Contents
- Overview
- Step 1: create an Active Directory group
- Step 2: create an Active Directory user
- Step 3: create an LDAP connection
- Step 4: create an LDAP repository
- Step 5: create a test policy for LDAP authentication and RBAC
- Step 6: use the LDAP policy to protect management services
- Add an LDAP user with limited access to management services
This topic explains how to use Local Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) to authenticate and perform Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) of management services. You can use the sample Protect Management Interfaces (LDAP) policy instead of the Protect Management Interfaces policy. This means that an LDAP repository is used instead of the local Admin User store for authentication and RBAC of users attempting to access management services. This topic describes how to configure the server to use an example Microsoft Active Directory LDAP repository.
![[Note]](../common_oracle/images/admon/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
|
This topic applies to both API Gateway and API Gateway Analytics. |
To create a new user group in Active Directory, perform the following example steps:
-
Click Start > Administrative Tools > Active Directory Users and Computers.
-
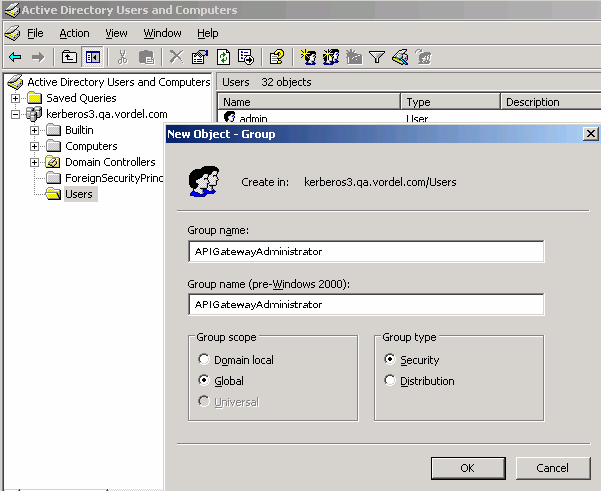
On the Users directory, right-click, and select New > Group.
-
Enter the Group name (for example,
APIGatewayAdministrator).
You should add groups for the following default RBAC roles to give the LDAP users appropriate access to the API Gateway management services:
-
API Gateway Administrator -
API Gateway Operator -
Deployer -
KPS Administrator -
Policy Developer
These RBAC roles are located in the roles section of the following file:
INSTALL_DIR\apigateway\conf\acl.json
 |
You can view the newly created groups using an LDAP Browser.
You will most likely be unable to create an admin user with a password
of changeme because this password is not strong enough to be accepted by
Active Directory. Using Active Directory Users and Computers, perform
the following steps:
-
On the Users directory, right-click, and select New > User.
-
Enter a user name (for example,
admin).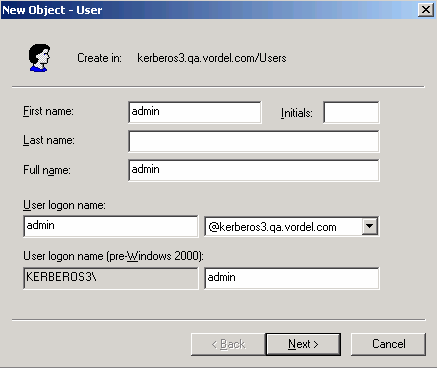
-
Click Next.
-
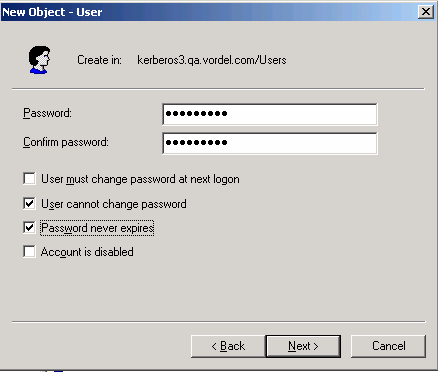
Enter a password (for example,
Oracle123). -
Select User cannot change password and Password never expires.
-
Ensure User must change password at next logon is not selected.
-
Click Next.
