7 Overview to Resource Requirements Planning
This chapter contains these topics:
7.1 Objectives
-
To create a profile of a work center's load that the system uses to validate a forecast
-
To determine available capacity
-
To determine long-range requirements for a work center
-
To review the actual and planned load on work centers, either together (as a dispatch group) or individually
-
To understand the different ways you can view actual and planned load information
-
To set up Resource Requirements Planning (RRP)
7.2 About Resource Requirements Planning
Figure 7-1 Elements of Resource Requirements Planning
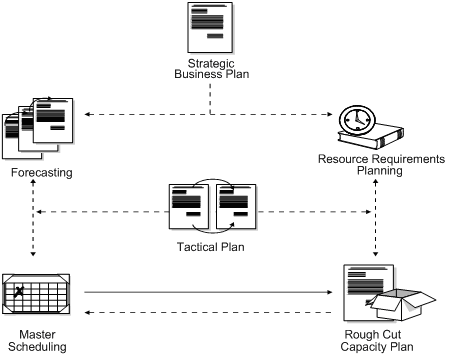
Description of ''Figure 7-1 Elements of Resource Requirements Planning''
You generate a resource requirements plan after you generate your long-term forecast, but before you run the Master Scheduling program. Resource Requirements Planning uses data from a forecast of future sales to estimate the time and resources that are required to make a product.
RRP can help you resolve long-range planning issues, such as:
-
Expanding existing facilities
-
Acquiring new facilities
-
Staffing loads
-
Determining capital expenditures for equipment
RRP enables you to support your company's strategic business plan with a realistic tactical plan that:
-
Is shorter in range than the strategic plan and has a planning horizon of 12 months to 3 years
-
Allows planning at the product family level and is in greater detail than the strategic plan
-
Validates the monetary amounts allotted to the business plan as closely as possible
7.2.1 How Do You Use Demand Forecasting?
Demand forecasting is the logical starting point for developing a resource requirements plan. However, it is important to remember that the demand forecast is not the actual plan, but that you use it only as an input to the plan. Because you use the forecast in place of work orders, RRP provides an estimate of the time and resources that you will need to produce a product.
Manufacturing must determine whether the production plan is supportable as is or if additional future resource requirements are needed, such as:
-
Additional skilled labor
-
New machinery
-
New facilities or additional real estate
7.2.2 What Factors Should You Consider?
You must consider the following factors when you generate the resource requirement plan:
-
Include allowances for forecast error
-
Use inventory to absorb fluctuations in demand and to level the work center load
-
Weigh the cost of carrying inventory versus the cost of lost revenues if you are out of stock
7.2.3 How Do You Determine Long-Range Capacity Plans?
The Resource Requirements Planning program generates a capacity plan by critical work center. In order to answer long-range planning questions, you need to know your current capacity and the requirements to support the planned work load.
Complete the following tasks:
-
Enter work centers
-
Determine available capacity
-
Determine long-range load
-
Generate resource requirements plans
-
Review resource requirements plans
-
Set up resource requirements plans
Entering work centers defines the work center as machine or labor-paced and whether it is a critical work center. You also specify other values, such as the percent efficiency and utilization of the work center and the crew.
After you estimate how much capacity you will need to produce a product, you must determine how much capacity you actually have. You determine a work center's available capacity on a given day by entering resource units.
Long-range load is an estimate of how many load hours are required to meet sales projections. To determine long-range load, the system uses resource profiles. The resource profile is a list of all work centers and their load requirements for a master scheduled item.
After you have entered resource units and resource profiles, you generate the resource requirements plan to obtain long-range estimates of the capacity needs at your work centers.
After you generate the resource requirements plan, the system creates a load profile that shows the load during each planning period for critical work centers. You can view this as a spreadsheet or as a graphical display. You can also review summaries of each period.
The system records resource requirements planning information in the following tables: