| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Security Guide for Oracle WebLogic Portal 10g Release 3 (10.3.6) Part Number E14251-08 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Fusion Middleware Security Guide for Oracle WebLogic Portal 10g Release 3 (10.3.6) Part Number E14251-08 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter describes how to view and configure authentication and role mapping providers and security provider services.
In the Users, Groups, & Roles > Security Providers menu, you can view detailed information about how providers have been configured to interact with the WebLogic Portal Administration Console. This menu shows the access privileges for each provider you have configured to supply authentication and role-based authorization capabilities, including whether or not you can view, remove, or modify users, groups, and roles.
In the Configuration Settings > Service Administration menu, you can determine whether or not text entry of users and groups is allowed for security providers that do not allow read access, and you can prevent specific users or groups from being created or deleted. You can also configure user management and group management roles that determine runtime operations that can be performed by these roles using the UserProvider and GroupProvider APIs.
This chapter includes the following sections:
Section 6.8, "Viewing Authentication Provider Service Details"
Section 6.9, "Adding Authentication Security Provider Services"
Section 6.10, "Configuring Authentication Provider Services"
Section 6.15, "Configuring OAM Single Sign-On with WebLogic Portal"
Use the WebLogic Portal Administration Console to view the access privileges for each provider you have configured to supply authentication and role-based authorization capabilities.
The authentication providers and role mappers you connect to WebLogic Server are configured in specific ways. For example, the WebLogic SQL Authenticator is typically configured to allow you to add and remove users and groups using the WebLogic Portal Administration Console, while a custom authenticator may be configured to provide only read access to users and groups.
Perform the following steps to view the configured security providers:
Choose Users, Groups, & Roles > Security Providers.
Select Security Providers in the Security Providers tree.
The Browse Security Providers tab shows the title and description for each category of provider, including authentication providers and role mappers, as shown in Figure 6-1.
From this tab, you can choose a type of security provider, either Authentication Providers or Role Mappers, to view additional information.
Authentication providers store users, passwords, and groups, which can be viewed and managed directly in those providers. The providers are also configured with rules for how tools such as the WebLogic Portal Administration Console interact with them.
The WebLogic SQL Authenticator (the default authentication provider) and WebLogic LDAP Authenticator provide read and write access from the WebLogic Portal Administration Console (and the WebLogic Server Administration Console) by default.
The typical configuration for users and groups in supported external authentication providers is read-only access from the WebLogic Portal Administration Console (and the WebLogic Server Administration Console). To provide write access to external users and groups from the WebLogic Portal Administration Console, you must develop your custom authentication provider to allow write access. If you are using any custom authentication providers, develop them according to the guidelines in "How to Develop a Custom Authentication Provider" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing Security Providers for Oracle WebLogic Server.
Perform the following steps to view the configured authentication providers:
Choose Users, Groups, & Roles > Security Providers.
Select Authentication Providers in the Security Providers tree.
The Browse Authentication Providers tab shows the title and description for each authentication provider, as shown in Figure 6-2. At least one authentication provider, SQLAuthenticator, is present by default.
Tip:
You can also build group hierarchy trees for authentication providers in the WebLogic Portal Administration Console. A tree view of groups provides a convenient visual mode for changing profile values, finding users within groups, and adding users and groups to delegated administration and visitor entitlement roles. For more information, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware User Management Guide for Oracle WebLogic Portal.
Perform the following steps to view the details for a configured authentication provider:
Choose Users, Groups, & Roles > Security Providers.
Select Authentication Providers in the Security Providers tree.
Select the authentication provider for which you would like to see details.
The Authentication Provider Details tab shows the name, description, and version of the authentication provider. It also shows which management interfaces are implemented for the provider.
