46 Set Up Earnings Information
This chapter contains these topics:
46.1 Setting Up Earnings Information
You set up earnings information to define the types of pay that your employees receive. Earnings information consists of:
Setting up earnings consists of the following tasks:
-
Setting Up Pay Types
-
Assigning a Sequence of Leave DBAs
-
Setting Up Shift Rate Differentials
-
Setting Up Pay Type Cross-Reference Tables
-
Setting Up Pay Grades
-
Setting Up Pay Grade Steps
-
Reviewing the Pay Types Report
-
Reviewing the Shift Table Report
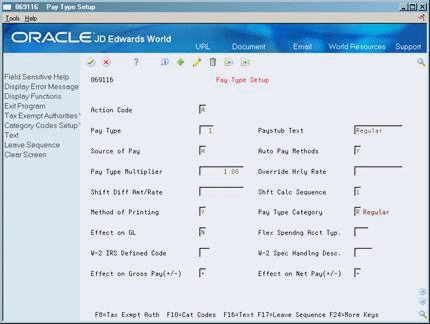
46.2 Setting Up Pay Types
From Payroll Master (G07), enter 29
From Payroll Setup (G074), choose Pay/Deductions/Benefits
From Pay/Deductions/Benefits (G0742), choose Pay Type Setup
You set up pay types to categorize the various earnings employees receive to direct labor to different accounts in the general ledger. You can specify up to 999 different pay types, using the range of numbers 001 to 999.
Setting up pay types also allows you to:
-
Specify how different pay types are used when computing employee pay
-
Assign automatic pay methods for autopay employees
-
Specify that a pay type is tax exempt
-
Specify information to be printed on 1099 and W2 forms for the associated pay type for U.S. payroll
-
Specify whether hours and dollar amounts should be passed to the general ledger
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Pay Type
-
Paystub Text
-
Source of Pay
-
Automatic Pay Methods
-
Pay Type Multiplier
-
Shift Differential Calculation Sequence
-
Method of Printing
-
Pay Type Category
-
Effect on General Ledger
-
Effect on Gross Pay
-
Effect on Net Pay
-
-
Complete the following optional fields:
-
Override Hourly Rate
-
Shift Differential Amount/Rate
-
Flex Spending Account Type
-
W-2 IRS Defined Code
-
W-2 Special Handling Description
-
Flex Spending Account Type
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Pay Type | A code to define the type of pay, deduction, benefit, or accrual.
Pay types are numbered from 1 to 999. Deductions and benefits are numbered from 1000 to 9999. Form-specific information Pay type 001 is typically defined for regular pay. JD Edwards World recommends that you do not change this pay type. Autopay uses pay type 001 as the default pay type unless otherwise noted at the employee level. |
| Paystub Text | A description, remark, explanation, name, or address.
Form-specific information The text that you want the system to print on the employee's pay stub. For the Time Accounting system: The Time Accounting system does not create paychecks. However, this field is required to complete the form. Generally, the information you enter in this field is a description of the pay type. |
| Source of Pay | A user defined code (07/PB) that identifies the value upon which the system bases the employee's pay, for example, H for hours worked.
