Understanding Profit Manager Tools
The profit manager is a set of integrated tools that enable true multidimensional profitability reporting. To obtain true and meaningful profitability reports, you need a central repository as well as reliable and consistent data, and you need to consolidate and enrich the data from your general ledger and other sources.
PeopleSoft EPM infrastructure is the underlying framework that provides reliable and consistent data and consolidates data sources such as your general ledger and the EPM Analytical Applications such as PeopleSoft Activity-Based Management, Scorecard, Funds Transfer Pricing, Risk-Weighted Capital, Global Consolidations, and Workforce Analytics, which are application engines that enrich and transform data.
The features that are described in this topic are tightly integrated with the PeopleSoft analytical applications and provide you with ways to:
Move data from your PeopleSoft general ledger using the Ledger Mapper.
Verify the accuracy of your data before you post it to the performance ledger table using the PF Edit engine.
Track data movement to and from the performance ledger table (PF_LEDGER_F00) using ledger drill down.
Control batch processing using the PF Post and PF Unpost engines.
Keep the contents of the journal table (PF_JRNL_F00) clean using the PF Journal Cleanup engine.
Reconcile final table amounts using the balancing and reconciliation features.
After you set up and run a source engine or map ledger balances using the Ledger Mapper, the enriched data is moved to the performance journal table (PF_JRNL_F00). You can run the PF Journal Edit engine to check data integrity at any time. Use PF Journal Modification to revise errors. The PF Ledger Post process moves your data from the performance journal table to the performance ledger table (PF_LEDGER_F00) for reporting.
To check that data migration and enrichment is accurate:
Use the PF ledger drill down feature to track the source of general ledger data for a particular performance ledger after you populate the performance ledger table.
Use the Reconciliation utility to check balances between tables such as GL_LEDGER and PF_LEDGER.
Image: Profit Manager loading the performance ledger table
This diagram illustrates how the Profit Manager loads the performance ledger table.
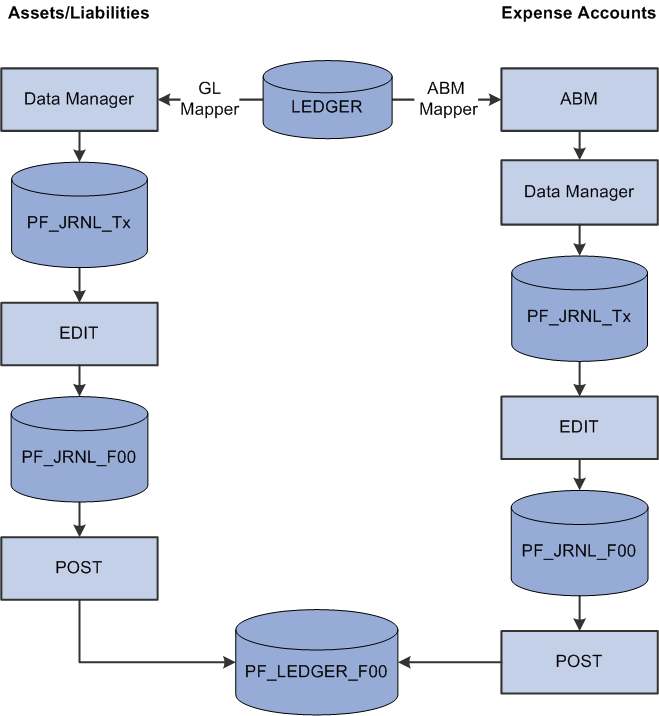
Ledger Mapper
Use the Ledger Mapper to map data, such as assets and liabilities, that does not enter the system through one of the optional analytical applications. After you define the ledger mapping rules, you must set up Data Manager rules using the GL mapper method and then run the Data Manager or Allocation Manager engine to populate the performance journal table (PF_JRNL_F00).
For example, PeopleSoft uses the Ledger Mapper to map expense data from the general ledger to Activity-Based Management resources.
To map ledger amounts, you:
Load the GL_LEDGER table.
Use the general ledger mapper method in Data Manager to move the general ledger data into the GLSTG temporary table that you identify as the source table for further data movement.
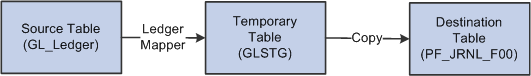
Note: You might decide to move data directly into the performance journal table (PF_JRNL_F00) using the copy method. You can also create multidimensional data using the prorata or spread even methods.
Note: A number of steps in this process use the Data Manager or the Allocation Manager engine. You must define tablemaps, datamaps, constraints, and filters, and then set up the Data Manager or Allocation Manager rules that use this metadata to produce multidimensional results. In addition, you must set up job metadata and jobstreams.
The following two diagrams illustrate how Ledger Mapper moves the data.
Image: Using the Ledger Mapper and copy methods to load the performance journal table (PF_JRNL_F00)
This diagram illustrates Ledger Mapper and the copy method.
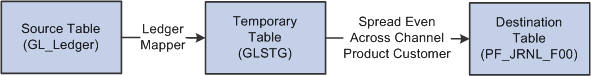
The second diagram illustrates a method in which multidimensional data is created:
Image: Using the Ledger Mapper to move ledger data, create multidimensional data, and load the performance journal table (PF_JRNL_F00)
This example illustrates Using the Ledger Mapper to move ledger data, create multidimensional data, and load the performance journal table (PF_JRNL_F00).
The Ledger Mapper uses the business unit relationships that you established in EPM to map amounts. To map multiple general ledger accounts to one performance account, set up ledger mapping rules on the Ledger Mapper page.
Note: You must define your general ledger and warehouse business units and the relationship between them before you set up and run the Ledger Mapper. In addition, before you map ledgers, you must define the tablemaps, datamaps, and constraints to use when you run the Data Manager or Allocation Manager engines. EPM is delivered with predefined tablemaps, datamaps, constraints, and Ledger Mapper Data Manager rules for the SHARE SetID.
See Understanding Warehouse Business Unit Setup, Understanding Warehouse Business Units, TableSet Sharing, and SetID Mapping, and Understanding Metadata.