| Oracle Agile Engineering Data Management Web Services Guide for Agile Release e6.2.0.0 E52562-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle Agile Engineering Data Management Web Services Guide for Agile Release e6.2.0.0 E52562-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
The Web Services configuration can be used to configure the Web Services security. Since Web Services are not secured by default, it is required to configure/establish a Web Service policy that meets your security strategy requirements.
|
Note: The Agile e6 Web Service needs user credentials to connect to the Agile e6 application server. These credentials are provided by the Agile e6 authentication provider which passes this information to the Web Service. The Web Service has to be configured to be secure. An unauthorized Web Service cannot work. |
|
Note: or information about Web Service single sign-on please refer to the Security Guide for Agile e6.2.0.0. |
|
Note: The SSL port needs to be activated for the domain where Web Services are deployed. The standard listen port (non-SSL) must be disabled for the domain where Web Services are deployed. |
In the examples used in this chapter, a Web Service security policy is used to secure the entire Web Service. The client has to provide the WSS: SOAP message security user name token encrypted with an X.509 certificate.
|
Note: The certificate will be authenticated, too. The certificate must be valid and the certificate name must be available in the system. |
|
Note: In the current release of Agile e6 Core Web Services security policies are supported, except for the StreamingFileServices uploadFile and downloadFile. The file streaming only works with SSL (by using HTTPS). It does not work if HTTPS is enforced by adding a policy. All other Web Services can be controlled by the Web Services security policies. |
For more details on setting up Web Service Security Policies, see http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E24329_01/web.1211/e24488/message.htm#i244059
X.509 Authentication
For X.509 authentication, you need to configure the Web Service Security Configurations.
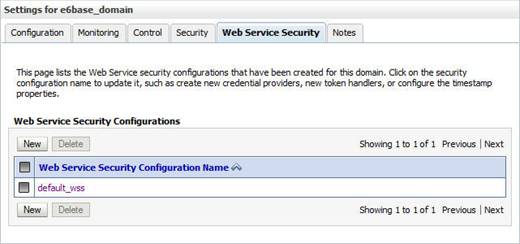
Use the default providers given by the WebLogic server.
In this example, when you click on the default Web Service default_wss, the Settings for default_wss mask opens. The Credential Provider column lists a number of available default providers, created for the Web Service security configuration.

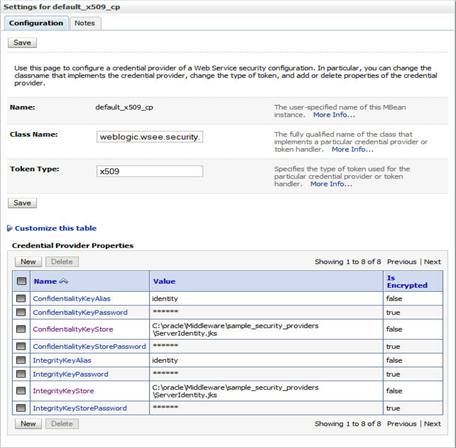
Store the x509 server certificate in a Java keystore.
The following screenshot shows how it can be configured.
The caller of an Agile e6 Web Service has to provide user credentials to gain access to the Agile e6 application. The attributes of these credentials depend on the used Web Service policy. The following is an example of an unauthenticated Web Service call:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<S:Envelope xmlns:S="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<S:Body>
<ns4:getVersion xmlns:ns2="http://xmlns.oracle.com/Agile/e6/Metadata/v0"
xmlns:ns3="http://xmlns.oracle.com/Agile/e6/plm"
xmlns:ns4="http://xmlns.oracle.com/Agile/e6/HelloWorld/v0" />
</S:Body>
</S:Envelope>
You can use the basic authentication of HTTP/S to secure a Web Service. With this basic authentication of HTTP/S, the user credentials are stored in the HTTP/S header. The SOAP message does not carry any security information.
|
Note: Basic authentication without SSL must not be used in a production environment as the passwords and data are transferred in plain text. Ideally, HTTP/S must be configured.WebLogic production servers should always use SSL (HTTP/S) and should not provide unencrypted access to any of the services. |
For complete details on WebLogic Security Fundamentals and Transport Level Security, refer to the WebLogic documentation on OTN.
To add the HTTP/S basic authentication to a SOAP request, the code may look like the following example:
MetadataService service = new MetadataService(wsdlURL, serviceQName);
BindingProvider bindingProvider = (BindingProvider) service.getPort();
bindingProvider.getRequestContext().put(BindingProvider.USERNAME_PROPERTY, username);
bindingProvider.getRequestContext().put(BindingProvider.PASSWORD_PROPERTY, password);
bindingProvider.getRequestContext().put(BindingProvider.SESSION_MAINTAIN_PROPERTY, Boolean.TRUE);
|
Note: The last line of this example configures HTTP/S session handling. If you do not add this code, each Web Service call creates a new HTTP/S session which leads to a new EDM Server instance starting up. |
A detailed sample for Web Services Security can be found in chapter Appendix, section Web Services Security.