameindicates the VTSS identifier. - MAXmig(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum number of concurrent automatic migration, immediate migration, and migrate-to-threshold tasks.
nnindicates the number of tasks. Valid values are 1 to the number of RTDs attached to the VTSS. There is no default; if you do not specify a value, the current value is unchanged. - MINMIG(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the minimum number of concurrent automatic migration, immediate migration, and migrate-to-threshold tasks.
nnindicates the number of tasks. Valid values are 1 to theMAXMIGsetting. There is no default; if you do not specify a value, the current value is unchanged. - HIGHthld(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the new high AMT.
nnindicates the new high AMT as a percent of VTSS space. Valid values are 5 to 95 and must be greater than theLOWthldvalue. - LOWthld(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the new low AMT.
nnindicates the new low AMT as a percent of VTSS space. Valid values are 5 to 95 and must be less than theHIGHthldvalue.
SET NEWHOST
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-152, the SET NEWHOST command includes the following parameters:
- newhost
-
a 18 character host ID, which represents the SMF system ID for both JES2 and JES3.
-
The new host to be added cannot exceed the maximum limitation of 16 hosts.
-
newhostcannot already be defined in the CDS. -
You must delimit the
HOSTIDwith quotes whennewhostis in lower case.
-
- LIKEHOST(model-host)
-
specifies that an existing configuration, as currently defined in the
LIBGEN, is to be used for the new host. Settings used include the following:-
SLILIBRY NNLBDRV(nonlibrary drive esoteric) -
SLIACS ACSDRV(ACS drive esoteric) -
SLISTATN ADDRESS(ACS 3270 station addresses) -
SLIDRIVS ADDRESS(drive addresses)
model-hostindicates a 1 to 8character host ID. -
SET RMM
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-153, the SET RMM command includes the following parameters:
- ENable
-
enables the VTCS to
DFSMSrmminterface. With the interface enabled, VTCS communicates withDFSMSrmmon all scratch mounts and scratch requests of VTVs whose Management Class specifiesDELSCR(YES). - DISable
-
disables the VTCS to
DFSMSrmminterface. With PTF L1H139T installed, the interface is automatically disabled at VTCS initialization.
If you do not specify a parameter, VTCS displays the current setting of the interface.
Note:
-
Enabling the
DFSMSrmminterface is required only for sites that do not have IBM APAR OA03368 applied and the following (minimum) VTSS microcode levels installed:VSM3: N01.00.65
VSM4: D01.00.03
VSM5: all microcode levels have the required change
-
If required, Oracle recommends adding the VTCS
SET RMM ENAcommand to theSLSSYSxxPARMLIBmember read at HSC initialization. -
Enabling this interface can cause delays in scratch mount processing.
SET SCRLABL
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The SET SCRLABL command specifies the scratch label type.
To add to the scratch pool, the REPLaceall function is run before the Scratch Update utility. Otherwise, the Scratch Update utility should be run to update the scratch pools after using this function.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-154, the SET SCRLABL command includes the following parameters:
- SL
-
specifies that nonspecific requests for standardlabeled tapes are to be automated.
- AL
-
specifies that nonspecific requests for ANSIlabeled tapes are to be automated.
- NL
-
specifies that nonspecific requests for nonlabeled tapes are to be automated.
- NSL
-
specifies that nonspecific requests for nonstandard labeled tapes are to be automated.
SET SLIDRIVS
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The SET SLIDRIVS command adds or changes device numbers for drives in a particular panel.
-
For 9310 and 9740 libraries, these changes take effect when you recycle the affected HSC system(s). See "Running SET SLIDRIVS With the HSC Active" for more information.
-
For SL3000 and SL8500 libraries, these changes take effect when you issue a
MODIFY CONFIG UPD ACS(XX)for the ACS that the drives were added to. NCO adds the drives to the configuration. There is no need to recycle the HSC.
Caution:
For 9310 and 9740 libraries, Oracle recommends you bring the HSC down on all hosts before specifying this parameter, and recycle the HSC after everySET SLIDRIVS operation. Table 3-15 describes some instances where the HSC can remain active, however, unpredictable results can occur.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-155, the SET SLIDRIVS command includes the following parameters:
- addr0,...addr31
-
the device numbers for the panel. The numbers are from the top of the panel down. If a device number is omitted, this means that the host cannot access a drive in that particular position in the panel, or the drive does not exist. Blanks as well as commas may be used to separate the drive specifications.
The total number of drives specified (including comma placeholders) must be:
-
4, 10, or 20 for a 9310
-
16 for an SL8500
-
8, 16, 24 or 32 for an SL3000
-
You cannot specify 20-drive panels on 9740 (TimberWolf) LSMs or SL8500 libraries.
-
10drive and 20drive panels cannot be specified on 4410 LSMs.
Before this utility can be executed, all cells in the panel must be empty if the user is moving to or from a 20drive panel configuration.
The user can change a drive panel between a 4 or 10drive panel (normal) and a 20drive panel (wide) without running a reconfiguration. Affected panels must be empty and no cells in the panels can be allocated to cartridges.
To make sure that drive panels being changed from normal to wide configurations (or vice versa) remain empty, freeze them with the
SET FREEZEutility. Then, move all cartridges to other panels or LSMs.If a panel type is changed by
SET SLIDRIVS, the new panel will not be frozen. Frozen panels whose panel type did not change remain frozen afterSET SLIDRIVS.HSC does not allow duplicate addresses for drives. If it becomes necessary to exchange the drive addresses on one panel with the drive addresses on another panel, the addresses on one of the panels must first be changed to temporary addresses that are not currently defined. For example:
LSM00, PANEL10, ADDRESSES400,401,402,403 LSM01, PANEL11, ADDRESSES404,405,406,407
If the 400403 addresses are to be moved to LSM01 and 404407 are to be moved to LSM0, the
SETutility must first be run to change the LSM0 addresses (400403) to 900903 (or some other addresses that are not currently defined). TheSETutility is then run to change the LSM01 addresses to 400403. The utility is run a third time to change the temporary LSM0 addresses (900903) to 404407.On all 9310 LSMs, drives are defined to the HSC from top to bottom, with addr0 representing the topmost drive and
addrnthe bottommost drive.However, on a 9740 10drive panel LSM, the drives are populated and configured to the 9740 LSM from bottom to top. (9740 4drive panels are configured to the 9740 LSM from top to bottom, as are all other LSM drive panels.)
An example showing how to define a 9740 10drive panel containing five 9840 drives is:
SET SLIDRIVS(,,,,,BD4,BD3,BD2,BD1,BD0),FORLSMID(lsm-id), FORPANEL(panel)For the SL3000, drives are defined from top to bottom, right to left, as looking from the front to the back of the library.
For the SL8500, drives are defined from top to bottom, right to left, as viewed from the outside of the library.
-
- FORLSMID(lsm-id)
-
specifies that the operation is being restricted to a specific LSM.
lsmidindicates the LSMid (AA:LL) containing the drive panel whose addresses are being changed. An LSMid (lsm-id) is made up of the ACSid (decimal 00-99) and the LSM number (decimal 00-99) separated by a colon (:). - FORPANEL(panel)
-
specifies that the operation is being restricted to a specific panel.
panelindicates the 2digit ID of the panel containing the drives whose addresses are being changed. See "Panels" for a list of valid values.Note:
The specifiedpanelmust be an existing drive panel in the LSM. - MODEL(model-type)
-
optionally, specifies the transport model number.
model-typeindicates the model type.See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for a list of valid
model-typevalues.Note:
TheMODELparameter is only used to specify the drive type for manual RTDs., which are defined in a nonexistent ACS. When an LSM is brought online, the (non-manual) drive type is automatically set. - FORHOST(host-id)
-
specifies that the operation is being restricted to a specific host. Only the specified hosts' drive device numbers are set. If omitted, the device numbers for all hosts are changed.
hostidindicates the 1 to 8character host ID of the host, to which the operation is restricted.Note:
The number of drive positions for a specific host must equal the number of drive positions defined globally (issuingSET SLIDRIVSwithout theFORHOSTparameter).
Running SET SLIDRIVS With the HSC Active
The following applies to 9310 and 9740 LSMs only. It does not apply to the SL8500 or SL3000.
Ideally, the HSC should be shut down on all hosts when you specify the SET SLIDRIVS parameter. In some cases, however, the HSC can be left active without causing adverse results. Table 3-15 defines options for running SET SLIDRIVS.
Table 3-15 HSC State/SET SLIDRIVS Operation
| HSC State | Effect on SET SLIDRIVS |
|---|---|
|
Down |
If the HSC is down on all hosts, the HSC recognizes all new drive locations when it is initialized. |
|
Active |
The HSC can be up on all hosts only if new drives are being added at new drive locations. The HSC recognizes the new drive locations when it is recycled on a host. |
|
Active |
If unit addresses are changed or deleted for an existing drive location, either the affected LSM must be offline until the HSC has been recycled on all hosts, or the affected ACS must be offline to all affected hosts that access an HSC that has not been recycled. |
SET SLIDRIVS Procedure
The following procedures show one method for changing unit addresses with the HSC active.
For the 9310 and 9740:
For one host:
-
Modify the affected LSM offline (
MODifylsmidOFFline). The LSM will be offline to all hosts. -
Use
SET SLIDRIVSto update the CDS drive records while the Oracle StorageTek CSE(s) is making the hardware changes. -
Recycle the HSC on one host.
-
Vary the affected ACS offline (
Vary ACS(acsid)OFFline) on all hosts running an HSC that has not been recycled. -
Modify the affected LSM online (
MODifylsmidONline). The LSM will be online to all hosts where the ACS is online. Only hosts that are online to the ACS and running a recycled HSC will mount to drives connected to this LSM.
For the remaining hosts, recycle the HSC, and the affected ACS will come up.
SET SLISTATN
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The SET SLISTATN command adds or changes LMU station addresses in an ACS. The change does not take effect until the affected HSC(s) is recycled.
An affected HSC is one that resides in the host specified in FORHOST. If FORHOST is omitted, all HSCs are relevant because the operation is not restricted to a specific host.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-156, the SET SLISTATN command includes the following parameters:
- stat1,...,stat16
-
the LMU station addresses associated with a particular ACS. No station addresses are required. Up to 16 can be specified, separated by commas.
When adding one or more station addresses to an existing list of stations, you must specify all old stations as well as new ones. Any stations (for this ACS and Host ID) not specified here will be deleted and no longer available for use.
To remove station addresses for an ACS or host, do not specify station addresses following the
SLISTATNparameter. For example:SET SLISTATN(),FORACS(01),FORHOST(HSCA) - FORACS(acs-id)
-
specifies the ACS for which station addresses are being changed.
acsidindicates the ACSid whose stations are being changed (00 FF). - FORHOST(host-id)
-
specifies that the operation is being restricted to a specific host. Only the specified hosts' stations are set. If omitted, the stations for all hosts are changed.
hostidindicates the 1 to 8character host ID for the host to which the operation is restricted.
SET SMF
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The SET SMF command adds a new SMF record type for HSC.
Until the HSC is recycled on all CPUs, the ACTIvities command produces incorrect results because some HSC systems are writing records with the old SMF type, and some with the new record type.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-157, the SET SMF command includes the following parameters:
- libtype
-
the SMF record type. The range is from 0 to 255, inclusive.
Since 128 through 255 are for userdefined records, it is recommended that a number from 128 through 255 be chosen, and that the number does not conflict with other userdefined record types.
SET TAPEPlex
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-158, the SET TAPEPlex command includes the following parameters:
- tapeplex-name
-
the 1-8 character TapePlex name.
The TapePlex name must start with an alphabetic or numeric character. Remaining characters may be letters, numbers, or hyphens, however, a hyphen may not be the last character. You can specify a
NULLvalue (TAPEPLEX()) to allow the TapePlex name to be set automatically by the next SMC transaction.
Note:
This name must match the TapePlex name specified on the SMCTAPEPlex command on ALL SMC systems that communicate with this HSC system. See "TAPEPlex" for more information about the SMC TapePlex command.SET TCHNIQE
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The SET TCHNIQE command sets the control data set recovery technique. This replaces the recovery technique currently defined in the CDS.
Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring HSC and VTCS for information about the LIBGEN SLIRCVRY macro. A recovery technique value must be specified. There is no default value.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-159, the SET TCHNIQE command includes the following parameters:
- NONE
-
specifies no form of recovery is used for the control data set. Thus, the primary control data set must be rebuilt, if inaccessible.
- SHADOW
-
specifies that there is to be two distinct copies of the control data set (primary and secondary) for recovery purposes. It is recommended that these data sets reside on separate HDAs and separate strings. A journal is not recorded.
- STANDBY
-
specifies that primary, secondary, and standby control data sets are to be recorded for recovery purposes. No journals are recorded during HSC operation.
