| Oracle® Health Sciences Mobile Clinical Research Associate Server Security Guide Release 1.3 E38752-04 |
|
| PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Health Sciences Mobile Clinical Research Associate Server Security Guide Release 1.3 E38752-04 |
|
| PDF · Mobi · ePub |
Security Guide
Release 1.3
E38752-04
March 2014
The Oracle Health Sciences Mobile Clinical Research Associate Server (Mobile CRA) mobile application supports the clinical research analyst in conducting site visits. This release provides the CRA with alerts or notifications sent to the mobile device, location capture vis-à-vis the sites, the ability to view the status of a site at a glance, and access the trip report. Mobile CRA consolidates the CRA's view of the trial, collecting data from clinical data management systems, clinical trial management systems, drug supply systems, randomization systems and other systems, through an open application programming interface (API) or web services model.
The system has been designed to interact with on premise Oracle clinical development management aggregation system, Oracle Health Sciences Clinical Data Analytics (CDA) and on premise Seibel Clinical Trial Management System (CTMS).
This document contains the following sections:
The following principles are fundamental to using any application securely.
One of the principles of good security practice is to keep all software versions and patches up to date.
Oracle continually improves its software and documentation. Critical Patch Updates are the primary means of releasing security fixes for Oracle products to customers with valid support contracts. They are released on the Tuesday closest to the 17th day of January, April, July and October. Oracle recommends you apply these patches as soon as they are released.
Although the importance of passwords is well known, the following basic rule of security management is worth repeating:
Ensure all your passwords are strong passwords. Oracle recommends that you use a mix of uppercase and lowercase alphabets, numbers, and symbols.
You can strengthen passwords by creating and using password policies for your organization. For guidelines on securing passwords and for additional ways to protect passwords, refer to the Oracle Database Security Guide specific to the database release you are using.
You should modify the following passwords to use your policy-compliant strings:
Passwords for the database default accounts, such as SYS and SYSTEM.
Passwords for the database application-specific schema accounts.
You should not configure a password for the database listener as that enables remote administration. For more information, refer to the section "Removing the Listener Password" of Oracle® Database Net Services Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2).
For more information, refer to the Oracle 11gR2 Database Security Guide.
The principle of least privilege states that users should be given the least amount of privilege to perform their jobs. Overly ambitious granting of responsibilities, roles, grants - especially early on in an organization's life cycle when people are few and work needs to be done quickly - often leaves a system wide open for abuse. User privileges should be reviewed periodically to determine relevance to current job responsibilities.
Before executing DDL scripts, a database user should be created with the specified limited set of privileges. DBA access should not be given to the user.
Mobile CRA has system and object level privileges. Minimum privileges, such as connecting to the schema, are granted to schema owners. Application users do not have access to the database layer and must access it from the application.
For security purposes, you must revoke all unnecessary grants on the schema. You require DBA privileges to perform this action.
This section suggests various unused operating system level services that you can disable to improve security.
Oracle Health Sciences Mobile CRA does not use the Telnet service.
Telnet listens on port 23 by default. If the Telnet service is available on any computer, Oracle recommends that you disable Telnet in favor of Secure Shell (SSH). Telnet, which sends clear-text passwords and user names through a log-in, is a security risk to your servers. Disabling Telnet tightens and protects your system security.
Oracle Health Sciences Mobile CRA does not use the following services or information for any functionality:
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP). This protocol is an Internet standard for E-mail transmission across Internet Protocol (IP) networks.
Identification Protocol (identd). This protocol is generally used to identify the owner of a TCP connection on UNIX.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). This protocol is a method for managing and reporting information about different systems.
File transfer Protocol (FTP). This protocol is used for downloading or uploading files from the file server.
Therefore, restricting these services or information does not affect the use of Oracle Health Sciences Mobile CRA. If you are not using these services for other applications, Oracle recommends that you disable these services to minimize your security exposure. If you need SMTP, identd, or SNMP for other applications, be sure to upgrade to the latest version of the protocol to provide the most up-to-date security for your system.
When designing a secure deployment, design multiple layers of protection. If a hacker should gain access to one layer, such as the application server, that should not automatically give them easy access to other layers, such as the database server.
Providing multiple layers of protection may include:
Enabling only those ports required for communication between different tiers, for example, only allowing communication to the database tier on the port used for SQL*NET communications, (1521 by default).
