| Oracle® Health Sciences Data Management Workbench User's Guide Release 2.4 E52292-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
Home > User's Guide > Configuring Your Discrepanc...
| Oracle® Health Sciences Data Management Workbench User's Guide Release 2.4 E52292-02 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
Home > User's Guide > Configuring Your Discrepanc...
Discrepancies are equivalent to Oracle Health Sciences InForm queries. They can be raised against InForm and non-InForm data in Oracle Health Sciences Data Management Workbench (Oracle DMW).
Queries raised in InForm are loaded into Oracle DMW as discrepancies with the same state as in InForm.
Either a validation check or a user can raise a discrepancy in Oracle DMW against data that originated in InForm or a lab. When sent to InForm, they are created as queries.
Discrepancy state changes made in Oracle DMW are sent to InForm almost immediately using a web service.
Note:
The exception is discrepancies raised in Oracle DMW against items that are hidden in InForm. InForm does not accept queries against hidden items, so these are never sent to InForm. Any resolution must occur within Oracle DMW.Changes to queries made in InForm are updated in Oracle DMW in the next data load from InForm for the study.
Discrepancies raised against lab data can be exported to a spreadsheet and then sent to the source lab. Updates made in the lab are imported during the next data load.
See also:
Oracle DMW comes with a set of discrepancy states, allowed transitions between them, and actions that change the state of the discrepancy and/or apply a tag. You can define custom actions, following the same rules.
When a discrepancy is sent to InForm, the system limits the actions an Oracle DMW user can take on the discrepancy. The same limited actions are allowed whether the discrepancy originated in InForm or in Oracle DMW.
While a discrepancy is in InForm, Oracle DMW users can apply comments and categories to it. These are never sent to InForm.
While a discrepancy is in Oracle DMW, a user can apply an action that changes the state of the discrepancy and must supply a reason for the change. The reason for change is sent to InForm.
Figure 7-1 Discrepancy States and Allowed Transitions for Discrepancies
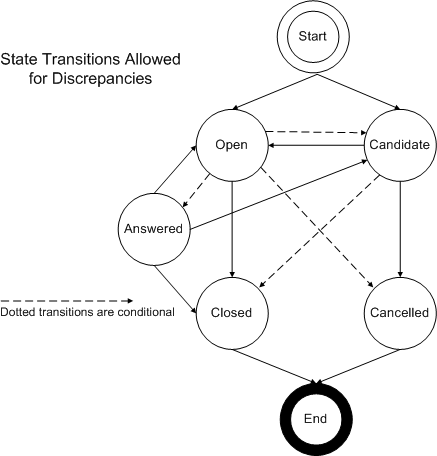
The diagram shows valid transitions for discrepancies in Oracle DMW:
Candidate and Open are the two valid beginning states for a discrepancy.
Cancelled and Closed are the two valid end states for a discrepancy.
Candidate discrepancies can always move to Open.
Candidate discrepancies can always move to Cancelled.
Candidate discrepancies can move to Closed if they have not been sent to InForm (no matter what kind of data they are on). Also, Candidate discrepancies that ARE in InForm (whether they originated in InForm or DMW) can move to Closed if they were previously in the Open state within InFormâbecause this matches InForm rules.
Open discrepancies can move to Answered if they were created in Oracle DMW and have not been sent to InForm (no matter what kind of data they are on).
Open discrepancies can always move to Closed.
Open discrepancies can move to Cancelled only if they were created in Oracle DMW and have not been sent to InForm (no matter what kind of data they are on).
Open discrepancies can move to Candidate if they were created in Oracle DMW and have not been sent to InForm.
Answered discrepancies can be reopened in either the Open or Candidate state.
Discrepancies can be always be closed from the Open or Answered state.
Users apply actions to discrepancies to move them from one state or tag label to another. The system comes with a set of predefined actions, and you can create your own custom actions. An action includes:
Start and Result States: An action is available to a user only for discrepancies that are in the action's defined start state. When the user applies an action to a discrepancy, the discrepancy's state changes to the defined result state. If you create custom actions, the start and result states must constitute an allowed transition (see "Discrepancy States and Allowed Transitions") or be the same. If the start and result states are the same, they normally have different start tags, result tags, or both.
Note:
No defined action is required to create a discrepancy. Users and validation checks can create discrepancies in either of the two valid start states, Candidate or Open.Start and Result Tags (Optional): Tags can be used to allow a dialog between users without changing the state or to effectively create a substate. Users can filter records in the Discrepancies page based on tag values.
A tag is a label applied to a discrepancy when a user performs an action that specifies it. An action with a start tag specified is available to a user only for discrepancies that have that tag.
When the user applies an action to a discrepancy, the system applies the action's defined result tag (if there is one) to the discrepancy.
Enabled: This attribute determines whether an action is available for use. You can use this attribute, for example, to ensure that users have access only to the custom actions you define, and not to the predefined actions.
Each time a user applies an action, the system maintains an unmodifiable audit trail of the event.
Note:
Users with access to the Discrepancies page can add comments to a discrepancy at any time. It is not necessary to apply an action in order to add a comment.Note:
Users must select and/or enter a reason for change when they apply an action to a discrepancy. You can create a list of valid reasons for users to select by adding values to the DME_DSC_ACTION_REASON lookup.The system comes with a set of actions that users can apply to move a discrepancy from one state to another and, in most cases, apply a tag to the discrepancy.
