Defining Business Units
This section provides an overview of business units and discusses how to establish business units for Global Consolidations.
Page Used to Define Business Units
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Warehouse Business Unit |
BUS_UNIT_TBL_PF1 |
|
Establish warehouse business units and specify their base currency and type. |
Understanding Business Units
Business units in Global Consolidations can be legal entities, a portion of a legal entity, or a collection point for consolidation-specific entries. Several categories of business units are used in Global Consolidations. It is important to understand how they differ and the terms used to refer to them.
You must define a warehouse business unit for each subsidiary, affiliate, and consolidation tree node. You will also need to establish warehouse business units to hold elimination results for each node on the consolidation tree.
Warehouse Business Unit Page
Use the Warehouse Business Unit page (BUS_UNIT_TBL_PF1) to establish warehouse business units and specify their base currency and type.
Image: Warehouse Business Unit page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Warehouse Business Unit page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
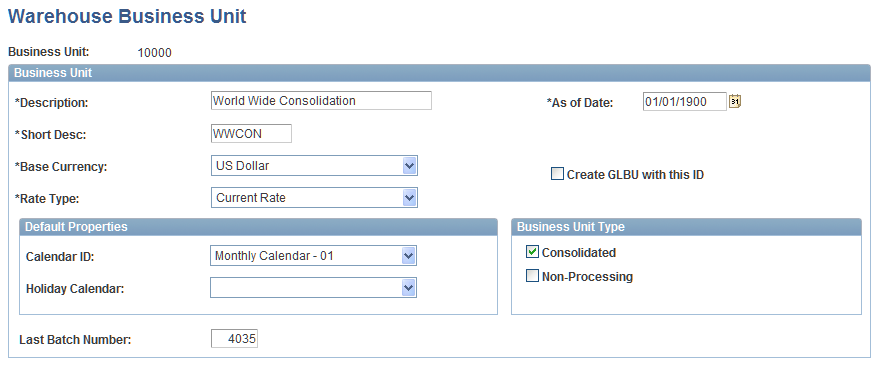
This page is described in detail in the PeopleSoft Enterprise Performance Management Fundamentals Documentaion. The Business Unit Type group box is particularly important to PeopleSoft Global Consolidations, and includes these options:
This example shows a simple consolidation tree and how business units are hierarchically arranged on the tree:
Image: Sample business unit consolidation tree
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Sample business unit consolidation tree. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.

In the example, AMERI and USCON are summarization nodes, so they should be set up as non-processing business units. Business units E1000, E1300, and E1330 are elimination business units, and they should also be set up as non-processing business units. The root node, business unit 10000 in this example, is the common consolidation business unit.
Note: It is not a requirement for the common consolidation business unit to be the root node on the consolidation tree.