1 Getting Started
This chapter introduces the Oracle Communications MetaSolv Solution flow-through package concept, and describes how a flow-through package fits into the overall architecture of MetaSolv Solution and Oracle Communications ASAP.
Assumptions
The samples provided in this document assume that you have MetaSolv Solution with the XML API Option and ASAP installed. It also assumes that you have Oracle WebLogic Server installed to support MetaSolv Solution and ASAP.
About the Flow-Through Package
A flow-through package includes:
-
A sample integration that demonstrates how to integrate MetaSolv Solution and ASAP. The files include workflows that control events, order management, and data transformation.
-
Documentation that provides best practice information on setup and configuration of both products.
The flow-through package demonstrates how to set up a MetaSolv Solution order (POTS or DSL) so that it can activated on the network automatically by ASAP. The files are intended as a learning tool to make integration easier whether you already know Oracle products or whether you are using an Oracle product for the first time.
The MetaSolv Solution installation provides a flow-through package that demonstrates POTS and DSL. Every MetaSolv Solution service that can be activated using ASAP has a representative example for integrating these two Oracle products.
Differences in business processes between companies mean that no single example integration will work in every case. The sample files should be used as an example of one way to integrate the products rather than a step-by-step process that must be followed exactly. The documentation clearly indicates each step in an example that Oracle considers a best practice.
What a Flow-Through Package Demonstrates
The following types of information are available through the sample code or this document:
-
MetaSolv Solution setup information to collect and send the right data for ASAP activation
-
Product catalog setup in MetaSolv Solution
-
Setting up gateway events
-
Workaround solutions that capture data required for ASAP
-
-
Workflows in WebLogic Workshop that create a sample XML API integration with ASAP
-
WebLogic Server setup for communication between products
-
Foreign JMS server
-
Authentication credentials
-
WLI Message Broker channels
-
-
Data mapping between MetaSolv Solution and ASAP
Process Used to Create the Flow-Through Packages
The following steps show the process used to create the sample integration between MetaSolv Solution and ASAP.
-
Plan the process.
-
Modeling of ASAP CSDL commands and the specific parameters required to activate service for a specific type of order (for example, POTS) on a specific network element (for example, a Lucent 5ESS switch).
For information on this process, see the ASAP documentation available on the Oracle software delivery website.
-
Identify information in MetaSolv Solution that maps to the ASAP CSDL parameters.
-
Complete a gap analysis to determine information required by ASAP for activation not currently collected by MetaSolv Solution.
-
-
Set up the ASAP environment.
-
Install Oracle WebLogic Server 10.3.1
-
Create and configure an ASAP WebLogic domain.
-
Install and deploy ASAP.
-
Deploy the ASAP cartridge responsible for activating service.
-
-
Set up the MetaSolv Solution environment.
-
Install Oracle WebLogic Server 10.3.1 for MetaSolv Solution.
-
Create and configure a MetaSolv Solution WebLogic domain.
See MetaSolv Solution Installation Guide and MetaSolv Solution System Administrator's Guide for information on configuring a domain.
-
Complete a standard installation and deployment of MetaSolv Solution with the XML API option.
See the MetaSolv Solution Installation Guide for more information.
-
Install the MetaSolv Solution flow-through package.
See "Setting Up the Flow-Through Package" for more information.
-
-
Configure communication between MetaSolv Solution and ASAP.
-
Set up the Foreign JMS server in the MetaSolv Solution domain.
-
Create authentication credentials.
-
Create WebLogic Integration channels.
-
-
Set up the following areas in MetaSolv Solution to provide data required by ASAP for activation:
-
Product specification
-
Product catalog
-
Provisioning plan
-
Gateway event
-
Equipment
-
Custom attributes
-
Special setup in the user interface required by ASAP because of vendor or other requirements.
-
-
Create integration workflows in WebLogic Workshop.
-
Create .jpd files that define the steps in the integration process for XML API.
-
Create .xq files that map MetaSolv Solution order data to ASAP data.
-
Create .jcx files for communication.
-
-
Test integration workflows.