Valid values include:
|
| Auto Pay Methods | A code that determines how the system treats this pay type when computing automatically generated pay (typically for salaried employees). It also identifies supplemental pay. Valid codes are:
Y – The dollars with this pay type are part of the employee's base pay, for example, regular, holiday, sick, and vacation pay. N – The dollars with this pay type are in addition to the employee's base pay, for example, overtime pay and time off without pay. S – The hours with this pay type are subtracted from the employee's base pay at standard rate and added back at the entered pay rate. B – The dollars with this pay type are in addition to the employee's base pay and are treated as supplemental pay for taxation purposes, for example, bonuses, commissions and payoffs. C – The hours/dollars entered using this pay type override all autopay instructions. If multiple jobs are used, a Y in this field might cause the pay type to be paid in addition to the regular pay. If you have overridden the job code/job step, home business unit, or position at time entry, multiple active jobs exist for this employee, and the overridden information does not match an existing active job record, this system processes this as additional pay. JD Edwards World recommends that you always use a pay type with N in this field when paying someone for work in addition to their regular pay. This ensures that the system processes the pay type the same in multiple-job or single-job situations. If your company docks employees' pay when they take leave in excess of what has been earned, you should have pay type 997 set up as the pay type to dock pay. Enter N as the autopay method for this pay type. If your company attaches contract calendars to employees to accumulate wages, you should have pay type 996 set up as the pay type to dock pay. Enter C as the autopay method for this pay type. |
| Pay Type Multiplier | A factor by which the base hourly rate is multiplied to obtain the actual payment hourly rate. For example, you could use 1.5 to designate time-and-one-half for overtime pay. Zero (0) is not a valid multiplier. |
| Shft Calc Sequence | A code that specifies how the system should calculate shift differential.
1 – The pay type multiplier is applied to the shift differential: Gross = (rate + shift differential) x (multiplier) x hours 2 – The pay type multiplier is applied only to the hourly rate and does not include the shift differential: Gross = (rate x multiplier) + (shift differential) x hours The multiplier is the pay rate multiplier from the Pay Type file. When the pay rate is derived from the Union Rate Table, the multiplier is assumed to be 1 as it is built into the table. In this case, both methods produce the same result. Form-specific information You can specify a code in this field or on the Shift Rate Differentials form. |
| Method of Printing | Identifies whether the item is to be printed on the pay stub and whether the item is to be printed on a separate check from other payroll items. Valid codes are:
Pay Types/Payroll Taxes: Y – Print on pay stub (default) S – Print separate check (one item per check) C – Print separate check (C types combined) N – Do not print on pay stub Deduction/Benefit/Accrual Types: Y – Print as total deductions (default) S – Print separate check (one item per check) C – Print separate check (include detail) N – Do not print on pay stub I – Print individual transactions T – Print by DBA Print Group The separate check feature is not available for any payroll taxes being withheld from the employee's paycheck. |
| Pay Type Category | A user defined code (07/PC) that specifies the pay type categories you want to use:
Form-specific information Pay type category codes provide a method for grouping different pay types. Enter the pay type category code that corresponds to the desired group. Standard codes are R – Regular V – Overtime O – Other You can have more than one type of pay for each category. For example: R – Might include four pay types: regular, holiday sick, and vacation V – Might include two types of pay: time and a half and double time O – Might include pay types such as: time without pay, short-term disability, jury duty, military leave The Automatic Timecard Generator program uses the hours associated with each pay type in the group to determine an individual's overtime hours. To include a timecard in automatic overtime calculation, its pay types must be included in the pay type category you specify. |
| Effect on GL | A code that indicates whether you want journal entries passed from payroll to the general ledger and the method you want to use. Valid codes are:
Y – Pass dollars only to the general ledger. N – Pass dollars and hours to the general ledger. M – Do not pass dollars or hours to the general ledger and do not calculate workers' compensation and general liability. H – Pass hours only to the general ledger. This code is valid for Generate Timecard Journals. It should not be used when journals are generated through the pay cycle. W – Do not pass dollars or hours to the general ledger but calculate workers' compensation and general liability. Workers' compensation and general liability amounts will be passed to the general ledger. |