SET TCHNIQE Procedure
Use the following procedure to invoke the TCHNIQE utility and to set the appropriate recovery technique value:
-
ALLOCATE, based on existing CDS definitions, any new CDS copies that will be needed for the subsequentSETrecovery technique. -
Stop the HSCs on all hosts configured to use the CDS you are intending to update with
SETrecovery technique. -
Run the
BACKuputility. -
Run the
RESToreutility to restore all CDS copies required to support the current recovery technique. If the recovery technique update in the following step requires new CDS copies, then include them in this restore. -
Run the
SETutility with the appropriate recovery technique value. It is important to note that theSETutility for this recovery technique update must include DD statements for all CDS copies defined in either the old or the new recovery technique. -
Run the
BACKuputility again. This backup provides you with the ability to restore the updated CDS.
SET VAULT
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The SET VAULT command defines VAULT information for a server complex. This information is stored in the CDS and serves as the VAULT information source for all server systems that access the CDS.
Note:
Before running this utility for the first time, you must run theSET VAULTVOL utility to create the Vault Volume records in the CDS.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-160, the SET VAULT command includes the following parameters:
- ADD NAME(cccc)
-
Add a specified Vault to the CDS.
ccccindicates the Vault name. You can specify a maximum of 8 characters.NAME(cccc)is required. - SLOTS(nnnn)
-
optionally, specifies the number of slots in the Vault.
nnnnindicates the number of slots. The slot number can be 1-999,999,999. When specified with theMODoption, theSLOTSnumber must be greater than the current number ofSLOTSdefined to the Vault.The total number of slots for all Vaults cannot exceed the number of Vault Volumes set by the
SET VAULTVOLutility.- DESC(aaaa)
-
optionally, specifies the description of the Vault.
aaaaindicates the description. You can specify a maximum of 120 characters. If blank characters are included, the entire value must be enclosed in single quotes. This parameter is only valid with theADDandMODparameters. - TMSNAME(bbbb)
-
optionally, specifies the TMS Vault name.
bbbbindicates the Vault name. You can specify a maximum of 8 characters. This parameter is only valid with theADDandMODparameters.
- DEL NAME(cccc)
-
Delete a specified Vault from the CDS.
ccccindicates the Vault name. You can specify a maximum of 8 characters.NAME(cccc)is required. - MOD NAME(cccc)
-
Modify a specified Vault from the CDS.
ccccindicates the Vault name. You can specify a maximum of 8 characters.NAME(cccc)is required.- SLOTS(nnnn)
-
optionally, specifies the number of slots in the Vault.
nnnnindicates the number of slots. The slot number can be 1-999,999,999. When specified with theMODoption, theSLOTSnumber must be greater than the current number ofSLOTSdefined to the Vault.The total number of slots for all Vaults cannot exceed the number of Vault Volumes set by the
SET VAULTVOLutility. - DESC(aaaa)
-
optionally, specifies the description of the Vault.
aaaaindicates the description. You can specify a maximum of 120 characters. If blank characters are included, the entire value must be enclosed in single quotes. This parameter is only valid with theADDandMODparameters. - TMSNAME(bbbb)
-
optionally, specifies the TMS Vault name.
bbbbindicates the Vault name. You can specify a maximum of 8 characters. This parameter is only valid with theADDandMODparameters. - NEWNAME(cccc)
-
optionially, specifies the new name of the Vault.
ccccindicates the Vault name. You can specify a maximum of 8 characters. This parameter is only valid with theMODparameter.
SET VAULTVOL
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The SET VAULTVOL command defines the VAULT volume area. This information is stored in the CDS and serves the VAULT volume area information source for all server systems that access the CDS.
Note:
-
You must run this utility before running the
SET VAULTutility. -
There is no
SETutility command to increase, decrease, or remove all vault volume records once theSET VAULTVOLutility is run. To increase the number of vault volume records, use theMerge CDSutility to migrate vaults and vaulted volumes to a CDS that has been configured with a greater number of vault volumes.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-161, the SET VAULTVOL command includes the following parameters:
- NBRVOLS(nnnnnn)
-
specifies the number of VAULT volumes to be added to the CDS.
nnnnnnindicates the number of volumes. This number can be 1-9,999,999,999.
Note:
-
Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring HSC and VTCS for details on calculating CDS space requirements for Vaulting.
-
The number of Vault volumes must be greater than the total number of slots for all Vaults created with the
SET VAULTutility.
SET VOLPARM
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The SET VOLPARM command defines the volume and pool information for a server complex. This information is stored in the CDS and is the volume and pool information source for all server systems (ELS 7.0 or higher) that access the CDS.
SET VOLPARM reads POOLPARM and VOLPARM control statements that define VOLUME/POOL information in the form of named pools of specific types, and their associated volser ranges.
Once SET VOLPARM is run, older volume and pool definitions are disabled for all server systems (ELS 7.0 or higher) that access the common CDS.
Note:
-
HSC 6.2 or lower systems are unaware of the presence of the
SET VOLPARMdata and continue to operate as though theSET VOLPARMutility had not been run. -
Specify
REGION=0Mon theEXEC PGM=SLUADMINstatement when the number of input statements exceeds 10,000 card images. -
If you delete MVCs or VTVs from the configuration as a result of either
SET VOLPARMorCONFIG MVCVOLorCONFIG VTVVOLprocessing:If MVCs were deleted, you cannot re-enter the volsers into the configuration as VTVs.
If VTVs were deleted, you cannot re-enter the volsers into the configuration as MVCs.
Do not use the volsers for native HSC tapes.
Message SLS6944I indicates the number of MVCs or VTVs that have been deleted.
The following commands are disabled for systems (ELS 7.0 or higher) after SET VOLPARM:
HSC:
-
VOLDEF -
SCRPDEF
VTCS:
-
MVCDEF -
CONFIG VTVVOLorCONFIG MVCVOL
The HSC/VTCS systems do not need to be recycled for the new volume and pool definitions to take effect. The attached HSC/VTCS in the CDS complex are notified of the definition changes and the volume and pool definitions are automatically active.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-162, the SET VOLPARM command includes the following parameters:
- APPLY
-
specifies whether the
POOLPARMorVOLPARMdefinitions are to be applied to the CDS:- NO
-
Validate the definitions but do not apply them to the CDS (the default).
- YES
-
Apply the definitions. If you specify
YES, theSLSPARMdata set containingPOOLPARMandVOLPARMcontrol statements is read and applied to the CDS. Additionally, the date and time of this action is stored in the CDS, and is output by theDisplay CDScommand.
POOLPARM and VOLPARM control statements are defined in the SLSPARM data set, and define VOLUME or POOL information in the form of named pools of specific types, and their associated volser ranges.
-
When a
POOLPARMstatement is read, all subsequentVOLPARMsencountered until the nextPOOLPARMstatement are applied to the priorPOOLPARM. -
When
VOLPARMstatements are read without a priorPOOLPARM, thoseVOLSERvolumes will be considered non sub-pool (subpool 0) volumes.
See "POOLPARM Control Statement" and "VOLPARM Control Statement" for more information.
Additional JCL Requirements
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statement applies to the SET VOLPARM JCL:
- SLSPARM
-
specifies the data set that contains the
POOLPARMandVOLPARMcontrol statements that define volumes and pools.
Using SET VOLPARM to Disable POOLPARM/VOLPARM
To disable POOLPARM or VOLPARM, run the SET VOLPARM utility with an empty SLSPARM input file.
Once POOLPARM or VOLPARM is disabled:
-
The previous version of
POOLPARMorVOLPARMremains in effect for MVC and VTV definitions until you run VTCSCONFIg. -
The previous
POOLPARMorVOLPARMPOOLdefinitions remain in effect until you run theVOLDEF,SCRPDEFandMVCDEFcommands on the HSC host(s).
POOLPARM Control Statement
POOLPARM control statements define pool information for a server complex in the form of named pools of specific types.
VOLPARM statements define a volser, volser list, or volser range to be associated with the specified POOLPARM statement.
POOLPARM and VOLPARM statements are defined in the SLSPARM data set, and are loaded using the SET VOLPARM utility. See "SET VOLPARM" for more information.
-
When a
POOLPARMstatement is read, all subsequentVOLPARMstatements encountered before the nextPOOLPARMstatement are applied. -
When
VOLPARMstatements are read without a priorPOOLPARM, thoseVOLSERvolumes are considered non-subpool (subpool 0) volumes.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-163, the POOLPARM control statement includes the following parameters:
- TYPE
-
specifies the type of pool definition. Valid types include
SCRATCH,CLEAN,MVC, andEXTERNAL.
TYPE(SCRATCH) Subparameters
If you specify TYPE(SCRATCH), the following subparameters apply:
- NAME(nnnn)
-
specifies the name of the volume pool.
NAMEis required forTYPE(SCRATCH)pools. Additonally,NAME(DEFAULTPOOL)is not valid forTYPE(SCRATCH)pools.nnnnindicates the volume pool name. A maximum of 13 characters is allowed. Blank spaces are not allowed.- HOSTid(host-id)
-
optionally, defines the hosts that can access the named sub-pool.
host-idindicates the host id. Multiplehost-idsmay be specified, separating eachhost-idvalue with a comma. If ahost-idis not specified, the default is all hosts.HOSTiddetermines which client hosts can mount volumes from the named subpool. If a mount request is received from a client not specified in theHOSTidlist, the HSC rejects the mount request and the mount is not satisfied. If you did not specify anALIASHOSTon the SMCSERVercommand, then specify the 4 characterSMFIDof the MVS hosts that will access the subpool. Otherwise, you can specify up to 8 characters for the host name matching the SMCALIASHOSTspecification. - LABEL
-
optionally, specifies the label type associated with the named subpool. Specify one of the following:
-
SLindicates standardlabeled tape. This is the default if the parameter is omitted. -
ALindicates ANSIlabeled tape. -
NLindicates nonlabeled tape. -
NSLindicates nonstandard labeled tape.
Note:
Scratch volume requests without a sub-pool (sub-pool 0) will come from volumes not defined in named subpools. -
- DRTEST
-
optionally, specifies that the scratch pool is to be used in
DRTESTenvironments.
TYPE(CLEAN) Subparameters
If you specify TYPE(CLEAN), the following subparameters apply:
- MAXclean
-
optionally, specifies the maximum cleaning cartridge usage for the named sub-pool. Do not specify values that exceed the manufacturer's recommendation for usage.
The volumes defined in the
CLEANsub-pools must begin with the cleaning cartridge prefix defined in theLIBGEN.Note:
IfMAXcleanis not specified in theVOLPARMstatement, the value or default of theMAXcleanparameter in theMNTDoperator command is used for all cleaning cartridge counts.
TYPE(MVC) Subparameters
If you specify TYPE(MVC), the following subparameters apply:
- NAME(nnnn)
-
specifies the name of the volume pool. This parameter is optional for
TYPE(MVC)pools. Additionally,NAME(DEFAULTPOOL)is not valid forTYPE(MVC).NAME(ALL)is not valid forTYPE(MVC)pools.nnnnindicates the volume pool name. A maximum of 13 characters is allowed. Blank spaces are not allowed.- DRTEST
-
optionally, specifies that the MVC pool is to be used only in
DRTESTenvironments. - INITMVC
-
optionally, enables or disables the MVC initialization feature.
- YES
-
enables the MVC initialization feature.
- NO
-
disables the MVC initialization feature.
- MVCFREE(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the minimum number of free MVCs in the MVC pool. A free MVC has 100% usable space and does not contain any migrated VTVs.
nnindicates the number of MVCs. Valid values are 0 to 255. There is no default; if not specified, theCONFIG RECLAIMvalue (or default) is used.If free MVCs is equal or less than this value, VTCS issues message
SLS6616Iand initiates an automatic space reclamation. - MAXMVC(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum number of MVCs to be processed in a single space reclamation run.
nnindicates the number of MVCs. Valid values are 1 to 98. There is no default; if not specified, theCONFIG RECLAIMvalue (or default) is used.For automatic space reclamation to start, the number of eligible MVCs (determined by the
THRESHparameter) must also exceed theMAXMVCvalue. - START=nn
-
optionally, specifies the level at which automatic space reclamation starts for each ACS (not globally for all ACSs), or, if specified, for a Named MVC Pool.
nnis a percentage value, which is equal to:Reclaim Candidates/(Reclaim Candidates+Free MVCs)* 100Where:
-
Reclaim Candidatesindicates the number of Reclaim Candidates determined by theCONFIG RECLAIM THRESHLDparameter. -
Reclaim Candidates+Free MVCsequals the number of Reclaim Candidates plus the number of free MVCs.
