The derivation of a user identity address from the ingress Diameter Request message is governed by the rules determined by User Identity Full Address Resolution configuration. The configuration defines the supported Application IDs, the supported Command Codes associated with each Application ID, the preferred User Identity Types to search, and the associated AVPs that contain the User Identity addresses.
The FABR application processes the Diameter Request message based on the configuration, to extract the User Identity addresses.
- First determine whether the Application ID in the message header is defined in the configuration.
- If a valid (configured) Application ID is received in a Diameter Request message, validate whether the pair (Application ID, Command Code) received in the message is defined in the configuration.
- If the pair is configured, select the highest priority User Identity type associated with the pair in the configuration, for User Identity address searching.
- Search for a valid User Identity address from an AVP in the ingress message, based on a prioritized set of AVPs assigned to the triplet (Application ID, Command Code, Routing Entity Type).
If a User Identity address cannot be found in searching the configured User Identity types and AVPs, the "No Valid Routing Entity Address" Routing Exception Handling procedure is invoked.
Routing Exception Handling
When an ingress FABR Request message cannot be resolved to a Destination (no address matched, no valid digits decoded, or any other error is returned), FABR will invoke a Routing Exception Handling procedure based on user-defined configuration.
Routing Exception Handling procedures will result in one of the following configured actions:
- Forward the message unchanged
- Forward the message using a user-defined default Destination
- Send an Answer response with a user-defined Result-Code AVP value
- Send an Answer response with user-defined Experimental-Code AVP values
- Abandon Request
The following types of Routing Exceptions will be supported:
- Unknown Command Code
- No valid Routing Entity addresses were found
- A valid Routing Entity address did not resolve to a configured address
- Blacklisted Subscriber
- DP congestion
- DP errors
Supported AVPs
FABR supports the AVPs associated with the User Identity Types as defined in Table 1.
| AVPs | AVP Code | AVP Type | AVP Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
|
User-Identity:
|
700 |
Grouped |
Section 6.3.1 of 3GPP 29.329 |
|
701 |
OctetString |
Section 6.3.2 of 3GPP 29.329 |
|
601 |
UTF8String |
Section 6.3.2 of 3GPP 29.229 |
|
Service-Information
|
873 |
Grouped |
Section 7.2.192 of 3GPP 32.299 |
|
Subscription-Id
|
443 |
Grouped |
Section 8.46 of RFC 4006 |
|
450 |
Enumerated |
Section 8.47 of RFC 4006 |
|
444 |
UTF8String |
Section 8.47 of RFC 4006 |
|
User-Name |
1 |
UTF8String |
Section 8.14 of RFC 3588bis |
|
Wildcarded-Public-Identity |
634 |
UTF8String |
Section 6.3.35 of 3GPP 29.229 |
|
MSISDN |
701 |
OctetString |
Section 6.3.2 of 3GPP 29.329 |
|
Public Identity |
601 |
UTF8String |
Section 6.3.2 of 3GPP 29.229 |
Each of the configured User Identity types supported in FABR is associated with certain AVPs that contain the User Identity type as defined by various Diameter application standards. Table 2 presents all possible combinations of the User Identity types and the associated AVPs.
| User Identity Types |
IMSI |
MSISDN |
IMPI |
IMPU |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVPs | ||||
|
MSISDN |
Applicable |
Applicable |
||
|
User-Identity: MSISDN |
Applicable |
Applicable |
||
|
Public-Identity |
Applicable |
Applicable |
Applicable |
Applicable |
|
User-Identity: Public-Identity |
Applicable |
Applicable |
Applicable |
Applicable |
|
User-Name |
Applicable |
Applicable |
||
|
Subscription-ID-Data (0-E.164) |
Applicable |
Applicable |
||
|
Service-Information: Subscription-ID-Data (0-E.164) |
Applicable |
Applicable |
||
|
Subscription-ID-Data (1-IMSI) |
Applicable |
Applicable |
||
|
Service-Information: Subscription-ID-Data (1-IMSI) |
Applicable |
Applicable |
||
|
Subscription-ID-Data (2-SIP URI) |
Applicable |
Applicable |
Applicable |
Applicable |
|
Service-Information: Subscription-ID-Data (2-SIP URI) |
Applicable |
Applicable |
Applicable |
Applicable |
|
Subscription-ID-Data (3-NAI) |
Applicable |
Applicable |
Applicable |
Applicable |
|
Service -Information: Subscription-ID-Data (3-NAI) |
Applicable |
Applicable |
Applicable |
Applicable |
|
Wildcarded-Public-Identity |
Applicable |
A User Identity type can be associated with one or more data formats that will be examined when deriving the user identity address from the associated AVPs. The relation between User Identity types and the corresponding data formats to be encountered in the ingress Diameter request message are listed in Table 3.