| Effect on Gross Pay(+/-) | This code indicates whether the pay type is added to, subtracted from, or does not affect the employee's gross pay. Valid values are:
(+) – Pay type will be added to the employee's gross pay. (-) – Pay type will be subtracted from the employee's gross pay. ( ) – Pay type will not affect the employee's gross pay. A pay type should not have a negative effect on gross pay. If you set up a pay type to have a negative effect on gross or net pay, gross-to-net errors appear on the Payroll Register. |
| Effect on Net Pay(+/-) | This code indicates whether the pay type is added to, subtracted from, or does not affect the employee's net pay. Valid values are:
(+) – Pay type will be added to the employee's net pay. (-) – Pay type will be subtracted from the employee's net pay. ( ) – Pay type will not have an effect on the employee's net pay. A pay type should not have a negative effect on net pay. If you set up a pay type to have a negative effect on gross or net pay, gross-to-net errors appear on the Payroll Register. |
| Override Hrly Rate | The value in this field is either a percentage, a monetary amount, or an hourly rate, depending on where it is used:
1 – For a deduction, benefit, or accrual, the meaning of this field depends on the Method of Calculation. The method determines if the deduction is a flat dollar amount, a percentage, or a multiplication rate. Table method DBAs, depending on which table method they use, can either use this amount in the calculation or ignore it. If there are exceptions to the table calculation, you can override the table code in the fold area, set up a flat dollar DBA amount, or override the amount in One Time Overrides. 2 – For a pay type, amounts entered in this field override the hourly rate. Form-specific information A dollar amount or hourly rate that overrides any default values for rate, for example, per diem rates. |
| Shift Diff Amt/Rate | An additional rate, expressed in dollars or percent, added to an employee's hourly rate, depending on the shift worked. This rate can be applied in one of two ways as defined by the Shift Differential Calculation Sequence (data item CMTH).
Form-specific information Percentage amount not applicable to this form. This amount should be expressed in dollars only. |
| Flex Spendng Acct Typ | Defines which type of spending account is being used. An example of a spending account type setup might be:
MED – Medical expenses spending account (where the annual amount is accrued on Jan 1 or year begin). DCR – Dependent care expenses (where accrual of available funds is on a pay period by pay period basis). Form-specific information Set up a pay type and a DBA for each type of flexible spending account. Enter the same code in this field that you enter on DBA Additional Information. |
46.2.1 What You Should Know About
46.3 Assigning a Sequence of Leave DBAs
Some companies deduct, or dock, an employee's pay when the employee takes leave in excess of what has been earned to date. For example, your company might dock pay when an employee uses 30 hours of sick leave, but has earned only 20 hours. On the employee's next payment, you want to deduct the employee's standard pay earned to "repay" the 10 hours of sick pay.
If you want to dock employees' standard pay when they take leave in excess of what has been earned, you must set up a DBA for each source of leave associated with the leave. You must also assign a sequence number to each leave DBA associated with the pay type.
Most companies provide one source of leave for a leave type. For example, an employee earns a specified amount of sick leave each pay period. Even though this is the only source for sick leave you must assign a sequence of one DBA. The sequence assignment provides the system with the instructions required to dock employees' pay if they take more leave than they have earned.
Some organizations, such as public school systems, provide hours for employee leave from various sources. For example, employees might earn sick time from both a state source and the local school district. Frequently, the employees must deplete the leave from one source before using the hours from another source. These leave sources are often called leave banks.
If your organization uses such leave banks, you must sequence the leave DBAs associated with each pay type that has more than one source of leave time. This setup provides the system instructions. The sequence identifies the order the system should use to deduct hours from the leave banks.
When an employee uses all the available leave from all the leave banks, the system docks the employee's standard pay for any leave taken in excess.
46.3.1 Before You Begin
-
Verify that pay type 997 has been set up as the pay type to dock pay. If you want to use pay type 997 for a different purpose, set up the pay type you will use to dock employees' pay. Do not assign a sequence of leave DBAs to this pay type.
-
Verify that pay type 997 (or the pay type you want to use to dock pay) is defined as the default pay type for item #DOK in the data dictionary.
-
Set up a DBA for each type of leave that you list in the sequence of leaves.
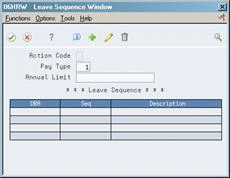
46.3.2 Assigning a sequence of leave DBAs
On Pay Type Setup
-
Complete the steps to set up a pay type.
-
Choose the Leave Sequence function.