Implementation Architecture
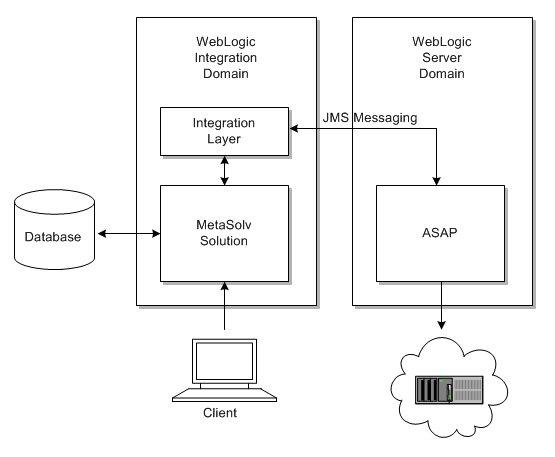
Oracle recommends setting up MetaSolv Solution and ASAP in separate WebLogic domains located on separate machines.
Figure 1-1 shows the recommended hardware and software configuration.
For complete information on installing MetaSolv Solution and ASAP, refer to the following documents:
-
ASAP Installation Guide
-
MetaSolv Solution Installation Guide
These documents are available on the Oracle software delivery website.
Data Flow for the Sample Integrations
Figure 1-2 shows how order data flows from MetaSolv Solution to ASAP and back to MetaSolv Solution for the automatic activation of an order.
Figure 1-2 Data Flow for Flow-Through Activation
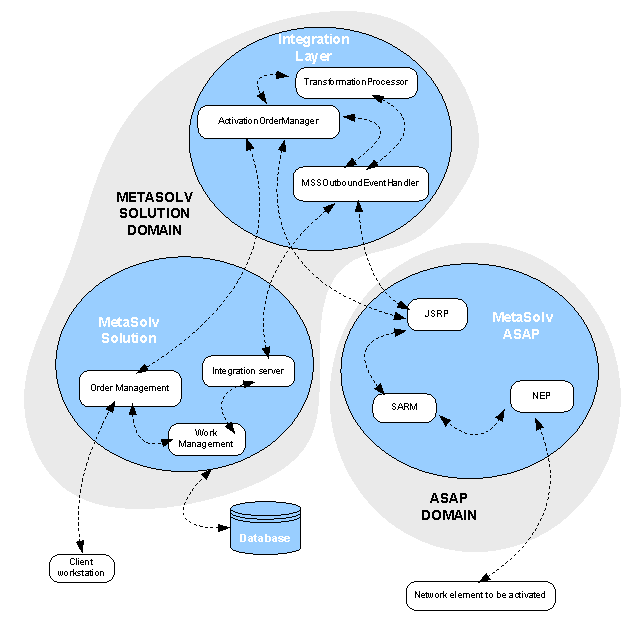
Description of "Figure 1-2 Data Flow for Flow-Through Activation"
-
A CSR enters an order for service in Order Management in MetaSolv Solution and assigns a provisioning plan for the order.
-
The order is processed, and the provisioning plan tasks (which includes an activation task for turning up service) are set up in a Work Management queue.
-
The Activate task in Work Management is completed, which triggers an activation gateway event to the Integration server.
-
The Integration server routes the gateway event to the MSSOutboundEventHandler in the integration layer.
-
MSSOutBoundEventHandler detects the activation gateway event and sends the appropriate message to the ActivationOrderManager.
-
The ActivationOrderManager associates the appropriate workflow with the service requested on the order, and sends the request to the TransformationProcessor to transform it into the MetaSolv Solution format.
-
The TransformationProcessor returns the transformed request data to the ActivationOrderManager, which sends the request to MetaSolv Solution.
-
MetaSolv Solution responds by processing the request and sending the data back to the ActivationOrderManager through the Activation API.
-
The ActivationOrderManager sends the response to the TransformationProcessor where the data is transformed from MetaSolv Solution format to the MetaSolv Information Model (MIM format) and returned.
-
The ActivationOrderManager decomposes the exported MetaSolv Solution data and maps the relevant portions into the appropriate ASAP CSDL commands for the service being requested.
The flow-through package that this document describes has a single MetaSolv Solution order to a single ASAP order. This was done to simplify the order for demonstration purposes. In everyday practice, there can be many ASAP activation orders resulting from a single MetaSolv Solution order for service.
-
The ActivationOrderManager sends the newly mapped ASAP CSDL request data to the TransformationProcessor where the data (which is in MIM format) is mapped into the XML format accepted by ASAP.