| Configurable User Identity Types |
IMSI |
MSISDN |
IMPI |
IMPU |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| User Identity Formats in Messages | ||||
|
IMSI Format: ASCII Example: 311480123456789 |
Applicable |
Applicable |
||
|
MSISDN Format: ASCII and TBCD Example: 19194605500 |
Applicable |
Applicable |
||
|
SIP URI with IMSI Format: ASCII |
Applicable |
Applicable |
||
Examples: sip:123456789012345@nai.epc.mnc456.mcc123.3gppnetwork.org sip:6311150999995555@ims.mnc015.mcc311.3gppnetwork.org sip:311480999995555@my.network.org sip: 6311480999995555@my.network.org |
||||
|
SIP URI with MSISDN Format: ASCII Examples: sip:+1-919-460-5500@xyz.com;user=phone sip:311480999995555@my.network.org |
Applicable |
Applicable |
||
|
SIP URI with NAI Format: ASCII Example: sip:handy.manny@xyz.com |
Applicable |
Applicable |
||
|
SIP URI with Wildcarded PSI Format: ASCII Example: sip:WP-A_ServiceType-!.*!@att.com |
Applicable |
|||
|
TEL URI with MSISDN FORMAT: ASCII |
Applicable |
Applicable |
||
Examples: tel:+1-919-460-5500;phone-context=example.com tel:+19258889999 tel:19195551212 |
||||
|
NAI with IMSI/MSISDN Format: ASCII |
Applicable |
Applicable |
Applicable |
Applicable |
Examples: 123456789012345@xyz.com 123456789012345 311480999995555@ims.mnc480.mcc311.3gppnetwork.org 6311150999995555@xyz.com 6311150999995555@ims.mnc015.mcc311.3gppnetwork.org |
||||
|
NAI Format: ASCII Example: handy.manny@xyz.com |
Applicable |
Applicable |
||
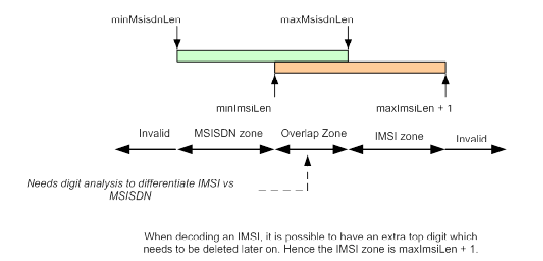
Identifying IMSIs and MSISDNs
In certain Diameter messages over the Cx interface (and possibly over the Sh interface), certain AVPs that typically carry an IMSI sometimes can carry an MSISDN.
Address resolution applications like Full Address Based Resolution (FABR) and Range Based Address Resolution (RBAR) need to categorize User Identities (digit strings) decoded from the Diameter Request AVPs as either MSISDN or IMSI, to allow looking up the User Identity in the appropriate lookup table.
- The configured Routing Entity Type
- The contents of the AVP
For instance, if the User Identity has been decoded from a SIP URI that has a "+" sign before the digits (such as sig:+1-919-460-5500@oracle.com), it can be directly categorized as an MSISDN.
- The number of digits in the User Identity
In certain cases, none of these methods allow a clear categorization (for example, if the number of digits needs to be used and the received number of digits are applicable to both IMSIs and MSISDNs, and thus leads to an ambiguous determination; or if there is no ""+" sign before the digits).
if FABR has been configured to decode an IMPU from a User Identity (digit string) but cannot determine whether the user identity is an IMSI or an MSISDN based on digit analysis, a tie-breaker is needed to properly categorize the User Identity.
- FABR extracts the first 5 or 6 digits of the User Identity and compares them against a list of configured 5- or 6-digit MCC-MNC combinations.
The Diameter Common > Network Identifiers > MCCMNC GUI pages can be used to configure up to 2500 distinct combinations of Mobile Country Code (MCC) and Mobile Network Code (MNC). (Refer to the "MCCMNC Configuration" section of the Diameter Common User's Guide and Help for procedures to configure MCC-MNC combinations.)
- If a match occurs, the User Identity is considered as an IMSI and used for IMSI lookup.
- If a match does not occur, the User Identity is considered as a MSISDN and used for MSISDN lookup.