-
Click Finish.
Adding the User to the Group
To make the user a member of the group using Active Directory Users and Computers, perform the following steps:
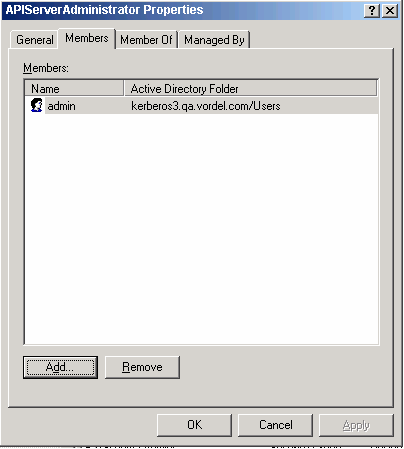
-
Select the APIGatewayAdministrator group, right-click, and select Properties.
-
Click the Members tab.
-
Click Add.
-
Click Advanced.
-
Click Find Now.
-
Select the
adminuser. -
Click OK.
You can view the newly created user using an LDAP Browser.
![[Note]](../common_oracle/images/admon/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
|
The |
To create an new LDAP Connection, perform the following steps:
-
In the Policy Studio, select Open File , and select the Admin Node Manager configuration file (for example,
INSTALL_DIR\apigateway\conf\fed\configs.xml. -
In the Policy Studio tree, select External Connections > LDAP Connections.
-
Right-click, and select Create an LDAP Connection.
-
Complete the fields in the dialog as appropriate. The specified User Name should be an LDAP administrator that has access to search the full directory for users. For example:
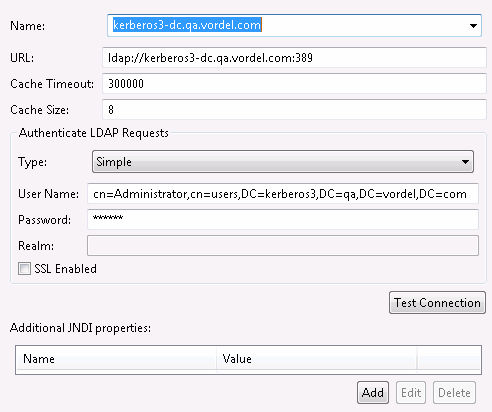
-
Click Test Connection to ensure the connection details are correct.
To create an new LDAP Repository, perform the following steps:
-
In the Policy Studio tree, select External Connections > Authentication Repository Profiles > LDAP Repositories.
-
Right-click, and select Add a new Repository.
-
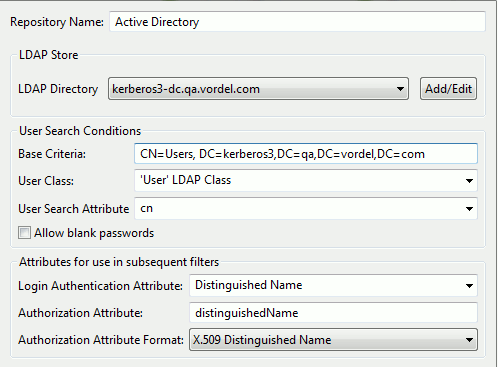
Complete the following fields in the dialog:
Repository Name Enter an appropriate name for the repository. LDAP Directory Use the LDAP directory created in the section called “Step 3: create an LDAP connection”. Base Criteria Enter the LDAP node that contains the users. User Search Attribute Enter cn. This is the username entered at login time (in this case,admin).Authorization Attribute Enter distinguishedName. This is the username entered at login time (admin). Theauthentication.subject.idmessage attribute is set to the value of this LDAP attribute (see example below). Theauthentication.subject.idis used as the base criteria in the filter that loads the LDAP groups (the user’s roles). This enables you to narrow the search to a particular user node in the LDAP tree. For more details, see the Retrieve Attributes from Directory Server filter in the section called “Step 5: create a test policy for LDAP authentication and RBAC”.
