| Oracle Agile Engineering Data Management Architecture Guide Release e6.2.0.0 E52551-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle Agile Engineering Data Management Architecture Guide Release e6.2.0.0 E52551-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
The Agile e6 system architecture is called a 3-Tier architecture, which contains the following parts:
Client - The client is responsible for the presentation logic.
Application Server - The application server process is responsible for the business logic.
Database - The database server takes care of the physical storage of all data.
Two types of clients are available, serving the different needs of casual users and power users.
Java Client
Web Client
|
Note: For more information about the Clients please see the chapter Application Clients. Please be aware that there are more client side components with service specific client side functionality (e.g. Workflow Editor, File Server Client). |
With each client process launched, an EDM server process is started in parallel. The EDM server process provides the core Agile e6 functionalities, like Item Management, BOM Management, Document Management, and Change Management, etc. User data (stored in the Oracle database) is accessed by the EDM server process. The connection to the database is realized with the OCI protocol. This is regarded as standard and not described any further in this document. This ensures that the clients do not require a direct database connection.
Some responsibilities of the application server process have been assigned to dedicated services, being able to service several client processes in parallel. These include for example the File Management Service "FMS", the Business Services, and Technical Services.
The Business Services provide Agile e6 functionalities for Workflow Management, Product Configurator and Permission Manager.
Technical Services encompass the following:
Java Client WebStart deployment
Responsible to provide a centralized Java Client, deployable via WebStart technology.
Java Client HTTPS support
To enable an encrypted client server communication for the Java Client.
Web Presentation Service
To run the Web Client.
Web Fileservice
To provide file access via HTTP/HTTPS.
Core Web Services
Technologies for building distributed applications.
StreamingFileServices
For the DFM Web Service, containing uplaodFile and downloadFile operations.
Administration Client
Provides the front end to administrate the application.
The Business Services as well as the Technical Services run on top of the Oracle WebLogic Application Server.
|
Note: There are additional components beside File Management Service, which are not shown in the architecture overview. |
The following diagram gives an overview of the main services which are used in the architecture of Agile e6:
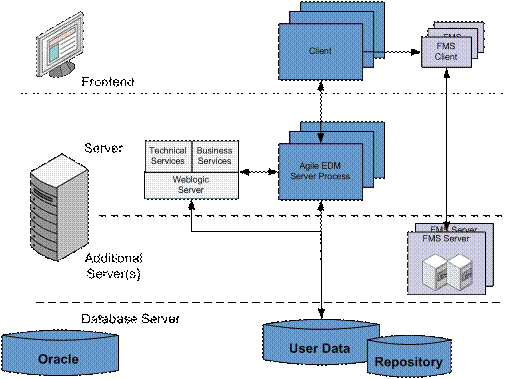
Server-Side Components
File Management Services
ViewServer
(External) component of AutoVue Viewer used to view and redline documents (Office documents, 2D/3D-CAD Models).
LDAP Server
(External) component (e.g. Oracle Identity Management Suite) to provide centralized store for managing user/password.
Kerberos Server
(External) component (e.g. Windows Domain Controller) to provide single sign-on feature.
Batch Client
Component to run EDM batch processes.
Java Daemon
Component to start an EDM server.
FMS Daemon
Component to contact the File Server.
PLM API Proxy
Component to support HTTPS connection.
For more details, refer to the chapter Application Server Components.
Client-Side Components
Workflow Editor
To model and view workflows.
Office Suite
To check-in/check-out documents from/to Microsoft Office.
Agile e6 AutoVue Integration plug-in
To view various file formats with an integrated viewer.
Refer to the chapter Application Clients for more details.
Agile e6 uses an object oriented repository. It is unique in that it stores the complete metadata which defines the application with respect to:
Object model
User interface
Business logic
The Business Logic consists of:
Lifecycle definitions
Workflow processes
Consistency Checks
Automation Scripts (Decision Tables and Scripting Language LogiView)
Owing to the repository based approach of Agile e6, each application server process interprets the repository during initialization and thus can dynamically reflect any changes applied to the metadata. Modifications of the User Interface and/or adaptation of the business logic can be carried out instantly.
The repository ensures the separation of system description and physical structure. Because all metadata is stored in the database, deployment and upgrade processes are simplified.
Depending on the number and user profiles of involved sites, used Agile e6 components, and the availability requirements for the system, different installation types are possible.
All components are installed on a single site. The different Agile e6 services can be distributed to one or more servers depending on the number of users working with the installation.
The preferred architecture is a set of servers where every server hosts a complete set of all EDM server components that are installed in a cluster, e.g. as NLB cluster where load balancing tools are used to distribute the load to the servers.
The load balancer connects Agile e6 clients to a server node. On this server node the Agile e6 native server processes run as well as the J2EE components deployed in WebLogic application server. If the server node crashes, the user has to re-login. In this case, the load balancer connects the user automatically to one of the running servers. The native server and the WebLogic components open a connection to an Oracle Database. The Oracle Database could be a single or a Real Application Database as shown in the graphic below.
As we have a permission manager running on every node, the content of the related cache will be synchronized over all nodes in the cluster.

Especially for UNIX there is a 2nd way to setup Agile e6. There could be only one single J2EE Server on a separate node, hosting the WebLogic with all J2EE components for Agile e6. In addition, there is a set of servers, hosting the Agile e6 components. The native nodes could be installed in a cluster, e.g. as NLB cluster, and load balancing tools can be used to distribute the load to the servers. The database could be a RAC in the scenario, too.
Normally a 2nd WebLogic server on separate nodes will be installed and prepared. The second WebLogic node remains inactive as failover server until the main WebLogic server stops working.

Native as well as J2EE components of Agile e6 could be configured to connect to a RAC database. The Agile e6 applications connect to a cluster of database instances. If one database node crashes, the session will be automatically transferred to one of the running instances. The current transaction is rolled back, thus a new login for the Agile e6 user is not necessary.
The following scenarios are possible to support remote sites:
Central installation with local clients.
The central installation with local clients is frequently implemented and allows a simple, centralized management with worldwide access.
All services, besides the client, are installed on one central site and accessed via network.
In addition, a central management of the client via Webstart is possible. The user will connect to a central Webstart URL and download the software in case of updates.
Central installation with local clients and distributed file management setup.
Distributed file management means that clients and vaults are installed locally on several sites and one central application server and central installation is available. Files are (partially) distributed/ replicated. This leads to an improved availability of managed files. To support DFM functionality with the Web Services, a set of local Web Services is deployed to a TOMCAT installation on the remote site.
Central installation with full remote deployment, including local clients, distributed file management, and decentralized AutoVue server.
Depending on the number of local users and network bandwidth, a decentralized View server can be used on sites with DFM setup. The viewer uses the local File Server vaults as source and triggers file replication if necessary.
