16 Enter an Interbranch Sales Order
This chapter contains these topics:
From ECS Sales Order Management (G4910), choose ECS Sales Order Processing
From ECS Sales Order Processing (G491011), choose Enter Orders (Page Mode)
16.1 Entering an Interbranch Sales Order (ECS)
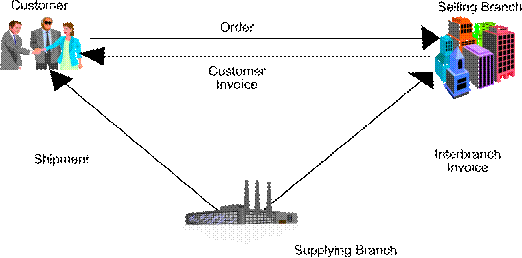
You enter an interbranch sales order to ship inventory from another supply branch/plant within your company directly to a customer. For example, you use an interbranch sales order when a customer orders an item from your branch/plant, but your branch/plant does not carry the item. Or, you regularly sell from one location but fill and ship the orders from another location, such as a central supply warehouse.
Before you enter interbranch sales, you must create a specific document type for interbranch sales orders. You must also set the processing options for the Sales Order Entry program to process interbranch sales.
The system processes interbranch sales orders in the same way as other sales orders with the following exceptions:
-
During invoice processing, the system prints an invoice for the customer. You have the option to print an interbranch invoice for the selling branch/plant
-
During sales update, you can choose to have the system perform one of the following:
-
Create accounts payable and accounts receivable journal entries for the selling branch/plant and accounts receivable entries for the supplying branch/plant
-
Create accounts receivable entries only for the selling branch/plant
-
Choose a pricing method for the supplying branch/plant to use for interbranch orders in the same way as other sales orders. For example, the supplying branch/plant can charge a transfer price or a cost markup to the selling branch/plant.
The transfer price can be any price that is set by the supplying branch/plant. The cost markup price is a specific price that you set up in the Branch Sales Markup table. This markup is applied to the inventory cost.
Specify the pricing method to use in a processing option in the Sales Order Entry program.
The system retrieves payment terms and payment instrument information for the selling branch/plant and the customer from the Customer Master table. You can override payment information for the customer and the branch/plant.
The system also retrieves exchange rate information from the currency code that is set up in Customer Master table for the supplying branch/plant to the selling branch/plant and the selling branch/plant to the customer. You can override the currency information for the customer, which is helpful if you process international sales orders in different currencies.
16.2 Applying Markup Costs for Interbranch Sales (ECS)
Typically, companies apply transfer costs to interbranch sales. You set up transfer costs in the Branch Sales Markup tables so that the branch/plant placing the order (the demand branch/plant) pays a markup amount to the supplying branch/plant.
Example: Applying Markup Costs for Interbranch Sales
The following example illustrates the accounting entries for an interbranch sales transaction entered in branch/plant 40 and shipped from branch/plant 30.
Assume the following information for the example:
-
Demand branch/plant number = 40
-
Supply branch/plant number = 30
-
Item Cost = 1000.00 (cost to the supplying branch/plant)
-
Transfer Cost = 50.00 (add-on cost to the demand branch/plant)
-
Sales Price = 1500.00 (price paid by the customer)
| Activity | Description |
|---|---|
| Sale of goods | The system records the sale of goods from the supply branch/plant (30) to the demand branch/plant (40) with the following accounting entries:
|
| Relieve inventory | The system makes the following accounting entries to record the relieved inventory and increased cost of goods sold (COGS) for the supplying branch/plant:
|
| Sale to customer | The system records the sale to the customer with the following accounting entries:
|
16.2.1 Before You Begin
-
Verify that a user defined code for the interbranch sales order document type has been set up in the user defined code table. See Work with User Defined Codes in the JD Edwards World Technical Foundation Guide.
-
Verify that the processing options for the Sales Order Entry program have been set up to process interbranch sales orders.
-
Verify that the Branch Sales Markups tables are set up. See Section 42.1, "Setting Up Branch Sales Markups (ECS)."
To enter an interbranch sales order
You can use an interbranch order to fill a sales order from a branch/plant other than the selling branch/plant. This is helpful if your company sells from one location but fills and ships orders from another location, such as a central supply warehouse.