Placing firewalls between servers so that only expected traffic can move between servers.
MobileCRA application timeout should be reasonably timed. It should not be too long and pose a security risk, while a small timeout hampers productivity.
This section describes security guidelines for Mobile CRA database objects and database options.
CRA contains database objects. You can use DDL scripts, PL/SQL procedures and functions to create database objects, and DML scripts to create seed data. These files are part of the media pack.
The guidelines for installing and configuring Oracle Database Server are available here http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E11882_01/network.112/e16543/toc.htm.
The Mobile CRA application has the following different schemas:
Rules Engine
System Grants provided or needed
Connect, Resource, Create Materialized View, Create Job, Create Synonym, Create View, Select Any Table, Unlimited Tablespace
Grant Select on CDA (RXI) schema for following tables:
W_RXI_STUDY_D
W_RXI_STUDY_SITE_D
W_HS_STUDY_ACCESS_SEC
W_HS_APPLICATION_USER_D
W_HS_STUDY_SITE_ACCESS_SEC
MobileCRA Server
System Grants provided or needed
Connect, Resource
MobileCRA CTMS (Trip Report)
System Grants provided or needed
Connect, Resource
Push Notification Server
System Grants provided or needed
Connect, Resource
MobileAQ
System Grants provided or needed
Connect, Resource
AQ related grants
Grant aq_user_role
Grant execute ON sys.dbms_aqadm
Grant execute ON sys.dbms_aq
Grant execute ON sys.dbms_aqin
Grant execute ON sys.dbms_aqjms
The Oracle Database has options that provide additional security features. Mobile CRA may include data that falls under HIPAA guidelines in the United States and similar guidelines elsewhere. These features can help you comply with those guidelines.
Mobile CRA includes data that may fall under HIPAA or other regulations outside the United States. These data are highly sensitive and only those with a need to know should have access to it. To prevent database administrators and others from seeing the data, Oracle recommends that Oracle Database Vault be used to limit access to the Mobile CRA schema to the Mobile CRA user to prevent DBAs and other "superuser" accounts from accessing the data. Database Vault requires a separate license.
Oracle Audit Vault automates the audit collection, monitoring, and reporting process, turning audit data into a key security resource for detecting unauthorized activity.
Consider using this feature to satisfy compliance regulations such as SOX, PCI, and HIPAA, and to mitigate security risks. Oracle Audit Vault requires a separate license.
Transparent Data Encryption is one of the three components of the Oracle Advanced Security option for Oracle Database 11g Release 2 Enterprise Edition. It provides transparent encryption of stored data to support your compliance efforts. If you employ Transparent Data Encryption, applications do not have to be modified and continue to work seamlessly as before. Data is automatically encrypted when it is written to disk and automatically decrypted when accessed by the application. Key management is built in, eliminating the complex task of creating, managing and securing encryption keys. The Advanced Security Option is licensed separately from the database.
Tablespace Encryption is another component of the Oracle Advanced Security option for Oracle Database 11g Release 2 Enterprise Edition. Tablespace encryption facilitates encryption of the entire tablespace contents, rather than having to configure encryption on a column-by-column basis. It encrypts data at the datafile level to keep users from viewing the oracle datafiles directly. Oracle recommends that you perform tablespace encryption for maximum protection.
This section describes the security guidelines for the Mobile CRA middle tier.
The server should only use https.
Mobile CRA uses a system account credential from CDA and the Health Sciences Push Notification Server (HSPNS). All these accounts are configured safely in the Oracle Credential store. For more details, refer to the Oracle Health Sciences Mobile Clinical Research Associate Server Installation Guide.
Mobile CRA uses Single sign on (SSO) token from CTMS. SSO token should be generated in CTMS and used for accessing CTMS. SSO token is safe because it can be regenerated without exposing user passwords. Mobile CRA uses this SSO token to access CTMS on behalf of various users.
Mobile CRA supports Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) and SSO. LDAP configuration for Mobile CRA should be done in the Oracle WebLogic server (WLS). For more information, refer to Oracle WebLogic server documentation.
If configuring against LDAP, both CTMS and Mobile CRA should be setup to the centralized LDAP.