Figure 6-3 Authentication Provider Details
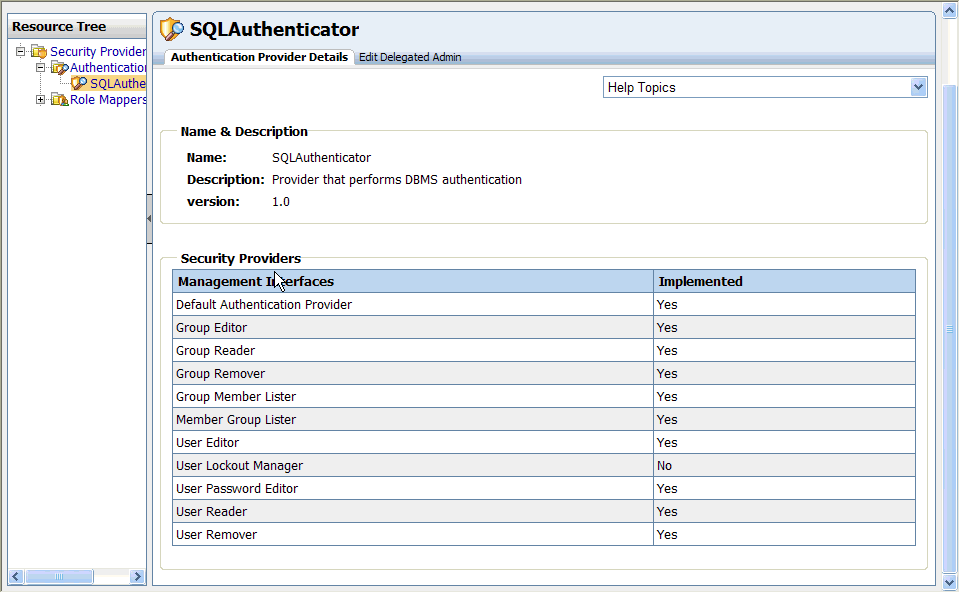
Descriptions of the available management interfaces are listed in Table 6-1.
Table 6-1 Authentication Provider Management Interfaces
| Management Interface | Description |
|---|---|
|
Default Authentication Provider |
Indicates whether or not this was the first authentication provider configured in WebLogic Server. The default does not change, regardless of which authentication provider is currently being used. |
|
Group Editor |
Indicates whether or not you can manage groups with the WebLogic Portal Administration Console; for example, whether you can add groups, move groups, and add users to groups. |
|
Group Reader |
Indicates whether or not you can view groups with theWebLogic Portal Administration Console. |
|
Group Remover |
Indicates whether or not you can remove groups with the WebLogic Portal Administration Console. |
|
Group Member Lister |
Indicates whether or not you can use the WebLogic Portal Administration Console to search within a group for users or subgroups that match a given name pattern. |
|
Member Group Lister |
Indicates whether or not you can view groups in the WebLogic Portal Administration Console that directly contain a user or a group. |
|
User Editor |
Indicates whether or not you can modify group membership for users with the WebLogic Portal Administration Console. |
|
User Lockout Manager |
User lockout settings include how many unsuccessful login attempts a user can make before being prevented from future login attempts. For information about how to modify user lockout settings in the WebLogic Server Administration Console, see the topic "Set User Lockout Attributes" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help. |
|
User Password Editor |
Indicates whether or not you can modify user passwords in the WebLogic Portal Administration Console. |
|
User Reader |
Indicates whether or not you can view users in the WebLogic Portal Administration Console. |
|
User Remover |
Indicates whether or not you can delete users in the WebLogic Portal Administration Console. |
To provide write access to external users and groups from the WebLogic Portal Administration Console, the authentication provider must be configured to allow it. This is a development task. For more information, see "Configuring WebLogic Security Providers" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Securing Oracle WebLogic Server.
If an authentication provider does not provide read access to users and groups with the WebLogic Portal Administration Console, you can still use text entry fields to type in the names of existing users and groups for selection. For example, if you want to change the user profile property values for a user stored in a provider that does not support read access, you can type the name of the user in the Users Management tree to select the user for property modifications. For information about allowing text entry, see Section 6.10.1, "Enabling Text Entry for Authentication Providers."
For information on determining if you need to develop a custom authentication provider, and how to develop one, see "How to Develop a Custom Authentication Provider" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing Security Providers for Oracle WebLogic Server. If you want to add an authentication provider, see Section 2.2, "Choosing WebLogic and Custom Authentication Providers."
If you remove an authentication provider using the WebLogic Server Administration Console, be sure to also remove the provider from the WebLogic Portal Administration Console from the Service Administration > Authentication Hierarchy Service tree. For more information, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware User Management Guide for Oracle WebLogic Portal.