-
On DBA Leave Sequence if employees are restricted on this pay type to a maximum number of hours, complete the following field:
-
Annual Limit
-
-
Complete the following fields:
-
DBA
-
Sequence
-
-
If you have more than one source of leave that employees can draw from, complete the following fields for each source:
-
DBA
-
Sequence
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Annual Limit | The maximum amount to be withheld or accrued in a year. For a deduction or a benefit, this amount is expressed in dollars. For an accrual, this amount is expressed as a limit on hours.
Note: For the Payroll system, this field can represent either an initial annual limitation or a final limitation in a year:
Form-specific information For Leave Sequence: This value limits the number of hours employees can be paid with this pay type in any year. Enter the maximum number of hours an employee can be paid for all DBAs listed in the sequence. The system deducts the employee's standard pay for any leave for this pay type taken in excess of this annual limit. |
| Seq | A code to define the type of pay, deduction, benefit or accrual.
Pay types are numbered from 1 to 999 Deductions and benefits from 1000 to 9999. Form-specific information For Leave Sequence: The order in which the system should deplete the leave type. Enter values beginning with 1 through the number of leave types listed in the sequence. Do not enter the PDBA type in this field. The system will subtract leave from a leave type with a relief order sequence of 1 before it subtracts from a leave type with a relief order sequence of 2. If your company has more than one source of leave, or banks of leaves, for a pay type, include all the sources in the list. If your company does not have more than one source of leave, but you want to deduct, or dock, the employee's pay if the employee uses more leave than earned, you must list that DBA and assign it a sequence of 1. You can include a DBA in the sequence for more than one pay type. |
46.3.3 What You Should Know About
46.4 Setting Up Shift Rate Differentials
From Payroll Master (G07), enter 29
From Payroll Setup (G074), choose Group Constants
From Group Constants (G0745), choose Shift Rate Differentials
A shift differential is a flat dollar or percentage amount added to an employee's hourly rate. You set up shift rate differential codes to assign them to employees who receive additional compensation for shift work.
You assign shift differentials to user defined shift codes (07/SH). You can also assign business units and union codes to shift differentials. When you define a shift differential, you must set effective dates for the table. The system compares the effective dates to the work dates you enter in time entry.
A shift rate differential can be either a flat dollar amount or a percentage of the employee's hourly rate. The system uses a flat dollar amount or a percentage shift differential with either of the following two methods:
-
The first method is hourly rate plus the shift differential, multiplied by the pay type multiplier and then multiplied by the hours worked.
-
The second method is hourly rate multiplied by the pay type multiplier plus the shift differential and then multiplied by the hours worked.
The difference between the two methods is significant only when a multiplier other than 1 is specified.
Use shift code information to ensure that an employee is paid the correct amount for working on a shift with a rate differential. If an employee:
-
Always works a shift for which a shift rate differential is applicable, include the shift code in the employee's master record
-
Occasionally works a different shift, you can override the information on the applicable time card
To set up shift rate differentials
Figure 46-3 Shift Rate Differentials screen
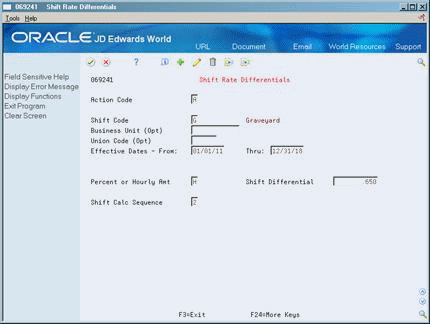
Description of ''Figure 46-3 Shift Rate Differentials screen''
Complete the following fields:
-
Shift Code
-
Effective Date From
-
Effective Date Thru
-
Percent or Hourly Amount
-
Shift Differential
-
Shift Calculation Sequence
46.5 Setting Up Pay Type Cross-Reference Tables
From Payroll Master (G07), enter 29
From Payroll Setup (G074), choose Group Constants
From Group Constants (G0745), choose Classifications/Pay X-Reference
You set up pay type cross-reference tables to indicate valid pay types by job type and job step. For example, use these tables to prevent a salaried person from receiving overtime pay or a temporary employee from receiving holiday pay.
