The Oracle MaxRep Replication Engine can be configured with Fibre Channel (FC) interfaces to Oracle FS Systems. The following describes configuring FC interfaces.
Before you can create and use protection plans, you must configure the FC ports in the Replication Engine. Configuring the ports is a simple operation, however the following information is useful to understand when there are configuration issues. Upon installation, all four FC ports are configured as initiator ports. For replication, the Replication Engine requires initiator FC ports for source and target LUNs, and target FC ports.
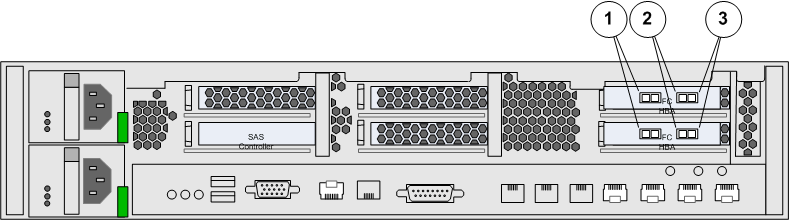
Replication Engines that are configured for FC connectivity, contain two FC HBAs with two FC ports, for a total of four FC ports.
To provide expanded LUN access support and reduce the number of physical ports required by each Replication Engine, Oracle MaxRep for SAN uses Node Port (or N_Port) ID Virtualization (NPIV) to create virtual initiators across two of the FC ports on the installed HBAs.
The Replication Engines are further divided into three types of host bus adapter (HBA) ports.
- Initiator Ports (AIS)
The default configuration for a port on a Replication Engine is an appliance initiator port for source LUN access (AIS). An initiator port communicates only with zoned target ports within the SAN fabric. After proper configuration, the Replication Engine has four virtualized NPIV ports that are available as AIS ports. Zone the AIS ports to all of the Controller ports on the Oracle FS Systems that are registered to the Replication Engine.
Initiator ports are used for the following communications:During resynchronization Step 1 or Step 2 of an initial synchronization, the AIS port is used for read-only access to a source LUN.
During Step 1 or Step 2 of a resynchronization, the AIS port is used for read-only access to a source LUN.
In the differential synchronization mode, if the used cache for a protection plan exceeds the Differential File Threshold setting for the protection plan, the AIS port is used for read-only access to a source LUN.
The AIS port is used to read data from a target LUN during a data recovery.
- Initiator for Target LUN Mapping Ports (AIT)
The appliance initiator port for target LUN access (AIT) communicates only with zoned target ports within the SAN fabric. Zone the AIT port to all Controller ports on the Oracle FS Systems that are registered to the Replication Engine. After proper configuration, the Replication Engine has four virtualized NPIV ports that are available as AIT ports.
Initiator for target ports is used for the following types of communications:Write access to a target LUN during all phases of initial synchronization, resynchronization, and differential synchronization mode.
Read-write access to the home, back up and retention LUNs on the Oracle FS System.
Write operations to a source LUN during a data recovery.
- Target Ports (AT)
- An appliance target (AT) port communicates only with zoned initiator ports within the SAN fabric. After proper configuration, the Replication Engine has two physical ports that are available as AT ports. The zoned initiator ports include the following:
All Controller ports from the Oracle FS Systems that are registered to the Replication Engine.
Any hosts that mount virtual snapshots that are exported from the Replication Engine.
Target ports are used for the following types of communications:During the differential synchronization mode, the AT port accepts writes to a source LUN by way of the splitter driver on the Controller of the primary Oracle FS System.
After a virtual snapshot is exported to a host, the host accesses the virtual snapshot through the AT port.
NPIV provides multiple virtual ports form a single physical FC port. NPIV does not create virtual ports across multiple physical ports. On each HBA, port 1 is used as the physical ports for four virtualized AIS and four virtualized AIT ports. All 16 total (8 AIS and 8 AIT) virtualized NPIV ports are configured on these two physical ports. The Replication Engine uses port 2 on each HBA as a dedicated AT port.
For more information on zoning and SAN fabric management, refer to the SAN switch user manuals for your SAN fabric.