| Oracle Agile Engineering Data Management Architecture Guide Release e6.2.0.0 E52551-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle Agile Engineering Data Management Architecture Guide Release e6.2.0.0 E52551-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
The lines of communication when launching the Java Client are depicted in the following graphic:
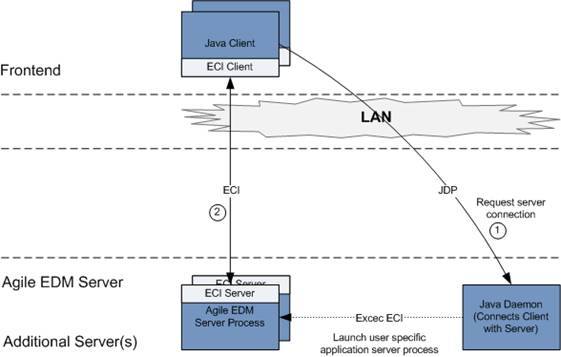
The following steps are executed when you launch the Java Client:
The Java Client connects to the Java Daemon, requesting to launch a user specific Application Server Process and to return the connection information for this process.
The Java Client connects to the given Application Server Process and starts communicating.
The communication line between the Java Client and the Application Server Process utilizes the ECI (Enterprise Communication Interface) protocol. This is the same as used e.g. by an M-CAD system to communicate with an Agile e6 client on the front end.
The following table describes the relevant lines of communication:
| Line of Communication | Type | Port or Range of Ports |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | Application specific protocol based on Sockets | Port 16077 by default (can be configured during installation) |
| (2) | Application specific protocol based on Sockets | One unprivileged port per Application Server Process from range as configured for Java Daemon (5000 to 5999 by default) |
The new Firewall Friendliness allows the communication to Agile e6 application server through firewalls (via HTTP). This is accomplished by using ECI via Web Service with SOAP communicating through HTTP.
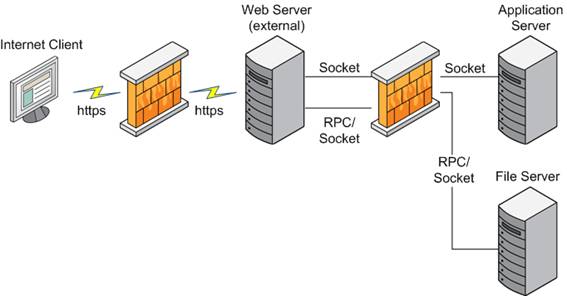
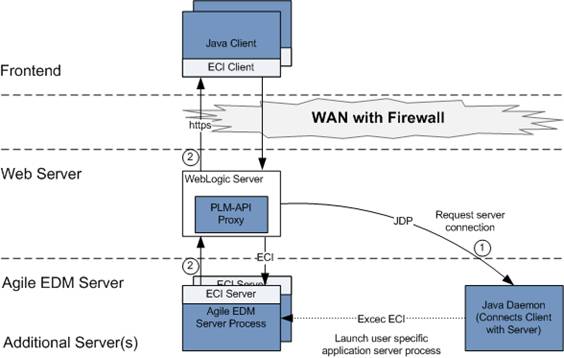
The Java Client sends an HTTP requests to the proxy server. First, the proxy server connects with the Java Daemon to get the address for the EDM Server. Then it connects itself with the EDM Server for further calls from the Java Client.
|
Note: This configuration only supports client which are installed via Webstart. Clients installed locally are not supported. |
|
Note: The proxy server is built from a Web Service container (e.g. WebLogic) and Web Services. |
|
Note: Using the new Firewall Friendliness can have an influence on the performance of the Java Client. |
The connection between Java Client and Agile e6 through HTTP occurs through a component called PLM-API Proxy, which provides the HTTP communication capability.
The Java Client makes two connections:
With Java Daemon
To bootstrap the actual communication.
Connects to Agile e6
To start the actual communication with EDM Server and then close the connection with Java Daemon.
The connections are socket based and use a proprietary protocol. In a WAN scenario, this is not possible as there is almost always a firewall which restricts the communication. But as a standard, the firewall does allow HTTP communication through standard port number 80 for HTTP, and 443 for HTTPS.
In case of a HTTP communication, there is a web server between Java Client and Agile server components (EDM Server and Java Daemon) inside the firewall. The PLM-API Proxy should be deployed in this web server.
The Java Client connects to the PLM-API proxy and the PLM-API bootstraps the connection for the Java Client by first connecting to Java Daemon, and then to EDM Server by using the credentials sent from Java Client. Once the PLM-API has finished the connection bootstrapping, the Java Client can communicate through PLM-API proxy with EDM Server.
The Java Client supports Kerberos based single sign-on interface, which allows you to e.g. authenticate on the Windows Operating system level and to open Agile e6 without further authentication dialog.