An example value of the authentication.subject.id message attribute is
as follows:
CN=admin, CN=Users,DC=kerberos3,DC=qa,DC=vordel,DC=com
Connect to other LDAP repositories
This topic uses Microsoft Active Directory as an example LDAP repository. Other LDAP repositories such as Oracle Directory Server (formerly iPlanet and Sun Directory Server) and OpenLDAP are also supported. For an example of querying an Oracle Directory Server repository, see the Retrieve Attributes from Directory Server filter in the section called “Step 5: create a test policy for LDAP authentication and RBAC”. For details on using OpenLDAP, see OpenLDAP for authentication and RBAC of management services.
To avoid locking yourself out of the Policy Studio, you can create a test policy for LDAP authentication and RBAC, which is invoked when a test URI is called on the server (and not a management services URI). For an example policy, select Policies > Management Services > Sample LDAP Policies > Protect Management Interfaces (LDAP) when the Admin Node Manager configuration is loaded.
Create the test policy
Perform the following steps:
-
Select Open File and load the Admin Node Manager configuration file in the Policy Studio. For example:
INSTALL_DIR/apigateway/conf/fed/configs.xml
-
Right-click the Policies node in the tree view of the Policy Studio, and select Add Policy.
-
Enter a suitable name (for example
Test Policy) for the new policy in the Name field, and click OK. -
Click the new policy in the tree to start configuring the policy filters. You can configure the policy by dragging the required filters from the filter palette on the right, and dropping them on to the policy canvas.
For more details on creating policies, see the API Gateway User Guide.
Configure the test policy
Configure the test policy with the following filters:
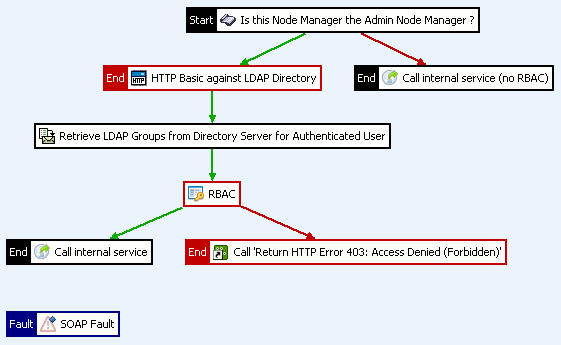
Scripting Language filter
This includes the following settings:
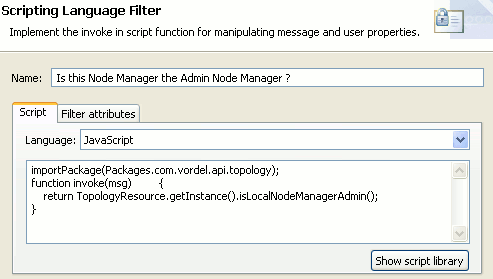
The Scripting Language filter performs the following tasks:
-
Returns true if the Node Manager is the Admin Node Manager and passes control to the HTTP Basic Authentication filter.
-
Otherwise, calls the Call Internal Service (no RBAC) filter without adding the
authentication.subject.roleandauthentication.subject.idHTTP headers.
Call Internal Service (no RBAC) filter
This filter is called without adding any HTTP headers as follows:
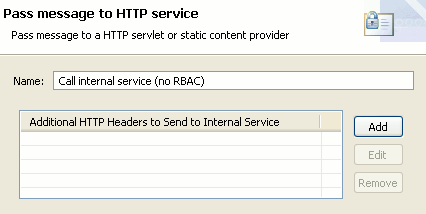
HTTP Basic Authentication filter
This filter uses the LDAP repository configured in the section called “Step 4: create an LDAP repository”, and includes the following settings:
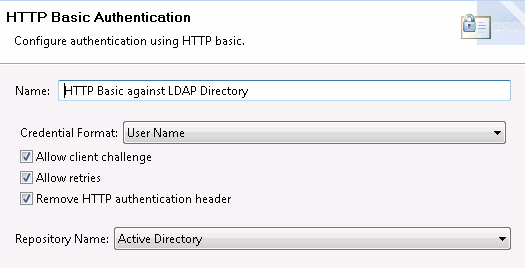
The HTTP Basic Authentication filter performs the following tasks:
-
Connects to the LDAP directory using the connection details specified in the LDAP directory.
