Understanding Models
A model is a complete set of rules used to define model objects and their relationship to the general ledger. Models let you define how to measure performance within your organization by providing insight to such questions as:
Which cost object do I want to measure—customers, products, or channels?
What activities are key to my organization and how do they relate to the cost objects?
You can define, run, and analyze models using Activity-Based Management.
Model Configuration Steps
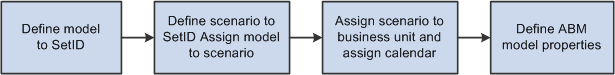
To configure a Activity-Based Management model:
Establish a model under a SetID.
This model is accessible to all business units using that SetID for the Activity-Based Management Models record group.
Create a scenario ID under the SetID, and then assign the model ID to the scenario.
Associate the scenario ID with a business unit and calendar.
Note: The calendar defined here overrides the calendar defined for the PF business unit, letting you associate quarterly models with a monthly PF business unit, for example.
Define the Activity-Based Management model properties.
This documentation discusses only the last of these four steps. For the first three steps, refer to information in the Enterprise Performance Management Fundamentals 9.1 for details on setting up a model ID and scenario.
See Defining Models and Scenarios.
Image: Model configuration setup procedures
The following diagram illustrates the steps to create a Activity-Based Management model.
Understanding Object-Oriented Modeling and Scenarios
PeopleSoft Enterprise Performance Management (PeopleSoft EPM) lets you modify a model and view the results of the impact. Employing object-oriented modeling lets you copy the data that must be changed instead of copying an entire model by defining a what-if scenario in the Scenario Manager, a parent model, and a child model.
For example, the parent model could represent your current business operations. This is the model that you want to use as the basis to assess the impact of any changes. The child model could represent these changes.
You can create scenarios for each child and parent combination.