Valid values are 1 to 98. There is no default. If not specified, the
CONFIG RECLAIMvalue (or default) is used. -
- THRESH(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the percentage of fragmented space that makes an MVC eligible for demand or automatic reclamation.
nnindicates the percentage. Valid values are 4 to 98. There is no default; if not specified, theCONFIG RECLAIMvalue (or default) is used. - INPTHRSH(nn)
-
optionally, specifies the percentage of fragmented space that makes an MVC in partitioned format (within the pool) eligible for dynamic reclaim processing.
This value overrides the global
INPTHRSHvalue specified in theCONFIg RECLAIMstatement. If this parameter is not specified, the current active globalINPTHRSHvalue is used.nnindicates a percentage between 3 and 97. This value must be less than theTHRESHLDvalue.Note:
IfINPTHRSHis specified,THRESHLDmust also be specified. BothINPTHRSHandTHRESHLDplay roles when space reclamation processes MVCs in partitioned format. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Configuring HSC and VTCS for more information. - RECLaim
-
optionally, specifies space reclaim behavior of the
MVCPOOL.- AUTo
-
VTCS will output message
SLS6699Eand schedule automatic space reclaims. Reclaims may also be invoked using theRECLAIMcommand. This is the default. - DEMand
-
VTCS will not output message
SLS6699Eand will not schedule automatic space reclaims. Reclaims may be invoked using theRECLAIMcommand.RECLaim(DEMand)is mutually exclusive withMVCFREEandSTART. - REPortonly
-
VTCS will output message
SLS6699Ebut will not schedule automatic space reclaims. Reclaims may not be invoked using theRECLAIMcommand.RECLaim(REPortonly)is mutually exclusive withMAXMVC,START, andTHRESH.Note:
REPortonlyis equivalent to, and replaces, theNORECLAMparameter thoughNORECLAMis still tolerated if theRECLaimparameter is not specified. - NONe
-
VTCS will not output message
SLS6699Eand will not schedule automatic space reclaims. Reclaims may not be invoked using theRECLAIMcommand.RECLaim(NONe)is mutually exclusive withMVCFREE,MAXMVC,START, andTHRESH.
- NORECLAM
-
optionally, specifies that the named
MVCPOOLwill not be eligible for space reclamation.Note:
The use of theMVCFREE,MAXMVC,THRESH,INPTHRandSTARTparameters override the values specified onCONFIGfor the namedsub-pool. - NOMIGRAT
-
optionally, specifies that the
MVCPOOLwill not be eligible for selection for migration MVCs This enables MVC information to be retained in the CDS virtual area. The MVCs will not be used for new migrations.
TYPE(EXTERNAL) Subparameters
If you specify TYPE(EXTERNAL), the following subparameters apply:
- NAME(nnnn)
-
specifies the name of the volume pool. This parameter is required for
TYPE(EXTERNAL)pools.nnnnindicates the volume pool name. A maximum of 13 characters is allowed. Blank spaces are not allowed.- OWNRPLEX
-
optionally, specifies the name of the TapePlex that owns the volumes in the external pool.
For VTVs, this controls volumes imported via Cross-TapePlex Replication. A VTV can only be imported if the sending system's TapePlex name matches the
OWNRPLEXvalue.Volumes in an
EXTERNALpool can be scratched only if the scratch request originates from the TapePlex matching theOWNRPLEXname. The TapePlex name is defined via the SMCTAPEPLEX NAMEparameter and theCONFIG TAPEPLEX THISPLEXparameter.Alternatively, volumes in an external pool with an
OWNRPLEXname ofLOCALHSCcan be scratched on the local system (but not used as scratch volumes on the local system).Note:
Refer to Oracle's ELS publications Managing HSC and VTCS and ELS Disaster Recovery and Offsite Data Management Guide for more information about Cross-TapePlex Replication.
VOLPARM Control Statement
VOLPARM control statements define volume attributes for a server complex. These statements define a volser, volser list, or volser range to be associated with a specified POOLPARM statement.
POOLPARM and VOLPARM statements are defined in the SLSPARM data set, and are loaded using the SET VOLPARM utility. See "SET VOLPARM" for more information.
VOLPARM statements follow a POOLPARM statement and apply only to that POOLPARM.
-
When a
POOLPARMstatement is read, all subsequentVOLPARMstatements encountered before the nextPOOLPARMstatement are applied. -
When
VOLPARMstatements are read without a priorPOOLPARM, thoseVOLSERvolumes are considered non-subpool volumes.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-164, the VOLPARM control statement includes the following parameters:
- VOLSER(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
specifies one or more volumes to which this definition applies.
volser,volrange, orvollistindicates a single VOLSER, a VOLSER range, or a list of VOLSERs.Do not overlap the ranges. Doing so causes an error which invalidates the entire
POOLPARMdefinition. - MEDia(media-type)
-
optionally, specifies the media type for the volume(s) specified on the
VOLSERparameter.media-typeindicates the media type.See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for a list of valid
media-typevalues.Note the following:
-
Only specific media types can be entered. Generic media types, that is,
LONGItudandHELicalcannot be specified. -
If this parameter is not specified, a default is chosen based on the value of the
RECtechparameter. Table A-2 shows default values used ifMEDiais omitted. -
If both media type and recording technique are omitted, all media types and recording techniques are assumed to be eligible. It is recommended that
MEDiaalways be specified on allVOLPARMstatements.
-
- RECtech(recording-technique)
-
optionally, specifies the method used to record data on the media for the volume(s) specified on the
VOLSERparameter.recording-techniqueindicates the recording technique.See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for valid
recording-techniquevalues.If this parameter is not specified on any matching
VOLPARMstatement, a default is chosen based on the value of theMEDiaparameter. Table A-4 shows default values used ifRECtechis omitted. - INITSCR
-
optionally, specifies that the
VIRTUALvolume has an initial status ofSCRATCH.The
INITSCRparameter is only valid withMEDIA(VIRTUAL)and/orRECTECH(VIRTUAL)volumes.INITSCRonly has meaning when the VTV is first defined. - DRTEST
-
optionally, specifies that the volumes in the defined range are to be used only in
DRTESTenvironments. TheDRTESTparameter is only valid forVOLPARMstatements defined before the firstPOOLPARMstatement.
SET VOLPARM UPDATE
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The SET VOLPARM UPDATE command defines the changes to the volume and pool information for a server complex. The information stored in the CDS by the SET VOLPARM utility is changed to reflect the new VOLUME or POOL information.
The HSC/VTCS systems do not need to be recycled for the updated volume pool definitions to take effect. The attached HSC/VTCS in the CDS complex are notified of the definition changes and the volume and pool definitions are automatically active.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-165, the SET VOLPARM UPDATE command includes the following parameters:
- APPLY
-
specifies whether the
POOLPARMorVOLPARMchanges are to be applied to the CDS:- NO
-
Validate the changes but do not apply them to the CDS (the default).
- YES
-
Apply the changes. If you specify
YES, theSLSPARMdata set containing thePOOLPARMandVOLPARMchangecontrol statements is read and applied to the CDS.
POOLPARM and VOLPARM change control statements are defined in the SLSPARM data set and define VOLUME or POOL information in the form of named pools of specific types, and their associated volser ranges.
-
When a
POOLPARMstatement is read, all subsequentVOLPARMstatements encountered until the nextPOOLPARMstatement are applied to the priorPOOLPARM. -
When
VOLPARMstatements are read without a priorPOOLPARM, those VOLSER volumes will be considered non-subpool (subpool 0) volumes.
Additional JCL Requirements
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statement applies to the SET VOLPARM UPDATE JCL:
- SLSPARM
-
specifies the data set that contains the
POOLPARMandVOLPARMchange control statements that define the pool and volume changes to the CDS volume and pool information.
POOLPARM Change Control Statement
POOLPARM Change control statements define new pool information for a server complex in the form of named pools of specific types.
VOLPARM Change control statements define or remove a volser, volser list, or volser range associated with the specified POOLPARM Change statement.
POOLPARM and VOLPARM Change statements are defined in the SLSPARM data set, and are loaded using the SET VOLPARM UPDATE utility. See "SET VOLPARM" for more information.
-
When a
POOLPARMChangestatement is read, all subsequentVOLPARMChangestatements encountered before the nextPOOLPARMChangestatement are applied. -
When
VOLPARMChangestatements are read without a priorPOOLPARM, those VOLSER volumes are considered non-subpool (subpool 0) volumes.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-166, the POOLPARM Change control statement includes the following parameters:
- change-type
-
specify one of the following to add, delete, or update a pool:
- ADD
-
A new pool is to be added to the server complex.
VOLPARMchangestatements that follow thisPOOLPARM changestatement will define the volumes associated with this pool. - DELETE
-
An existing pool is to be deleted. When the pool is deleted, the associated volumes will also be deleted.
- UPDATE
-
An existing pool definition is to be changed.
UPDATEcan be used to changePOOLPARMparameters. For example, the value of theMVCFREEparameter may be changed.UPDATEis also used to associate theVOLPARM changestatements that follow with the correct pool.Note:
UPDATEcannot be used to change the name of a pool.
- pool-parameters
-
The
POOLPARMstatement parameters. See "POOLPARM Control Statement" for valid parameters.Note:
When deleting or updating aPOOLPARMstatement, specify all of the parameters of the originalPOOLPARMstatement.
VOLPARM Change Control Statement
VOLPARM change control statements define or remove a specific volser, volser list, or volser range associated with the previous POOLPARM UPDATE change statement.
POOLPARM and VOLPARM change statements are defined in the SLSPARM data set, and are loaded using the SET VOLPARM UPDATE utility.
-
When a
POOLPARMchangestatement is read, all subsequentVOLPARMchangestatements encountered before the nextPOOLPARMchangestatement are applied. -
When
VOLPARMchangestatements are read without a priorPOOLPARM, those VOLSER volumes are considered non-subpool (subpool 0) volumes.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-167, the VOLPARM Change control statement includes the following parameters:
- change-type
-
specify one of the following to add or delete a volume:
- ADD
-
A new volume, volume list or range is added to the pool defined by the previous POOLPARM UPDATE statement. When no prior POOLPARM UPDATE statement exists, the VOLPARM information will be added as non-subpool (subpool 0) volumes.
- DELETE
-
An existing volume, volume list or range is to be deleted.
- volume-parameters
-
The
VOLPARMstatement parameters. See "VOLPARM Control Statement" for valid parameters.Note:
When deleting aVOLPARMstatement, specify all of the parameters of the originalVOLPARMstatement.
SET VOLPARM JOIN
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The SET VOLPARM JOIN command merges contiguous volume ranges defined on multiple VOLPARM statements into one new VOLPARM statement.
The output of this utility can be used as input to the SET VOLPARM utility to replace the original server complex volume and pool information in the CDS.
Additional JCL Requirements
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statement applies to the SET VOLPARM JOIN JCL:
- SLSPARM
-
specifies the input data set that contains the
POOLPARMandVOLPARMcontrol statements that define the pool and volume contained in the CDS. - SLSPARM2
-
specifies the output data set that contains the
POOLPARMand theVOLPARMstatements after the volume range merge operations have been accomplished.
SRVlev
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Description
The SRVlev command sets the HSC service level. See "HSC Service Levels" for information about BASE and FULL service levels.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-169, the SRVlev command includes the following parameters:
- BASE
-
specifies that the HSC is to operate at the
BASEservice level.Note:
When the HSC service level drops toBASE, hosttohost communications using the LMU method are switched to the CDS method. When the HSCFULLservice level is restored, you must issue theCOMMPathcommand to return to LMU communications. - FULL
-
specifies that the HSC is to operate at the
FULLservice level.Note:
When the HSC service level is brought fromBASEup toFULL, outstanding mount requests are resolved.
STOPMN
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Description
The STOPMN command stops monitoring of cartridge move requests from the programmatic interface.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-170, the STOPMN command includes the following parameters:
- PGMI
-
specifies that monitoring of cartridge move requests from the programmatic interface is to be terminated.
- ,L(
ccorname) -
optionally, identifies the console where the monitoring information is being displayed. If this parameter is omitted or if
L=is specified without a console ID or console name, the monitoring being displayed on the console that issued the command is terminated.ccoptionally indicates the console ID. Allowable values are decimal in the range from 00 through 99. Specifying 00 stops information from being sent explicitly to the hardcopy log.nameoptionally indicates the console name.
- ,L(
SWitch
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The SWitch command can be used to manually reverse the roles of the master and standby LMUs or Library Controllers (LCs). The following configurations support switching:
-
dual LMU
-
SL8500 dual Library Controller (LC)
In a dual LMU environment, this command initiates an IPL in the master LMU, causing the current standby LMU to become the master LMU. If the former master LMU completes the IPL successfully, it then assumes the role of the standby LMU.
In a dual LC configuration for a multiple SL8500 library ACS, the SWitch command issues a request to the LMU to switch the library LCs by library ID.