To verify pay types against the pay type cross-reference tables, you must set the appropriate processing options in the time entry programs.
To set up pay type cross-reference tables
On Classification/Pay Cross-Reference
Figure 46-4 Classification/Pay Cross-Reference screen
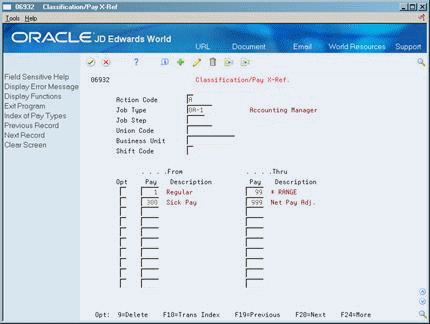
Description of ''Figure 46-4 Classification/Pay Cross-Reference screen''
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Job Type
-
From Pay Type
-
Thru Pay Type
-
-
Complete the following optional fields:
-
Job Step
-
Union Code
-
Business Unit
-
Shift Code
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| From | The number and description of the PDBA you want the system to use to calculate the corresponding DBA.
Form-specific information When you are defining the range of pay types, and the range includes only one pay type, the from and thru fields must contain the same pay type number. |
| Thru | The number and description of the pay type you want the system to use to calculate the corresponding pay type. This is the ending number in the range that is the basis of the calculation.
Test for conditional import. Form-specific information When you are defining the range of pay types, the thru value must be greater than or equal to the value in the from field. If the range includes only one pay type, the from and thru fields must contain the same pay type number. |
| Shift Code | A user defined code (07/SH) that identifies daily work shifts. In payroll systems, you can use a shift code to add a percent or amount to the hourly rate on a timecard.
For payroll and time entry: If an employee always works a shift for which a shift rate differential is applicable, enter that shift code on the employee's master record. When you enter the shift on the employee's master record, you do not need to enter the code on the timecard when you enter time. If an employee occasionally works a different shift, you enter the shift code on each applicable timecard to override the default. |
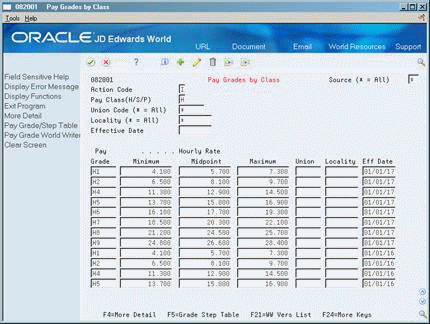
46.6 Setting Up Pay Grades
From Payroll Master (G07), enter 29
From Payroll Setup (G074), choose Pay Grade / Contract Setup
From Pay Grade / Calendar Setup (G0749), choose Pay Grades by Class
To establish categories for grouping employees according to pay ranges, you can set up pay grades for each pay class within your organization. (A pay class indicates how an employee is paid, such as salary, hourly, and so on.) For example, within the pay class Salaried you can set up pay grades 1 through 10. For each of these pay grades, you define a minimum, midpoint, and maximum salary amount. These amounts define the pay range for the pay grade. For example, the pay range for pay grade 1 might be:
Minimum = 20000.00
Midpoint = 25000.00
Maximum = 30000.00
This means that the annual salary for an employee in pay grade 1 can be any amount between 20000.00 and 30000.00.
When you define pay grades by class, you establish a permanent record of the pay ranges for your organization's pay grades. The system uses these pay ranges to calculate compa-ratios for the employees that you assign to these pay grades. When you enter employee information, the system displays an error or warning message when you enter a rate that is not within the pay range for the employee's pay grade.
This program updates the Pay Grade and Salary Range Table (F082001).
