51 Overview to Bank Statement Processing
This chapter contains these topics:
51.1 Objectives
-
To understand the sequence of tasks when processing a bank statement
-
To identify the various transaction types on a bank statement
-
To create journal entries from a bank statement
-
To post cash receipts from a bank statement
-
To review and post the bank statement
-
To reconcile the transactions on a bank statement
51.2 About Bank Statement Processing
Banking practices in some countries rely heavily on magnetic media processing, electronic fund transfers, and direct bank involvement in settling outstanding debts. For these countries, the bank statement serves as the source document for all banking activity.
Bank statement processing consists of:
-
Understanding transaction codes
-
Working with bank statements
-
Updating the reconciliation table
-
Reconciling bank statements
-
Posting bank statement transactions
-
Reconciling bank statements manually
-
Printing bank statement reports
The system accepts and clears transactions in the following tables:
-
Accounts Receivable Ledger (F0311)
-
Account Ledger (F0911)
-
Account Ledger for Reconciliation worktable (F0911R)
The system also uses the following tables for bank statement information:
-
Bank Statement Header (F0916)
-
Bank Statement Detail (F0917)
The following illustrates how to process your bank statements.
Figure 51-1 How To Process Your Bank Statements
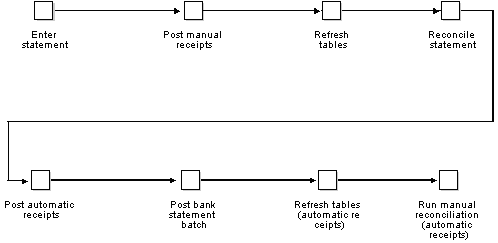
Description of "Figure 51-1 How To Process Your Bank Statements"
| Step | Overview |
|---|---|
| Enter statement | Enter the transactions that appear on your bank statement. |
| Post manual receipts | Post manual receipts if you enter a cash receipt (for example, if a customer makes a payment directly to your bank account). |
| Refresh tables | Update the Account Ledger for Reconciliation worktable (F0911R) by refreshing the reconciliation table. |
| Reconcile statement | Reconcile the transactions to update tables, create accounting batches, and generate reconciliation reports. |
| Post automatic receipts | Post automatic receipts in batch mode if you enter a cash receipt (for example, if a customer makes a payment directly to your bank account). |
| Post bank statement batch | Post general journal batches to update the bank statement batch to the Account Ledger (F0911) and Account Balances (F0902) tables. |
| Refresh and reconcile | Refresh the reconciliation table and manually reconcile if you have entered automatic receipts and you are not using a transit account. |
51.2.1 Bank Statement Processing Using Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
You can process bank statement information using Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) media. Electronic Data Interchange is the computer-to-computer exchange of transactions into a standard format that can be processed. You can receive information regarding specific bank accounts through EDI and reconcile the bank statements stored on JD Edwards World software. To set up your system to receive bank statement information using EDI, see the JD Edwards World Electronic Commerce Guide.