An application group, mobilecra-admins, should be created in WLS or LDAP for Mobile CRA. An admin user has to be a part of this administration group to manage or configure the Mobile CRA application. General WLS user and password management guidelines apply.
AdminUI, an ADF based application, can be configured with SSO. For more information, refer to Oracle SSO documentation.
Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition (OBIEE) has its own credential store, which is the WLS security realm.
Currently, the Oracle WebLogic Server installation includes the entire JDK and some additional Oracle WebLogic Server development utilities (for example, wlsvc). These applications are not needed and should be removed. The following are recommendations for making a Oracle WebLogic Server installation more secure:
Do not install the Oracle WebLogic Server sample applications.
Delete development tools, such as the Configuration Wizard and the jCOM tools.
Delete the Derby database, which is bundled with Oracle WebLogic Server for use by the sample applications and code examples as a demonstration database.
For more details, refer to the Determining Your Security Needs section in Oracle® Fusion Middleware Securing a Production Environment for Oracle WebLogic Server 12c Release 1 (12.1.1)
Due to the complexity in setting up SSL it is not enabled by default during installation. Communications between the browser and the application servers should be restricted to SSL.
It is optional to enable SSL, but Oracle recommends SSL for a production environment.
To enable SSL:
Log into Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
Click the Environment node in the Domain Structure pane and click Servers in Environment table.
Click the server where you deployed the oracle.hs.mobilecra.ear file.
Click the Configuration tab.
Click the General tab.
If Save is disabled, click Lock & Edit in the Change Center pane.
Select the SSL Listen Port Enabled check box and enter a port number.
To disable non-SSL port, deselect the Listen Port Enabled check box.
Click Save.
Click Activate Changes in the Change Center pane, if it is enabled.
Click the Control tab.
Click the Start/Stop tab.
Click Restart SSL
Click Yes. The following message appears.
SSL channels have been successfully restarted.
You must also configure SSL, identity, and trust. For more information, refer to Oracle® Fusion Middleware Securing Oracle WebLogic Server 11g Release 1 (10.3.5).
To set up SSL, perform the following steps:
Obtain an identity (private key and digital certificates) and trust (certificates of trusted certificate authorities) for Oracle WebLogic Server. Use the digital certificates, private keys, and trusted CA certificates provided by Oracle WebLogic Server, the CertGen utility, the keytool utility, or a reputable vendor such as Entrust or Verisign to perform this step.
Store the identity and trust. Private keys and trusted CA certificates which specify identity and trust are stored in keystores.
Configure the identity and trust keystores for Oracle WebLogic Server in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
Set SSL configuration options for the private key alias and password in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console. Optionally, set configuration options that require the presentation of client certificates (for two-way SSL).
For more details, refer to Configuring SSL section in Oracle® Fusion Middleware Securing Oracle WebLogic Server 12c Release 1 (12.1.1).
Oracle Health Sciences Mobile CRA does not use the following services or information for any functionality:
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP). This protocol is an Internet standard for E-mail transmission across Internet Protocol (IP) networks.
Identification Protocol (identd). This protocol is generally used to identify the owner of a TCP connection on UNIX.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). This protocol is a method for managing and reporting information about different systems.
File transfer Protocol (FTP). This protocol is used for downloading or uploading files from the file server.
Therefore, restricting these services or information does not affect the use of Mobile CRA. If you are not using these services for other applications, Oracle recommends that you disable these services to minimize your security exposure. If you need SMTP, identd, or SNMP for other applications, be sure to upgrade to the latest version of the protocol to provide the most up-to-date security for your system.
Oracle WebLogic Server defines a set of configuration options to protect user accounts from intruders. In the default security configuration, these options are set for maximum protection. You can use the Administration Console to modify these options on the Configuration > User Lockout page.
As a system administrator, you have the option of turning off all the configuration options, increasing the number of login attempts before a user account is locked, increasing the time period in which invalid login attempts are made before locking the user account, and changing the amount of time a user account is locked. Remember that changing the configuration options lessens security and leaves user accounts vulnerable to security attacks. For more details, refer to Configuring Security for a WebLogic Domain section in Oracle® Fusion Middleware Securing Oracle WebLogic Server 12c Release 1 (12.1.1).
This section contains the following topics:
To define the credentials used by Mobile CRA in the Oracle credential store, perform the following:
Log in to WebLogic Enterprise Manager as admin by navigating to the URL. For example, http://<servername>/em.
