BDD supports many different deployment configurations. Before installing, you can configure your deployment to have one that best supports your needs. This topic describes three types of deployments suitable for demonstration purposes, development, and production.
While this topic illustrates three types of deployments and lists their possible variations, you can deploy BDD into any configuration that meets your data processing needs; you are not limited to the configurations described in this topic.
Single-node deployment for a demo environment
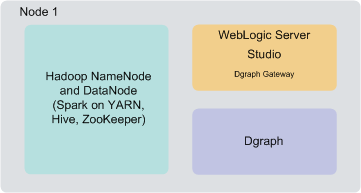
You can deploy BDD to a demo environment running on a single physical or virtual machine. This configuration can only handle a limited amount of data, so it is recommended solely for demonstrating the product's functionality with a small sample index.
In a single-node deployment, Hadoop (including the NameNode and one DataNode), the WebLogic Server with Studio and Dgraph Gateway, and the Dgraph instance are all hosted on the same node.
Two-node deployment for a development environment
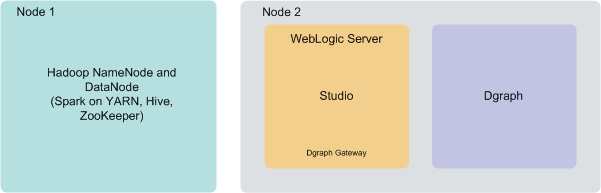
You can deploy BDD to two nodes for a development environment. This configuration can handle a slightly larger index than a single-node configuration, but is not recommended for production as it does not provide high availability of Dgraph or Studio services and also has limited capacity for processing queries on high volumes of data.
In a two-node configuration, Hadoop (including the NameNode and one DataNode) is hosted on the first node. The WebLogic Server (including Studio and the Dgraph Gateway) and the Dgraph instance are hosted on the second node.
Six-node deployment for a production environment
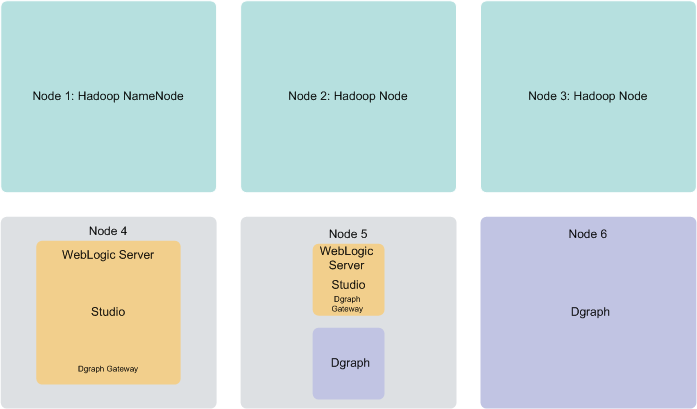
A production environment can consist of any number of nodes required for scale; however, a cluster of six nodes, with BDD deployed on at least three Hadoop nodes, provides maximum availability guarantees.
- Nodes 1, 2 and 3 are running Hadoop. Note that BDD is also deployed on these nodes. After the installation, Data Processing jobs are launched from these nodes and run on other BDD nodes. Having three Hadoop nodes ensures enhanced availability of BDD services, including query processing performed by the Dgraph.
- Nodes 4 and 5 are running WebLogic Server with Studio. This ensures minimal redundancy of the Studio instances.
- Nodes 5 and 6 are running the Dgraph instances. This creates a Dgraph cluster within the BDD cluster, which in turn increases the availability of query processing.
About the number of nodes
This documentation does not provide sizing recommendations. To determine an appropriate size for your deployment, use the following guidelines along with your site's specific requirements.
- Hadoop nodes. Your BDD deployment must include at least one Hadoop node. For high availability, Oracle recommends having at least three. (Note: Your pre-existing Hadoop cluster may have more than three nodes. The Hadoop nodes that are discussed here are those BDD has also been deployed on.) The BDD installer will automatically install Data Processing on all qualified Hadoop nodes in the cluster.
- WebLogic Server nodes. Your deployment must include at least one WebLogic Server node running Studio and Dgraph Gateway. There is no recommended number of Studio instances, but if you expect to have a large number of end users generating concurrent query requests to BDD, it may be desirable to run two Studio instances (and thus configure two WebLogic Server nodes). If you have more than one WebLogic Server node, Oracle recommends configuring an external load balancer that is connected to the Studio instances running on these nodes. You must specify the number of WebLogic Server nodes in the installer's configuration file before installing.
- Dgraph nodes. Your deployment must include at least one Dgraph instance. If it includes more than one, the Dgraph instances will be run as a cluster within the BDD cluster. Having a cluster of Dgraphs is desirable because it enhances high availability of query processing. You must specify the number of Dgraph nodes in the installer's configuration file before installing.
About co-locating Hadoop, WebLogic Server, and the Dgraph
One way to configure your cluster is to co-locate different components on the same nodes. For example, a single node in your BDD cluster deployment can host any combination of Hadoop, the Weblogic Server, and the Dgraph, including all three components together.
Co-locating components enables you to use your hardware more efficiently, since you don't have to devote an entire server to any specific BDD component. However, it does mean that the co-located components must compete for memory, which can have a negative impact on performance.
The decision to host different components on the same nodes depends on your site's production requirements and the capacity of the machines running each component.
Possible component combinations include:
- The Dgraph and Hadoop. For best performance, Oracle recommends dedicating specific nodes to running the Dgraph (one Dgraph per machine); however, it's possible to host the Dgraph on Hadoop DataNodes. If you decide to co-locate the Dgraph and Hadoop, Oracle recommends that you use a node that isn't running Spark on YARN. Additionally, you should allocate a specific amount of memory to the Dgraph process using Linux cgroups (control groups) and Dgraph flags to prevent it from crashing. For more information on Dgraph flags, see the Administrator's Guide.
- The Dgraph and WebLogic Server. The Dgraph and WebLogic Server can be hosted on the same node. If you do this, you should configure the WebLogic Server to consume a limited amount of memory to ensure the Dgraph process has access to sufficient resources for its query processing.
- WebLogic Server and Hadoop. WebLogic Server and Hadoop can be co-located. If do this, you should configure the WebLogic Server to consume a limited amount of memory to ensure that Hadoop has access to sufficient resources for processing.
