4 Process Integration for Product
This chapter provides an overview of the process integration for product and discusses business process flows, assumptions and constraints, Siebel Customer Relationship Management (Siebel CRM) and Oracle Transportation Management (OTM) interfaces, core Oracle Application Integration Architecture (Oracle AIA) components, and integration services.
This chapter includes the following sections:
4.1 Overview
In the Oracle Order Management for OTM, oracle E-Business Suite (Oracle EBS), Siebel CRM prebuilt integration there are four different types of products:
-
Commodity
-
Transportation
-
Accessorial
-
Special Services
Whenever a product is created or updated in Siebel CRM, a synchronization flow is initiated to route these to the oracle AIA layer. However, Oracle AIA routes only the product type of commodity to OTM.
For every commodity type product from Siebel CRM, these objects are created, updated, or both in OTM:
-
Item
-
Commodity
-
Packaged Item
One-to-one mapping should exist among the item, commodity, and packaged item in OTM.
-
The transportation order in Siebel CRM has certain order lines that have product of type commodity associated to them.
-
In OTM application, the order release has release lines and ship units associated to it.
-
In the release line, the packaged item is associated to it, whereas in the release ship unit, a commodity is associated.
-
Additionally in OTM, the packaged item is referred to in the ship unit in the sell shipment.
The process integration for product supports these integration flows:
-
Creating product
-
Updating product
4.2 Business Process Flows
Figure 4-1 shows the product process integration:
Figure 4-1 Product Process Integration Flow
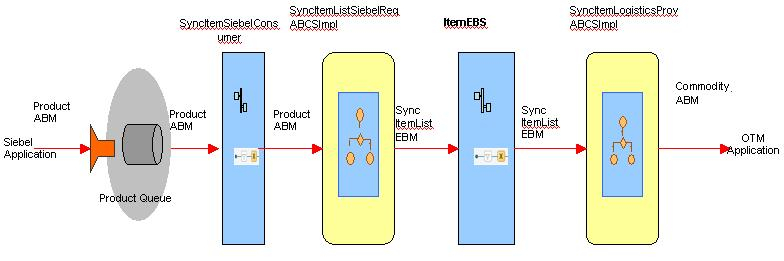
Description of "Figure 4-1 Product Process Integration Flow"
Whenever a product is created, updated, or both in Siebel CRM, Siebel CRM sends a message in their schema in a queue. Oracle AIA receives the message and converts it to the EBM format, and then converts the EBO into appropriate OTM format and finally sends it to OTM.
One-to-one mapping should exist among the item, commodity, and packaged item in OTM.
4.2.1 Synchronizing Product Information
When a product of type commodity is created or updated in Siebel CRM, the updated record must be synchronized to OTM.
Figure 4-2 shows the synchronization of a product details from Siebel CRM to OTM:
Figure 4-2 Synchronizing Product Information from Siebel to OTM Sequence Diagram
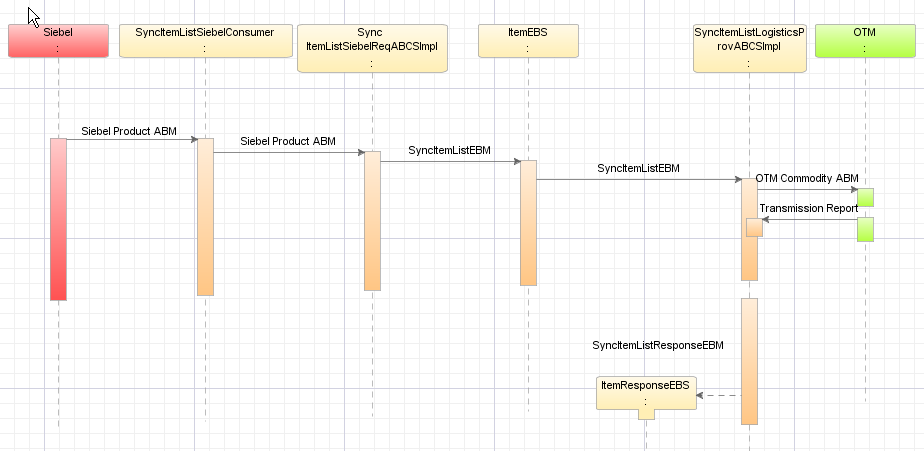
Description of "Figure 4-2 Synchronizing Product Information from Siebel to OTM Sequence Diagram"
4.2.1.1 Product Synchronization
The synchronization flow is described here:
-
Whenever a product is created or updated, Siebel publishes a product application business message (ABM).
