Introduction to Operating System Provisioning
The provisioning feature provides a method of automatically and consistently installing operating systems on managed systems from the Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center UI.
You can provision the following:
-
Oracle Solaris operating systems
-
Linux operating systems
-
Oracle VM Server for SPARC
-
Logical Domains
-
Oracle Solaris Clusters
This chapter focuses on basic OS provisioning. Many of the concepts apply to other types of provisioning.
Provisioning an operating system installs a specific operating system release with your defined configuration. Earlier versions of the software used a single OS Provisioning profile to define both the operating system and the configuration. Beginning with Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center 12.2.0.0.0, the single profile is replaced with an OS Provisioning profile and an OS Configuration profile.
Note:
If you created OS Provisioning profiles in versions of the software earlier than 12c Release 2, see Migrating OS Provisioning Profiles to the New Format for how Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center updates your profiles and plans to the new format.
The following are needed to define your OS provisioning job:
-
OS Provisioning profile: Defines the image, provisioning, and installation requirements, including the basic OS configuration and boot network information.
-
OS Configuration profile: Defines the networking configuration. You can use a simple networking interface for any Oracle Solaris or Linux operating system, or advanced networking configurations for Oracle Solaris.
When you create a configuration profile for Oracle Solaris, you can configure the following advanced networking options:
-
Link aggregation: Provides high availability and higher throughput by aggregating multiple interfaces at the MAC layer. Link aggregation enables you to combine the capacity of multiple full-duplex Ethernet links into a single logical link.
-
IP multipathing (IPMP): Provides features such as higher availability at the IP layer. IPMP enables you to configure multiple IP interfaces into a single IPMP group.
You can implement both Link Aggregation and IPMP methods on the same network because they work at different layers of the network stack.
After you create the profiles, you create a deployment plan to apply the profiles. As part of applying the plan, you can change some of the options that you defined earlier in the profiles.
-
-
Provision OS deployment plan: Defines the OS Provisioning and OS Configuration profiles to use and the targets to provision. The plan also provides you with an opportunity to provide a specific IP address and to make changes to the network and interface for the target.
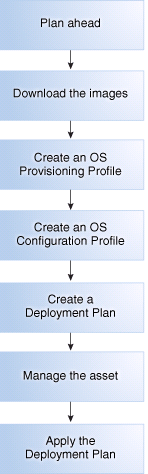
Figure 7-1 shows the basic steps that you need to plan for, and complete, a provisioning job:
As shown in Figure 7-1, the following are the basic steps that you need to plan for, and complete, a provisioning job:
-
Plan ahead. See Planning for Operating System Provisioning for items to consider before provisioning.
-
Download a file with the OS image into the Software Library.
-
Create an OS Provisioning profile, edit an existing profile, or reuse an existing profile.
-
Create an OS Configuration profile, edit an existing profile, or reuse an existing OS Configuration profile.
-
For provisioning OS on logical domains, you cannot use the OS Provisioning and OS Configuration profiles created for bare-metal provisioning. You must select the Logical Domain subtype when you create OS provisioning profiles for logical domains.
-
Create or configure a deployment plan that includes the OS Provisioning profile and the OS Configuration profile.
Note:
To successfully provision an operating system, the plan must contain an OS Provisioning profile and an OS Configuration profile with the same platform, either SPARC or x86. For Oracle VM Server for SPARC, the control domain (CDom) version must be the same.
-
Manage the service processor for one or more systems that you want to provision.
-
To provision an existing system with a new operating system, verify that the service processor is discovered.
-
To provision a bare metal system, manage the service processor.
-
-
Apply the deployment plan on one or more targets. When you choose a group as a target, it must be a homogeneous group where all members are the same.
Note:
The target must have a discovered and managed service processor for Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center to identify the system as a target.
Default Profiles and Plans
All default profiles and plans have a naming convention that begins with default and includes the type of profile or plan and ISO image information.
For example, the software creates the following for an Oracle Solaris 11.0 SPARC-10.1.0 Oracle Solaris Desktop package:
-
OS Provisioning profile:
default-profile-Oracle Solaris 11.0 sparc-10.1.0-OracleSolarisDesktop v1 -
OS Configuration profile:
default-osc-profile-Oracle Solaris 11.0 sparc-10.1.0-OracleSolarisDesktop v1 -
Deployment Plan:
default-profile-Oracle Solaris 11.0 sparc-10.1.0-OracleSolarisDesktop-plan
The default deployment plan references the associated default profiles for the package. You can edit the default profiles and plans, you can create copies of the default profiles and plans and edit them, or you can create your own profiles and plans.
Deployment Plans
A deployment plan defines the OS Provisioning and OS Configuration profiles to apply, the managed targets to provision, the network configuration and IP addresses for the targets, and the tasks to perform. Several different deployment plans let you provision an operating system.
The Provision OS plan is a simple plan with the sole task of provisioning the operating system. The Provision OS plan lets you install the OS on a single system, one or more groups of systems, or a combination of systems that are attached to your network. Other plans are multi-step or complex plans where OS provisioning is one of several tasks performed.
In some cases, the requirements are determined by the target type that you are provisioning. Each target type has different requirements and options.
Note:
To provision Oracle Solaris 11 or to manage Oracle Solaris 11 boot environments, both the Enterprise Controller and Proxy Controller must be installed on a system that is running Oracle Solaris 11.
To provision Oracle Solaris 9 and 10, you can use a Proxy Controller that is installed on a system that is running either Oracle Solaris or Linux.
To provision Oracle Solaris 10 using JET customization, the Enterprise Controller must be installed on a system that is running an Oracle Solaris operating system.