-
Complete the following field:
-
Pay Class
-
-
To specify information that applies to all (or most) of the pay grades in this pay class, complete any of the following fields:
-
Source
-
Union Code
-
Locality
-
Effective Date
-
-
To define a pay grade, complete the following fields:
-
Pay Grade
-
Minimum
-
Midpoint
-
Maximum
-
-
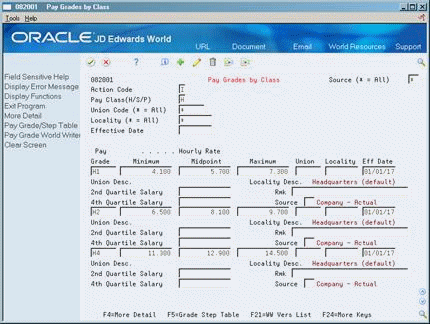
To enter information that varies from the information that you entered for the pay class, complete the following optional fields:
-
Union
-
Locality
-
Effective Date
-
-
Complete any of the following optional fields:
-
Second Quartile
-
Fourth Quartile
-
Remark
-
Source
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Source (* = All) | A user defined code (08/SS) that identifies the source of the salary information. To display all pay grades regardless of the source, place an asterisk (*) in this field. |
| Pay Class (H/S/P) | A code that indicates how an employee is paid. Valid codes are:
" " – Blank H – Hourly S – Salaried P – Piecework |
| Union | A user defined code (07/UN) that represents the union or plan in which the employee or group of employees work or participate. |
| Locality (* = All) | A user defined code (07/SL) that defines the different salary localities within an organization. For example, you can compare salaries for employees on the East Coast with employees in the Midwest.
Form-specific information This field appears in following two sections of this form:
|
| Effective Date | The date on which this transaction takes effect. The effective date is used generically. It can be the date of the next raise, a lease effective date, a price or cost effective date, a currency effective date, a tax rate effective date, change in well status, or whatever is appropriate. |
| Pay Grade | A code that designates a category for grouping employees according to pay ranges. For each pay grade, you enter a pay range that includes a minimum, a midpoint, and a maximum pay rate. The system uses these pay ranges to calculate compa-ratios for the employees that you assign to pay grades. After you enter a pay grade for an employee, the system displays an error or warning message if you enter a rate for the employee that is not within the pay range for the employee's pay grade.
To set up pay grades, use Pay Grades by Class (P082001). |
| Minimum | The minimum salary or hourly rate allowed for a pay grade.
The system displays a warning or error message (depending on processing options) when you enter a pay rate for an employee that is lower than the minimum rate for the pay grade. |
| Midpoint | The midpoint salary or hourly rate for a pay grade or pay range.
For job IDs with a defined pay grade, you enter the midpoint amount in the Pay Grade table (F082001). For job IDs that you evaluated by points, the system calculates the midpoint amount using a Pay Range Formula table (F08290). The system calculates a compa-ratio (data item #CRA) for an employee by dividing the employee's salary or rate by the midpoint for the employee's pay grade. |
| Maximum | The maximum salary or hourly rate for a pay grade.
The system displays a warning or error message (depending on processing options) when you enter a pay rate for an employee that is higher than the maximum rate for the pay grade. |
| Rmk | A generic field that you use for a remark, description, name, or address. |
46.6.1 What You Should Know About
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Setting up pay grades in the Pay Grade/Step table | If you use pay grade steps, you can define the pay grades at the same time that you define pay grade steps. You do not need to define a pay grade in the Pay Grade and Salary Range table (F082001) to set up pay grade steps. |
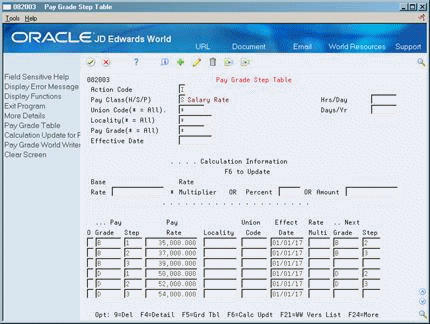
46.7 Setting Up Pay Grade Steps
From Payroll Master (G07), enter 29
From Payroll Setup (G074), choose Pay Grade / Contract Setup
From Pay Grade / Calendar Setup (G0749), choose Pay Grade Step Table
To ensure that all of the employees working in a job receive the same rate of pay, and to establish progression within a pay grade, you can set up pay grade steps. For example, you might have a pay grade A that contains pay steps A1, A2, and A3. Employees in step A1 receive 15.00 per hour, employees in step A2 receive 15.50 per hour, and employees in step A3 receive 16.00 per hour.