Select WebLogic Domain from the server_domain panel on the left side.
Select the domain name.
The details of server_domain are displayed on the right-side window panel.
Under server_domain, select WebLogic_domain.
From the WebLogic Domain drop-down list, select Security > Credentials.
The Credentials screen is displayed.
Click Create Map to create a new credential and enter oracle.hs.mobilecra. The updated list of credentials is displayed.
Select oracle.hs.mobilecra, click Create Key. The Select Map field is updated with the map name. Perform the following:
Enter key as notificationService.Credential. This is the user name and password provided by Oracle for accessing the push notification service. Mobile CRA uses this information to access the Oracle push notification service.
Enter type as Password.
Enter the mobile notification server user name and password provided by Oracle.
Re-enter the password in the Confirm Password field.
If you wish, provide the description of the key in the Description field.
Click OK.
You can edit the details in the Edit Key screen.
Click OK.
Click Create Key to create another key. The Select Map field is updated with the map name. Now perform the following:
Enter key as ctmsAdapter.systemCredential. This is the CTMS admin user name and the CTMS SSO token password. Mobile CRA uses this information to access CTMS.
Enter type as Password.
Enter the CTMS super user name and the CTMS SSO token password.
Re-enter the password in the Confirm Password field.
If you wish, provide the description of the key in the Description field.
Click OK.
You can edit the details in the Edit Key screen.
Click OK.
Click Create Key to create another key. The Select Map field is updated with the map name. Now perform the following:
Enter ctmsAdapter.SSOTokenCredential as the key.
This is the SSO token that is generated in CTMS. For generating the CTMS SSO token, refer to the Oracle Siebel Clinical Trial Management System Installation Guide. Mobile CRA uses this token to access CTMS on behalf of CTMS users.
Enter type as Generic.
If you wish, provide the description of the key in the Description field.
Enter the user name and password credentials which are a token on CTMS instance.
Click OK.
You can edit the details in the Edit Key screen.
Click OK.
Click Create Key to create another key. The Select Map field is updated with the map name. Now perform the following:
Enter key as cdaAdapter.ObieeCredential. This is the user name and password for OBIEE. This credential has access to all the OBIEE answers used in alerts.
Select Map. This field is already populated with the name of the map being updated.
Enter type as Password.
Enter the user name and password.
Re-enter the password in the Confirm Password field.
If you wish, provide the description of the key in the Description field.
Click OK.
You can edit the details in the Edit Key screen.
Click OK.
To configure user-level security using Enterprise Manager, perform the following:
Log in to WebLogic Server as admin by entering the URL. For example, http://server:7001/console).
Click Lock and Edit in the Change Center panel on the left side.
Click Security Realms on the Domain Structure window.
The Summary of Security Realms screen is displayed.
Figure 9 Summary of Security Realms Screen
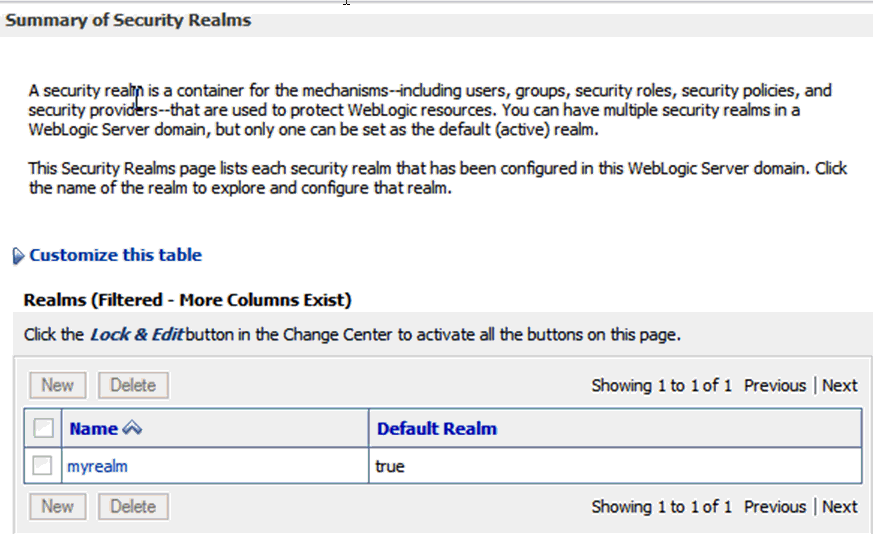
Select myrealm from the list.
