56 Set Up Disposal Account Rules
This chapter contains these topics:
Disposal account rules specify the accounts the disposal program uses for disposal journal entries. You set up the disposal account rules to direct the disposal journal entries to the appropriate offsetting account.
The disposal account rules make use of the balance character code to determine the nature of the journal entry. You can create separate rules for net book value disposal accounts, disposal cash clearing accounts, and disposal proceeds accounts. In addition, you can specify override accounts for the cost and accumulated depreciation accounts. This allows you to retain the amounts in the Item Balances table (F1202) and place these amounts in a reserve account.
56.1 Setting Up Disposal Account Rules
From Fixed Assets (G12), enter 29
From Fixed Asset System Setup (G1241), choose Disposal Account Rules
You can set up company-specific rules or use the default company 00000 to set up the rules for all companies at one time. You can also specify different accounts by disposal method and ledger type.
|
Caution: You must set up at least a set of rules for company 00000 and ledger type AA. It is recommended that you set up separate accounts for net book value, cash clearing, and proceeds. |
To set up disposal account rules
On Disposal Account Rules
Figure 56-1 Disposal Account Rules screen
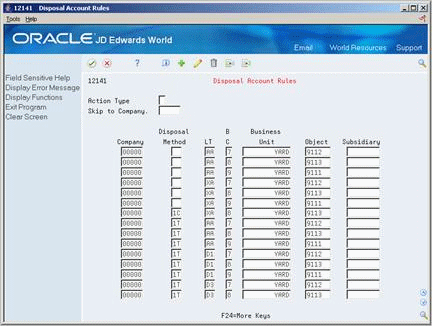
Description of "Figure 56-1 Disposal Account Rules screen"
56.2 Balance Character Code
The Balance Character Code is a numeric one-character field (CHCD) in the Asset Account Balances table (F1202) and is used to identify the type of record, based on the values below. Every F1202 record should be stamped with a CHCD value from 1 - 9, with one exception: not all expense accounts will have a balance character code. To enhance performance, programs in the Fixed Asset module use the balance character code to quickly determine which records represent cost, accumulated depreciation and depreciation expense. The balance character code can be updated using the Balance Character Code Update (P12920 on menu G1232). It updates the Balance Character Codes in the F1202 based on the AAI ranges in Fixed Assets system.
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Company Number | A code that identifies the company that owns or is assigned to an asset or group of assets. You set up companies in the system to represent a reporting level that has a complete balance sheet and any intercompany transactions with other companies. You can define a specific organization, entity, partnership, and so on, as a company. You use Company Numbers and Names to define the companies in your system.
Note: Use Company 00000 only for default values, such as dates and Automatic Accounting Instructions (AAIs). You cannot use Company 00000 when entering transactions. |
| Balance Character Code | A code that indicates in which range of accounts the account in the Item Balance falls. Valid values are:
A – Revaluation Cost Asset B – Revaluation Accumulated Depreciation C – Revaluation Secondary A/D 1 – Cost 2 – Accumulated Depreciation 3 – Secondary Accumulated Depreciation 4 – Depreciation Expense 5 – Depreciation Expense - Secondary 6 – Depreciation Expense - Tertiary 7 – Net Book Value - Disposal 8 – Disposal Clearing 9 – Disposal Proceeds Blank – Miscellaneous Expense (any expense which is defined above) |
| Object Account | The object account portion of a general ledger account. The term "object account" refers to the breakdown of the Cost Code (for example, labor, materials, and equipment) into subcategories (for example, dividing labor into regular time, premium time, and burden). If you are using a flexible chart of accounts and the object is set to 6 digits, it is recommended that you use all 6 digits. For example, entering 000456 is not the same as entering 456, because the system enters three blank spaces to fill a 6-digit object. |
| Equipment Status | A user defined code (12/ES) that identifies the equipment or disposal status of an asset, such as available, down, or disposed. |
| Ledger Type | The user defined ledger type code (list 09, type LT) that identifies the account ledger, or book, for the asset. You can maintain as many sets of depreciation books (ledger types) for an asset as you need so you can depreciate an asset in different ways for different purposes. For example, an asset might have a three-year life for tax purposes, but a five-year life for financial statement purposes. Each set of books can have different depreciation methods and depreciation values. |
| Business Unit | The accounting entity (business unit) that is responsible for the asset's cost or expense. You assign a business unit to an asset. The responsible business unit is used for responsibility reporting purposes.
Note: You can enter numbers and characters in this field. The system right-justifies them (for example, CO123 appears as _ _ _ CO123). You cannot inquire on business units for which you have no authority. |
| Subsidiary | A subdivision of an object account. Subsidiary accounts include more detailed records of the accounting activity for an object account. |