A role mapping provider determines which security roles apply to operations performed on a resource.The default role mapping provider is the WebLogic XACML provider, XACMLRoleMapper, which uses the RDBMS security store to store role policies.
Note:
The WebLogic XACML role mapping provider is required for WebLogic Portal, and suitable for most needs. It is unlikely that you will need to configure a custom role mapping provider.
Perform the following steps to view the configured role mappers:
Choose Users, Groups, & Roles > Security Providers.
Select Role Mappers in the Security Providers tree.
The Browse Role Mappers tab shows the title and description for each role mapper. The default role mapper, XACMLRoleMapper, is present by default, as shown in Figure 6-4.
Perform the following steps to view the details for a configured role mapper:
Choose Users, Groups, & Roles > Security Providers.
Select Role Mappers in the Security Providers tree.
Select the role mapper for which you would like to see details from the tab or from the tree.
The Role Mapper Details tab shows the name, description, and version of the role mapper. It also shows which management interfaces are implemented for the role mapper.
Descriptions of the available management interfaces are listed in Table 6-2.
Table 6-2 Role Mapper Management Interfaces
| Management Interface | Description |
|---|---|
|
Default Role Provider |
Indicates whether or not this was the first role mapper configured in WebLogic Server. The default does not change, regardless of which role mapper is currently being used. |
|
Role Editor |
Indicates whether or not you can modify role definitions in the WebLogic Portal Administration Console. |
|
Role Reader |
Indicates whether or not you can read roles in the WebLogic Portal Administration Console. |
Perform the following steps to view the configured authentication provider services:
Choose Configuration Settings > Service Administration.
In the tree, select Application Configuration Settings > Security > Authentication Security Provider Service.
The Authentication Security Provider Service window shows the name and description for each service that has been configured. The AllAtnProviders service configuration settings apply to all authentication provider services, unless the settings are overridden for an individual authentication provider service.
Perform the following steps to view detailed information about a configured authentication provider service:
Choose Configuration Settings > Service Administration.
In the tree, select Application Configuration Settings > Security > Authentication Security Provider Service.
Select the authentication provider service for which you want to see detailed information. The AllAtnProviders service configuration settings apply to all authentication provider services; these settings can be overridden for an individual authentication provider service.
Detailed information about the selected authentication provider service is displayed.
The Predicate Text Entry Enabled? check box determines whether delegated administrators can add user, group, and role names to role and security policies by entering their names in a text box. For more information, see Section 6.10.1, "Enabling Text Entry for Authentication Providers."
You can also see which roles have the capability to create, read, update, or delete groups and users using the GroupProvider and UserProvider APIs.
The Anonymous role includes any unauthenticated user. The Self role is the logged in authenticated user, and indicates whether that user can perform operations for themselves, such as adding themselves to a group or changing their password.
Table 6-3 describes the group management and user management capabilities.
Table 6-3 Descriptions of Group Management and User Management Capabilities
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
|
Can Create |
Determines whether the role can create groups or users, using the GroupProvider API or UserProvider API, respectively. |
|
Can Read |
Determines whether the role can see groups or users, using the GroupProvider API or UserProvider API, respectively. |
|
Can Update |
Determines whether the role can update groups or users, using the GroupProvider API or UserProvider API, respectively. |
|
Can Delete |
Determines whether the role can delete groups or users, using the GroupProvider API or UserProvider API, respectively. |
You can also restrict groups and users with specified names from being created or deleted.
Table 6-4 describes group and user naming restrictions you can set.
Table 6-4 Descriptions of Naming Restrictions
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
|
Protected |
Determines whether a group or user with the specified name can be deleted. |
|
Reserved |
Determines whether a group or user with the specified name can be created. |
From this window, you can add an authentication provider service to configure, as described next, or edit configuration settings, as described in Section 6.10, "Configuring Authentication Provider Services."
You can add an existing authentication provider service so that you can view and edit its configuration settings in the Service Administration menu.
Perform the following steps to add an authentication security provider service:
Choose Configuration Settings > Service Administration.
Select Security > Authentication Security Provider Service in the Application Configuration Settings tree.
Click Add Security Provider Service.