The settings for the myrealm screen are displayed in the right-side window panel.
Click the Users and Groups tab and then click the Users subtab.
The list of existing users is displayed.
Click New to create a new user. The Create a New User screen is displayed.
Enter the name.
Provide the description for the user in the Description field.
Select the default Provider, that is, DefaultAuthenticator.
Enter a password of your choice.
Re-enter the password in the Confirm Password field.
Click OK.
Repeat Step 6 to create another user.
Exit the WebLogic server.
To configure security for Mobile CRA, perform the following:
Log in to the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
Within Server Administration, select Security Realms.
The Summary of Security Realm screen is displayed.
Select the security realm.
Figure 13 Summary of Security Realm screen
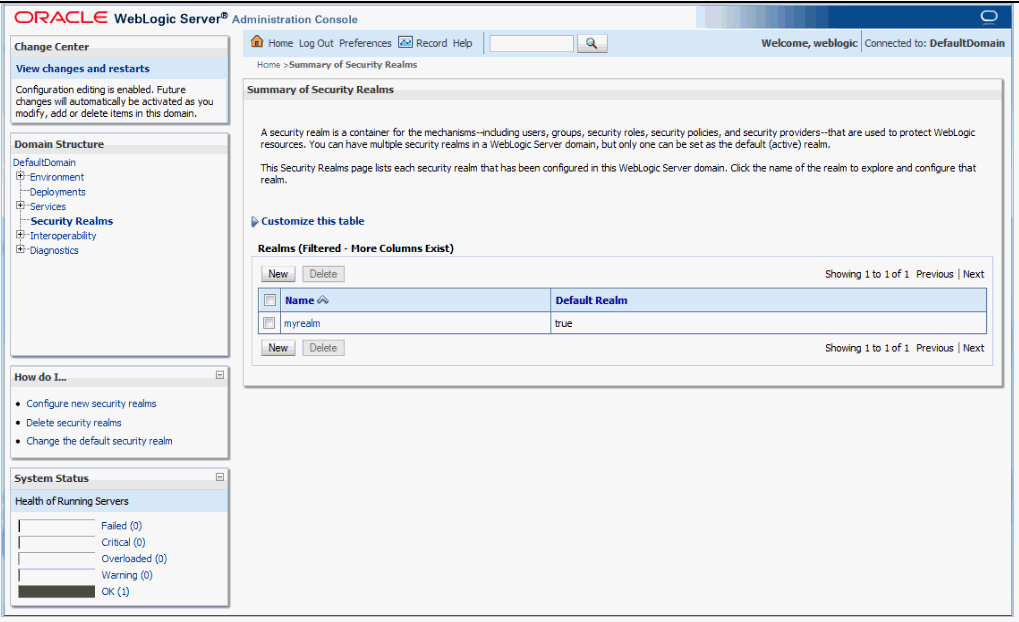
The Settings for myrealm screen is displayed.
Select Users and Groups and then the Groups subtab.
Create a new group with the name mobilecra-admins and the description as Mobile CRA Administrator Group.
Validate to confirm the administrator group has been successfully created.