-
Finds the user using the specified base criteria and search filter.
-
If the user is found, verifies the user's name and password against the LDAP repository by performing a bind.
-
If authentication fails, always throws a 401. This allows retry for browser users.
-
The
distinguishedName(DName) is held in theauthentication.subject.idmessage attribute. This is specified by the Authorization Attribute field in the LDAP repository configuration. -
The user’s roles (LDAP groups) are not available yet.
Retrieve Attributes from Directory Server filter
On the Database tab, this filter uses the LDAP directory configured in the section called “Step 3: create an LDAP connection”, and includes the following settings:
-
Base Criteria:
${authentication.subject.id} -
Search Filter:
(objectclass=User) -
Attribute Name:
memberOf
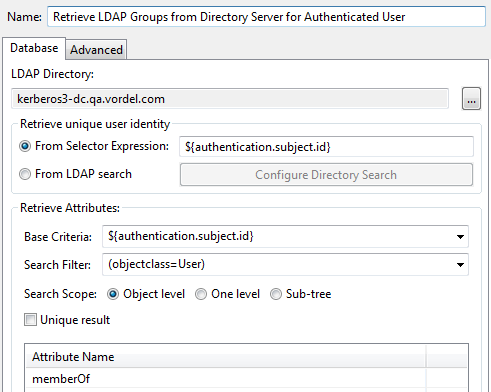
![[Note]](../common_oracle/images/admon/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
|
On the Advanced tab, you must ensure that the Enable legacy attribute naming for retrieved attributes setting is selected. |
The Retrieve Attributes from Directory Server filter performs the following tasks:
-
Using the user’s DName as the search start point, find the user’s
memberOfattribute, and load the LDAP groups for the user. -
If the user is in one group, the group name is contained in the
user.memberOfmessage attribute. -
If the user is in multiple (n) LDAP groups, the group names are held in
user.memberOf.1...user.memberOf.nmessage attributes.
Alternatively, the following screen shows an example of querying an Oracle Directory Server repository. The following Search Filter setting returns the authenticated user’s groups instead of the user object:
(&(objectclass=groupOfUniqueNames)(uniqueMember=${authentication.subject.id}))

You should be able to query any LDAP directory in this way. Assuming that the user’s groups or roles can be retrieved as attributes of an object, the query does not need to be for the user object.
Management Services RBAC filter
This filter includes a the following setting:
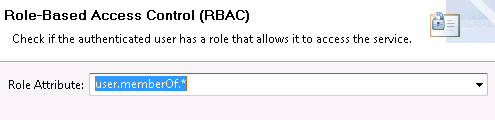
The Management Services RBAC filter performs the following tasks:
-
Reads the roles from the
user.memberOf.*message attribute. It understands the meaning of the wildcard, and loads the roles as required. It creates a string version of the roles, and places it in theauthentication.subject.rolemessage attribute for consumption by the Call Internal Service filter, which receives the roles as an HTTP header value. -
Determines which Management Service URI is currently being invoked.
-
Returns true if one of the roles has access to the Management Service currently being invoked, as defined in the
acl.json file. -
Otherwise, returns false and the Return HTTP Error 403: Access Denied (Forbidden) policy is called. This message content of this filter is shown when a valid user has logged into the browser, but their role(s) does not give them access to the URI they have invoked. For example, this occurs if a new user is created and they have not yet been assigned any roles.