The following graphic depicts a typical infrastructure consisting of Windows Domain Servers (e.g. Windows Active Directory server), responsible for the identity management, and the Agile e6 client and server applications.
As part of the initial authentication at the Windows Domain Server, the client machine will receive a so-called Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT), which is later used to request a service ticket from the Key Distribution Center (KDC) to start the Agile e6 application.
The service ticket allows the Agile e6 client to start Agile e6 without further authentication.
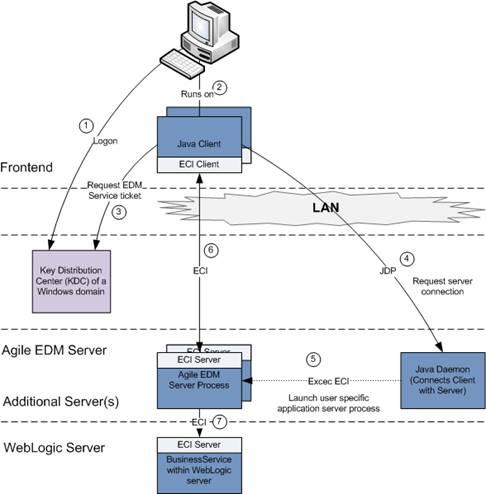
The following steps are executed when you launch the Java Client:
The Windows domain login is based on Kerberos and the user authenticates himself during the Windows logon against the Kerberos server. During the login the Kerberos server creates a TGT which is stored on the client machine.
The user starts the Java Client
The Java Client uses the TGT of the client machine to request a service ticket for Agile EDM.
The Java Client connects to the Java Daemon, requesting to launch a user specific Agile EDM server process and to return the connection information for this process
The Java Daemon starts the Agile EDM Server process
The Java Client connects to the given Agile EDM Server process and starts communication
The Agile EDM server delegates the authentication to the Business Services which validates the service ticket which is used for the authentication
The Java Client supported different options to access files depending on how the Java Client is deployed on the client machine.
The local installed (MSI Installation) Java Client uses the external FMS Client to communicate with the FMS Server directly.
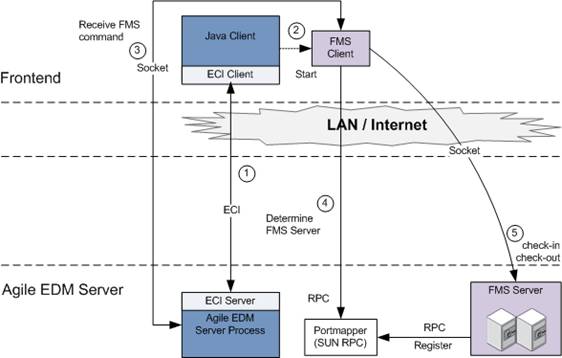
The following steps are executed when the user performs a check-in or a check-out operation in the Java Client:
The user initiates the FMS operation and the Agile EDM Server calls the Java Client to start the external FMS Client.
The Java Client starts the external FMS Client and passes the connection information of the Agile EDM Server.
The FMS Client opens the command channel between the Agile EDM Server and the FMS Client. Via this channel, the FMS Client receives the command and the information to access the FMS Server.
The FMS Client contacts the RPC portmapper to gain the RPC connection information of the FMS Server.
The FMS Client connects to the FMS Server to check-in or a check-out the file.
The WebStart Java Client supports a build-in native FMS Client for direct connections to the FMS Server. This is normally used in DFM (Distributed File Management) environments where RPC communication is possible.
In a pure web environment, the Java Client communicates via HTTPS with the Agile system.
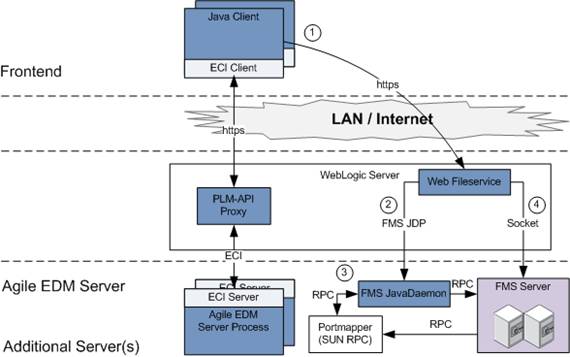
The communication between the Java Client, the EDM Server process, the Web Fileservice, and the FMS Server is depicted in the following figure:
|
Note: f the Java Client uses the HTTP protocol to communicate with the Agile EDM Server, the client must use HTTP for the communication with the FMS server, too. |
The following steps are executed when the user performs a check-in or a check-out operation in the Java Client:
The embedded FMS Client connects to a Web Fileservice, which is hosted by a servlet engine. The address of the Web Fileservice is taken from the configuration of the corresponding vault in the Agile e6 database.