Figure 16 Validate the Creation of the Group
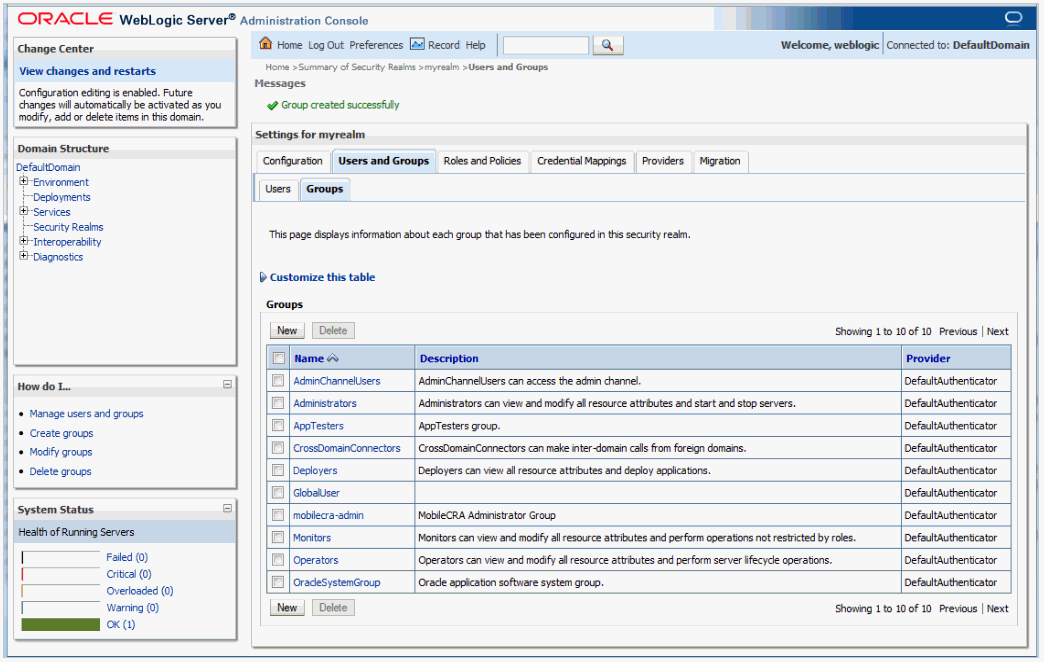
Select the Users tab within the Security section.
The Create a New User screen is displayed.
Create a new arbitrary or predefined user with the name mobile-admin and the description as Mobile CRA Administrator.
Add the group mobilecra-admin to the newly created administrator user.
Validate to check if the administrator user has been successfully created.
Figure 19 Validate the Creation of the Administrator User
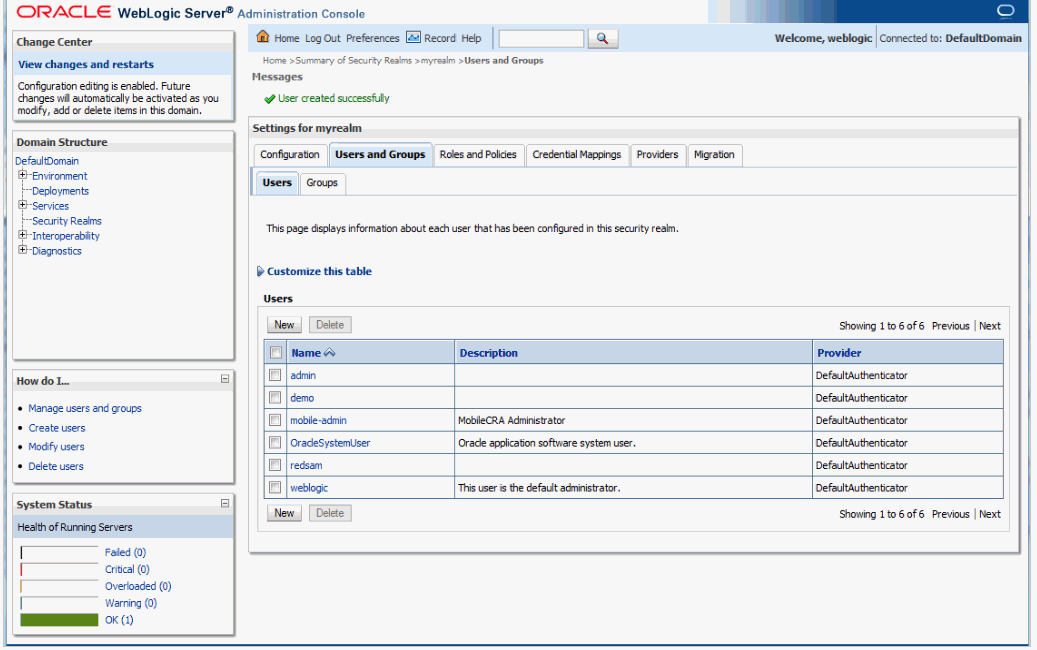
Note:
For integration with other security providers, such as Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) or Single Sign-On (SSO), see the Oracle WebLogic Administration Guide.The Site At A Glance (SAAG) is a very important feature that helps the CRAs in site-monitoring and keeping themselves abreast with the site performances. Mobile CRA is redesigned to make the SAAG an open feature by exposing APIs using which any system can push in KPI information for the SAAG, once registered into the system. This is called Adaptive SAAG feature.