Test the policy configuration
To test this policy configuration, perform the following steps:
-
Update the
acl.jsonfile with the new LDAP group as follows:"CN=APIGatewayAdministrator,CN=Users,DC=kerberos3,DC=qa,DC=vordel,DC=com" : [ "emc", "mgmt", "mgmt_modify", "dashboard", "dashboard_modify", "deploy" "config", "monitoring", "events", "traffic_monitor", "settings", settings_modify", "logs" ]
-
Update the
adminUsers.jsonfile with the new role as follows:{ "name" : "CN=APIGatewayAdministrator,CN=Users,DC=kerberos3,DC=qa,DC=vordel,DC=com", "id" : "role-8" }And increase the number of roles, for example:
"uniqueIdCounters" : { "Role" : 9, "User" : 2 }, -
In the Policy Studio tree, select Listeners > Node Manager > Add HTTP Services, and enter a service name (for example,
LDAP Test). -
Right-click the HTTP service, and select Add Interface > HTTP.
-
Enter an available port to test the created policy (for example,
8888), and click OK. -
Right-click the HTTP service, and select Add Relative Path.
-
Enter a relative path (for example,
/test). -
Set the Path Specify Policy to the Protect Management Interfaces (LDAP) policy, and click OK.
-
Close the connection to the Admin Node Manager file, and restart the Admin Node Manager so it loads the updated configuration.
-
Use API Gateway Explorer to call
http://localhost:8080/test. -
Enter the HTTP Basic credentials (for example, username
adminand passwordOracle123). If authentication is passed, the Admin Node Manager should return an HTTP 404 code (not found).
![[Important]](../common_oracle/images/admon/important.png) |
Important |
|---|---|
|
Do not use the Admin Users tab in the API Gateway Manager to manage user roles because these are managed in LDAP. |
If the authentication and RBAC filters pass, you can now use this policy to protect the management interfaces. To ensure that you do not lock yourself out of the server, perform the following steps:
-
Make a copy of the
conf/feddirectory contents from the server installation, and put it into a directory accessible from the Policy Studio. -
Make another backup copy of the
conf/feddirectory, which will remain unmodified. -
In the Policy Studio, select File > Open, and browse to
configs.xmlin the first copy of thefeddirectory. -
Under the Listeners > Management Services node, select the
/and the/configuration/deploymentsrelative paths, and set the Path Specify Policy to the Protect Management Interfaces (LDAP) policy. -
Remove the previously created
LDAP TestHTTP Services. -
Close the connection to the file.
-
Copy the
feddirectory back to the Admin Node Manager’sconfdirectory. -
Reboot the Admin Node Manager.
-
Start the Policy Studio, and connect to the Admin Node Manager using
adminand passwordOracle123(the LDAP user credentials). You should now be able to edit API Gateway configurations as usual.
You can add an LDAP user with limited access to management services. For example,
assume there is already a user named Fred defined in Active Directory.
Fred has the following DName:
CN=Fred,CN=Users,DC=kerberos3,DC=qa,DC=vordel,DC=com
Fred belongs to an existing LDAP group called TraceAnalyzers.
He can also belong to other LDAP groups that have no meaning for RBAC in the API Gateway.
The TraceAnalyzers LDAP group has the following DName:
CN=TraceAnalyzers,CN=Users,DC=kerberos3,DC=qa,DC=vordel,DC=com
The user Fred should be able to read server trace files in a browser.
No other access to management services should be given to Fred.
Adding Limited Access Rights
You must perform the following steps to allow Fred to view the trace
files:
-
Add the following entry in the
rolessection in theacl.jsonfile:"CN=TraceAnalyzers,CN=Users,DC=kerberos3,DC=qa,DC=vordel,DC=com" : [ "emc", "mgmt", "logs" ]
-
Update the
adminUsers.jsonfile with the new role as follows:{ "name" : "CN=TraceAnalyzers,CN=Users,DC=kerberos3,DC=qa,DC=vordel,DC=com", "id" : "role-8" }]And increase the number of roles, for example:
"uniqueIdCounters" : { "Role" : 9, "User" : 2 }, -
Restart the Admin Node Manager so that the
acl.jsonandadminUsers.jsonfile updates are picked up. -
Enter the following URL in your browser:
http://localhost:8090/ -
Enter user credentials for
Fredwhen prompted in the browser. -
The API Gateway Manager displays a Logs tab enabling access to the trace files that
Fredcan view.
![[Note]](../common_oracle/images/admon/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
|
|