For a check-out operation, the FMS Client sends the corresponding request parameter to the Web File Server.
For a check-in operation, the FMS Client sends the corresponding file to the Web File Server.
With the information about the FMS Server, the Web File Service connects to the Portmapper to determine the port of the corresponding FMS Server.
The Web Fileservice can now request the FMS Server to create an individual thread and return the connection parameter.
The file data is transmitted between the Web File Service and the FMS Server thread. The Web Fileservice itself returns the call to the embedded FMS Client.
Files are not stored temporarily, but transferred directly between the front end and the FMS Server.
The following table contains the details about the relevant lines of communication:
| Line of Communication | Type | Port or Range of Ports |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | HTTP (or HTTPS) | Port 8088 by default (can be configured during installation) |
| (2) | RPC | Port 111 (used by Sun RPC) |
| (3) | RPC | One unprivileged port for each file FMS Server (typically only one), assigned by Portmapper - see (2) |
| (4) | Application specific protocol based on Sockets | One port for each concurrent file upload or download in range from 52517 to 53516 |
The file replication can happen online, on demand, or asynchronous via a batch replication. With the batch replication you can execute the file transfer during a time slot where the bandwidth is not used by other users.
The Agile e6 system supports a distributed file management which allows having a File Server installed on the remote location. The different File Servers are able to replicate files for performance reasons.
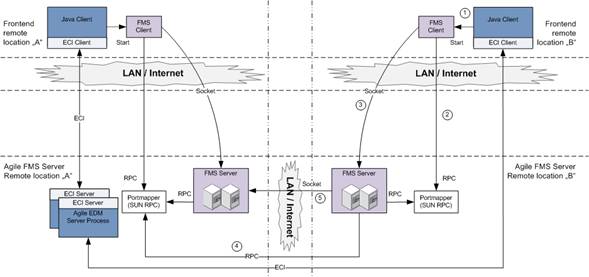
In this example the remote location "A" is the main DFM location where the Agile EDM server is installed. The remote location "B" is a pure DFM location, here is no Agile EDM server available. Client on the remote location "B" are connected to the Agile EDM server process which is running on the remote location "A".
The following steps are executed when the user performs a replication of a file (On-Line):
The Java Client starts the external FMS Client if necessary.
The FMS Client requests the connection information for the FMS Server of the local location (B).
The FMS Client connects to the FMS Server and triggers a replication operation.
The FMS Server on the local location requests the connection information for the remote FMS Server (A).
The FMS Server requests the file to replicate from location "A" to the location "B".
In a DFM environment the FMS Client always connects to the FMS Server on the same location. If a file replication is necessary the local FMS Server requests the file from the remote FMS Server, the FMS Client never contacts the remote FMS Server.
All FMS Servers are master File Servers. The Agile EDM Server administers on which FMS Server the instances of a file are present and if an instance is out-dated.
For example; if a file instance is only available on location "A", and a user wants to change it on location "B", Agile e6 initiates a file replication and the FMS Server on location "B" requests the file from the FMS Server on location "A". Now both FMS servers have the newest file instances. Now, when the user changes and re-checks-in the file on location "B", the Agile e6 system marks the file instance on location "A" as outdated in the database.
For batch replication, a Batch Client can be configured to execute batch replication jobs.
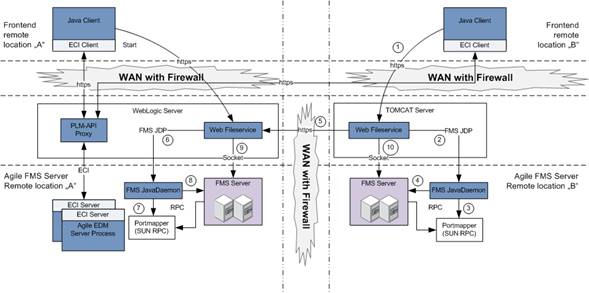
This example shows the same scenario as above, but with firewall friendly communication between the remote locations.
The following steps are executed when the user performs a replication of a file (On-Line):
The Java Client initiates the file replication by calling the Web Fileservice.
The Web Fileservice calls the FMS Java Daemon to get the access to the FMS Server.
The FMS Java Daemon gets the RPC connect information from the Portmapper.
The FMS Java Daemon calls the FMS Server to get the port for the file transfer.
After the Web Fileservice received the port to access the FMS Server, it calls the remote Web Fileservice to request the file which should be replicated.
The remote Web Fileservice uses its FMS Java Daemon to get the access port for the FMS Server.
The FMS Java Daemon gets the RPC connect information from the Portmapper.
The FMS Java Daemon calls the remote FMS Server to get the port for the file transfer.
After the Web File Service received the port to access the FMS Server, it requests the file from the FMS Server and sends the file back to the calling Web Fileservice.
The Web Fileservice sends the received file to its local FMS Server.