To build a Smart Query, you apply composite filters to select unions, complements, and intersections of members from the different sets. Unions are selections of members that belong to either but not both of two sets. Intersections are selections of members that belong to all specified sets. Complements are selections of members of one specified set that are not members of another specified set.
You can use sets and composite filters in any combination to create highly complex Smart Queries.
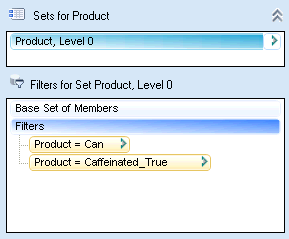
To select members that belong to either but not both sets, define two or more filters as described in Defining Set Filters from the dimension in Sets for.... For example, in Figure 29, Union of Sets, the query will return only Product, Level 0 members that are EITHER packaged in cans (Product = Can) OR are caffeinated (Product = Caffeinated_True).
Intersections include only the members that are common to all specified sets.
 To select members common to all specified sets:
To select members common to all specified sets:
Define a filter for a set as described in Defining Set Filters.
Click the arrow next to the filter name and select Add Filter.
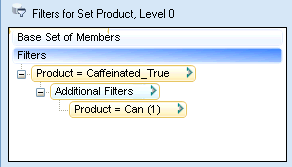
In Figure 30, Intersection of Sets, the query will return only Product, Level 0 members that are caffeinated AND packaged in a can.
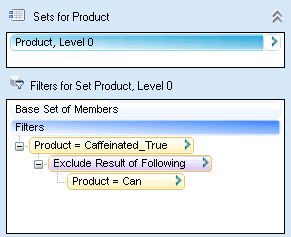
In Figure 31, Complement of Sets, the query will return only Product, Level 0 members that are caffeinated but are not packaged in a can.
When you have built the Smart Query, proceed to Completing the Smart Query.