Caution:
-
Issue the
Display Acscommand before you enter theSWitchcommand to ensure the library to switch includes an assigned TCP/IP address or host name for the standby. If it does not, do not switch the library because doing so causes the HSC to lose communication with the library. -
Before you issue the
SWitchcommand, stop all HSC activity. -
After you issue the
SWitchcommand, do not start HSC on any other hosts and do not start any HSC activity (mounts, dismounts,Display ACS, or any other commands) until the switch process is complete.
Note:
-
For this release, only the SL8500 library is supported for dual LC switching.
-
For an automatic switch to occur (for example, from
LCAtoLCBor visa versa), the LC must fail. In this case, if there is a network/communication problem withLCA, the HSC goes into network recovery for theLCAconnection(s). If you cannot recover or fix the connection, issue theSWitchcommand to switchLCAtoLCBmanually. -
Before you issue the
SWitchcommand, if the library is partitioned, be aware of other host software groups (ACSLS, HSC, ELS) using other partitions in the same library.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-171, the SWitch command includes the following parameters:
- Acs acs-id
-
optionally, indicates that an ACSid is being specified. This parameter is required for a multipleACS environment configuration or if an
acsidis specified.acsididentifies the ACS that must switch the current active connection as standby and bring the standby connection online as active.In a single ACS configuration,
Acsacsidis optional and defaults toACS 00. If theacs-iddefaults to 00 or is specified with no other parameters, then all of the ACS's active connections are switched to standby, and the standby connections are switched to active.- RESET
-
Optionally, used in conjunction with
ACSacs-idto reset the internal switch setting and internal conflict counts for an ACS. This is helpful when aSWitchis invoked for an SL8500 library and one or more LSMs fail to reach ready state after theSWitchprocess completes.Before issuing a
SWitch RESETcommand, it is recommended that you enter theDisplay Statuscommand to determine which ACS(s) are in the switch process and which ACSs are conflict active.Verify that the library has completed the
SWitchprocess before you consider issuing aSWitch RESETcommand. Also verify that aSWitch RESETis complete before you consider issuing anotherSWitchcommand.Use the following guidelines to determine when to issue a
SWitch RESETcommand after aSWitch ACScommand is issued:-
Issue
SWitch RESETafter theSWitchprocess completes, as indicated by the following message:SLS0694I ACS aa: Switch has completedIf this message is not displayed, wait for the
SLS6013Imessage to be displayed for the active connection before issuing theSWitch RESETcommand. -
If you receive the following message after the switch process has completed:
SLS1004I ACS aa cannot switch; ACS is busyIssue the
SWitch RESETcommand on another host. If theSLS1004Imessage is displayed again, bring up another HSC host and issue theSWitch RESETcommand, or restart an HSC host and then issue theSWitch RESETcommand.
-
- LIBrary lib-id
-
optionally, specifies the SL8500 library ID for the connection switch. This parameter applies only to the SL8500 library.
lib-idindicates the library id from 1 to 9 or A to G.For an SL8500 four library ACS cluster, each library is assigned an ID from 1 to 4, as shown in the following figure:
An ACS can have up to 16 library connections with A and B Library Controller (LC) connections. For the initial release, only one library (preferred to be ID 1) can have A and B LC connections. The other libraries can have a single LC connection. Each LC can handle dual TCP/IP (2B and 2A). The following table describes the LSM ID correlation to Library ID:
Note:
-
Before issuing this command, use the
Display ACSacs-id command to see if the library to switch has a TCP/IP address or Host Name assigned to the standby. If there is not a TCP/IP address or Host Name assigned to the standby, do not switch the library as this will cause HSC to lose communication to the library. -
For a switch to occur (for example, from
LCAtoLCB), the LC must fail. For example, if there is a network/communication problem withLCA, HSC enters network recovery for theLCAconnection(s). If you cannot recover/fix the connection, then issue the HSCSWitchcommand to manually switchLCAtoLCB. -
If the library is partitioned, please be aware of the other host software groups (ACSLS, HSC, ELS) that are using other partitions in the same library before issuing the
SWitchcommand.
TRace
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Description
The TRace command enables or disables tracing of events for selected HSC and VTCS components.
The MVS GTF GTRACE facility performs the actual tracing. To create GTF output for the event, GTF must be started and the TRace command must be issued before the event.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-173, the TRace command includes the following parameters:
- OFF
-
optionally, turns off tracing for the specified component(s).
- comp-name or comp-list
-
one or more components for which tracing is to be enabled or disabled. If a list of component names is specified, separate the identifiers with blank spaces or commas. Valid component names are listed below. Uppercase letters denote the minimum abbreviations allowed.
The following table describes valid components:
Component Name Description ALlocAllocation volume lookup
AScommAddress Space Communications
CApCAP Common
COnfigurConfiguration Control
DatabaseDatabase server
FPFunction Points. FP tracing is used only by Oracle developers.
HCommHost Communications
InitialiInitialization
LmuLMU server
LSLibraryStation
MountMount/Dismount
OperatorOperator Commands
RecoveryRecovery (Note: must also trace SERvice)
SERviceServices
UtilitieUtilities
UUIUnified User Interface
VolumeVolume/Cell
VTcsVTCS
WtoWTO Services
XMlXML Interface
Note:
-
When tracing is enabled or disabled for one or more components, the status of all component tracing is displayed.
-
By default, all
TRacecommand output goes to GTF. For example, to trace an LMU and send the output to GTF, issueTR LMU. No other parameters are necessary. -
To trace the Recovery component, you must also trace the
SERvicecomponent (a service is used to trace Recovery). -
The
LScomponent displays in messageSLS0068Ionly if LibraryStation has been initialized.
TRACELKP
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Description
The TRACELKP command enables or disables tracing of LOOKUP events associated with HSC definition files. The GTF GTRACE facility is used to perform the tracing.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-174, the TRACELKP command includes the following parameters:
- table-name or table-list
-
one or more
LOOKUPdefinition files for which tracing is to be enabled or disabled. If a list of event names is specified, separate the identifiers with blank spaces or commas.When
LOOKUPtracing is enabled or disabled for one or more files, the status of allLOOKUPtracing is displayed. AllLOOKUPtracing output goes to GTF.Valid
LOOKUPtable names are listed in the table below. Uppercase letters denote the minimum abbreviations allowed.Table 3-18 TRACELKP Lookup Names
LOOKUP name Description VOLATTRVOLATTR(VOLDEF) tableLMUPATHLMUPATH(LMUPDEF) tableMVCPOOLMVCPOOL(MVCDEF) tableMGMTCLASMGMTCLAS(MGMTDEF) tableSTORCLASSTORCLAS(STORDEF) tableLOOKFAILTrace the
LOOKUPfailures in detail. IfLOOKFAILis specified, the detail failure trace records are output for all events that areON.MIGRSELMIGRSEL(MGMTDEF) tableMIGRVTVMIGRVTV(MGMTDEF) table - OFF table-name
-
optionally, disables tracing for the specified component(s).
table-nameindicates the components to be disabled.
UEXIT
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Description
The UEXIT command defines how HSC processes your user exits.
HSC user exits allow you to invoke your own processing routines at particular points during HSC processing. User exits controlled by the HSC are loaded at HSC initialization from the load library identified by DDNAME SLSUEXIT. The following user exits are managed by the HSC using the UEXIT command:
-
SLSUX03 -
SLSUX05 -
SLSUX06 -
SLSUX14 -
SLSUX15
Using the UEXIT command, you can start the HSC with a user exit disabled and then enable the exit at any time the HSC is operational. If an exit does not perform as expected, make the necessary changes and load it again.
The UEXIT command optionally enables you to provide unique user exit load module names and to create different versions of an exit that can be run at different times (for example, day shift versus night shift). The load modules are contained in a user-defined load module library described at HSC startup.
Note:
-
User Exit 03 and User Exit 05 are legacy interfaces and have been replaced by alternative facilities that do not require a User Exit.
-
User Exit 03 is enabled at HSC initialization. The
UEXITcommand cannot be used to enable, disable, or reload this exit.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-175, the UEXIT command includes the following parameters:
- nn
-
specifies the user exit number. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Legacy Interfaces Reference for user exit numbers.
- Load
-
causes the specified module to be loaded into storage.
- SLSUXnn
-
specifies the default name for the user exit. If name is not specified, then the default name is used when the HSC loads the module into storage.
- name
-
the name of the module to be used for this exit. This is the entry point name which is used to linkedit the load module.
- Enable
-
indicates that upon completion of the command the specified exit is considered as being active.
Enableis the default. - Disable
-
indicates that upon completion of the command the specified exit is considered as being inactive.
- Enable
-
optionally, specifies that the most current module for the specified user exit (
nn) is to be enabled. This parameter may also be specified with theLoadparameter. - Disable
-
optionally, specifies that the most current module for the specified user exit (
nn) is to be disabled. This parameter may also be specified with theLoadparameter. - nn, nn-range, or nn-list
-
can be used with the
Queryparameter to specify a single user exit, a range of exits, or a list of exits.When specifying a range of user exit numbers, the beginning number must be separated from the ending number by a hyphen. For example:(0409)In a list of user exits, the user exit numbers must be separated by commas and the list must be enclosed in parentheses. For example:(01,04,10) - Query
-
requests the status of all the currently loaded versions of the specified user exit number(s). A display of user exit status may be specified for a single user exit, a range of exits, or a list of exits.
UNSCratch
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-176, the UNSCratch command includes the following parameters:
- VOLser(vol-list)
-
specifies the list of volume serial numbers to be added, deleted, or replaced in the scratch list(s).
vollistindicates the volume serial numbers; this can be a single volume, a list of volume serial numbers, ranges of volume serial numbers, or combinations of lists with ranges delimited by commas. You can specify a maximum of 100 volume serial numbers. The entire list must be enclosed in parentheses.
UNSElect
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The UNSElect command unselects a volume that is erroneously in a selected state.
Note:
-
Use this utility only if you are certain that the HSC has incorrectly left the volume selected. Incorrect use of this utility can result in HSC abends and errant volumes.
Issue a
Display Volume DEtailcommand to determine which host has the volume in question. Then, issueDisplay DRivesandDisplay Requestscommands on the host that has the volume in question to see if that volume is being used.If the selected volume is mounted on a transport, issue a
DISMountcommand for the transport. If there is a request active to the LMU for the volume, wait for the request to complete. If the overdue response handler indicates the request has timed out, you may want to abort the request. -
The
UNSElectfunction can only be invoked whenSLUADMINis invoked APF authorized, key 0 through 7, or supervisor state. The load module invoked byUNSElectisSLUNSEL. Restricting access to this module restricts access to this utility function.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-177, the UNSElect command includes the following parameters:
- VOLser(volser)
-
indicates that a VOLSER is being specified for unselection.
volserindicates the VOLSER to be unselected. - ,FORCE
-
optionally, indicates that the volume is to be unselected even if communication with the host that has the volume selected is not possible.
Vary
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIB(Vary ACS) -
Console or utility, UUI All (
Vary CLINK,RTD, orVTSS) -
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
-
Active HSC at
FULLservice level (Vary ACS) -
Active HSC/VTCS (
Vary CLINK,RTD, orVTSS)
Description
The Vary command changes the online/offline state for the following:
-
ACSorstation -
CLINK -
PATH -
RTD -
VTSS
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-178, the Vary command includes the following parameters:
- ACS(acs-id, acs-range, or acs-list)
-
optionally, specifies the ACS to be made online, offline, or standby to this host.
acs-id,acs-range, oracs-listindicates one or more ACSs to be varied. Eachacs-listelement can be either a single ACSid or an ACSid range. Ranges are separated by a dash. The elements in a list must be separated by commas or blanks, and the entire list must be enclosed in parentheses. - NETC(net-id, net-range, or net-list)
-
optionally, used in conjunction with ACS
acs-idto vary online/offline a single, range, or list of HSC library network connections.net-id,net-range, ornet-listindicates one or more network connection to be varied. Eachnet-listelement can be either a singlenet-idor anet-idrange. Ranges are separated by a dash. The elements in a list must be separated by commas or blanks, and the entire list must be enclosed in parentheses. - ONline
-
specifies that the stations are to be made online or standby to this host.
- OFFline
-
specifies that the stations are to be made offline to this host.
- FORCE
-
optionally, indicates that the stations are to be made offline immediately. The
FORCEoption can be specified when the HSC is at theFULLservice level or is past theBASEservice level going to theFULLservice level.This parameter applies only to the
OFFlineoperand.
- STation(dev-id, dev-range, or dev-list)
-
optionally, specifies the stations to be made online, offline, or standby to this host.