In the Add Authentication Security Provider Service to Security Service dialog, select the name of the authentication provider from the drop-down list.
Optionally, add a description of the service.
Optionally, check the box to enable predicate text entry for the service. For more information, see Section 6.10.1, "Enabling Text Entry for Authentication Providers."
Click Update.
The service you have added appears in the list of services.
Updates to any of these settings require either enterprise application redeployment or server restart.
You can modify the following configuration settings for authentication provider services:
Enable and disable text entry fields in the WebLogic Portal Administration Console for entering known user and group names in authentication providers that do not allow read access
Specify which roles can be used in runtime operations using the GroupProvider and UserProvider APIs
Prevent specific users or groups from being created or deleted
Some authentication providers may not allow read access to users and groups by external tools such as the WebLogic Portal Administration Console. If providers do not allow read access to users and groups, you can enable a text entry field that allows you to type in user and group names in the User Management, Groups Management, Delegated Administration, and Visitor Entitlements menus for those providers. By enabling text entry, you override the requirement that SSPI providers implement reader interfaces.
The text box, which appears in the tree section when text entry is enabled, allows you enter the names of known users and groups. You can assign profiles for those users or groups, and define delegated administration and visitor entitlements policies using those users and groups. When a user from a non-readable authentication provider logs in, the profile created for that user enables authorization checks to be performed for the user.
To enable text entry for an authentication security provider service:
Choose Configuration Settings > Service Administration.
In the tree, select Application Configuration Settings > Security > Authentication Security Provider Service.
Select the authentication provider service for which you want to see detailed information.
Click the Edit icon next to Configuration Settings for: ServiceName.
Select the Predicate Text Entry Enabled? check box.
This change requires either enterprise application redeployment or server restart.
When you add a group management role to an authentication provider service, you enable capabilities for manual runtime checks performed by API calls to group providers. This provides a low-level alternative to using visitor entitlements on groups. For each group management capability (create, read, update, and delete), you can specify which roles are allowed to perform the task.
Note:
Use existing global or enterprise-application scoped roles.
Perform the following steps to add role capabilities for the GroupProvider API:
Choose Configuration Settings > Service Administration.
In the tree, select Application Configuration Settings > Security > Authentication Security Provider Service.
Select the authentication provider service for which you want to add a group management role.
In the Group Management Delegated Administration section, click Add Group Management Role.
Enter a role name. Use existing global or enterprise-application scoped role names.
Select the capabilities for the role, as described in Table 6-2.
Click Update.
The new role appears in the list of Group Management Roles. This change requires either enterprise application redeployment or server restart.
Group Management role capabilities are used for manual runtime checks performed by API calls to group providers. This provides a low-level alternative to using visitor entitlements on groups.
Perform the following steps to edit group management role capabilities for the GroupProvider API:
Choose Configuration Settings > Service Administration.
In the tree, select Application Configuration Settings > Security > Authentication Security Provider Service.
Select the authentication provider service for which you want to edit a group management role.
Click the role name or the Edit icon for the role you want to edit.
Select the capabilities for the role, as described in Table 6-2.
Click Update.
The updated role appears in the list of Group Management Roles. This change requires either enterprise application redeployment or server restart.
When you add a user management role to an authentication provider service, you enable capabilities for manual runtime checks performed by API calls to user providers. For each user management capability (create, read, update, and delete), you can specify which roles are allowed to perform the task.
Note:
Use existing global or enterprise-application scoped roles.
Perform the following steps to add user management role capabilities for the UserProvider API:
Choose Configuration Settings > Service Administration.
In the tree, select Application Configuration Settings > Security > Authentication Security Provider Service.
Select the authentication provider service for which you want to add a user management role.
In the User Management Delegated Administration section, click Add User Management Role.
Enter a role name. Use existing global or enterprise-application scoped role names.
Select the capabilities for the role, as described in Table 6-2.
Click Update.
The new role appears in the list of User Management Roles. This change requires either enterprise application redeployment or server restart.
User Management role capabilities are used for manual runtime checks performed by API calls to group user.
Perform the following steps to edit user management role capabilities for the UserProvider API:
Choose Configuration Settings > Service Administration.
In the tree, select Application Configuration Settings > Security > Authentication Security Provider Service.