Key sequences are assigned for the order to ensure that ASAP's return data is correctly matched to its original request.
-
The TransformationProcessor returns the activation request data to the ActivationOrderProcessor, which sends the data to the Java Service Request Processor (JSRP) module in ASAP.
-
In ASAP, the JSRP module validates the request and sends a message to the MSSOutboutEventProcessor that the request is good.
-
The message is relayed to the Integration server in MetaSolv Solution which updates the activation task in Work Management to Processing.
A method is available that allows you to update the Events tab on the Work Management window as event messages are received from ASAP. The XSD for the method is XmlOrderManagementEvents.xsd.
-
The JSRP maps the order CSDL parameters to the appropriate CSDL commands and sends the order to the Service Activation Request Manager (SARM)
-
In the SARM, the order data from the JSRP that contains the CSDL commands and parameters is decomposed into lower-level ASDL commands that describe the exact tasks to be performed.
-
The SARM sends the order data (in ASDL commands) to the Network Element Processor (NEP).
-
ASAP executes the order, locates the network element, and activates service.
-
An event is sent from the ASAP JSRP to MSSOutboundEventProcessor indicating that the activation request was successful.
-
The event processor sends the event information to the Integration server.
-
The Integration server updates the activation task in Work Management to Complete.
-
The GUI is updated to show the status of the activation task in Work Management for the workstation.
Event Handling
Activation requires handling events from MetaSolv Solution and ASAP. A MetaSolv Solution gateway event triggers the activation process, and events from ASAP report progress back to MetaSolv Solution on activation results.
About MetaSolv Solution gateway events.
A MetaSolv Solution gateway event can be triggered at the order-level or at the service-item level. An order can have an order-level or service-level event associated with it, but it cannot have both. Almost all gateway events that trigger activation are fired at the order level. POTS is the only service that can have either order-level and service-item-level gateway events. Features for a line, such as call waiting or call forwarding would use a service-item-level gateway event. Hunt groups are not supported by service-item-level gateway events.
For example, POTS can require a service-item-level gateway event for each telephone number. Therefore, if an order requests activation of 10 telephone numbers, each number triggers a separate gateway event and data is sent to ASAP for each separate telephone number. DSL, on the other hand, requires order-level activation. A DSL order triggers a single order-level gateway event for activation.
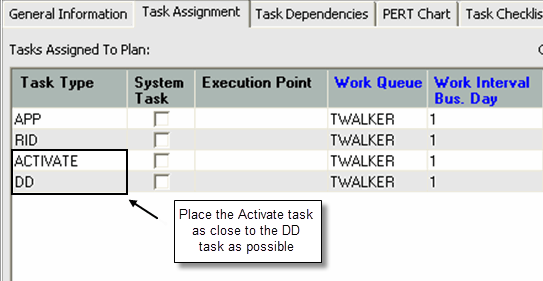
Figure 1-3 shows an example of an Activate task.
How MetaSolv Solution Handles Activation Events
This section describes the how MetaSolv Solution interfaces with the integration layer using the gateway event to report successes and failures on activation requests.
The descriptions that follow assume that the preference Bypass Pending Gateway Events on a Proc Supp Cancel is set to Y. This preference is located in the MetaSolv Solution Preferences under Work Management, then Work Queue Management.
Figure 1-4 Setting a Preference for Gateway Events
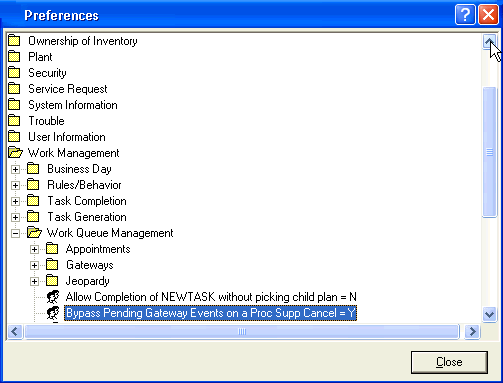
Description of "Figure 1-4 Setting a Preference for Gateway Events"
Successful Activation
-
An order is placed, provisioned, and is in work in Work Management.
-
The Activate task for an order is opened in the work queue of Work Management, and the gateway event status is set to Pending.
-
The system initiates the gateway event server, and the gateway event status is set to Sending, which indicates the system is looking for an integration layer to which it can pass a message.