In an ACS, a connection between the host CPU and an LMU is referred to as a ”station.” Each station appears to the host CPU as a 3278-2 device and is physically connected to a port on a supported 3174, 3274 or compatible terminal controller. Each LMU can contain a maximum of 16 stations. Depending on the number of host CPUs connected to the ACS, each host CPU can have either one or several stations to each LMU.
devid,devrange, ordevlistindicates the stations to an LMU to be varied. Eachdevlistelement can be either a single device number or a range of device numbers. Ranges are separated by a dash.The elements in a list must be separated by commas or blanks, and the entire list must be enclosed in parentheses. Each device number identifies a device attached to the host issuing the command. Allowable values are 000-FFF. - CLInk(clink-id)
-
the specified CLINK.
clink–idindicates the link ID. - VTSS(vtssname)
-
the sending VTSS in the Cluster.
vtssnameindicates the 1 to 8 character identifier of the sending VTSS. - ONline
-
specifies that the stations are to be made online or standby to this host.
- OFFLine
-
Vary the specified CLINK offline.
- PATH(rtd-name or rtdname-list)
-
optionally, specifies the path (from a VTSS to RTDs) to be made online, offline, or standby to this host. This permits the individual
RTDPATHfrom a VTSS to a device to be varied to the desired state. This path may represent either a direct connection to a RTD from a VTSS or a connection to a Virtual Library.rtd-nameorrtdname-listindicates the names assigned to the paths for accessing RTDs for Virtual Libraries from a VTSS - ONline
-
Vary the specified path (from a VTSS to RTDs) to an online state.
- OFFLine
-
Vary the specified path (from a VTSS to RTDs) to an offline state.
- MAINt
-
Vary the specified path (from a VTSS to RTDs) to an offline (maintenance mode) state.
- RTD(rtd-name, rtd-list, or rtd-range)
-
Change the state of the specified RTDs.
rtd-name,rtd-range, orrtd-listindicates the unit addresses of one or more RTDs. Lists and ranges of RTDs are limited to 64 items for VSM2s and VSM3s and 256 items for VSM4s. - ONline
-
Vary the specified RTDs online to their connected VTSSs.
- OFFLine
-
Vary the specified RTDs offline to their connected VTSSs.
- MAINt
-
Vary the specified RTDs offline (maintenance mode) to their connected VTSSs.
- VTSS(name)
-
Change the state of the specified VTSS.
nameindicates the VTSS identifier.Note:
Vary VTSS does not change the state of the VTDs or RTDs associated with the specified VTSS. - ONline
-
Vary the specified VTSS online.
- OFFline
-
Vary the specified VTSS offline.
- QUIESCED
-
Vary the specified VTSS to quiesced state.
Note:
Vary VTSS does not change the state of the VTDs or RTDs associated with the specified VTSS.
VIew
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at FULL service level
Description
The VIew command enables you to see specified internal components of the LSM when video monitors are attached to the LSM.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-179, the VIew command includes the following parameters:
- CAp
-
indicates that a camera is to focus on a cell location in a CAP. If you do not specify the
CAPIDorLsmparameter, the command defaults toCAPid 00:00:00. If you do not specify theRowandColumnparameters, the command defaults torow 0,column 0.- CAPID(cap-id)
-
identifies one CAP in an LSM that contains multiple CAPs.
capidindicates the CAP that you want to view. The format of acapidisAA:LL:CC, whereAA:LLindicates the LSMid, andCCindicates the CAP. See "CAPid" for a list of valid values. - Lsm(lsm-id)
-
identifies an LSM that contains a single CAP.
lsmidindicates the single CAP that you want to view. The format of an LSMid isAA:LL, whereAAindicates the ACSid (decimal 00-99) andLLindicates the LSM number (decimal 00-99). - Row(rr)
-
identifies a row number in a CAP. If you do not specify this parameter the command defaults to
row 0.rrindicates the row number. Allowable values forrrare decimal and are specific to the LSM type. See "Rows" for a list of valid values. - Column(cc)
-
identifies the column number within a CAP. If you do not specify this parameter the command defaults to column 0.
ccindicates the column number. Allowable values forccare decimal and are specific to the LSM type. Columns are numbered starting at the left of the panel. See "Columns" for a list of valid values.
- CEll
-
indicates that a camera is to focus on a cartridge storage or diagnostic cell in an LSM panel. If you do not specify the
Lsm,Panel,Row, andColumnparameters, the command defaults toLSM 00:00,panel 0,row 0,column 0.- Lsm(lsm-id)
-
identifies an LSM. If you do not specify this parameter, the command defaults to
LSMid 00:00.lsmidindicates the LSMid. The format of an LSMid isAA:LL, whereAAindicates the ACSid (decimal 00-99) andLLindicates the LSM number (decimal 00-99). - Panel(pp)
-
designates the LSM panel number containing the cartridge storage or diagnostic cell that the camera is to view. If you do not specify this parameter the command defaults to panel 0.
ppindicates the panel number. Allowable values forppare decimal and are specific to the LSM type. See "Panels" for a list of valid values. - Row(rr)
-
identifies a row number in an LSM panel. If you do not specify this parameter the command defaults to row 0.
rrindicates the row number. Allowable values forrrare decimal and are specific to the LSM type. See "Rows" for a list of valid values.Column 3 on panel 2 allows row entries only on rows 28-41. The cells on panel 3 are optional.
- Column(cc)
-
identifies the column number within a panel. If you do not specify this parameter the command defaults to column 0.
ccindicates the column number. Allowable values forccare decimal and are specific to the LSM type. Columns are numbered starting at the left of the panel. See "Columns" for a list of valid values.
- DRive
-
indicates that a camera is to focus on a cartridge drive. You must designate the
Addressparameter to identify the drive. TheHostparameter enables you to view a drive defined to another host.- Address(xxx)
-
specifies the address of a cartridge drive. The
Addressparameter defines the operating system address of the transport you want to inspect.xxxindicates the hexadecimal address of the transport. The HSC verifies that the specified address matches theLIBGENdefined address for the given host. - Host(host-id)
-
gives meaning to the Address parameter when the drive being inspected is not defined in the
LIBGENfor the host from which theVIewcommand is being entered.If you do not specify the
Hostparameter, the HSC checks theLIBGENdefined drive list for the host from which you entered theVIewcommand. If the address is found in the drive list, the command is executed.hostidindicates the host where the transport is defined.
- PLaygrnd
-
indicates that a camera is to focus on a playground cell. If the
LsmandColumnparameters are not specified, the command defaults to the relative location of the cell in the playground inLSM 00:00.Note:
The playground is a reserved area of cells where the robot deposits cartridges that it finds in its hands during LSM initialization. Normal LSM initialization recovery processing moves cartridges from the playground cells to either their home cells or their intended destinations, but under abnormal circumstances cartridges may be left in playground cells. Refer to the appropriate Oracle StorageTek hardware publication for the location of the playground in the LSM.- Lsm(lsm-id)
-
identifies an LSM. If you do not specify this parameter, the command defaults to
LSMid 00:00.lsmidindicates the LSMid. The format of an LSMid isAA:LL, whereAAindicates the ACSid (decimal 00-99) andLLindicates the LSM number (decimal 00-99). - Column(cc)
-
identifies the relative location of the cell in the playground for a panel. If you do not specify this parameter, the command defaults to the relative location of the cell in the playground.
ccindicates the relative location of the cell in the playground. Allowable values forccare decimal and are specific to the LSM type. (Some LSMs have multiple playground cells and some have only one.)
- PTp
-
indicates that a camera is to focus on a passthru port (PTP) cell. You can designate a particular PTP using the
LsmandXlsmparameters, a particular cell using theColumnparameter, and specify the viewing time using theTimeparameter.Note:
When the PTP is being shared by two different LSM types, the upper limit of the column value is determined by the LSM with the smaller PTP capacity.- Lsm(lsm-id)
-
identifies an LSM. If you do not specify this parameter, the command defaults to
LSMid 00:00.lsmidindicates the LSMid. The format of an LSMid isAA:LL, whereAAindicates the ACSid (decimal 00-99) andLLindicates the LSM number (decimal 00-99). - Xlsm(ll)
-
identifies the PTP to be inspected by defining the LSM that shares the PTP.
Each PTP is identified by the two LSMs it services. The
Lsmparameter identifies which robot is used to view the PTP, and theXlsmparameter identifies the LSM that shares the PTP. This distinction is necessary whenever an LSM contains more than one PTP.If
Xlsmis not specified for an LSM containing two or more PTPs, the HSC examines theLIBGENand selects the first PTP defined there forLsm(lsmid).llindicates the LSM number of the adjacent LSM. Values forllare decimal in the range from 00-99. (The ACS is identified in theLsmparameter.) - Column(c)
-
identifies the column number within a panel. If you do not specify this parameter the command defaults to
column 0.cindicates the column number. Allowable values for c are decimal and are specific to the LSM type:-
0-3 for LSM Models 4410, 9310, and 9740
-
0 or 1 for WolfCreek LSMs (all models).
Note:
When the PTP is being shared by two different LSM types, the upper limit of the column value is determined by the LSM with the smaller PTP capacity. -
- Time(ttt)
-
specifies the video monitor viewing time.
tttindicates the time, in seconds.
VLEMAINT
Interfaces:
-
Console or utility
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC/VTCS
Description
The VLEMAINT utility command moves or copies VLE based MVC (VMVC) data content to a specified VLE system, without using VTSS storage resources.
This utility should only be used under the guidance of Oracle Support personnel.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-180, the VLEMAINT command includes the following parameters:
- MOVEMVC(mvc-list or mvc-range)
-
specifies a list or range of VLE based MVCs whose content is to be moved to the specified target VLE system. MVCs selected in the target VLE system inherit the storage class of the source MVC.
mvc-listormvc-rangeindicates the list or range of MVCs.MOVEMVCis mutually exclusive withCOPYMVC. - TOVLE(name)
-
specifies the target VLE to receive the source VMVC data. This parameter is required.
nameindicates the target VLE name. This VLE must be valid (defined to the configuration). Otherwise, the utility aborts with a return code 8. - MGMTclas(name)
-
optionally, specifies a single management class used to filter data sent to the target VLE. Only VTVs with this management class are sent to the target VLE.
nameindicates the management class name. This name must be valid (defined inMGMTDEF). Otherwise, the utility aborts with return code 8. - COPYMVC(mvc-list or mvc-range)
-
specifies a list or range of VLE based MVCs whose content is to be copied to the specified target VLE system.
COPYMVCcreates an additional copy of the data to another storage class on the target VLE system.mvc-listormvc-rangeindicates the list or range of MVCs.COPYMVCis mutually exclusive withMOVEMVC.COPYMVCrequires aSTORclasname to be specified. - TOVLE(name)
-
specifies the target VLE to receive the source VMVC data. This parameter is required.
nameindicates the target VLE name. This VLE must be valid (defined to the configuration). Otherwise, the utility aborts with a return code 8. - STORclas(name)
-
optionally, specifies the storage class assigned to the VMVC selected at the target VLE for
COPYMVCprocessing. This parameter is required whenCOPYMVCis specified.nameindicates the storage class name. This name must be valid (defined inMGMTDEF). Otherwise, the utility aborts with a return code 8.
Optional Parameters (VLEMAINT COPYMVC)
If you specify VLEMAINT COPYMVC, the following optional parameters apply:
- MGMTclas(name)
-
optionally, specifies a single management class used to filter data sent to the target VLE. Only VTVs with this management class are sent to the target VLE.
nameindicates the management class name. This name must be valid (defined inMGMTDEF). Otherwise, the utility aborts with return code 8. - REPMGMT(name)
-
optionally, specifies a single management class name assigned to the VTV data after it is received by the target VLE system for
COPYMVCprocessing.nameindicates the management class name. This name must be valid (defined inMGMTDEF). Otherwise, the utility aborts with return code 8.
Note:
DuringCOPYMVC processing, any VTV found with the management class specified in REPMGMT is bypassed. This could potentially serve as a copy complete acknowledgment if utility restarts occur.VOLPCONV
Interfaces:
-
SLUADMINutility only -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The VOLPCONV command reads existing VOLDEF, SCRPDEF, MVCDEF, and VTCS CONFIG input statements and converts them to SET VOLPARM statements. The existing VTCS configuration is also input to the utility.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-181, the VOLPCONV command includes the following parameters:
- CLNPRFX(prefix or CLN)
-
specifies a prefix to apply to all types of cleaning cartridges.
prefixindicates a three-character prefix.CLNis the default.