Select the authentication provider service for which you want to edit a user management role.
Click the role name or the Edit icon for the role you want to edit.
Select the capabilities for the role, as described in Table 6-2.
Click Update.
The updated role appears in the list of User Management Roles. This change requires either enterprise application redeployment or server restart.
For each authentication provider, you can specify group names that cannot be created or deleted.
Perform the following steps to set restrictions on group names:
Choose Configuration Settings > Service Administration.
In the tree, select Application Configuration Settings > Security > Authentication Security Provider Service.
Select the authentication provider service for which you want to restrict group names.
In the Protected/Reserved Groups section, click Add Protected/Reserved Group.
Enter a group name.
Select the Protected check box if you want to prevent a group with this name from being deleted.
Select the Reserved check box if you want to prevent a group with this name from being created.
Click Update.
The group name role appears in the list of Protected/Reserved Groups. This change requires either enterprise application redeployment or server restart.
Perform the following steps to edit the restrictions for group names that are in the list of Protected/Reserved Groups:
Choose Configuration Settings > Service Administration.
In the tree, select Application Configuration Settings > Security > Authentication Security Provider Service.
Select the authentication provider service for which you want to change restrictions on group names.
In the Protected/Reserved Groups section, click a group name or the Edit icon for that group.
Select the Protected check box if you want to prevent a group with this name from being deleted.
Select the Reserved check box if you want to prevent a group with this name from being created.
Click Update.
The new restrictions for this group name role appears in the list of Protected/Reserved Groups. This change requires either enterprise application redeployment or server restart.
For each authentication provider, you can specify user names that cannot be created or deleted.
Perform the following steps to set restrictions on user names:
Choose Configuration Settings > Service Administration.
In the tree, select Application Configuration Settings > Security > Authentication Security Provider Service.
Select the authentication provider service for which you want to restrict user names.
In the Protected/Reserved Users section, click Add Protected/Reserved User.
Enter a user name.
Select the Protected check box if you want to prevent a user with this name from being deleted.
Select the Reserved check box if you want to prevent a user with this name from being created.
Click Update.
The user name role appears in the list of Protected/Reserved Users. This change requires either enterprise application redeployment or server restart.
Perform the following steps to edit the restrictions for user names that are in the list of Protected/Reserved Users:
Choose Configuration Settings > Service Administration.
In the tree, select Application Configuration Settings > Security > Authentication Security Provider Service.
Select the authentication provider service for which you want to change restrictions on user names.
In the Protected/Reserved Users section, click a user name or the Edit icon for that user.
Select the Protected check box if you want to prevent a user with this name from being deleted.
Select the Reserved check box if you want to prevent a user with this name from being created.
Click Update.
The new restriction for this user name appears in the list of Protected/Reserved Users. This change requires either enterprise application redeployment or server restart.
Perform the following steps to view the configured role provider services:
Choose Configuration Settings > Service Administration.
In the tree, select Application Configuration Settings > Security > Role Security Provider Service.
The Role Security Provider Service window shows the name and description for each service that has been configured. The AllRolePrividers service configuration settings apply to all role mapping provider services, unless the settings are overridden for an individual role provider service.
The default role mapping provider is the WebLogic XACML provider, XACMLRoleMapper, which uses the RDBMS security store to store role policies.
Note:
The WebLogic XACML role mapping provider is required for WebLogic Portal, and suitable for most needs. It is unlikely that you will need to configure a custom role mapping provider.
Perform the following steps to view detailed information about a configured role provider service:
Choose Configuration Settings > Service Administration.
In the tree, select Application Configuration Settings > Security > Role Security Provider Service.
Select the role provider service for which you want to see detailed information. The AllRoleProviders service configuration settings apply to all role provider services, unless the settings are overridden for an individual role provider service.
The Predicate Text Entry Enabled? capability determines whether delegated administrators can add user, group, and role name predicates to role and security policies by entering their names in a text box. For more information, see Section 6.14.1, "Enabling Text Entry for a Role Mapping Providers."
You can add an existing role provider service so that you can view and edit the configuration settings in the Service Administration menu.
Perform the following steps to add a role security provider service:
Choose Configuration Settings > Service Administration.
Select Security > Role Security Provider Service in the Application Configuration Settings tree.