The following external components use Adaptive SAAG:
Client: Client is an external entity where the application is hosted. Mobile CRA Server can be considered as a Client to Open SAAG Server.
Source: Source is a third party internal or external system to the Client. There are two types of sources supported, KPI and Alert. Each client would be having multiple sources created. These sources provide runtime KPI data and as well as Alert.
Users: Users of the application (Mobile CRA users).
To configure the Adaptive SAAG Server, perform the following:
Configure Health Sciences Push Notification Service (HSPNS) with key name as oracle.hs.oss.
Refer step 7 of Section 7.1, "Defining Credentials Used by Oracle Health Sciences Mobile Clinical Research Associate".
Configure administrator user on Weblogic console.
To configure user-level security using Enterprise Manager, perform the following:
Log in to WebLogic Server as administrator by entering the URL.
For example, http://server:7001/console
Click Lock & Edit in the Change Center panel on the left side.
Click Security Realms on the Domain Structure window.
The Summary of Security Realms screen is displayed.
Select myrealm from the list.
The settings for the myrealm screen are displayed in the right side window panel.
Click the Users and Groups tab and then click the Groups subtab.
The list of existing groups is displayed.
Click New and add a group with name OSSServiceAdmins.
Note:
Provider should be DefaultAuthenticator.Click Roles and Policies on the Settings for myrealm screen.
Select Realm Roles and then click Roles under Global Roles.
Click New to add a new Role.
Add OSSServiceAdminRole and Save.
Select User under Users and Groups tab.
Click New and add a new User.
Once the user is created select the user in user list and click user to edit it.
Click Groups tab to configure group for this user.
Under Parents group available, select OSSServiceAdmins Group and click Save.
Data is vulnerable at many points in any computer system, and many security techniques and types of functionality can be employed to protect it.
For information about Oracle's commitment to accessibility, visit the Oracle Accessibility Program website at http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=docacc.
Oracle customers have access to electronic support through My Oracle Support. For information, visit http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=info or visit http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=trs if you are hearing impaired.
Oracle Health Sciences Mobile Clinical Research Associate Server Security Guide, Release 1.3
E38752-04
Copyright © 2013, 2014 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
This software and related documentation are provided under a license agreement containing restrictions on use and disclosure and are protected by intellectual property laws. Except as expressly permitted in your license agreement or allowed by law, you may not use, copy, reproduce, translate, broadcast, modify, license, transmit, distribute, exhibit, perform, publish, or display any part, in any form, or by any means. Reverse engineering, disassembly, or decompilation of this software, unless required by law for interoperability, is prohibited.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice and is not warranted to be error-free. If you find any errors, please report them to us in writing.
If this is software or related documentation that is delivered to the U.S. Government or anyone licensing it on behalf of the U.S. Government, the following notice is applicable:
U.S. GOVERNMENT END USERS: Oracle programs, including any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed on the hardware, and/or documentation, delivered to U.S. Government end users are "commercial computer software" pursuant to the applicable Federal Acquisition Regulation and agency-specific supplemental regulations. As such, use, duplication, disclosure, modification, and adaptation of the programs, including any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed on the hardware, and/or documentation, shall be subject to license terms and license restrictions applicable to the programs. No other rights are granted to the U.S. Government.
This software or hardware is developed for general use in a variety of information management applications. It is not developed or intended for use in any inherently dangerous applications, including applications that may create a risk of personal injury. If you use this software or hardware in dangerous applications, then you shall be responsible to take all appropriate fail-safe, backup, redundancy, and other measures to ensure its safe use. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates disclaim any liability for any damages caused by use of this software or hardware in dangerous applications.
Oracle and Java are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Intel and Intel Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. All SPARC trademarks are used under license and are trademarks or registered trademarks of SPARC International, Inc. AMD, Opteron, the AMD logo, and the AMD Opteron logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
This software or hardware and documentation may provide access to or information on content, products, and services from third parties. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates are not responsible for and expressly disclaim all warranties of any kind with respect to third-party content, products, and services. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates will not be responsible for any loss, costs, or damages incurred due to your access to or use of third-party content, products, or services.