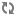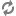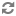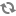The following is an example of a simple validator class:
package atg.cim.validator;
import atg.cim.util.Util;
import atg.cim.worker.IValidator;
import atg.cim.worker.ValidatorException;
/**
* This validator class validates if the property "title"
* equals "Hello World!"
*/
public class HelloWorldValidator implements IValidator {
String mMessage;
private String mTitle;
/**
* Returns the title string
* @return mTitle
*/
public String getTitle() {
return mTitle;
}
/**
* Sets the title
* @param pTitle
*/
public void setTitle(String pTitle) {
mTitle = pTitle;
}
/**
* assert that the title is not null/blank
*
* @return true if input parameter is not null/blank<br>
* false if input parameter is null/blank
*/
public boolean canValidate() {
if( Util.isNullOrBlank(mTitle) ) {
//unable to validate because title is null or blank
mMessage = "HelloWorldValidator cannot validate as string is null or blank";
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
/**
* validates that the value of title is "Hello World!"
* @return true if value of title is "Hello World!"; false otherwise
* @throws ValidatorException
*/
public boolean validate() throws ValidatorException {
if ( mTitle.equals("Hello World!") ) {
//title is equal to "Hello World!"
mMessage = "HelloWorldValidator has successfully validated the title" +
mTitle;
return true;
} else {
//title does not equals "Hello World!"
mMessage = "HelloWorldValidator has successfully validated and your title is
not Hello World!. It is " + mTitle;
return false;
}
}
public String getMessage()
{return mMessage;}
}