Additional JCL Requirements
In addition to the required JCL definition statements described in "Invoking SLUADMIN", the following definition statements apply to the VOLPCONV JCL:
- SLSVOLA
-
input
VOLDEFdefinitions in the form ofVOLATTRstatements.Note:
VOLATTRstatements coded with the masking character (%, ? or *) within theSERIALparameter are not supported and will cause messageSLS0227Ito be issued. AnyVOLATTRstatement using these masking characters must be converted to a range that spans the intent of the masking characters prior to runningVOLPCONV. - SLSSCRP
-
input
SCRPDEFdefinitions in the form ofSCRPOOLstatements. - SLSMVCP
-
input
MVCDEFdefinitions in the form ofMVCPOOLstatements. - SLSVTCS
-
input VTCS configuration definitions. The VTCS configuration definitions can be obtained by running the VTCS
DEComputility. - SLSPARM
-
output
VOLUMEorPOOLdefinitions in the form ofPOOLPARMandVOLPARMcontrol statements. The logical record size of theSLSPARMdata set is 80.
VOLRpt
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-182, the VOLRpt command includes the following parameters:
- ACS(acs-id)
-
optionally, specifies that a report is to be produced for only a particular ACS.
acsidindicates the one or two digit decimal ACS identifier.- LSM(lsm-list)
-
optionally, specifies that a report is to be produced for only certain LSMs within an ACS.
lsmlistindicates the LSMs. Anlsmlistcan be a single LSM number or a list of LSM numbers. An LSM number is decimal 00-99.An LSM range is not allowed. If a list is specified, the elements must be separated by blanks or commas, and the entire list enclosed in parentheses.
- VOLser or VOLume(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
optionally, specifies that the report only contain information on certain VOLSERs.
volser,volrange, orvollistindicates the volume serial numbers requested. Any subranges of volumes specified in thevollistthat are not in the control data set are listed in the Control Card Image Listing portion of the report using one line per subrange.A percent sign (’’%'') may be used as a ’’wildcard'' character in the VOLSER to specify pattern matching. The percent sign designates that any single character can match the corresponding position in the VOLSER.
For example, A9%%%% specifies that all of the sixcharacter volume serial numbers that begin with the characters ’’A9'' are selected for the report.
Q%12% specifies that all fivecharacter VOLSERs that begin with ’’Q'' and have a ’’12'' in the third and fourth positions of the VOLSER are selected for the report. The percent sign cannot be specified in a range specification. Therefore, ’’A%0000A%9999'' is invalid.
In the Volume Report Listing of the utility, the volumes requested which are not in the control data set are not listed.
- SORT
-
optionally specifies a specified sort sequence.
Multiple sort criteria may be specified. The order, from left to right, specifies the order in which the report is to be sorted.
For example,
SORT(INS,USE)produces a report sorted by date inserted in the control data set, and then for each date, sorted by select count.Note:
SORTandNOSORTare mutually exclusive.The following
SORToptions are available:- VOL
-
indicates that the report is to be sorted by volume serial number (
VOLis the default). - INS
-
indicates that the report is to be sorted by date and time the volume was inserted into the control data set.
- LOC
-
indicates that the report is to be sorted by location.
- SEL
-
indicates that the report is to be sorted by date and time the volume was last selected.
- USE
-
indicates that the report is to be sorted by selection count.
- MWL
-
indicates that the report is to be sorted by Media Warranty Life (
MWL) percentage, which indicates how much of the media life has been used.Media warranty life is considered to be expired at 100%.To collect and report media warranty life, tape libraries and transports must meet the following requirements:
-
SL8500 or SL3000 libraries
-
LMU compatibility level 21 or higher
-
T9x40: all media and models at firmware level 1.42 or higher (except 9840B)
-
T10000: all models and media at firmware level 1.38 or higher
Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Managing HSC and VTCS for more information about media warranty life.
-
- ASCend
-
optionally, specifies that the report is to be sorted in ascending order.
ASCendis the default. This parameter is ignored ifNOSORTis specified.ASCendis mutually exclusive withNOSORTandDEScend. - DEScend
-
optionally, specifies that the report is to be sorted in descending order. This parameter is ignored if
NOSORTis specified.DEScendis mutually exclusive withNOSORTandASCend. - NOSORT
-
specifies that an unsorted report is to be produced.
NOSORTis mutually exclusive withSORT,ASCend, andDEScend. - INCLude
-
optionally, specifies the criteria for including volume information in the report. If this keyword is specified, all volumes that match at least one of the specified criteria are tentatively selected for the report. Information about volumes may be removed from the list of volumes selected for the report if other options, such as
EXCLUDE,VOL,ACS, orLSMare specified.-
INCLudeparameters are applied beforeEXCLudeparameters in volume selection. -
Parameter values are not checked for the existence of their opposite values (for example,
SELis still flagged even ifNONSELis specified, and vice versa). -
Positive attributes are applied before negative attributes (for example,
SCRis applied beforeNONSCR).
- *
-
indicates that all volumes in the library are considered for being included in the report. The default is *. If more than one of the following parameters is specified, the parameters must be separated by commas.
- SCR
-
specifies that scratch volumes match the specified criteria.
- NONSCR
-
specifies that nonscratch volumes match the specified criteria.
- ERR
-
specifies that errant volumes match the criteria.
- NONERR
-
specifies that nonerrant volumes match the criteria.
- SEL
-
specifies that selected volumes match the criteria.
- NONSEL
-
specifies that nonselected volumes match the criteria.
- READable
-
specifies that volumes with a readable external label match the criteria.
- UNREADable
-
specifies that volumes with an unreadable external label match the criteria.
- MEDEQUAL
-
specifies that volumes for which the media types of the
VOLATTRand theVARare equal match the criteria. - NONMEDEQ
-
specifies that volumes for which the media types of the
VOLATTRand theVARare not equal match the criteria. - NOEXTernal
-
specifies that volumes without an external label match the criteria.
For example,
INCLUDE(SEL,ERR)tentatively chooses only selected and errant volumes for the report.INCLudeparameters are applied beforeEXCLudeparameters in volume selection. - MWLNA
-
specifies that volumes with an unknown media warranty life match the criteria. Media warranty life is obtained at volume dismount for tape libraries with an LMU compatibility level of 21 or above. Use the
Display ACScommand to obtain the LMU compatibility level. - MWLGE nnn
-
specifies that volumes with a media warranty life greater than or equal to
nnnpercent match the criteria. It also excludes all volumes with an unknown media warranty life.Specify
INCLUDE(MWLNA)to force inclusion of all volumes with an unknown media warranty life. Valid values for nnn are 0-254.To collect and report media warranty life, tape libraries and transports must meet the following requirements:
-
SL8500 or SL3000 libraries
-
LMU compatibility level 21 or higher
-
T9x40: all media and models at firmware level 1.42 or higher (except 9840B)
-
T10000: all models and media at firmware level 1.38 or higher
Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Managing HSC and VTCS for more information about media warranty life.
-
-
- EXCLude
-
optionally, specifies the criteria for excluding volume information from the report. Any volumes that match one or more of the exclusion criteria are excluded from the report.
EXCLudeparameter values are the same asINCLudevalues, except for the*parameter (see theINCLudeoptions list above).As an example,
EXCL(NONSEL)excludes nonselected volumes from the report.-
INCLudeparameters are applied beforeEXCLudeparameters in volume selection. -
If
MWLGEis specified in both theINCLUDEandEXCLUDEparameters, theEXCLUDElimit value must be greater than theINCLUDElimit value. -
Parameter values are not checked for the existence of their opposite values (for example,
SELis still flagged even ifNONSELis specified, and vice versa). -
Positive attributes are applied before negative attributes (for example,
SCRis applied beforeNONSCR).
- *
-
indicates that all volumes in the library are considered for being included in the report. The default is
*. If more than one of the following parameters is specified, the parameters must be separated by commas. - SCR
-
specifies that scratch volumes match the specified criteria.
- NONSCR
-
specifies that nonscratch volumes match the specified criteria.
- ERR
-
specifies that errant volumes match the criteria.
- NONERR
-
specifies that nonerrant volumes match the criteria.
- SEL
-
specifies that selected volumes match the criteria.
- NONSEL
-
specifies that nonselected volumes match the criteria.
- READable
-
specifies that volumes with a readable external label match the criteria.
- UNREADable
-
specifies that volumes with an unreadable external label match the criteria.
- MEDEQUAL
-
specifies that volumes for which the media types of the
VOLATTRand theVARare equal match the criteria. - NONMEDEQ
-
specifies that volumes for which the media types of the
VOLATTRand theVARare not equal match the criteria. - NOEXTernal
-
specifies that volumes without an external label match the criteria.
For example,
INCLUDE(SEL,ERR)tentatively chooses only selected and errant volumes for the report.INCLudeparameters are applied beforeEXCLudeparameters in volume selection. - MWLNA
-
specifies that volumes with an unknown media warranty life match the criteria. Media warranty life is obtained at volume dismount for tape libraries with an LMU compatibility level of 21 or above. Use the
Display ACScommand to obtain the LMU compatibility level. - MWLGE nnn
-
specifies that volumes with a media warranty life greater than or equal to
nnnpercent match the criteria. It also excludes all volumes with an unknown media warranty life.Specify
INCLUDE(MWLNA)to force inclusion of all volumes with an unknown media warranty life. Valid values fornnnare 0-254.To collect and report media warranty life, tape libraries and transports must meet the following requirements:
-
SL8500 or SL3000 libraries
-
LMU compatibility level 21 or higher
-
T9x40: all media and models at firmware level 1.42 or higher (except 9840B)
-
T10000: all models and media at firmware level 1.38 or higher
Refer to Oracle's ELS publication Managing HSC and VTCS for more information about media warranty life.
-
-
- MAXclean(nnnn)
-
optionally, specifies the maximum cleaning cartridge usage for the ”over max clean” column. The
MAXcleanspecified for eachPOOLPARM TYPE(CLEAN)overrides this value.nnnnindicates the maximum usage value. Valid values are 0-32767. - VAULT
-
optionally, specifies that vaulted volumes are to be included in the detail volume report.
VAULTis mutually exclusive withNOVOL,ACS, andLSM.If the vault CDS subfile does not exist, this parameter is ignored.
Vaulted volumes are not included in the
SUMMARYreports. In the detail report, the cell location for a vaulted volume is identified by the wordVAULTand theinsertion date/timeis the date/time that the volume was inserted into the vault; i.e., ejected from the tape library. Refer to the LCM User's Guide for more information about vaulting. - SUMMary
-
optionally, specifies that the utility provide totals of volume attributes on an LSM and ACS basis, and/or subpool data on an ACS or LSM basis. Totals are affected by the use of limiting parameters such as
ACS(and possiblyLSM),VOLserorVOLume, andINCLudeand/orEXCLude.If both
TOTalandSUBpoolare specified, both reports are provided. The time and date displayed in the header for the Summary Report(s) are the same as theVolume ReportListing header.- TOTal
-
specifies that totals of scratch, selected, errant, available cells, and external label status types be provided on an LSM, ACS, and library basis in the report.
The totals are listed on a separate listing, on a new page from the Volume Report Listing and the Control Card Listing.
- SUBpool
-
specifies that subpool totals be provided on an LSM, ACS, and library basis in the report.
Subpool information can be provided using the
VOLPARMfacility. See "VOLPARM Control Statement" for more information about definingVOLPARMinformation. For alternative methods of specifying subpool information, refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Legacy Interfaces Reference.The totals are listed on a separate listing, on a new page from the Volume Report Listing, the Control Card Listing, and the Volume Report Totals Listing.
If subpools overlap (that is, a volume belongs to more than one subpool), then each volume is reported only within the first subpool in which it occurs, and totals for the other subpools may be inaccurate.
- NOVOL
-
optionally, when used with
SUMMary, specifies to display summary and/or subpool totals without producing volume detail.NOVOLshould not be specified by itself.NOVOLis mutually exclusive withACS,VOLser,VOLume,SORT,NOSORT,INCLude,EXCLude,MAXclean, andVAULT.
Additional JCL Requirements
If you are not using the VOLPARM facility to define your volume characteristics, refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Legacy Interfaces Reference for a description of additional VOLRPT JCL statements that may be required.
Volume Report
The following is an example of a volume report produced by the VOLRpt command issued with the SUMMary(SUBpool) parameter:
Volume Cell Loc Err Sel Ext Cln |--- Inserted --| |-- Last Used --| Times MWL
Serial Media Rectech AA:LL:Pa:Ro:Co | Scr | Lbl Use Subpool ID Date Time Date Time Selected %
B00141 T10000T1 T1B35 01:01:02:08:01 Y R SMCT10K 20110725 15:52:13 20110920 10:44:52 13 0
Subpool Totals, all Ranges
Subpool ID Label Type Range Limits DRTEST?
DEFAULTPOOL SL N/A - N/A No
Fields
The VOLRpt report includes the following fields:
- Volume Serial
-
the volume serial number
- Media
-
the media type. See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values".