The processing options specific to Interbranch Orders, appear under the heading Transfer Price Update on Enter Orders (Page Mode) P4211.
-
Processing option 61 is used to designate special document types for interbranch orders. Typically SI is used for this purpose. You must use one of the special document types for interbranch orders when entering an interbranch sales order
-
Processing option 62 is used to specify the pricing method used on the order. It can either be set to 1 for Branch cost markup which is the default or 2 for Transfer price. This setting determines the cost of the item, which is explained in the Cost and Price section below
-
Processing option 63 tells the program whether inter-branch invoicing is allowed. By setting this to 1 you ensure that you can create an invoice from the supplying branch to the selling branch
-
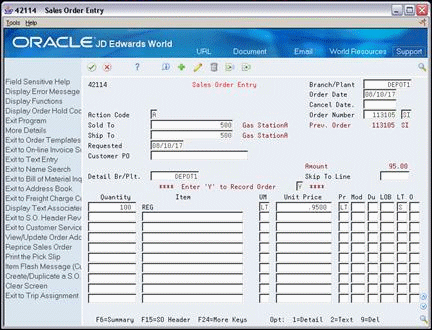
Complete the following fields:
-
Branch/Plant
-
Document Type
-
Sold To
-
Ship To
-
Detail Branch/Plant
-
Quantity
-
Item
-
-
Access the fold area to fill the order from more than one supplying branch/plant.
Figure 16-3 Sales Order Entry (Fold Area) screen
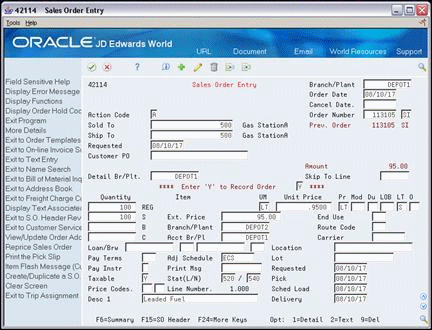
Description of "Figure 16-3 Sales Order Entry (Fold Area) screen"
-
-
Branch/Plant
-
16.2.2 What You Should Know About
16.3 Printing an Interbranch Invoice
From ECS Sales Order Management (G4910), choose Sales Order Processing
From ECS Sales Order Processing (G491011), choose Invoice Processing
From Invoice Processing (G42113), choose Invoice Print
In addition to printing the customer invoice for the selling branch/plant, the system can also print an interbranch invoice for the supplying branch/plant. Set processing option 61 in the Enter Orders (Page Mode) program to enable the system to print interbranch invoices.
To print interbranch invoices, you must also set up a separate DREAM Writer version in the Print Invoices program. Set the appropriate processing option to print interbranch invoices.
|
Note: JD Edwards World recommends that you copy the following demonstration versions to ensure that the system uses the correct data sequence to update records:"Sales Invoices - Interbranch - Batch" to print interbranch invoices by batch. "Sales Invoices - Interbranch - History" to print interbranch invoices from history. |
16.3.1 Before You Begin
-
Verify that the processing option for printing interbranch invoices is set in the Enter Orders (Page Mode) program
-
Verify that processing option (28) in the Print Invoices program for printing interbranch invoices or customer invoices is set, depending on the type of invoice that you want to print
16.3.2 What You Should Know About
16.4 Updating Interbranch Sales Information
From ECS Sales Order Management (G4910), choose End of Day Processing
From End of Day Processing (G491013), choose Update Customer Sales
During the sales update process, you can run the Update Customer Sales program to create journal entries for interbranch sales.
If you set the interbranch sales processing option (26) in the Sales Update program (P42800) to create accounts receivable and accounts payable entries for both the selling and the supplying branch/plants, the system creates the following types of batches:
16.4.1 Example: Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable Entries
-
Batch type I - Debits the COGS account, and credits the receivables accounts and inventory for the supplying branch/plant and selling branch/plant.
-
Batch type V - Credits the payables accounts and debits the inventory for the selling branch/plant.
In this example: Price to customer = $100, Cost at supplying branch = $60, Cost + 20% markup to selling branch = $72.
AAI 4260 is used to write the interbranch revenue.
