| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Solaris Cluster Concepts Guide Oracle Solaris Cluster 3.3 3/13 |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Solaris Cluster Concepts Guide Oracle Solaris Cluster 3.3 3/13 |
2. Key Concepts for Hardware Service Providers
3. Key Concepts for System Administrators and Application Developers
Device IDs and DID Pseudo Driver
Cluster Configuration Repository (CCR)
Local and Global Namespaces Example
Using the cldevice Command to Monitor and Administer Disk Paths
Using Oracle Solaris Cluster Manager to Monitor Disk Paths
Using the clnode set Command to Manage Disk Path Failure
Adhering to Quorum Device Requirements
Adhering to Quorum Device Best Practices
Recommended Quorum Configurations
Quorum in Two-Node Configurations
Quorum in Greater Than Two-Node Configurations
Characteristics of Scalable Services
Data Service API and Data Service Development Library API
Using the Cluster Interconnect for Data Service Traffic
Resources, Resource Groups, and Resource Types
Resource and Resource Group States and Settings
Resource and Resource Group Properties
Support for Oracle Solaris Zones
Support for Global-Cluster Non-Voting Nodes (Oracle Solaris Zones) Directly Through the RGM
Criteria for Using Support for Oracle Solaris Zones Directly Through the RGM
Requirements for Using Support for Oracle Solaris Zones Directly Through the RGM
Additional Information About Support for Solaris Zones Directly Through the RGM
Criteria for Using Oracle Solaris Cluster HA for Solaris Zones
Requirements for Using Oracle Solaris Cluster HA for Solaris Zones
Additional Information About Oracle Solaris Cluster HA for Solaris Zones
Data Service Project Configuration
Determining Requirements for Project Configuration
Setting Per-Process Virtual Memory Limits
Two-Node Cluster With Two Applications
Two-Node Cluster With Three Applications
Failover of Resource Group Only
Public Network Adapters and IP Network Multipathing
SPARC: Dynamic Reconfiguration Support
SPARC: Dynamic Reconfiguration General Description
SPARC: DR Clustering Considerations for CPU Devices
SPARC: DR Clustering Considerations for Memory
SPARC: DR Clustering Considerations for Disk and Tape Drives
SPARC: DR Clustering Considerations for Quorum Devices
SPARC: DR Clustering Considerations for Cluster Interconnect Interfaces
SPARC: DR Clustering Considerations for Public Network Interfaces
Oracle Solaris zones provide a means of creating virtualized operating system environments within an instance of the Oracle Solaris OS. Oracle Solaris zones enable one or more applications to run in isolation from other activity on your system. The Oracle Solaris zones facility is described in Part II, Zones, in System Administration Guide: Oracle Solaris Containers-Resource Management and Oracle Solaris Zones.
You can create any number of global-cluster non-voting nodes.
You can use Oracle Solaris Cluster software to manage the availability and scalability of applications that are running on global-cluster non-voting nodes.
You can configure a resource group to run on a global-cluster voting node or a global-cluster non-voting node. The RGM manages each global-cluster non-voting node as a switchover target. If a global-cluster non-voting node is specified in the node list of a resource group, the RGM brings the resource group online in the specified node.
The following figure illustrates the failover of resource groups between nodes in a two-node cluster. In this example, identical nodes are configured to simplify the administration of the cluster.
Figure 3-7 Failover of Resource Groups Between Nodes
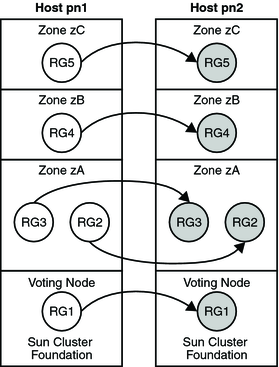
You can configure a scalable resource group (which uses network load balancing) to run in a cluster non-voting node as well.
Using Oracle Solaris Cluster commands, you specify a zone by appending the name of the zone to the name of the node and separating the names with a colon. For example:
phys-schost-1:zoneA
Use support for Oracle Solaris zones directly through the RGM if any of following criteria is met:
Your application cannot tolerate the additional failover time that is required to boot a zone.
You require minimum downtime during maintenance.
You require dual-partition software upgrade.
You are configuring a data service that uses a shared address resource for network load balancing.
If you plan to use support for Oracle Solaris zones directly through the RGM for an application, ensure that the following requirements are met:
The application is supported to run in non-global zones.
The data service for the application is supported to run on a global-cluster non-voting node.
If you use support for Oracle Solaris zones directly through the RGM, ensure that resource groups that are related by an affinity are configured to run on the same cluster node.
For information about how to configure support for Oracle Solaris zones directly through the RGM, see the following documentation:
Zone Names in Oracle Solaris Cluster Software Installation Guide
Oracle Solaris Cluster Data Services Planning and Administration Guide
Individual data service guides
The Oracle Solaris Cluster HA for Solaris Zones data service manages each zone as a resource that is controlled by the RGM.
Use the Oracle Solaris Cluster HA for Solaris Zones data service if any of following criteria is met:
You require delegated root access.
The application is not supported in a cluster.
You require affinities between resource groups that are to run in different zones on the same node.
If you plan to use the Oracle Solaris Cluster HA for Solaris Zones data service for an application, ensure that the following requirements are met:
The application is supported to run on global-cluster non-voting nodes.
The application is integrated with the Oracle Solaris OS through a script, a run-level script, or an Oracle Solaris Service Management Facility (SMF) manifest.
The additional failover time that is required to boot a zone is acceptable.
Some downtime during maintenance is acceptable.
For information about how to use the Oracle Solaris Cluster HA for Solaris Zones data service, see Oracle Solaris Cluster Data Service for Solaris Containers Guide.