-
The integration layer processes the order and determines the number of activation work orders that must be created.
-
The integration layer sends the following data to MetaSolv Solution:
Activation System Name = ASAP Activation Service Key = Represents the identifier for the activation work order Gateway Event Id = from gateway event Document Number = from gateway event Task Number = from gateway event Integration Status = In Progress Gateway Event name = from gateway event
-
The integration layer updates the gateway event status to In Progress.
-
Once the activation system processes the work orders, the integration system updates the gateway event status and the integration status to Complete.
-
The DD task completes successfully.
Activation Completes But the Due Date Task Fails
In this case, the basic flow shown in Figure 1-3 is successful through step 7. In step 8, the Due Date task fails to complete and an error message is displayed.
-
The user creates a supp order to correct the original order.
-
The user manually bypasses the gateway event if the status for any of the activation work orders is already completed.
-
If the user has to make engineering changes to correct the due date problem, the gateway event can be reinitiated. The Integration layer handles this order as a change order.
Activation Error on Some work Orders
-
When the activation system fails on any of the activation work orders the gateway event status will be set to Error.
-
The integration layer sets the gateway event status to Error for the failed work order and passes an error message to MetaSolv Solution.
The integration layer sets the error message to whatever message was returned by the activation system.
-
The integration layer sets the status to Complete for all successfully completed work orders.
-
In the work queue manager in MetaSolv Solution, the user can select the gateway event, right click and select the Display Work Order Option from the displayed selection menu.
-
The system displays the following information:
-
Activation work order number
-
Status (which is set to Error)
-
Error message
-
Date the error message was sent
-
-
The user has three options to correct the problem:
-
Supplement the order in MetaSolv Solution and manually re-initiate the gateway event. With this action, the process will start at basic flow Step 1.
-
Set the gateway event status to bypass and go the activation application's user interface to correct the issue.
-
Access ASAP and delete the work orders that were not successful, then reinitiate the gateway events.
-
Integration System Fails
-
When the integration system fails to create the activation work orders, only the gateway event status is updated.
The event-status is updated to Error, and the error message indicates the time and source of the error. The error details are included in the logs.
-
The user must reinitiate the gateway event. This action starts the basic flow at Step 1.
Order is Supp Canceled
-
If the CSR initiates a supp cancel of a PSR order, the order is appended with a supplement type of 1 and the activity code for all service items is set to A.
-
The system checks the gateway event status and the gateway event preference (Bypass Gateway Events on a Pending Supp Cancel) to determine processing.
-
If gateway event status = Pending and the preference is set to Yes, the gateway event status is set to Bypass and the gateway event status is not sent to the integration layer.
-
If the gateway event status = Sending or In Progress, the system waits until the gateway event completes or fails.
-
If the status is set to Complete, the gateway event must be re-initiated. The integration layer interprets the supplement type passed with the order information to determine whether all service items on the order are canceled and the services need to be disconnected.
-
If the status of the gateway event is set to Error, the user must determine what caused the error. If some activation work orders are complete, the gateway event is re-initiated so the integration layer can determine that a Disconnect order needs to be created for the activation system A user can also access the activation application's interface manually and disconnect the work orders.
Note:
To avoid the situation where an order is in progress, user's should place the gateway event as close as possible to the DD task. The user should backdate the Delay, Activate, and DD tasks. The Delay task keeps the Activate task from going live, which in turns triggers a gateway event.
-
-
Creating Custom Attributes in MetaSolv Solution
You may find it necessary to create custom attributes if ASAP requires data that MetaSolv Solution does not currently collect and a workaround for collecting the information is not readily available.
All custom attributes used to capture required or optional activation parameters must be associated with the appropriate building blocks (such as a DSL link or a DSLAM network element). In addition, custom attributes for each building block must be included in a layout that associates them with the Activation process point. This definition and association of custom attributes is performed in the MetaSolv Solution Utilities module.
Any label defined for a custom attribute must match the label expected by the integration layer. The generic custom attribute label can be overridden when the custom attribute is defined for the building block/process point. If the label is overridden, that is the value the API returns. Otherwise, the label from the generic custom attribute definition is returned.
Custom attributes are created using the MetaSolv Solution Utilities module. See the MetaSolv Solution online Help for more information on how to create custom attributes.