-
The Siebel requester ABCS receives this message, transforms the ABM to enterprise business message (EBM), updates the Siebel, and invokes the ItemEBS service.
-
The ItemEBS service routs this message to Oracle Transportation Management (OTM) Provider ABCS.
-
OTM Provider ABCS receives this enterprise business message (EBM), checks if the product type is commodity. If so, it transforms to OTM commodity ABM and invokes the OTM web service. It then waits for the transmission report from OTM.
-
After the transmission report is received, the OTM provider ABCS checks the status. If status is OK, it updates the OTM column in the ITEM_ITEMID cross-reference with the commodity GID.
4.3 Assumptions and Constraints
These are the solution assumptions and constraints:
-
This synchronization does not support initial loading of existing data of products.
-
No delete transactions exist for product records.
-
This integration synchronizes only products of type commodity to the OTM application.
-
If any error occurs in the service layer, AIA error handling framework is invoked. You should manually resubmit that transmission at various places that failed for reprocessing.
-
This integration does not validate and raise errors due to any business validation failure in OTM. It assumes such validations happen in OTM system.
-
This integration supports only synchronization of products whenever a product is created or updated.
-
OTM domain value is derived from business unit mapping. If you want to use your own logic for domain, you must use the extensible transformation template.
-
The provider side cross-references are populated based on the identifiers passed from main transformation to OTM. If you want to pass a different value in the OTM identifier, use the extensibility of the transformation to update the cross-reference.
4.4 Siebel CRM Interfaces
Use the Siebel CRM product schema for this integration.
4.5 OTM Interfaces
OTM provides an interface through a web service to connect to its application. This connectivity is established as a partner link in the provider service. The logistics web service immediately returns an acknowledgment with a transmission number. After processing is complete, it then sends a transmission report back indicating success or failure.
4.6 Core Oracle AIA Components
The integration flow uses these components:
-
Item EBO
-
Item EBM
The core enterprise business object (EBO) and enterprise business message (EBM) XSD files can be located by EBO within the $AIA_HOME/AIAMetaData/AIAComponents/EnterpriseObjectLibrary/Core/EBO/ parent folder.
The core enterprise business services (EBS) web services definition language (WSDL) files can be located by EBO within the $AIA_HOME/AIAMetaData/AIAComponents/EnterpriseBusinessServiceLibrary/Core/EBO/ parent folder.
For detailed documentation of individual EBOs and EBMs, click AIA Reference Doc link on EBO and EBM detail pages in the Oracle Enterprise Repository.
For more information about using the Oracle Enterprise Repository and configuring it to provide the AIA Reference Doc link, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Integration Architecture Foundation Pack, "Configuring and Using Oracle Enterprise Repository as the Oracle AIA SOA Repository."
EBOs can be extended, for instance, to add new data elements. These extensions are protected, and remain intact after a patch or an upgrade.
For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Integration Architecture Foundation Pack, "Extensibility for AIA Artifacts".
4.7 Integration Services
These are the services delivered with this integration:
-
Siebel Product Queue
-
SyncItemSiebelConsumer
-
SyncItemListSiebelReqABCSImpl
-
ItemEBS
-
SyncItemListLogisticsProvABCSImpl
4.7.1 Siebel Product Queue
Siebel Product Queue is used to queue Siebel product messages. This queue can reside on any Oracle database. For this integration, the AIA database is used as the place for this queue.
4.7.2 SyncItemSiebelConsumer
This service is invoked the moment Oracle Transportation Management (OTM) enqueues a message into AIA_SiebelItemJMSQueueV1 queue. This service routes and invokes the SyncItemListSiebelReqABCSImpl process.
4.7.3 SyncItemListSiebelReqABCSImpl
The SyncItemListSiebelReqABCSImpl is a BPEL process. This process receives the Siebel Product application business message (ABM) as input from Siebel system, transforms it to the SyncItemListEBM message, and invokes the ItemEBS service. In this transformation, in addition to mapping, the enterprise business message (EBM) Header and the cross-reference tables are populated.
4.7.5 SyncItemListLogisticsProvABCSImpl
SyncItemListLogisticsProvABCSImpl is a BPEL Process. This process receives the SyncItemListEBM as input from the ItemEBS, transforms the input into the LogisticsWebServiceABM and invokes the LogisticsWebService. When logistics sends the transmission report and the status in the transmission report is success, it updates the cross-reference tables with OTM IDs.