Click Add Security Provider Service.
Select the name of the role mapping provider from the drop-down list.
Optionally, add a description of the service.
Optionally, check the box to enable predicate text entry. For more information, see Section 6.14.1, "Enabling Text Entry for a Role Mapping Providers."
Click Update.
The service you have added appears in the list of services.
Updates to any of these settings require either enterprise application redeployment or server restart.
The default role mapping provider is the WebLogic XACML role mapping provider, which uses the RDBMS security store to store role policies. The WebLogic XACML role mapping provider is required for WebLogic Portal, and suitable for most needs. It is unlikely that you will need to configure a custom role mapping provider.
Some role providers may not allow read access to role policies by external tools such as the WebLogic Portal Administration Console. If providers do not allow read access to roles, you can enable a text entry field that allows you to type in role names in the Delegated Administration and Visitor Entitlements menus for those providers. By enabling text entry, you override the requirement that SSPI providers implement reader interfaces.
The text box, which appears in the menu tree when text entry is enabled, allows you enter the names of known roles. You can define delegated administration and visitor entitlements policies using these role names.
To enable text entry for a role security provider service:
Choose Configuration Settings > Service Administration.
In the tree, select Application Configuration Settings > Security > Role Security Provider Service.
Select the role provider service for which you want to see detailed information.
Click the Edit icon next to Configuration Settings for: ServiceName.
Select the Predicate Text Entry Enabled? check box.
This change requires either enterprise application redeployment or server restart.
This section explains how to configure WebLogic Portal to work with Oracle Access Manager 11g.
Oracle Access Manager allows users of your applications or IT systems to log in once and gain access to a broad range of IT resources. Oracle Access Manager provides an identity management and access control system that is shared by all your applications. The result is a centralized and automated single sign-on (SSO) solution for managing who has access to what information across your entire IT infrastructure.
Before performing the procedure described in this section, you must have the following components installed and running:
Oracle Access Manager 11g or 10g (10.1.4.3)
Oracle WebLogic Server 10.3.6
Verify that the oamAuthnProvider.jar file exists in your WebLogic Server installation.
The oamAuthnProvider.jar file is located in <MW_HOME>/wlserver_10.3/server/lib/mbeantypes, where <MW_HOME> is the directory where the WebLogic Platform software is installed. The JAR is available only if Oracle Access Manager with WebGates is installed. If you do not have this JAR, contact Oracle Customer Support to obtain it. Then, copy the JAR to this location, and restart WebLogic Server.
This section explains how to configure the OAM identity asserter and related authentication providers.
If it is not running, start WebLogic server. To do this, you can use the following command in your application's domain <DOMAIN_ROOT>/bin/startWebLogic.cmd (or .sh on UNIX systems). For example: <BEA_HOME>/user_projects/domains/mydomain/bin/startWebLogic.
In a browser, log in to the WebLogic Server Console. The URL is: http://host:port/console. For example, http://localhost:7001/console.
In the Domain Structure part of the console, select Security Realms.
In the Summary of Security Realms section, select the realm called myrealm.
In the "Settings for myrealm" section, select the Providers tab and the Authentication tab, as shown in Figure 6-6.
Figure 6-6 Providers and Authentication Tabs Selected
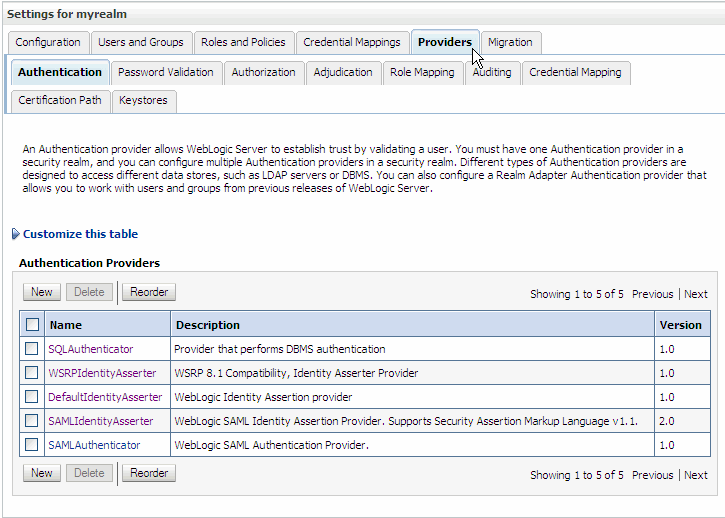
Above the Authentication Providers table, click New.