Mapping MetaSolv Solution Data to CSDL Command Parameters
ASAP has two levels of service modeling: CSDL commands and ASDL commands. Integrating to ASAP is always executed at the CSDL level. A CSDL command can map to many ASDL commands. ASDL represent low-level atomic actions on a particular network element. A CSDL command is an abstraction layer that allows service bundling and simplification.
CSDL and ASDL commands are typically similar for an ASAP cartridge. CSDL modeling is typically customer specific and occurs as part of the implementation of ASAP. The flow-through package describes integration to standard ASAP cartridges without customer-specific CSDL modeling. Therefore, the CSDL and ASDL commands are closely aligned for the flow-through package. If CSDL changes are required at customer implementation, mapping in the flow-through package can be changed accordingly.
MetaSolv Solution data is mapped to ASAP CSDL command parameters in the integration layer. To determine which ASAP commands are to be used, locate the ASAP cartridge guide for the equipment that will be activated. For example, if POTS service is to be activated on the Lucent 5ESS switch, locate the cartridge guide for that specific switch on the Oracle software delivery website.
Inside the guide, locate the CSDL command for the service activation that you want to accomplish. For example:
Add a POTS residential line:
C_LU-5ESS_16_ADD_POTS-RES-LINE
Add POTS call waiting:
C_LU-5ESS_16_ADD_POTS-CCW
The cartridge guide lists the required and optional parameters for the command. The required parameters must be mapped to MetaSolv Solution data coming from the Activation API.
Setting Up the Flow-Through Package
The following sections explain how to locate, set up, and view a flow-through package.
Where to Find the Flow-Through Package
The flow-through package is provided in the MSS_XML_API_R6_n_n_bnnn.jar file where:
R6_n_n is the release version
bnnn is the build version
For example: MSS_XML_API_R6_2_0_b123.jar
This jar file contains several files, including files that contain sample code. The file that contains the flow-through package sample code is flow_through_package.jar. This jar file contains code, libraries, and other files required for Oracle Workshop-based development for the flow-through package application.
Setting Up on The Workstation
To set up the XML API flow-through package for viewing:
-
Create a local directory and name it ServiceActivation_workspace.
-
Locate the MSS_XML_API_R6_n_n_bnnn.jar file.
-
Open the jar file and locate the flow_through_package.jar file.
-
Open the jar file and locate the ServiceActivation_workspace.jar file.
-
Open the jar file, and extract the contents of the ServiceActivation_workspace.jar file into your local directory, ServiceActivation_workspace.
-
Open the Workshop IDE.
The Workspace Launcher dialog box opens.
-
Populate the Workspace field by clicking Browse to navigate to your local directory, ServiceActivation_workspace.
-
Click OK.
The following figure shows the directories that appear in the extracted workspace.
Description of the illustration ftp_get_svc_act_ex_dirs.gif
-
Build the application in Workshop.
-
Run the workflows or browse through the workflows to see how they are constructed.
Viewing a Flow-Through Package
To view the samples in Workshop:
-
Expand the integration directory, and navigate to the workflow directory.
The directory path is: integration/src/com/metasolv/integration/activation/workflow
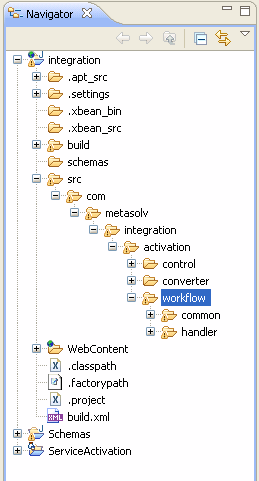
Description of the illustration ftp_get_svc_act_wrkfl_path.gif
-
Expand the workflow child directories, common and handler.
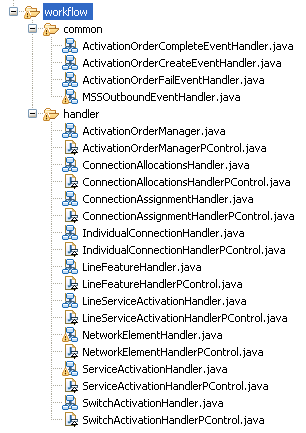
Description of the illustration ftp_get_svc_act_workflows.gif
-
Double-click a .java file located in one of the workflow child directories to see the contents of the workflow in Workshop.