Setting up pay grade steps lets you automate the following:
-
Tracking pay information for employees. When you enter employee information, the system calculates the employee's salary or hourly rate, based on the pay grade step that you enter for the employee.
-
Moving employees from one pay grade step to the next.
-
Updating pay rates for multiple pay grades and pay steps.
When you set up pay grade steps, you can save time and reduce calculation errors by having the system automatically calculate the pay rates for a group of steps. You enter a base pay rate that applies to the group of steps, and then enter a pay rate multiplier for each step. The system calculates the rate for each step by multiplying the base pay rate by the step's pay rate multiplier.
Setting up pay grade steps includes:
-
Setting up pay grade steps individually
-
Setting up pay grade steps using a pay rate multiplier
When you set up pay grade steps individually, you enter a pay rate for each pay grade step. When you set up pay grade steps using a pay rate multiplier, you enter a base pay rate, and apply a pay rate multiplier to each pay grade step.
This program updates the Pay Grade and Salary Range Table (F082001).
46.7.1 What You Should Know About
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Setting up pay grades in the Pay Grade/Step table | You can define the pay grades at the same time that you define pay grade steps. You do not need to define a pay grade in the Pay Grade and Salary Range table (F082001) to set up pay grade steps. |
46.7.2 Setting Up Pay Grade Steps Individually
When you set up pay grade steps individually, you enter a pay rate for each pay grade step. When you set up pay grade steps using a pay rate multiplier, you enter a base pay rate, and apply a pay rate multiplier to each pay grade step.
To set up pay grade steps individually
-
Complete the following field:
-
Pay Class
-
-
To specify information that applies to all (or most) of the pay grade steps you need to define, complete any of the following fields:
-
Union Code
-
Locality
-
Hours/Days
-
Days/Year
-
Effective Date
-
-
For each pay grade step that you need to define, complete the following fields:
-
Pay Grade
-
Pay Grade Step
-
Pay Rate
-
-
Complete the following optional fields:
-
Next Pay Grade
-
Next Pay Grade Step
-
-
Press F4 to access the detail area.
-
To specify information for this pay grade step that varies from the information that you entered for the pay class, complete the following fields:
-
Locality
-
Union Code
-
Effective Date
-
Hours/Day
-
Days/Year
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Hrs/Day | The number of hours in a day that the employee's normal work schedule is different from the standard. If you leave this field blank, the default is the standard number of hours per day as defined in the payroll company constants.
For example, if the standard number of hours in a day is 8 and an employee is scheduled for 7 hours per day on a regular basis, enter 7 in this field. |
| Days/Yr | The number of work days in a year. The number of standard days per year multiplied by the number of hours per day equals the standard hours per year. When you have set up the human resources constants to use the pay grade step table as the default pay rate source, the system calculates the salary for an employee by multiplying the standard days per year by the employee's hourly rate. |
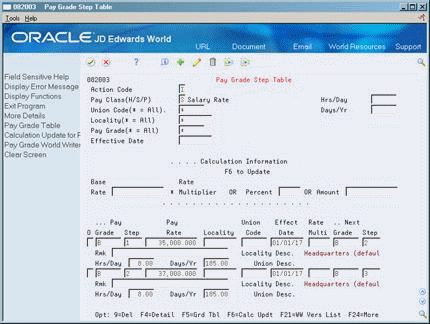
46.7.3 Setting Up Pay Grade Steps Using a Rate Multiplier
When you set up pay grade steps individually, you enter a pay rate for each pay grade step. When you set up pay grade steps using a pay rate multiplier, you enter a base pay rate, and apply a pay rate multiplier to each pay grade step.