Selling branch:
| AAI | Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|---|
| RC | A/R Trade | $100 | |
| 4230 | Revenue | $100 | |
| 4220 | Cost Of Goods Sold | $72 | |
| 4240 | Inventory | $72 |
Supplying branch:
| AAI | Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|---|
| RC | A/R Trade | $72 | |
| 4260 | Interbranch Revenue | $72 | |
| 4220 | Cost Of Goods Sold | $60 | |
| 4240 | Inventory | $60 |
Selling branch:
| AAI | Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4240 | Inventory | $72 | |
| PC | A/P Trade | $72 |
16.4.2 Example: Accounts Receivable Entries
If processing option 26 in P42800 is set to create only the accounts receivable entries, the system creates the following types of batches:
-
Batch type I - Credits the revenue accounts and inventory, and debits the COGS account of the selling branch/plant
-
Batch type ST - Credits the revenue account and inventory for the selling branch/plant, and debits the COGS accounts and inventory for the supplying branch/plant
In this example: Price to customer = $100, Cost at supplying branch = $60, Cost + 20% markup to selling branch = $72.
Selling branch:
| AAI | Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|---|
| RC | A/R Trade | $100 | |
| 4230 | Revenue | $100 | |
| 4220 | Cost Of Goods Sold | $72 | |
| 4240 | Inventory | $72 |
Supplying branch:
| AAI | Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4220 | Cost Of Goods Sold | $60 | |
| 4240 | Inventory | $60 |
Interbranch/Selling:
| AAI | Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4240 | Inventory | $72 |
Interbranch/Supplying:
| AAI | Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4260 | Interbranch Revenue | $72 |
General Ledger records (F0911) that have a batch type of ST for interbranch sales transfer are bypassed by the Item Ledger/Account Integrity report (P41543).
16.4.3 Before You Begin
-
Verify that the interbranch sales processing options in Update Customer Sales are set to:
-
Recognize the order type used to identify interbranch orders
-
Create necessary types of accounting entries
-
16.4.4 What You Should Know About
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Document types | If you are creating a V batch, you need to have the interbranch invoice document type (RT) setup in UDC tables 00/DT and 00/DV. Failure to do this will result in error 2362 being generated by sales update. |
16.5 Consignment Sales
A consignment sale is a sale in which one person or company acts as an agent to sell the goods from another person or company. In JD Edwards World, this is accomplished through an Interbranch Sales Order.
As an example, think of a company that sells large trucks and earth moving equipment. In order to support their customers, the company also sells replacement parts on behalf of other suppliers. These parts are therefore being sold on 'consignment' by the 'agent' on the behalf of the 'consignor'.
16.5.1 Set up and Process for Consignment Sales
Using the terms defined above, you can set up a vendor to provide consignment sales as follows:
-
Ensure that the consignor address book entry has a search type of V for vendor, and also set the Payables flag to Y
-
Set up supplier master and purchasing instructions for the consignor
-
Set up a separate company for consignment branches. This is so that the consignment goods are not kept on the books of your regular companies
-
Set up a consignment branch as a business unit in the new company. Enter the consignor address number as the Branch/Plant address number
-
All the items that are to be sold under consignment need to be set up in both the Branch/Plant from which your regular sales operate and also the consignment Branch/Plant
-
Set up price information on the items in the regular sales Branch/Plant but no quantities. The items in the consignment Branch/Plant should be set up with quantities and the cost of the item to the agent, which can be maintained in either the Cost file (F4105) or the Base Price file (F4106). This is the Branch/Plant from which the orders will be sourced, so all quantities are maintained here
-
Set processing options (61, 62, 63) behind Sales Order Entry (P4211) to trigger interbranch sales
-
On order entry set the agent Branch/Plant in the header of the order since it is the selling branch. Enter the consignment Branch/Plant in the detail of the order since it is the sourcing branch
-
After invoicing the customer, run Print Invoices (P42565) with the specific version that creates an interbranch invoice (XJDE0010)
-
The final step is to set processing options 25 and 26 on Sales Update (P42800) to ensure the correct journal entries are made. Sales update produces two batches:
-
Type I for invoices, with invoice numbers for both the customer and the consignor
-
Type V for the voucher which is the payable by which the agent pays the consignor
-