In some cases the action also triggers a routing action on the discrepancy, either sending it to InForm or exporting it to spreadsheet so it can be sent to a lab.
Table 7-1, "Predefined Actions Available at each Discrepancy State" lists all predefined actions. The system displays only those that are valid given the current state of the selected discrepancy. For example, although there are three predefined actions named Close, only one of them is displayed to the user at a time, depending on the current state of the discrepancy the user has selected; either Candidate, Open, or Answered.
For each action named Close the system applies a different tag, depending on the start state:
Discrepancies that started in the Candidate state get the tag ClosedAsIs.
Discrepancies that started in the Answered state get the tag ClosedByAnswer.
Discrepancies that started in the Open state get the tag ClosedByDataChange.
Only the appropriate action is available to the user.
Note:
None of the predefined actions specifies a starting tag. They can be applied to a discrepancy in the appropriate starting state with any tag or with no tag.Table 7-1 Predefined Actions Available at each Discrepancy State
Although Table 7-1 lists all valid actions based on the applicable state for a discrepancy, not all the actions are valid for every discrepancy in that state. The system filters available actions based on the following factors:
Existence of the specified Start Tag value, if any.
The data source. For example, the Send to InForm action is not available for discrepancies on lab data.
Using only predefined actions, you still have many options:
You can choose to create discrepancies in either the Candidate or Open state.
Note:
InForm queries are imported in their InForm state; you cannot change that.You can send either Candidate or Open discrepancies to their sourceâlab or InFormâfor review, or require manual review in Oracle DMW first.
You can require a formal medical review of each discrepancy or not.
You can require a formal data management review of each discrepancy or not.
You can set up validation checks so that when they run, they close discrepancies they created when the underlying data is corrected in such a way that the validation check logic no longer sees the data as discrepant.
Alternatively, you can require manual review of validation check-created discrepancies whose underlying data has been changed.
You can disable any actions you do not want to use.
A validation check with Autoclose set to Yes detects several lab test results that are out of range, and creates a discrepancy for each one. These discrepancies are displayed in the VC Listings page under the name of the validation check and in the Discrepancies page.
In the Discrepancies page, the data manager clicks Export All to Excel to export the records to a file on her personal computer and sends the file to the lab.
Lab personnel open the file in Microsoft Excel and check the test result values against the original source data. In Excel, they fix the data for all but one of the discrepancies, ready for the next data load back into Oracle DMW.
The lab personnel also send information separately about how the remaining discrepancy should be handled, and the data manager updates the discrepancy manually in Oracle DMW.
The next time the validation check runs, it closes the discrepancies on the corrected data and makes no change to the other discrepancy.
Using Custom Listings, a data manager detects several BMI values that are out of range, creates a discrepancy for each one, and sends the discrepancies to InForm as Open queries.
The CRA checks all the data in InForm and is able to resolve all queries by correcting one data point for each one. The CRA then sets all queries in InForm to Answered.
The InForm Connector detects the data changes and loads the updated data and queries (discrepancies) into the correct study InForm data model. In Oracle DMW the discrepancies will be updated to have the same state as in InForm and the discrepancy history will include an "Updated from InForm" entry.
In the Discrepancy page, the data manager looks for discrepancies in the Answered state and closes them. The system sends the update to Closed state to InForm to close the queries there.
Your company's standard operating procedures may require additional or different workflow steps. You can create a set of actions to suit your company's proceduresâwithin the predefined transition rulesâand disable any shipped actions you do not need. If you need more states, create tags to serve as substates and create actions that specify a starting and resulting tag.
To create new actions or edit the predefined ones, you must use public APIs. Information is included in the Oracle Health Sciences Life Sciences Warehouse Application Programming Interface Guide. You can define or modify the following attributes:
Name: The action's name is displayed in the user interface in the Actions drop-down for the user to select. It is required and the combination of Name and Start State must be unique in the database.
For example, you can have two actions with the name XYZ, one with a Start State of Open and the other with a Start State of Candidate, but you cannot have two actions named XYZ with a Start State of Open.
Menu Label: The label is required but is not used by the system. It does not need to be unique.
Start State: Select the state that discrepancies must have for this action to be available to a user. This action will be available to users only for discrepancies that are in this state.
Result State: Select the state that the system should apply to discrepancies when the user applies this action. The result state must be an allowed transition state from the start state; see "Discrepancy States and Allowed Transitions".
Start Tag (Optional): Select the tag that discrepancies must have for this action to be available to a user. You can create new tags in the Administration page; see "Viewing and Creating Discrepancy Tags". Tags can be used as substates, for communication within a state, and as filters in the Discrepancies page.
Result Tag (Optional): Select the tag that the system should apply to discrepancies when the user applies this action, if any.
Routing Operation ID (Optional): If the discrepancy needs to be checked or resolved in the source data system, select the appropriate operation:
Send to InForm: The system sends the discrepancy to InForm immediately and applies a transition restriction of Limited to it.
Send to Spreadsheet: The system creates a .csv file suitable for export to a lab as is or as an Excel spreadsheet.
Enabled: Select this attribute to make this action available for use. Deselect it to prevent the action's use.