The media field may be immediately preceded by an asterisk
*or dash-.-
An asterisk
*indicates that the media defined by aVOLATTRstatement is not compatible with the media label value. -
A dash
-indicates that the volume has noVOLATTRorVOLPARMdefined media value.
-
- Rectech
-
the recording technique. See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values".
- Cell Loc
-
the cell location field shows cartridge location by
ACS (AA),LSM(LL),panel (PA),row (RO), andcolumn (CO). - Err, Scr, Sel
-
A
Y(yes) flag under the Errant, Scratch, or Selected headings indicates that the volume is currently in that status.A volume in
Errant (Err)status shows the volume's home cell in the Cell Loc column.A
Y(yes) flag under the Selected heading indicates that the volume is currently selected, that is, being mounted, dismounted, ejected, or moved. AnMflag indicates that the volume is currently mounted. The Selected column on the totals report includes both selected and mounted volumes. The volume's home cell appears in the Cell Loc column. - Ext Lbl
-
External Label:
-
Rindicates that the volume has a readable external label. -
Uindicates that the volume has an unreadable external label. -
Nindicates that the volume has no external label.
-
- Cln Use
-
Cartridge Usability:
-
Nindicates that the volume is not usable, for example, a spent cleaning cartridge that is not usable because it has exhausted its cleaning surface. -
Mindicates that a cleaning cartridge has exceeded its maximum usage set by theMAXcleanvalue (as specified by theMNTD MAXcleanorVOLATTR MAXcleanparameters).
-
- Subpool ID
-
the subpool ID.
Scratch subpools for volumes are listed if scratch subpool definitions have been provided using
VOLPARMcontrol statements.-
*NON-VOLPARM*indicates thatVOLPARMis in effect, but this volume is not defined inVOLPARM. -
DEFAULTPOOLindicates that the volume is defined inVOLPARMwith no associated pool. -
*MVC*indicates that the volume is reserved for VTCS usage as a migration volume. -
*DEFAULT*indicates that the volume is a cleaning cartridge but has not been included in aVOLPARMdefined subpool,*DEFAULT*appears.
If
VOLPARMis not used, the generated report is the same as in the HSC 6.2 release. Refer to the HSC 6.2 System Programmer's Guide for more information. -
- Inserted
-
date and time that the volume was inserted.
- Last Used
-
date and time that the volume was last used
- MWL Media Warranty Life
-
Media Warranty Life (MWL) is a percentage value that is obtained at volume dismount for tape libraries that are at LMU compatibility level 21 or later. If you do not know the compatibility level, enter the HSC
Display Acscommand to display it. See "Display ACS" for more information.The MWL percent indicates how much of the media life has been used and is considered to be ”expired” at 100%. Values may range from 0 to 254. If the field is blank, the MWL is unknown.
Total Reports
Two totals reports can be produced:
-
volume report totals
-
subpool totals
Volume Report Totals
Total of cartridges with various characteristics are displayed for LSMs, ACSs, and the entire library.
The total selected volumes is the sum of the number of volumes currently selected and the number of volumes currently mounted.
Note:
The free storage cells reported do not include free cells on frozen panels. An LSM with at least one frozen panel is indicated by an asterisk after the free cell count.VTVMAINT
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The VTVMAINT command does the following:
-
Unlinks VTVs from MVCs,
-
Sets the VTV Management Class
-
Logically dismounts specified VTVs in an offline VTSS.
-
Specifies ownership of a VTV that has been electronically imported
-
Adds or deletes references to electronic exported copies of VTVs.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-183, the VTVMAINT command includes the following parameters:
- VTVid(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
specifies one or more VTVs.
volser,vol-range, orvol-listindicates the volsers of one or more VTVs. - ULINKMVC
-
optionally, unlink (logically delete) MVC copies of the specified VTVs.
volserindicates the volume serial number of the MVC. If no value is specified, then all MVC copies of the VTVs are deleted. - MGMTclas(mgmtclas-name)
-
optionally, set the Management Class of the VTVs.
mgmt-class-nameindicates the Management Class name that you specified on theMGMTclascontrol statement. For more information, see "MGMTclas Control Statement". - DISMOUNT VTSSid(name)
-
optionally, logically dismount the specified VTVs in the specified VTSS.
nameindicates the VTSS name.If migrated copies of the dismounted VTVs exist that an online VTSS can access, you can now use this VTSS to access the VTVs.
Caution:
If the VTV copy mounted in the offline VTSS was modified and not migrated, the MVC copy that you recall to an alternate VTSS is not current! Therefore, Oracle strongly recommends that you do not recall these non-current MVC copies!When the offline VTSS is ready to be brought back online, it is strongly recommended that you audit the VTSS before running production jobs that use the VTSS. Also ensure that you clear any boxed VTD conditions before issuing the
VTSS VARY ONLINEcommand. - OWNRPLEX(name)
-
optionally, specifies ownership of a VTV that has been electronically imported.
nameindicates the name of the TapePlex that owns the original copy of the VTV. This name must match one of the known TapePlex names in the configuration.If this name matches that indicated for the
THISPLEXparameter on theCONFIgTAPEPlexstatement, the electronic importing status is removed. - DELEXpot(name)
-
optionally, specifies which references to electronic exported copies of the VTVs are removed.
nameindicates the name of the TapePlex that is to be removed. If this parameter value is omitted, then all references to electronic export copies are removed.This parameter merely removes the reference to the external copy of the VTV from the VTV record. It does not cause a contact of the other TapePlex to modify the remote copy in any way. Depending upon the management class definition for the VTV, removing a reference could cause an automatic re-drive of the export at some later time.
- ADDEXpot(name)
-
optionally, specifies the addition of references to the electronic export copy of the VTV.
nameindicates the name of the TapePlex that is to be added. This name must match to one of the names that has been specified in the VTCS configuration.This parameter merely adds the reference to the external copy to the VTV record. It is assumed that the required copy of the VTV will have been physically placed there by some other process. The VTV record can track a maximum of two TapePlex locations.
Note:
TheDELEXpotoperation executes before theADDEXpotoperation. This makes it possible to replace the exported location information in a single call. For configurations where the electronic export function is not used, it is acceptable to use theADDEXpotandDELEXpotparameters to add dummy tracking or user information to the VTV. The information in the VTV record is always cleared when the VTV data is updated. - RENVTSS(vtss-name)
-
optionally, sets the name of the VTSS where the VTV was last mounted to
vtss-name.vtss-nameindicates the new VTSS name. This must be the name of an existing VTSS in your configuration.Note:
To useRENVTSS, the host on whichVTVMAINTis run must have access to the owning VTSS.
Return Codes
VTVMAINT includes the following return codes:
-
0indicates that all requested updates for the VTV completed successfully. -
4indicates that one requested update for the VTV failed and at lest one other requested update completed successfully. -
8indicates that all requested updates for the VTV failed.
Note:
The final return code for theVTVMAINT job is the largest return code generated by any single VTVs being updated. For example, if 5 VTVs generate a return code 0 and one VTV generates a return code 8, the final return code is 8.VTVMAINT Report
The following is an example of a VTVMAINT report produced by the following command:
VTVMAINT VTV(X00000-X00002) ULINKMVC MGMTCLAS(M1)
VTV RC
X00000 04
X00001 04
X00002 04
VTVMAINT EXCEPTION REPORT
VTV X00000 IS ALREADY IN MGMTCLAS M1
VTV X00001 IS ALREADY IN MGMTCLAS M1
VTV X00002 IS ALREADY IN MGMTCLAS M1
SLS1315I SWS500.V5.CDS WAS SELECTED AS THE PRIMARY CONTROL DATA SET
SLUADMIN (7.2.0) STORAGETEK ENTERPRISE LIBRARY SOFTWARE UTILITY SSYS=HSCI PAGE 00003
TIME 15:50:09 VTCS VTV REPORT DATE 2015-06-17
VTV SIZE COMP <----CREATION----> <--LAST USED--> MGR SCR REPL MGMT MAX
VOLSER (MB) % DATE TIME DATE TIME RES IMP EXPT CLASS MVC1 MVC2 MVC3 MVC4 VTV VTSSNAME
X00000 0.01 0 2012MAY19 05:02:08 2012MAY19 05:22 - - R - - M1 022550 022551 022552 022553 800
X00001 0.01 0 2012MAY19 05:02:08 2012MAY19 05:22 - - R - - M1 033550 033551 033552 033553 800
X00002 0.01 0 2012MAY19 05:02:08 2012MAY19 05:22 - - R - - M1 044550 044551 044552 044553 800
3 INITIALIZED VTVS PROCESSED
0 NON-INITIALIZED VTVS PROCESSED
The VTVMAINT report shows the following:
-
Status of VTVs processed - volser and return code (0 - all updates completed, 4 - some updates completed, 8 - no updates completed).
-
An exception report of the reason for all uncompleted updates.
-
A VTV report.
VTVRPt
The VTVRPt command reports the status of VTVs in your VSM system.
Issue this command with either of the options listed in the following table. Each option is described individually, and in more detail, on the pages to follow.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
generates a basic VTV report |
|
|
generates a VTV report indicating where all current copies of a VTV reside |
VTVRPt BASIC
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-184, the VTVRPt BASIC command includes the following parameters:
- VTVid(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
optionally, specifies the VTVs for the report. If you do not specify the VTVs, the report includes all initialized VTVs in your VSM system. A VTV is initialized when VTCS has used it at least once.
volser,vol-range, orvol-listindicates the volsers of one or more VTVs. - ALL
-
optionally, specifies to report on all VTVs (including non-initialized volumes). If you do not specify
ALL, only initialized VTVs are reported. - OPTION(UNAVAIL)
-
optionally, specifies to report only on unavailable VTVs (VTVs in an offline VTSS). The report lists only unavailable VTVs in three sections: unavailable mounted on a VTD, unavailable VTSS-resident, and unavailable VTSS-resident and fenced.
- SUPEMPTY
-
optionally, suppress the printing of empty VTVs.
The VTV report will not print details of VTVs that contain no data or VTVs that are fenced.
SUPEMPTYis mutually exclusive withALLandOPTION(UNAVAIL). - MANIFEST(ddname)
-
optionally, specifies the input DD name of the manifest file used to generate the report.
ddnameindicates the DD name of the manifest file. Note that you can specify a merged manifest file or multiple manifest files.MANIFESTis mutually exclusive withSINCE. - SINCE(nnnn)
-
optionally, specifies a time in minutes. Only VTVs that have been accessed within the specified time are processed.
nnnnindicates the time in minutes, from 1 to 9999.SINCEis mutually exclusive withMANIFEST.
VTV Report (Basic)
The following is an example of a VTV report produced by the VTVRPt BASIC command:
Example 3-60 VTVRPt BASIC report
SLUADMIN (7.2.0) STORAGETEK ENTERPRISE LIBRARY SOFTWARE UTILITY SSYS=HSCI PAGE 00002
TIME 15:50:09 VTCS VTV REPORT DATE 2015-06-17
SLS1315I HSC1.V70EC21.CDS WAS SELECTED AS THE PRIMARY CONTROL DATA SET
SLUADMIN (7.2.0) STORAGETEK ENTERPRISE LIBRARY SOFTWARE UTILITY SSYS=HSCI PAGE 00003
TIME 15:50:09 VTCS VTV REPORT DATE 2015-06-17
VTV SIZE COMP <----CREATION----> <--LAST USED--> MGR SCR REPL MGMT MAX
VOLSER (MB) % DATE TIME DATE TIME RES IMP EXPT CLASS MVC1 MVC2 MVC3 MVC4 VTV VTSSNAME
A00240 66.4 85 2010MAY22 16:27:44 2010MAY22 16:57 R - - - - TRACE 4.0 VTSS92
A00241 14.0 0 2010MAY21 13:02:30 2010MAY22 07:48 - M - - - MGMT2CP 702972 0.4 VTSS90
A00406 14.0 0 2010MAY21 13:03:50 2010MAY22 08:45 - M - - - EXHPDM 700486 4.0 VTSS90
...
X50000 2,430.0 0 2009NOV18 09:04:18 2009NOV18 09:07 R - - I - PE EEXPORT 4.0 VTSS91
X50047 280.0 96 2009DEC03 14:29:35 2010APR30 06:48 R M - I - PE QUADYES 700483 700491 700494 700498 4.0 VTSS91
X50048 280.0 96 2009DEC03 14:29:41 2010MAY27 21:06 - M - I - QUADYES 702979 700492 700497 700499 4.0 VTSS91
X50060 0.0 0 - - S I -
X50066 280.0 96 2009DEC03 14:56:17 2010MAY27 21:06 - M - I - DLVTVYES 702978 4.0 VTSS92
X50067 42.0 0 2010JAN21 11:28:55 2010JAN21 11:28 R - - I - EEXPORT 4.0 VTSS91
Y50000 4.8 0 2009NOV20 09:59:52 2009DEC18 11:56 R - - - - E OTHERDIR 0.4 VTSS91
Y50008 1,260.0 75 2009NOV20 09:59:56 2010MAY27 21:09 - M - - - E OTHERDIR 702978 0.4 VTSS92
Y50184 578.6 34 2010FEB02 22:25:27 2010MAY22 08:42 - M S - - APOOL 702972 0.4 VTSS90
485434 INITIALIZED VTVS PROCESSED
116566 NON-INITIALIZED VTVS PROCESSED
SLS0155I CONDITION CODE FOR UTILITY FUNCTION IS 0
Fields
The following list describes the fields for the report generated by a VTVRPt or VTVRPt BASIC command:
- VTV Volser
-
the VTV volser.