In the Name field, enter a name for the identity asserter. For this example, we chose "OAM Identity Asserter."
From the Type pull-down menu, select OAMIdentityAsserter, as shown in Figure 6-7.
Click OK. The new identity asserter appears in the Authentication Providers table.
In the Authentication Providers table, slick OAM Identity Asserter (the asserter you just added).
In the Settings for OAM Identity Asserter page, be sure the Configuration and Common tabs are selected.
Under the Common tab, set the Control Flag to SUFFICIENT.
Under Active Types, move both OAM_REMOTE_USER and ObSSOCookie to the Chosen column, as shown in Figure 6-8.
Figure 6-8 Setting Up the OAM Identity Asserter
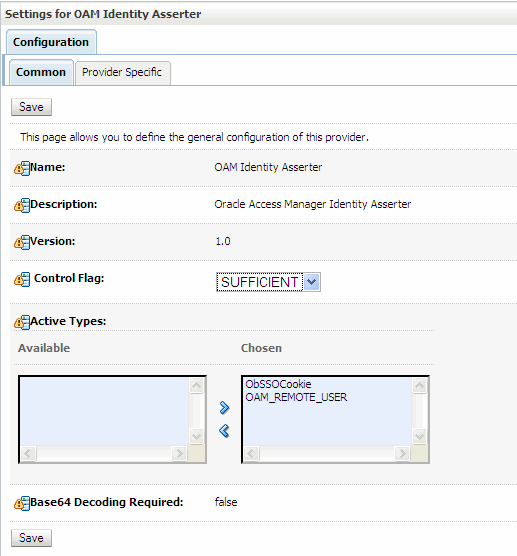
Click Save.
Return to the Providers page. The easiest way to do this is to select the Providers link from the breadcrumbs at the top of the page. See Figure 6-9.
Figure 6-9 Link to Return to the Providers Tab
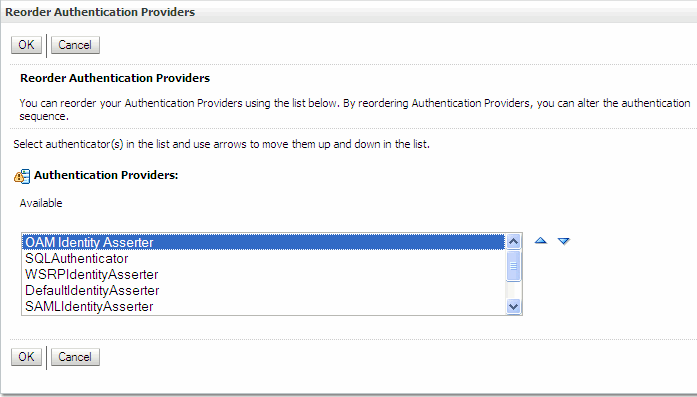
In the Authentication Providers table, click Reorder.
In the Reorder Authentication Providers, use the arrow button to move the OAM Identity Asserter provider to the top of the list, as shown in Figure 6-10. Then click OK.
Figure 6-10 Reordering the Authentication Providers
Now, you will add two more authentication providers.
Note:
The following steps illustrate how to add two more authentication providers, iPlanetAuthenticator and OracleInternetDirectorAuthenticator. These specific choices are not required; rather, they depend on the specific OAM configuration. For example, if the OAM identity store is an OID, you would need to add the OracleInternetDirectorAuthenticator. If the OAM uses Sun DSEE, then you would use iPlanetAuthenticator, but generally not both.
In the Authentication Providers table, click New.
In the Create a New Authentication Provider dialog, select iPlanetAuthenticator from the Type menu and enter iPlanet Authenticator in the Name field.
Click Save.
In the Authentication Providers table, click iPlanet Authenticator.
In the Settings for iPlanet Authenticator page, be sure the Configuration and Common tabs are selected.
Under the Common tab, set the Control Flag to SUFFICIENT.