To set up the pay grade steps using a rate multiplier
-
Complete the following field:
-
Pay Class
-
-
To specify information that applies to all (or most) of the pay grade steps that you need to define, complete any of the following fields:
-
Union Code
-
Locality
-
Hours/Days
-
Days/Year
-
Effective Date
-
-
Complete the following field:
-
Base Rate
-
-
For each pay grade step that you need to define, complete the following fields:
-
Pay Grade
-
Pay Grade Step
-
Rate Multiplier
-
-
Complete the following optional fields:
-
Next Pay Grade
-
Next Pay Grade Step
-
-
Access the detail area.
-
To specify information for this pay grade step that varies from the information that you entered for the pay class, complete the following fields:
-
Locality
-
Union Code
-
Effective Date
-
Hours/Day
-
Days/Year
-
-
To calculate the pay rate for each pay grade step you entered, choose the Calculation Update function.
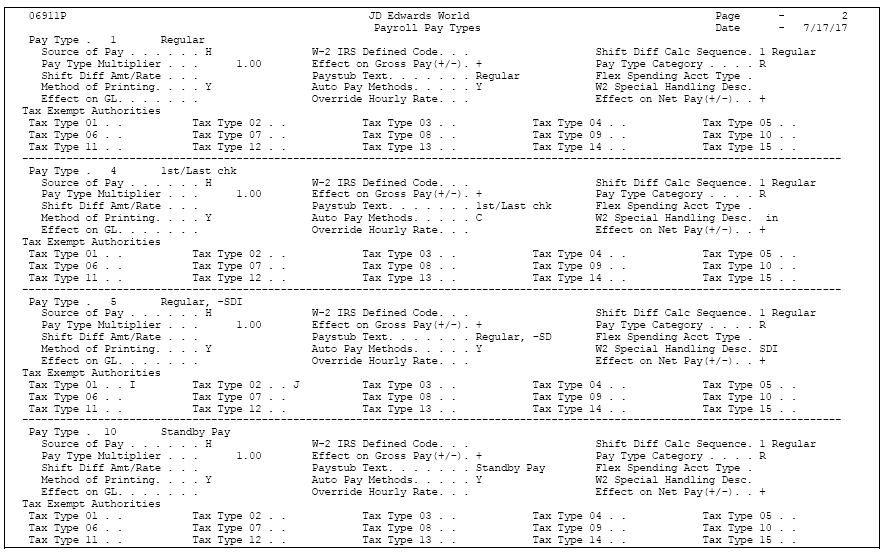
46.8 Reviewing the Pay Types Report
From Payroll Master (G07), enter 29
From Payroll Setup (G074), choose Pay/Deductions/Benefits
From Pay/Deductions/Benefits (G0742), choose Pay Types
The Pay Types report lists detailed information by pay type. Review the report to verify that the information you entered when you set up pay types is correct.
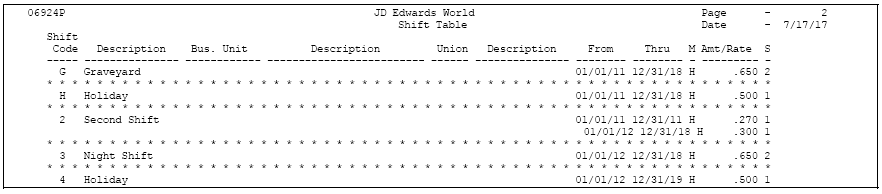
46.9 Reviewing the Shift Table Report
From Payroll Master (G07), enter 29
From Payroll Setup (G074), choose Group Constants
From Group Constants (G0745), choose Shift Rate Differentials
The Shift Table report prints a detailed list of the shift differential tables. Review the report to verify that the shift rate differential you entered is correct. You cannot change the data sequence or selection for this report.