- Size (MB)
-
the uncompressed size of the VTV (MB).
<MOUNT>indicates that the VTV was mounted when the report ran.<FENCED>indicates that the VTV's state is unknown. If<FENCED>appears, contact Oracle StorageTek Software Support. - Comp %
-
the VTV compression percentage achieved. This is the difference between the uncompressed and compressed VTV size expressed as a percentage of the uncompressed VTV size. For example if a 100 MB VTV compresses to 40 MB then the compression% will be given as 60%. A compression of 0% indicates that no compression was possible on the VTV
- Creation Date and Time
-
the date and time that the VTV was created.
- Last Used Date and Time
-
the date and time that the VTV was last used. This date and time value is updated by successful completion of a VTV mount, migrate, recall, or scratch.
- Mgr/Res
-
indicates the copy status of the VTV. The absence of a flag in the columns below indicates that there are no current copies of the VTV within this TapePlex.
-
An
Rin the left column indicates that there is a VTSS resident copy of the VTV -
An
Min the right column indicates that there is at lease one MVC copy of the VTV. As an alternative, if this column contains aCthen the VTV is also consolidated.
-
- Scr/Imp
-
indicates the usability of the VTV.
-
An
Sin the left column indicates that the VTV is in a scratched state. If the VTV has also been imported from a remote TapePlex, then the VTV cannot be picked for a scratch mount. -
An
Iin the right column indicates that the VTV has been imported from another TapePlex. Imported VTVs cannot be modified. -
An
Oin the left column indicates that the VTV has partial (write once)VOLSAFEprotection. -
An
Ain the left column indicates that the VTV has fullVOLSAFEprotection.
-
- Repl/Expt
-
indicates the replication or electronic export status of the VTV. A VTV that is not resident does not have any replication requirements.
It can be one of the following statuses in the left column:
- PR
-
The VTV is currently queued for replication.
- SR
-
Replication of the VTV has started.
- R
-
Replication has completed and another copy of the VTV resides in the partner to the currently resident VTSS.
It can be one of the following statuses in the right column:
- PE
-
The VTV requires electronic export.
- SE
-
Electronic export of the VTV has started.
- FE
-
Electronic export of the VTV has been rejected by the remote TapePlex.
- E
-
Electronic export has completed and another copy of the VTV resides in the partner to the currently resident VTSS.
- ME
-
electronic export of this VTV to one TapePlex completed successfully, but an electronic export of this VTV to another TapePlex failed.
VTVRPT COPIESwill provide the names of the two TapePlexes and indicate which one succeeded and which one failed.
- MGMT Class
-
the name of the Management Class for the VTV specified.
- MVC1, MVC2, MVC3, MVC4
-
the MVC(s) that contain the VTV (for both migration and consolidation). If all of these fields are empty, the VTV has not been migrated or consolidated. If one or more of these fields list an MVC volser, the VTV was migrated to each of these MVCs.
- Max VTV
-
the maximum size of the VTV in GB (.4, .8, 2, or 4).
- VTSSname
-
the VTSS where the VTV resides, or, if the VTV is migrated, the VTSS where the VTV was last resident. If this field is empty, the VTV is non-existent (not created or used, scratched, and deleted) or has been manually imported.
VTVRPt COPIES
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC not required
Description
The VTVRPt COPIES command generates a VTV report indicating where all current copies of a VTV reside.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-185, the VTVRPt COPIES command includes the following parameters:
- VTVid(volser, vol-range, or vol-list)
-
optionally, specifies the VTVs for the report. If you do not specify the VTVs, the report includes all initialized VTVs in your VSM system. A VTV is initialized when VTCS has used it at least once.
volser,vol-range, orvol-listindicates the volsers of one or more VTVs. - ALL
-
optionally, specifies to report on all VTVs (including non-initialized volumes). If you do not specify
ALL, only initialized VTVs are reported. - OPTION(UNAVAIL)
-
optionally, specifies to report only on unavailable VTVs (VTVs in an offline VTSS). The report lists only unavailable VTVs in three sections: unavailable mounted on a VTD, unavailable VTSS-resident, and unavailable VTSS-resident and fenced.
- SUPEMPTY
-
optionally, suppress the printing of empty VTVs.
The VTV report will not print details of VTVs that contain no data or VTVs that are fenced.
SUPEMPTYis mutually exclusive withALLandOPTION(UNAVAIL). - MANIFEST
-
optionally, specifies the input DD name of the manifest file used to generate the report.
ddnameindicates the DD name of the manifest file. Note that you can specify a merged manifest file or multiple manifest files.MANIFESTis mutually exclusive withSINCE. - SINCE(nnnn)
-
optionally, specifies a time in minutes. Only VTVs that have been accessed within the specified time are processed.
nnnnindicates the time in minutes, from 1 to 9999.SINCEis mutually exclusive withMANIFEST.
VTV Report (COPIES)
The following is an example of a VTV report produced by the VTVRPt COPIES command:
Example 3-61 VTVRPt COPIES report
SLUADMIN (7.2.0) STORAGETEK ENTERPRISE LIBRARY SOFTWARE UTILITY SSYS=HSCI PAGE 00002
TIME 15:50:43 VTCS VTV REPORT DATE 2015-06-17
SLS1315I HSC1.V70EC21.CDS WAS SELECTED AS THE PRIMARY CONTROL DATA SET
SLUADMIN (7.2.0) STORAGETEK ENTERPRISE LIBRARY SOFTWARE UTILITY SSYS=HSCI PAGE 00003
TIME 15:50:43 VTCS VTV REPORT DATE 2015-06-17
VTV SIZE MGMT <--VTSS COPIES--> OWNING <----MVC COPIES AND LOCATIONS----> <-EXPORT COPIES-->
VOLSER (MB) CLASS SCR PRIMARY REPLICA TAPEPLEX MVC1/3 ACS MVC2/4 ACS TAPEPLEX TAPEPLEX
00240 10.5 TRACE - VTSS92 - -
A00241 14.3 MGMT2CP - - - - 702972 00
A00406 14.1 EXHPDM - - - - 700486 00
...
X50000 2,462.3 EEXPORT - VTSS91 - EC20REM
X50047 11.4 DLVTVYES - VTSS91 - EC20REM 700483 00
X50048 11.4 DLVTVYES - - - EC20REM 702979 00
X50060 NO COPY DLVTVYES - SEC20REM
X50066 11.4 DLVTVYES - - - EC20REM 702978 00
X50067 42.5 EEXPORT - VTSS91 - EC20REM
Y50000 13.3 OTHERDIR - VTSS91 - - EC20REM
Y50008 316.6 OTHERDIR - - - - 702978 00 EC20REM
Y50184 385.2 APOOL S - - - 702972 00
485434 INITIALIZED VTVS PROCESSED
116566 NON-INITIALIZED VTVS PROCESSED
SLS0155I CONDITION CODE FOR UTILITY FUNCTION IS 0
Fields
The following list describes the fields for a report generated by the VTVRPt COPIES command:
- VTV Volser
-
the VTV volser.
- Size (MB)
-
the compressed size of the VTV (MB).
<MOUNT>indicates that the VTV was mounted when the report ran.<FENCED>indicates that the VTV's state is unknown. If<FENCED>appears, contact Oracle StorageTek Software Support. - MGMT Class
-
the name of the Management Class for the VTV specified.
- Scr
-
indicates whether the VTV is in a scratched state. An
Sin this column indicates that the VTV is in a scratched state. - Primary
-
the name of the VTSS that contains the primary VTSS resident copy of the VTV. If this field is blank, then there are currently no VTSS resident copies of the VTV.
- Replica
-
the name of the VTSS that contains a replica copy of the VTV. If this field is blank, then there are currently no VTSS resident replica copies of the VTV.
- Owning Tapeplex
-
the name of the TapePlex that has ownership of this VTV. If this field is blank, then the VTV is owned by another TapePlex and can be processed normally. If this field is set, then the VTV has been imported from another TapePlex and its contents cannot be modified.
- MVC1, MVC2, MVC3, MVC4
-
the MVC(s) that contain the VTV (for both migration and consolidation). If all of these fields are empty, the VTV has not been migrated or consolidated. The number next to each MVC volser is the ACS location of the MVC. If this is set to
--, then the MVC is not library resident. - Export Tapeplex
-
the names of the TapePlexes to which copies of the VTV have been exported. The copies within these TapePlexes will show the VTV as imported and having an owning TapePlex name. This list is not exhaustive as some of these TapePlexes may have forwarded copies onto further locations. An asterisk (
*) next to the name indicates an export that has been rejected by the target TapePlex.
VVAUDIT
Interfaces:
-
Utility only
-
UUI Support: Yes
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Description
The VVAUDIT command synchronizes the vault allocation map with the vault volume records. If the slot in the map indicates that it is allocated, then the vault volume records are searched. If the slot number is not found in any vault volume record, then the slot is freed.
Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-186, the VVAUDIT command includes the following parameters:
- VAULT(vault-name)
-
optionally, audits the specified vault-name. If
VAULTis not specified, then all vaults are be audited.vaultnameindicates the vault name.
Warn
Interfaces:
-
Console or
PARMLIBonly -
UUI Support: No
Subsystem Requirements:
Active HSC at BASE or FULL service level
Description
The Warn command sets scratch warning threshold values.
Setting a threshold value causes a warning message to be issued when the number of scratches falls below the specified threshold. The Warn command enables you to specify parameters that can narrow the scope of the threshold values you set:
-
If
SUBpool,MEDia, andRECtechare not supplied, the threshold value applies to scratch volumes for the specified ACS or LSM. -
If
SUBpoolis supplied, butMEDiaandRECtechare not, the threshold value applies to scratch volumes for the specified subpool and ACS or LSM. -
If
MEDiaandRECtechare supplied, butSUBpoolis not, the threshold value applies to scratch volumes for the specified media type, recording technique, and ACS or LSM. -
If
SUBpool,MEDia, andRECtechare supplied, the threshold value applies to scratch volumes for the specified subpool, media type, and recording technique in the ACS or LSM.
Note:
Use theDisplay THReshld command to display the current Warn threshold values. See "Display THReshld" for more information.Parameters
As shown in Figure 3-187, the Warn command includes the following parameters:
- SCRatch
-
indicates that scratch threshold values are to be set.
- acs-id
-
the ACS on which to alter threshold values. The ACSid is a decimal value from 00-99.
- lsm-id
-
the LSM on which to alter threshold values. The LSMid is comprised of the ACSid and the LSM number. The format of an LSMid is
AA:LL, whereAAindicates the ACSid (decimal 00-99) andLLindicates the LSM number (decimal 00-99). - VSM
-
specifies that threshold values are to be set only for subpools for virtual volumes. VSM is not allowed if
acs-idorlsm-idare also specified.
- SUBpool(subpool-name)
-
optionally, indicates that you want to designate a subpool. This parameter is optional.
subpoolnameindicates the name of the subpool.Note:
Scratch subpool names are specified with theSCRPOolcontrol statement. Refer to Oracle's ELS publication ELS Legacy Interfaces Reference for information. - THReshld(threshold-value)
-
indicates that you want to alter the threshold value.
thresholdvalueindicates the minimum number of scratch volumes that are allowed before the HSC issues a warning message. Allowable threshold values are decimal in the range from 0 through 99,999.The warning interval values are preset at five minutes.
Note:
When the number of scratch volumes in an ACS or LSM drops below the threshold value, the system issues a warning message. - MEDia(media-type)
-
optionally, specifies the media type for the threshold. When
MEDiais specified,RECtechmust also be specified.media-typeindicates the media type.See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for a list of valid
media-typevalues. - RECtech(recording-technique)
-
optionally, specifies the recording technique for the threshold.
RECtechindicates the method used to record data tracks on the tape surface. WhenRECtechis specified,MEDiamust also be specified.You can enter a list of recording techniques, but they must be separated by commas.
recording-techniqueindicates the recording technique.See Appendix A, "MEDia, RECtech, and MODel Values" for valid
recording-techniquevalues.Note:
A list specifies a generic pool from which a selection is made. There is no implied priority.