Click Save.
In the Authentication Providers table, click New.
In the Create a New Authentication Provider dialog, select OracleInternetDirectorAuthenticator from the Type menu and enter Oracle Internet Director Authenticator in the Name field.
Click Save.
In the Authentication Providers table, click Oracle Internet Director Authenticator.
In the Settings for Oracle Internet Director Authenticator page, be sure the Configuration and Common tabs are selected.
Under the Common tab, set the Control Flag to SUFFICIENT.
Click Save.
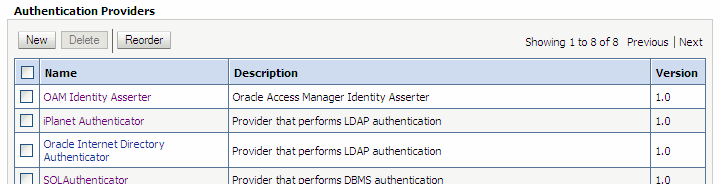
In the Authentication Providers table, click Reorder.
Move iPlanetAuthenticator so that it is second in the list of available Authentication Providers, and move OracleInternetDirectoryAuthenticator so that it is third.
Click OK. The first three rows of the Authentication Providers table should look like Figure 6-11.
Figure 6-11 Reordered Authentication Providers Table
Next, you need to enter some provider-specific values for the iPlanetAuthenticator and the OracleInternetDirectoryAuthenticator.
In the Authentication Providers table, click iPlanet Authenticator.
In the authenticator settings dialog, select the Configuration tab and select the Provider Specific Tab.
Enter LDAP server values for the Host, Port, Principal, and Credential fields. Additional information and online help is provided for each of these fields in the dialog box.
Click Save.
Repeat steps 35, 36, 37, and 38 for the OracleInternetDirectory Authenticator.
Restart the WebLogic Server.
This section describes the required WLP application configuration.
In your WLP application, open the web.xml file for editing.
In web.xml, change the authentication method to CLIENT-CERT. For example:
<login-config>
<auth-method>CLIENT-CERT</auth-method>
<realm-name>myrealm</realm-name>
</login-config>
If the <auth-method> entry is not present in web.xml, you must add it.
To test the configuration up to this point, redeploy the WLP application and verify that your portlets, including your login portlet, appear and function normally.
Finally, you need to configure the OAM server to recognize the WLP application.
Add the following code to the OHS_INSTALL_DIR/instances/instance1/config/OHS/ohs1/mod_wl_ohs.conf file. Update the WebLogicHost and WebLogicPort parameters to the values appropriate for your installation:
<Location /wlpWebProj>
SetHandler weblogic-handler
WebLogicHost localhost
WeblogicPort 7003
</Location>
<Location /wlpEarAdmin>
SetHandler weblogic-handler
WebLogicHost localhost
WeblogicPort 7003
</Location>
Restart the OAM server.
Clear the cache on the WebLogic Server where WebLogic Portal is deployed. To clear the cache, delete the tmp folder.
For example, use the following command to clear the cache:
rm -rf $WLS_HOME/user_projects/domains/yourdomain/servers/AdminServer/tmp
Where, WLS_HOME refers to WebLogic Home, and yourdomain refers to your Portal domain.
In a browser, log in to the OAM Console. You must log in as a user with administrative privileges. For example: http://localhost:7001/oamconsole.
In the OAM console, set /wlpWebProj and /wlpEarAdmin to be protected URLs. For more information on performing this task, see "Introduction to the OAM Policy Model, Single Sign-On" in the Oracle Access Manager Access Administration Guide.
Add the relevant authentication and authorization policies. This task differs depending on whether you are using OAM 11g or OAM 10g:
If you are using OAM 10g, refer to "Configuring Single Sign-On" in the Oracle Access Manager Access Administration Guide 10g (10.1.4.3).
If you are using OAM 11g, refer to "Introduction to the OAM Policy Model, Single Sign-On" in the Oracle Access Manager Access Administration Guide 11g Release 1 (11.1.1).
Access the WebLogic Portal application through the OAM Webgate Port. For more information on performing this task, see "Introduction to the OAM Policy Model, Single Sign-On" in the Oracle Access Manager Access Administration Guide.